Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(4):511-520
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190088
To characterize patients with chronic critical illness and identify predictors of development of chronic critical illness.
Prospective data was collected for 1 year in the intensive care unit of a general hospital in Southern Brazil. Three logistic regression models were constructed to identify factors associated with chronic critical illness.
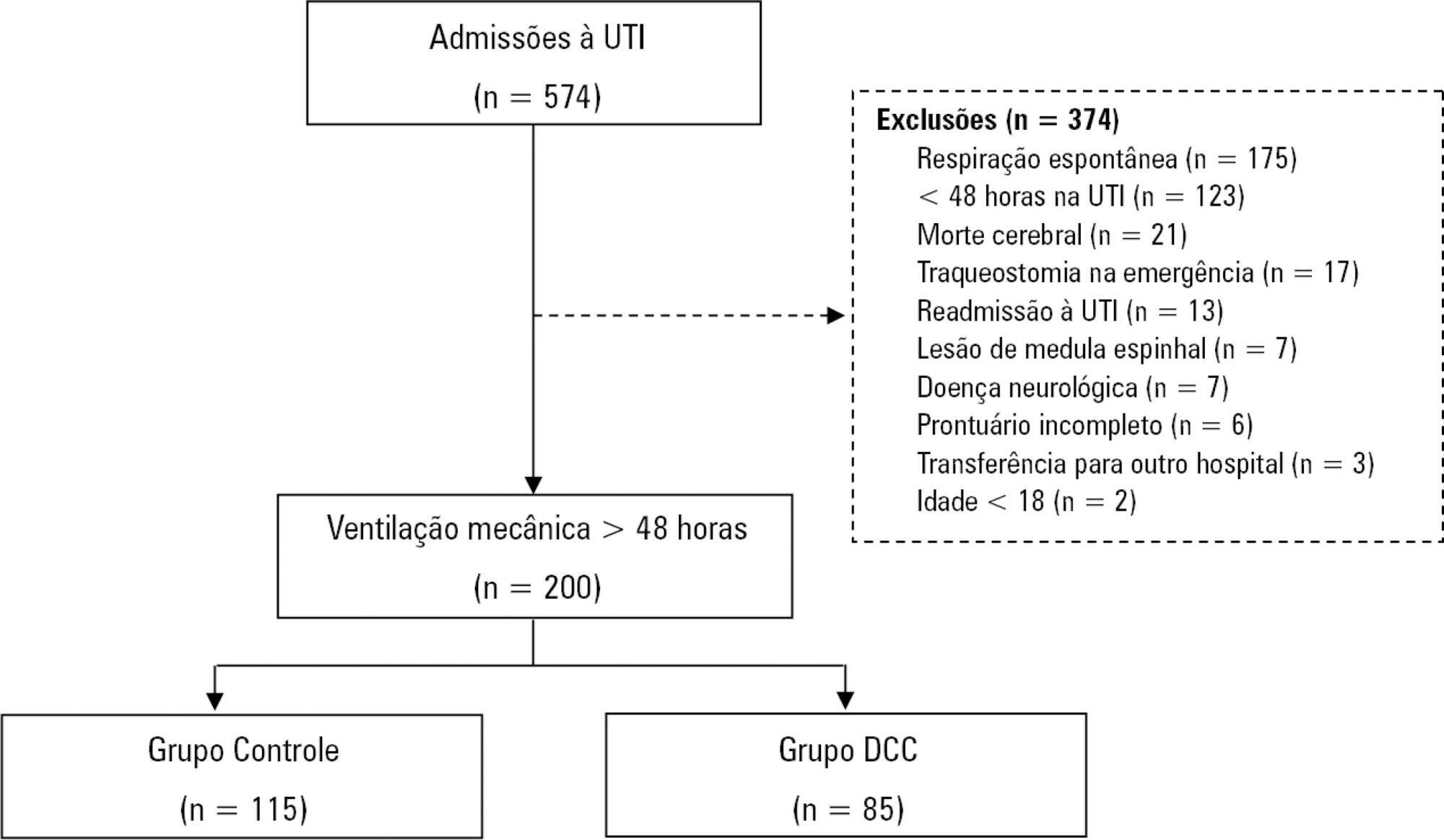
Among the 574 subjects admitted to the intensive care unit, 200 were submitted to mechanical ventilation. Of these patients, 85 (43.5%) developed chronic critical illness, composing 14.8% of all the patients admitted to the intensive care unit. The regression model that evaluated the association of chronic critical illness with conditions present prior to intensive care unit admission identified chronic renal failure in patients undergoing hemodialysis (OR 3.57; p = 0.04) and a neurological diagnosis at hospital admission (OR 2.25; p = 0.008) as independent factors. In the model that evaluated the association of chronic critical illness with situations that occurred during intensive care unit stay, muscle weakness (OR 2.86; p = 0.01) and pressure ulcers (OR 9.54; p < 0.001) had the strongest associations. In the global multivariate analysis (that assessed previous factors and situations that occurred in the intensive care unit), hospital admission due to neurological diseases (OR 2.61; p = 0.03) and the development of pressure ulcers (OR 9.08; p < 0.001) had the strongest associations.
The incidence of chronic critical illness in this study was similar to that observed in other studies and had a strong association with the diagnosis of neurological diseases at hospital admission and chronic renal failure in patients undergoing hemodialysis, as well as complications developed during hospitalization, such as pressure ulcers and muscle weakness.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2010;22(2):175-185
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2010000200012
OBJECTIVE: The avoidance of pressure ulcers development in critically ill patients is a major nursing challenge. Prevention is thus relevant for assurance of high quality care. This study aimed to evaluate the applicability of the Braden scale in intensive care unit patients. METHODS: This was a prospective study based which evaluated all adult patients staying in the intensive care unit from July 14 to August 10, 2009. The data were collected using the Braden's scale by three examiners who identified the pressure ulcer development risk. The data were analyzed using the SAS Statistical Software. For determination of the examiners' rates degree of coincidence, the Kappa value was used (95%CI). RESULTS: Regarding the related risk factors: 36.4% had mild sensory perception impairment; 50.9% had occasionally moist skin; 97.3% bedfast; 39.1% had very limited mobility; 45% probably had inappropriate nutrition; 61.8% had friction and shear problems. An agreement between the examiners was identified for nutrition and physical activity (38.1% to 100.0%); the Kappa population zero hypothesis was rejected; a paired examiners agreement (41.7% to 100.0%) was identified for the items humidity and physical activity, and the Kappa values ranged from 0.13 to 1. CONCLUSIONS: These intensive care patients were identified to have increased risk of developing pressure ulcers. This tool was considered appropriate to support the implementation of preventive measures.