Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(3):318-325
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190057
To validate the "Checklist for Managing Critical Patients' Daily Awakening" instrument.
This was a descriptive study that used a quantitative approach for content validation using the Delphi method to obtain the consensus of experts who evaluated the instrument using a Likert scale. The validity index of each item of the instrument was calculated, with a minimum consensus parameter above 0.78.
Three Delphi rounds were required, starting with 29 experts and ending with 15 experts who were invited in person and via e-mail to participate in the study. Of the 15 items in the instrument, 13 had a content validity index > 0.78. The instrument maintained its attributes, and six items were reformulated without the need to exclude any of them. The validated items enabled the assessment of and decisions regarding the dimensions related to the level of sedation and agitation, vital signs, ventilatory parameters and pain. The instrument presented psychometric indicators with acceptable content validity.
The instrument proposed in the study exhibited content validity for most of its items and emerges as a practical strategy for the management of the daily interruption of sedation of critical patients.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2010;22(2):175-185
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2010000200012
OBJECTIVE: The avoidance of pressure ulcers development in critically ill patients is a major nursing challenge. Prevention is thus relevant for assurance of high quality care. This study aimed to evaluate the applicability of the Braden scale in intensive care unit patients. METHODS: This was a prospective study based which evaluated all adult patients staying in the intensive care unit from July 14 to August 10, 2009. The data were collected using the Braden's scale by three examiners who identified the pressure ulcer development risk. The data were analyzed using the SAS Statistical Software. For determination of the examiners' rates degree of coincidence, the Kappa value was used (95%CI). RESULTS: Regarding the related risk factors: 36.4% had mild sensory perception impairment; 50.9% had occasionally moist skin; 97.3% bedfast; 39.1% had very limited mobility; 45% probably had inappropriate nutrition; 61.8% had friction and shear problems. An agreement between the examiners was identified for nutrition and physical activity (38.1% to 100.0%); the Kappa population zero hypothesis was rejected; a paired examiners agreement (41.7% to 100.0%) was identified for the items humidity and physical activity, and the Kappa values ranged from 0.13 to 1. CONCLUSIONS: These intensive care patients were identified to have increased risk of developing pressure ulcers. This tool was considered appropriate to support the implementation of preventive measures.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2006;18(3):268-275
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2006000300009
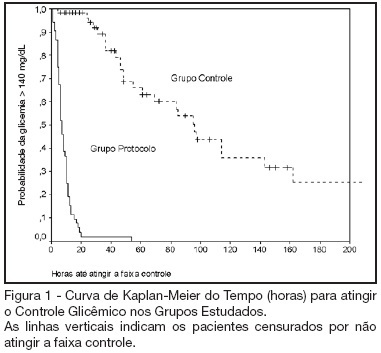
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: Actually tight glycemic control is a major concern in critical care. The objective of this study was to evaluate effectiveness and safety of Yale insulin infusion protocol in a Brazilian medical and surgical intensive care unit. METHODS: Retrospective, before-after cohort study. Selected end-points were mean blood glucose levels, time-to-reach target range of 80 - 140 mg/dL, and percent of blood glucose in target range and hypoglycemia incidence. RESULTS: Were studied 112 patients: 60 in control group (CG) and 52 in protocol group (PG). Bedside blood glucose was measured 5392 times for a mean value of 131.2 ± 14.7 mg/dL in the PG versus 2485 times for a mean value of 181.7 ± 36.1 mg/dL in the CG. Blood glucose values were in the target range 65% and 32% of the times, respectively for PG and CG groups (p < 0.001). The median time to reach glucose target range was 7 h (range 4 -10 h) for PG and 96 hr (range 46 - 278 h) for CG (p < 0.001). Incidence of severe hypoglycemia did not reach difference statistically significant: 4 patients in PG versus 2 patients in CG. CONCLUSIONS: Yale insulin infusion protocol was effective and safe to improve blood glucose control in a Brazilian medical and surgical intensive care unit.