You searched for:"Tamires Teixeira Gomes"
We found (2) results for your search.-
Original Article
Factors associated with functional decline in an intensive care unit: a prospective study on the level of physical activity and clinical factors
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(4):565-571
Abstract
Original ArticleFactors associated with functional decline in an intensive care unit: a prospective study on the level of physical activity and clinical factors
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(4):565-571
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20210073
Views1See moreABSTRACT
Objective:
To identify the factors associated with functional status decline in intensive care unit patients.
Methods:
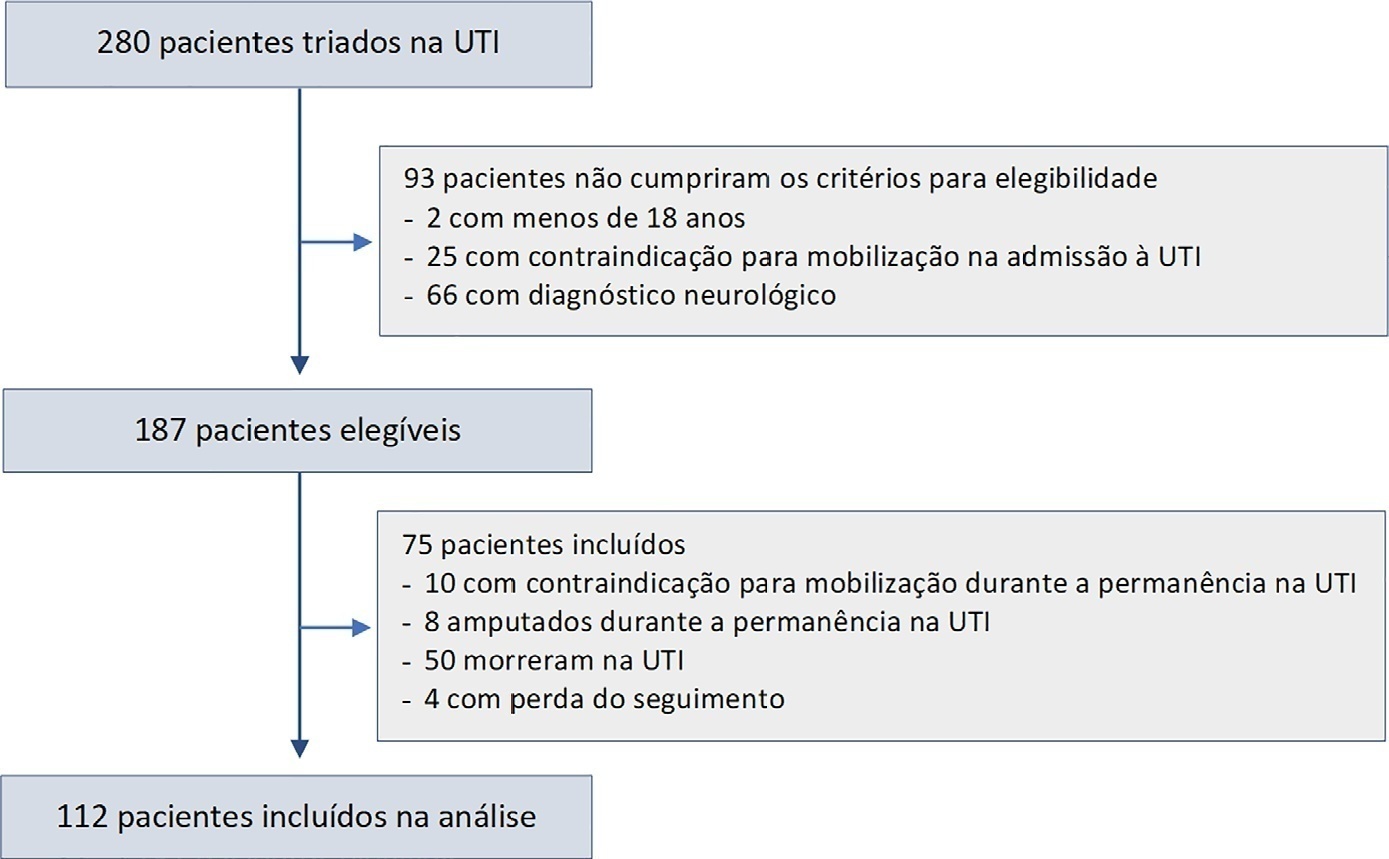
In this prospective study, patients in an intensive care unit aged 18 years or older without neurological disease or contraindications to mobilization were included. The exclusion criteria were patients who spent fewer than 4 days in the intensive care unit or died during the study period. Accelerometry was used to assess the physical activity level of patients. We recorded age, SAPS 3, days on mechanical ventilation, drugs used, comorbidities, and functional status after intensive care unit discharge. After intensive care unit discharge, the patients were assigned to a dependent group or an independent group according to their Barthel index. Logistic regression and the odds ratio were used in the analyses.
Results:
Sixty-three out of 112 included patients were assigned to the dependent group. The median Charlson comorbidity index was 3 (2 – 4). The mean SAPS 3 score was 53 ± 11. The patients spent 94 ± 4% of the time spent in inactivity and 4.8 ± 3.7% in light activities. The odds ratio showed that age (OR = 1.08; 95%CI 1.04 – 1.13) and time spent in inactivity (OR = 1.38; 95%CI 1.14 – 1.67) were factors associated with functional status decline. Time spent in light activity was associated with a better functional status (OR = 0.73; 95%CI 0.60 – 0.89).
Conclusions:
Age and time spent in inactivity during intensive care unit stay are associated with functional status decline. On the other hand, performing light activities seems to preserve the functional status of patients.
-
Original Articles
Rehabilitation through virtual reality: physical activity of patients admitted to the intensive care unit
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(4):456-463
Abstract
Original ArticlesRehabilitation through virtual reality: physical activity of patients admitted to the intensive care unit
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(4):456-463
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190078
Views1See moreABSTRACT
Objective:
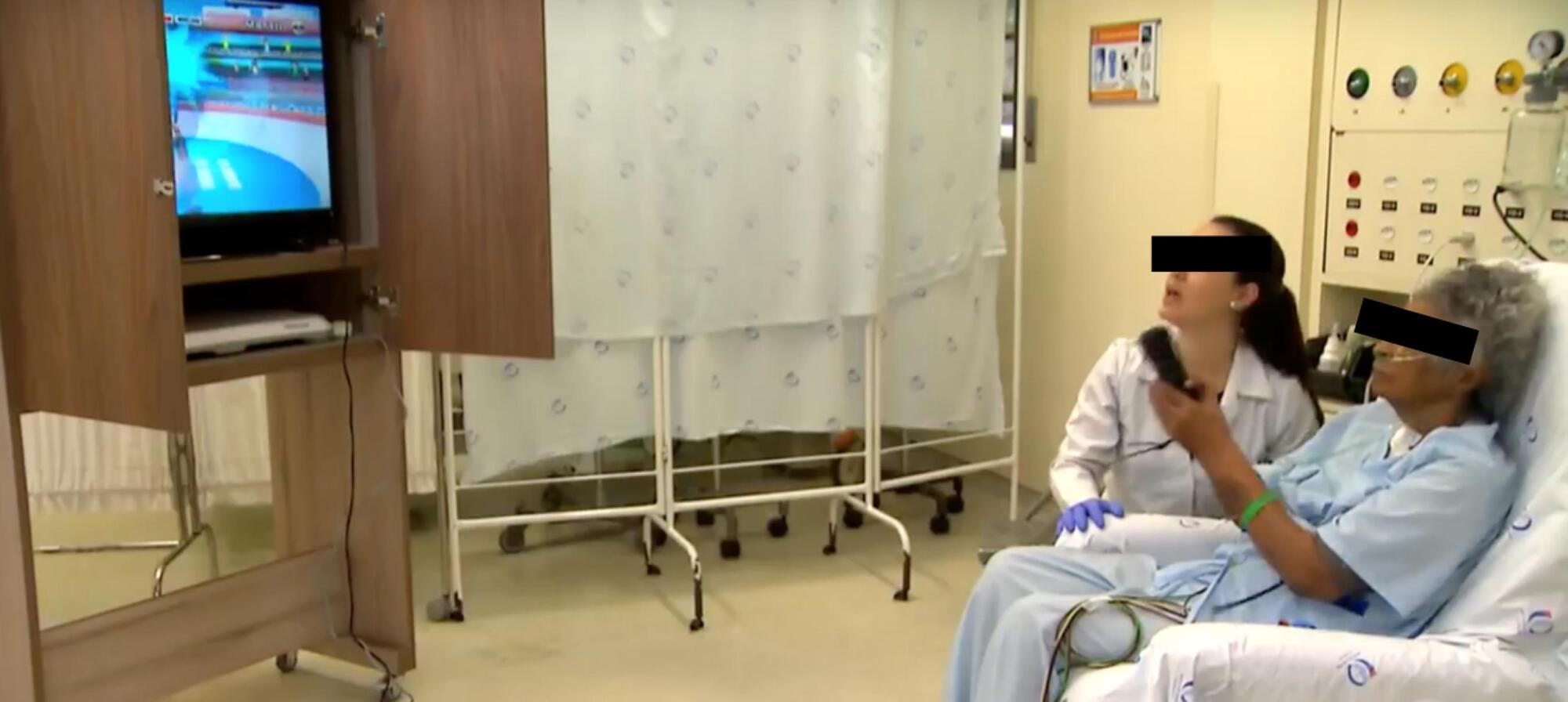
To evaluate the level of activity that Nintendo WiiTM can elicit in intensive care unit patients and its associated safety and patient satisfaction.
Methods:
Experimental, single-center study performed at a tertiary care hospital. Patients ≥ 18 years old who were admitted to the intensive care unit, participated in videogames as part of their physical therapy sessions and did not have mobility restrictions were included. Th exclusion criteria were the inability to comprehend instructions and the inability to follow simple commands. We included n = 60 patients and performed 100 sessions. We used the Nintendo WiiTM gaming system in the sessions. An accelerometer measured the level of physical activity of patients while they played videogames. We evaluated the level of activity, the modified Borg scale scores, the adverse events and the responses to a questionnaire on satisfaction with the activity.
Results:
One hundred physical therapy sessions were analyzed. When the patients played the videogame, they reached a light level of activity for 59% of the session duration and a moderate level of activity for 38% of the session duration. No adverse events occurred. A total of 86% of the patients reported that they would like to play the videogame in their future physical therapy sessions.
Conclusion:
Virtual rehabilitation elicited light to moderate levels of activity in intensive care unit patients. This therapy is a safe tool and is likely to be chosen by the patient during physical therapy.

Search
Search in:
KEY WORDS
Case reports Child Coronavirus infections COVID-19 Critical care Critical illness Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation Infant, newborn Intensive care Intensive care units Intensive care units, pediatric mechanical ventilation Mortality Physical therapy modalities Prognosis Respiration, artificial Respiratory insufficiency risk factors SARS-CoV-2 Sepsis




