Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(4):474-482
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190073
To compare cardiac output measurements by transthoracic echocardiography and a pulmonary artery catheter in mechanically ventilated patients with high positive end-expiratory pressure. To evaluate the effect of tricuspid regurgitation.
Sixteen mechanically ventilated patients were studied. Cardiac output was measured by pulmonary artery catheterization and transthoracic echocardiography. Measurements were performed at different levels of positive end-expiratory pressure (10cmH2O, 15cmH2O, and 20cmH2O). The effect of tricuspid regurgitation on cardiac output measurement was evaluated. The intraclass correlation coefficient was studied; the mean error and limits of agreement were studied with the Bland-Altman plot. The error rate was calculated.
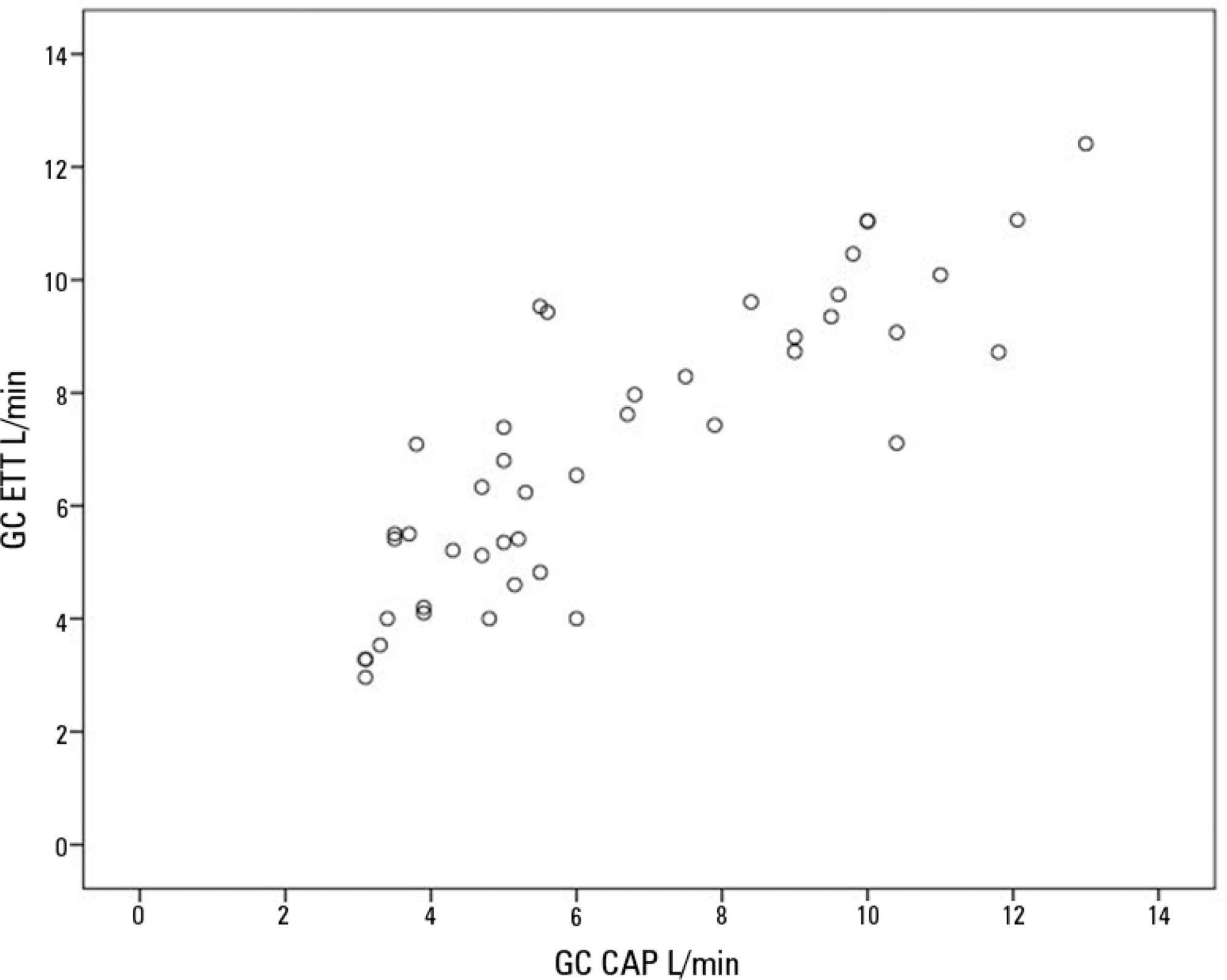
Forty-four pairs of cardiac output measurements were obtained. An intraclass correlation coefficient of 0.908 was found (p < 0.001). The mean error was 0.44L/min for cardiac output values between 5 and 13L/min. The limits of agreement were 3.25L/min and -2.37L/min. With tricuspid insufficiency, the intraclass correlation coefficient was 0.791, and without tricuspid insufficiency, 0.935. Tricuspid insufficiency increased the error rate from 32% to 52%.
In patients with high positive end-expiratory pressure, cardiac output measurement by transthoracic echocardiography is comparable to that with a pulmonary artery catheter. Tricuspid regurgitation influences the intraclass correlation coefficient. In patients with high positive end-expiratory pressure, the use of transthoracic echocardiography to measure cardiac output is comparable to invasive measures.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(4):483-489
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190071
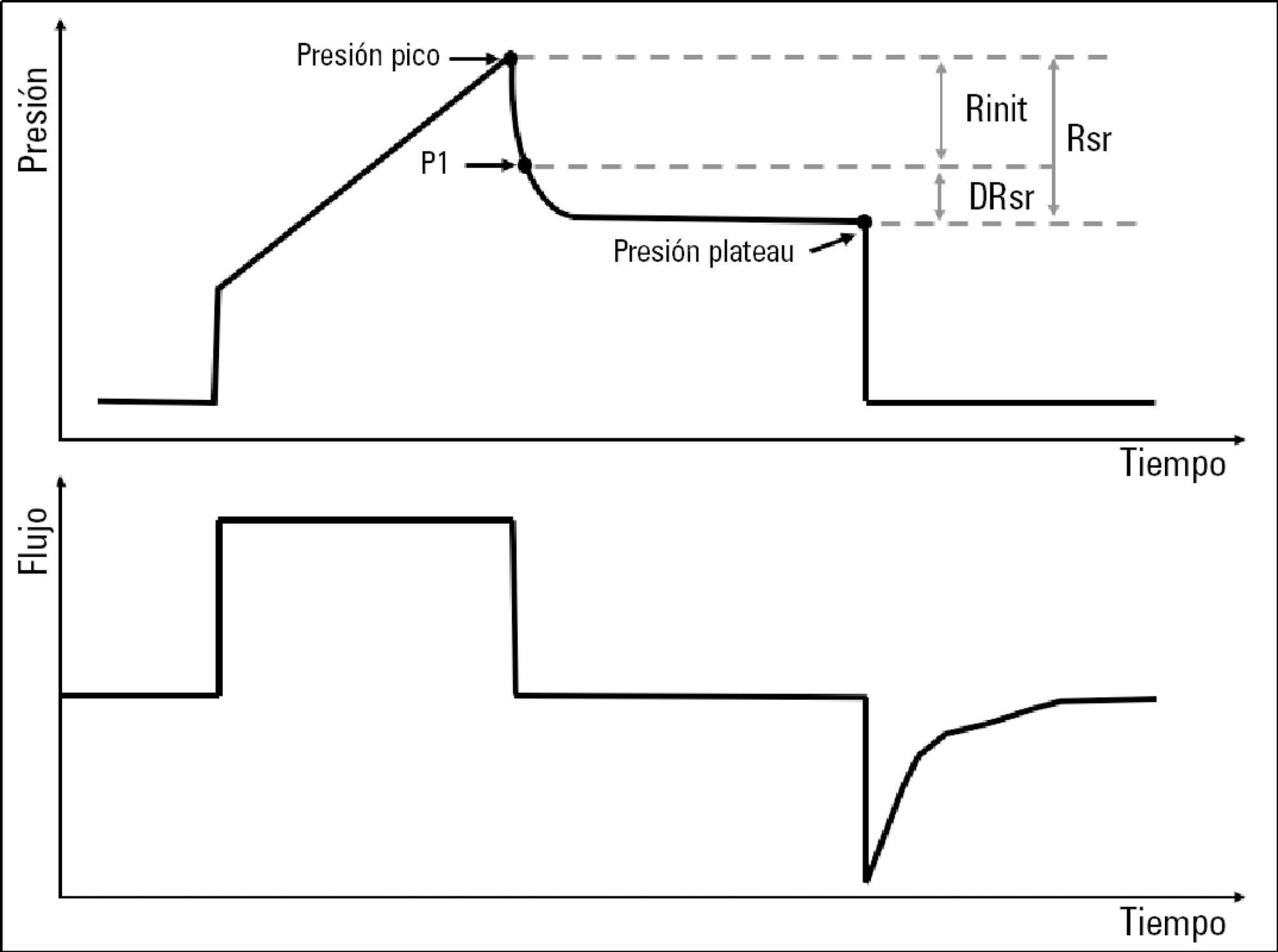
To describe the behavior of inspiratory resistance components when positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) increases in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome under a protective ventilation strategy.
In volume-controlled mode, at 6mL/kg and constant flow, end-inspiratory occlusions were performed at 0, 5 10, 15 and 20cmH2O PEEP. Peak, initial and plateau pressure values were assessed, calculating the maximum, minimum and differential resistances. The results were compared by repeated measures analysis of variance (ANOVA) with post hoc Bonferroni correction, considering p < 0.05 significant.
The highest maximum resistance was observed at the lowest PEEP levels. The values for 10 and 15cmH2O PEEP significantly differed from those for 5 and 0cmH2O PEEP, whereas that for 20cmH2O PEEP only significantly differed from that for 0cmH2O PEEP (p < 0.05). The minimum resistance behaved similarly to the maximum resistance; the values for PEEP levels from 10cmH2O to 20cmH2O significantly differed from those for 0 and 5cmH2O PEEP (p < 0.05). Differential resistance showed the opposite variation to the maximum and minimum resistances. The only PEEP level that showed significant differences from 0 and 5cmH2O PEEP was 20cmH2O PEEP. Significant differences were also found between 15 and 5cmH2O PEEP (p < 0.05).
During protective ventilation in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome, the maximum resistance of the respiratory system decreases with PEEP, reflecting the minimum resistance response, whereas differential resistance increases with PEEP.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(4):490-496
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190086
To evaluate the concordance between the modified NUTRIC and NUTRIC with C-reactive protein instruments in identifying nutritional risk patients and predicting mortality in critically ill patients. The risk of death in patient groups was also investigated according to nutritional risk and malnutrition detected by subjective global assessment.
A cohort study of patients admitted to an intensive care unit. Nutritional risk was assessed by modified NUTRIC and a version of NUTRIC with C-reactive protein. Subjective global assessment was applied to diagnose malnutrition. Kappa statistics were calculated, and an ROC curve was constructed considering modified NUTRIC as a reference. The predictive validity was assessed considering mortality in 28 days (whether in the intensive care unit or after discharge) as the outcome.
A total of 130 patients were studied (63.05 ± 16.46 years, 53.8% males). According to NUTRIC with C-reactive protein, 34.4% were classified as having a high score, while 28.5% of patients had this classification with modified NUTRIC. According to SGA 48.1% of patients were malnourished. There was excellent agreement between modified NUTRIC and NUTRIC with C-reactive protein (Kappa = 0.88, p < 0.001). The area under the ROC curve was equal to 0.942 (0.881 - 1.000) for NUTRIC with C-reactive protein. The risk of death within 28 days was increased in patients with high modified NUTRIC (HR = 1.827; 95%CI 1.029 - 3.244; p = 0.040) and NUTRIC with C-reactive protein (HR = 2.685; 95%CI 1.423 - 5.064; p = 0.002) scores. A high risk of death was observed in patients with high nutritional risk and malnutrition, independent of the version of the NUTRIC score applied.
An excellent agreement between modified NUTRIC and NUTRIC with C-reactive protein was observed. In addition, combining NUTRIC and subjective global assessment may increase the accuracy of predicting mortality in critically ill patients.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(4):497-503
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190087
To evaluate whether electromyographical findings could predict intensive care unit mortality among mechanically ventilated septic patients under profound sedation.
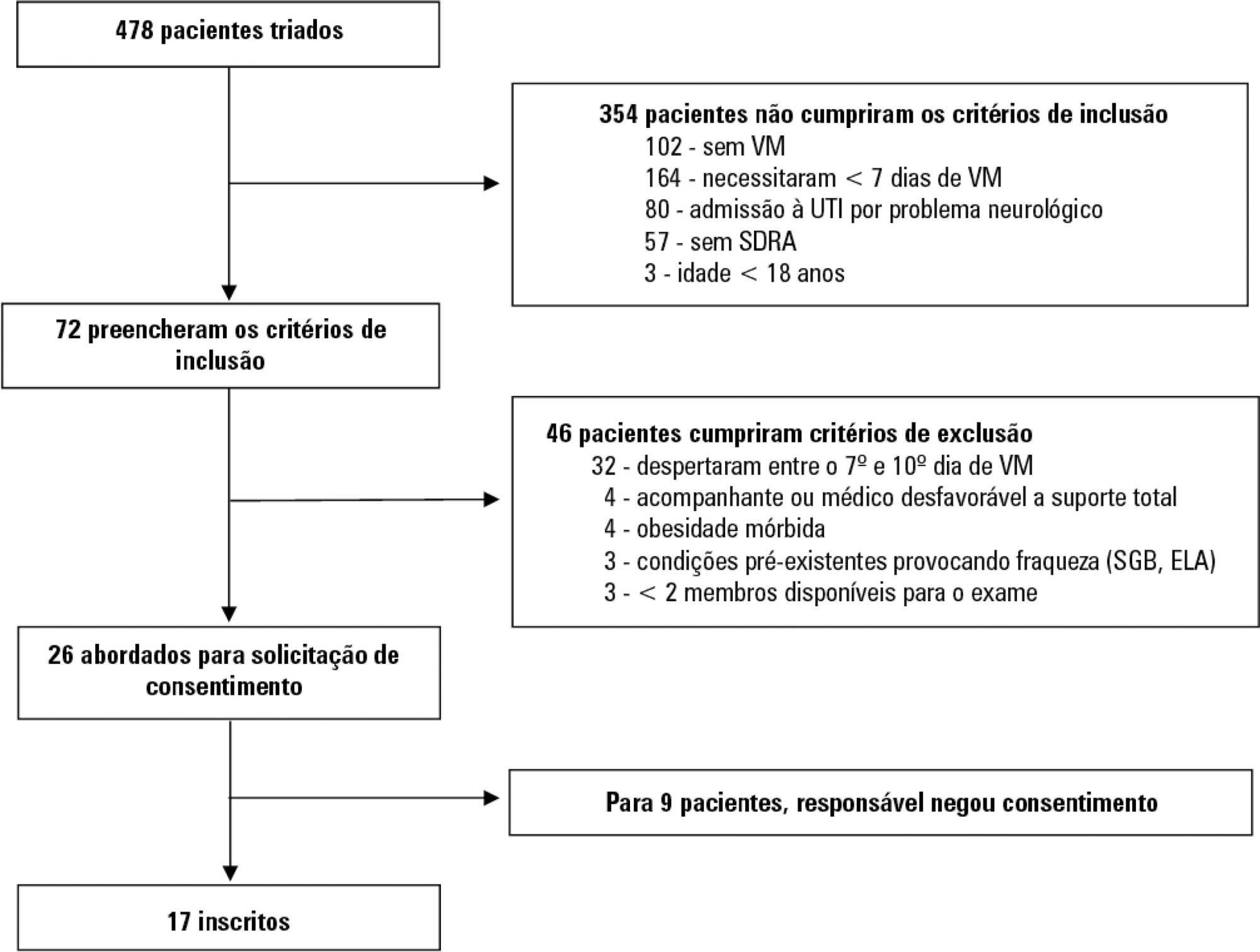
A prospective cohort study that consecutively enrolled moderate-severe acute respiratory distress syndrome (partial pressure of oxygen/fraction of inspired oxygen < 200) patients who were ≥ 18 years of age, dependent on mechanical ventilation for ≥ 7 days, and under profound sedation (Richmond Agitation Sedation Scale ≤ -4) was conducted. Electromyographic studies of the limbs were performed in all patients between the 7th and the 10th day of mechanical ventilation. Sensory nerve action potentials were recorded from the median and sural nerves. The compound muscle action potentials were recorded from the median (abductor pollicis brevis muscle) and common peroneal (extensor digitorum brevis muscle) nerves.
Seventeen patients were enrolled during the seven months of the study. Nine patients (53%) had electromyographic signs of critical illness myopathy or neuropathy. The risk of death during the intensive care unit stay was increased in patients with electromyographical signs of critical illness myopathy or neuropathy in comparison to those without these diagnostics (77.7% versus 12.5%, log-rank p = 0.02).
Electromyographical signs of critical illness myopathy or neuropathy between the 7th and the 10th day of mechanical ventilation may be associated with intensive care unit mortality among moderate-severe acute respiratory distress syndrome patients under profound sedation, in whom clinical strength assessment is not possible.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(4):504-510
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190067
To evaluate the risk factors for protein-caloric inadequacy in critically ill patients.
Prospective cohort study of patients hospitalized in an adult intensive care unit between February and November 2017. Patients were followed for 7 days. The conditional probability of inadequacy was calculated using the Kaplan-Meier method and the 95% log-rank test. To assess the risk of inadequacy, crude and adjusted hazard ratios (HR) were calculated using Cox regression with a 95% confidence interval.
Of the 130 patients, 63.8% were male, 73.8% were <60 years of age, and 49.2% were diagnosed with trauma. The mean APACHE II score was 24 points, and 70.0% of the patients had a protein-caloric adequacy >80%. In the univariate analysis, the significant variables for inadequacy were use of vasoactive drugs, interruptions of diet and failure to initiate nutrition early. In the final model, patients who presented with vomiting/gastric residue (adjusted HR = 22.5; 95%CI 5.14 - 98.87) and fasting for extubation (adjusted HR = 14.75; 95%CI 3.59 - 60.63) and for examinations and interventions (adjusted HR = 12.46; 95%CI 4.52 - 34.36) had a higher risk of not achieving protein-caloric adequacy.
Achievement of nutritional goals > 80.0% occurred in 70.0% of patients. The risk factors for protein-caloric inadequacy were nutritional interruptions, especially due to vomiting/gastric residue and fasting for extubation, exams and surgical procedures.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(4):511-520
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190088
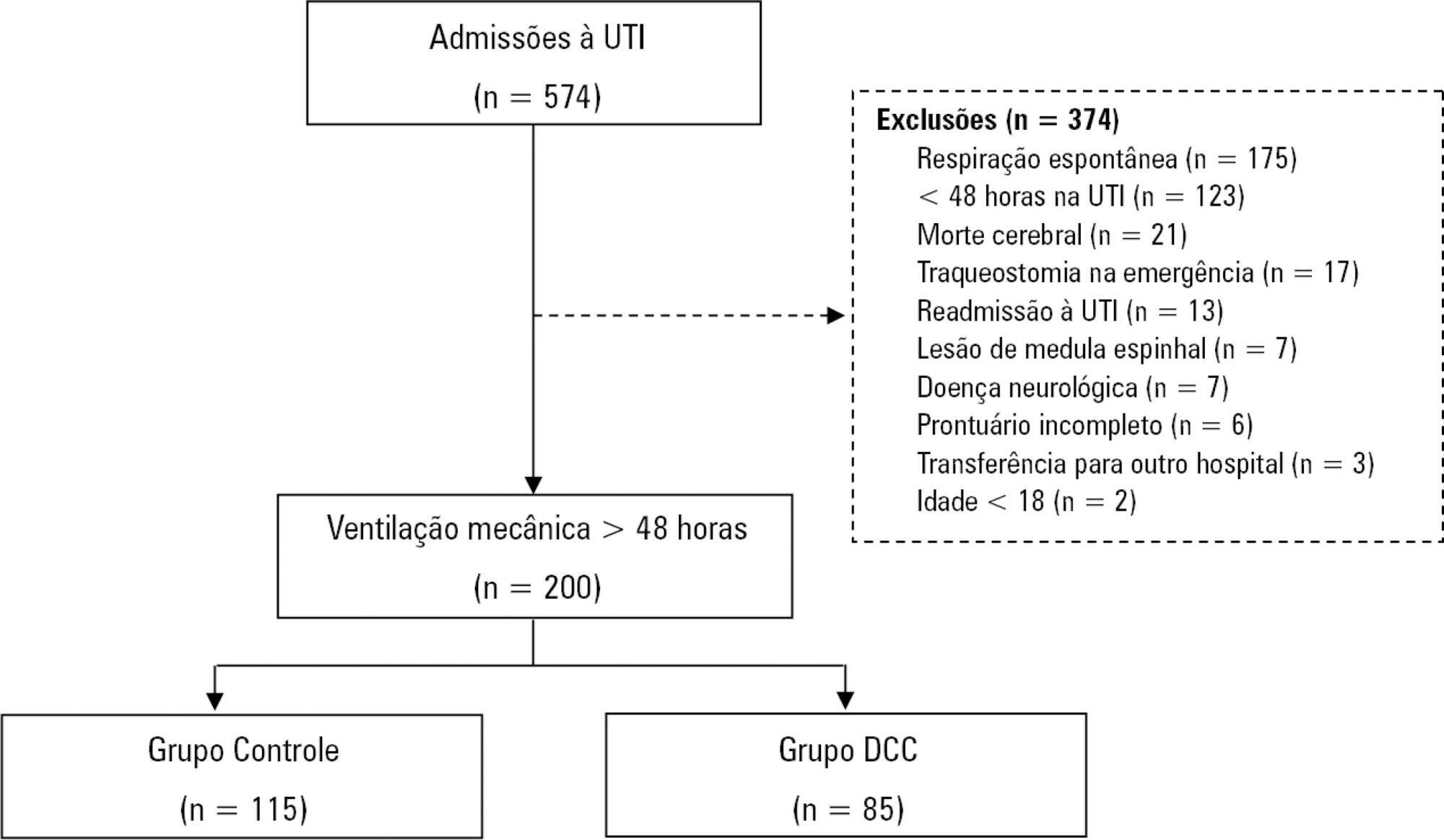
To characterize patients with chronic critical illness and identify predictors of development of chronic critical illness.
Prospective data was collected for 1 year in the intensive care unit of a general hospital in Southern Brazil. Three logistic regression models were constructed to identify factors associated with chronic critical illness.
Among the 574 subjects admitted to the intensive care unit, 200 were submitted to mechanical ventilation. Of these patients, 85 (43.5%) developed chronic critical illness, composing 14.8% of all the patients admitted to the intensive care unit. The regression model that evaluated the association of chronic critical illness with conditions present prior to intensive care unit admission identified chronic renal failure in patients undergoing hemodialysis (OR 3.57; p = 0.04) and a neurological diagnosis at hospital admission (OR 2.25; p = 0.008) as independent factors. In the model that evaluated the association of chronic critical illness with situations that occurred during intensive care unit stay, muscle weakness (OR 2.86; p = 0.01) and pressure ulcers (OR 9.54; p < 0.001) had the strongest associations. In the global multivariate analysis (that assessed previous factors and situations that occurred in the intensive care unit), hospital admission due to neurological diseases (OR 2.61; p = 0.03) and the development of pressure ulcers (OR 9.08; p < 0.001) had the strongest associations.
The incidence of chronic critical illness in this study was similar to that observed in other studies and had a strong association with the diagnosis of neurological diseases at hospital admission and chronic renal failure in patients undergoing hemodialysis, as well as complications developed during hospitalization, such as pressure ulcers and muscle weakness.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(4):521-528
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190065
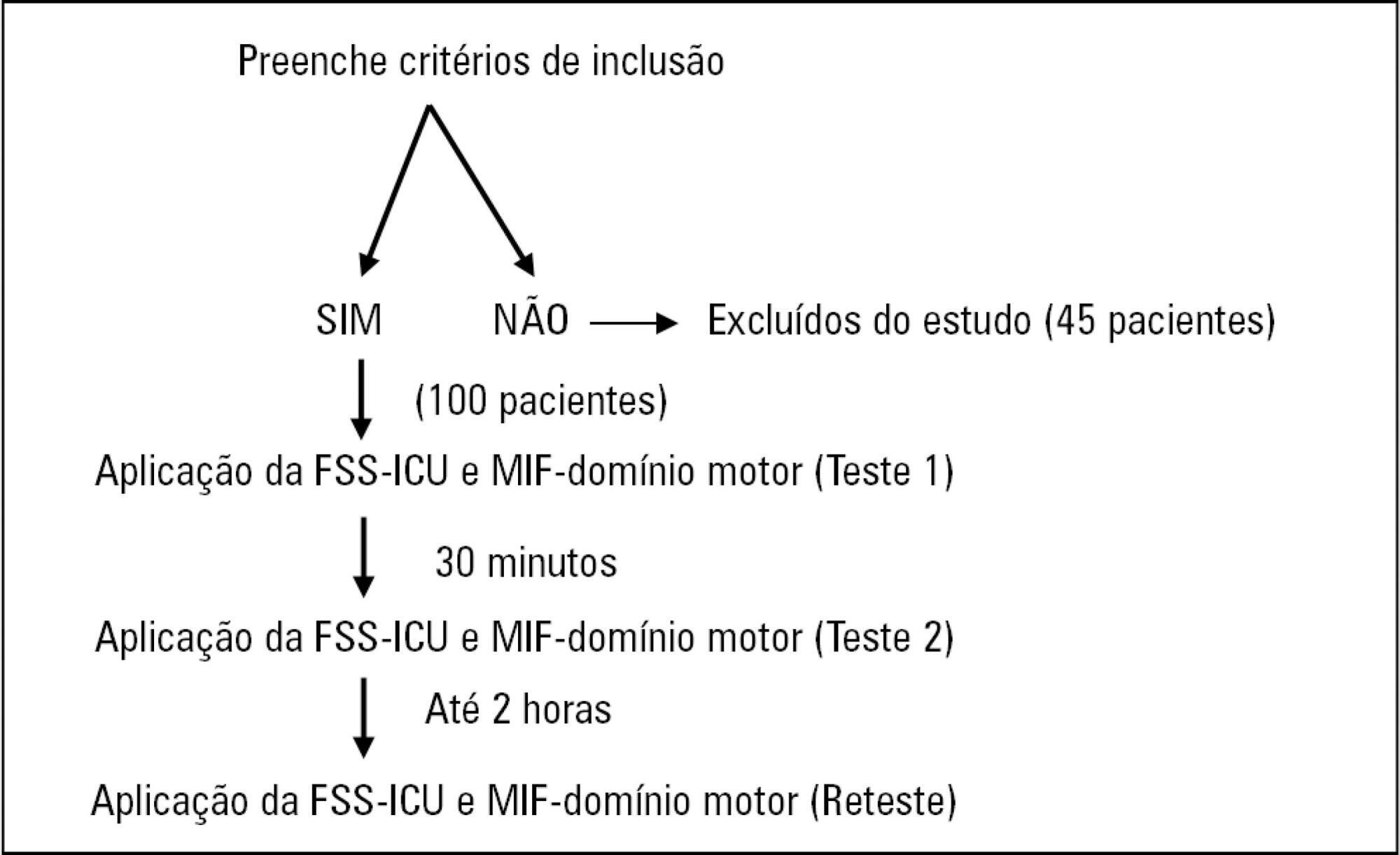
To compare the measurement properties (internal consistency, intra and interrater reliability, construct validity, and ceiling and floor effects) of the Functional Status Score for the ICU (FSS-ICU) and the Functional Independence Measure (FIM-motor domain).
In this study of measurement properties, the FSS-ICU and FIM were applied to 100 patients (72.1 ± 15.9 years; 53% male; Sequential Organ Failure Assessment = 11.0 ± 3.5 points, Simplified Acute Physiology Score 3 = 50.2 ± 16.8 points) in an intensive care unit at baseline and after 2 hours by physiotherapist 1 (test and retest) and 30 minutes after baseline by physiotherapist 2. The measurement properties evaluated were internal consistency (Cronbach's alpha), intra- and interrater reliability (intraclass correlation coefficient), agreement (standard error of measurement) and minimum detectable change at a 90% confidence level, ceiling and floor effects (frequency of maximum and minimum scores) and construct validity (Pearson's correlation).
The FSS-ICU and FIM presented adequate internal consistency (Cronbach's alpha, FSS-ICU = 0.95 and FIM = 0.86), intra-and interrater reliability for overall FSS-ICU and FIM score (ICC > 0.75), agreement (minimum detectable change at a 90% confidence level: FSS-ICU and FIM = 1.0 point; standard error of measurement: FSS-ICU = 2% and FIM = 1%) and construct validity (r = 0.94; p < 0.001). However, the FSS-ICU and FIM presented ceiling effects (maximum score for 16% of patients for the FSS-ICU and 18% for the FIM).
The FSS-ICU and FIM present adequate measurement properties to assess functionality in critically ill patients, although they present ceiling effects.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(4):529-535
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190066
To measure and compare the functionality of patients after discharge from the intensive care unit and at the time of hospital discharge.
Quantitative study of a prospective cohort performed between August of 2016 and December of 2017 at a university hospital. A 10-meter walk test was performed at 2 timepoints: after discharge from the intensive care unit and prior to hospital discharge. The data were analyzed using Student's t-test and Pearson or Spearman correlation. Statistical Package for Social Science (SPSS) version 21.0 was used for the analysis, and p ≤ 0.05 was adopted as the level of significance.
Forty patients, with a mean age of 57.1 ± 12.2 years and with a predominance of males (60%), were evaluated. For the post-intensive care unit test, a mean speed of 0.48m/s was observed, and for the pre-hospital discharge test, there was an increase to 0.71m/s, evidencing functional evolution during the hospital stay (p < 0.001).
There was significant improvement in walking speed at the time of hospital discharge when compared to the walking speed at the time of intensive care unit discharge.