Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(3):312-317
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190056
To investigate the influence of respiratory distress syndrome management on clinical and echocardiographic parameters used for hemodynamic evaluation in ≤ 32- week newborns.
Thirty-three ≤ 32-week newborns were prospectively evaluated and subjected to invasive mechanical ventilation. The need for exogenous surfactant and clinical and echocardiographic parameters in the first 24 hours of life was detailed in this group of patients.
The mean airway pressure was significantly higher in newborn infants who required inotropes [10.8 (8.8 - 23) cmH2O versus 9 (6.2 - 12) cmH2O; p = 0.04]. A negative correlation was found between the mean airway pressure and velocity-time integral of the pulmonary artery (r = -0.39; p = 0.026), right ventricular output (r = -0.43; p = 0.017) and measurements of the tricuspid annular plane excursion (r = -0.37; p = 0.036). A negative correlation was found between the number of doses of exogenous surfactant and the right ventricular output (r = -0.39; p = 0.028) and pulmonary artery velocity-time integral (r = -0.35; p = 0.043).
In ≤ 32-week newborns under invasive mechanical ventilation, increases in the mean airway pressure and number of surfactant doses are correlated with the worsening of early cardiac function. Therefore, more aggressive management of respiratory distress syndrome may contribute to the hemodynamic instability of these patients.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(3):318-325
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190057
To validate the "Checklist for Managing Critical Patients' Daily Awakening" instrument.
This was a descriptive study that used a quantitative approach for content validation using the Delphi method to obtain the consensus of experts who evaluated the instrument using a Likert scale. The validity index of each item of the instrument was calculated, with a minimum consensus parameter above 0.78.
Three Delphi rounds were required, starting with 29 experts and ending with 15 experts who were invited in person and via e-mail to participate in the study. Of the 15 items in the instrument, 13 had a content validity index > 0.78. The instrument maintained its attributes, and six items were reformulated without the need to exclude any of them. The validated items enabled the assessment of and decisions regarding the dimensions related to the level of sedation and agitation, vital signs, ventilatory parameters and pain. The instrument presented psychometric indicators with acceptable content validity.
The instrument proposed in the study exhibited content validity for most of its items and emerges as a practical strategy for the management of the daily interruption of sedation of critical patients.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(3):326-332
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190041
To evaluate possible associations between nutritional risk and the clinical outcomes of critical patients admitted to an intensive care unit.
A prospective study was carried out with a cohort comprising 200 patients admitted to a university hospital intensive care unit. Nutritional risk was assessed with the NRS-2002 and NUTRIC scores. Patients with scores ≥ 5 were considered at high nutritional risk. Clinical data and outcome measures were obtained from patients' medical records. Multiple logistic regression analysis was used to calculate odds ratios and their respective 95% confidence intervals (for clinical outcomes).
This sample of critical patients had a mean age of 59.4 ± 16.5 years and 53.5% were female. The proportions at high nutritional risk according to NRS-2002 and NUTRIC were 55% and 36.5%, respectively. Multiple logistic regression models adjusted for gender and type of admission indicated that high nutritional risk assessed by the NRS-2002 was positively associated with use of mechanical ventilation (OR = 2.34; 95%CI 1.31 - 4.19; p = 0.004); presence of infection (OR = 2.21; 95%CI 1.24 - 3.94; p = 0.007), and death (OR = 1.86; 95%CI 1.01 - 3.41; p = 0.045). When evaluated by NUTRIC, nutritional risk was associated with renal replacement therapy (OR = 2.10; 95%CI 1.02 - 4.15; p = 0.040) and death (OR = 3.48; 95%CI 1.88 - 6.44; p < 0.001).
In critically ill patients, high nutritional risk was positively associated with an increased risk of clinical outcomes including hospital death.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(3):333-339
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190045
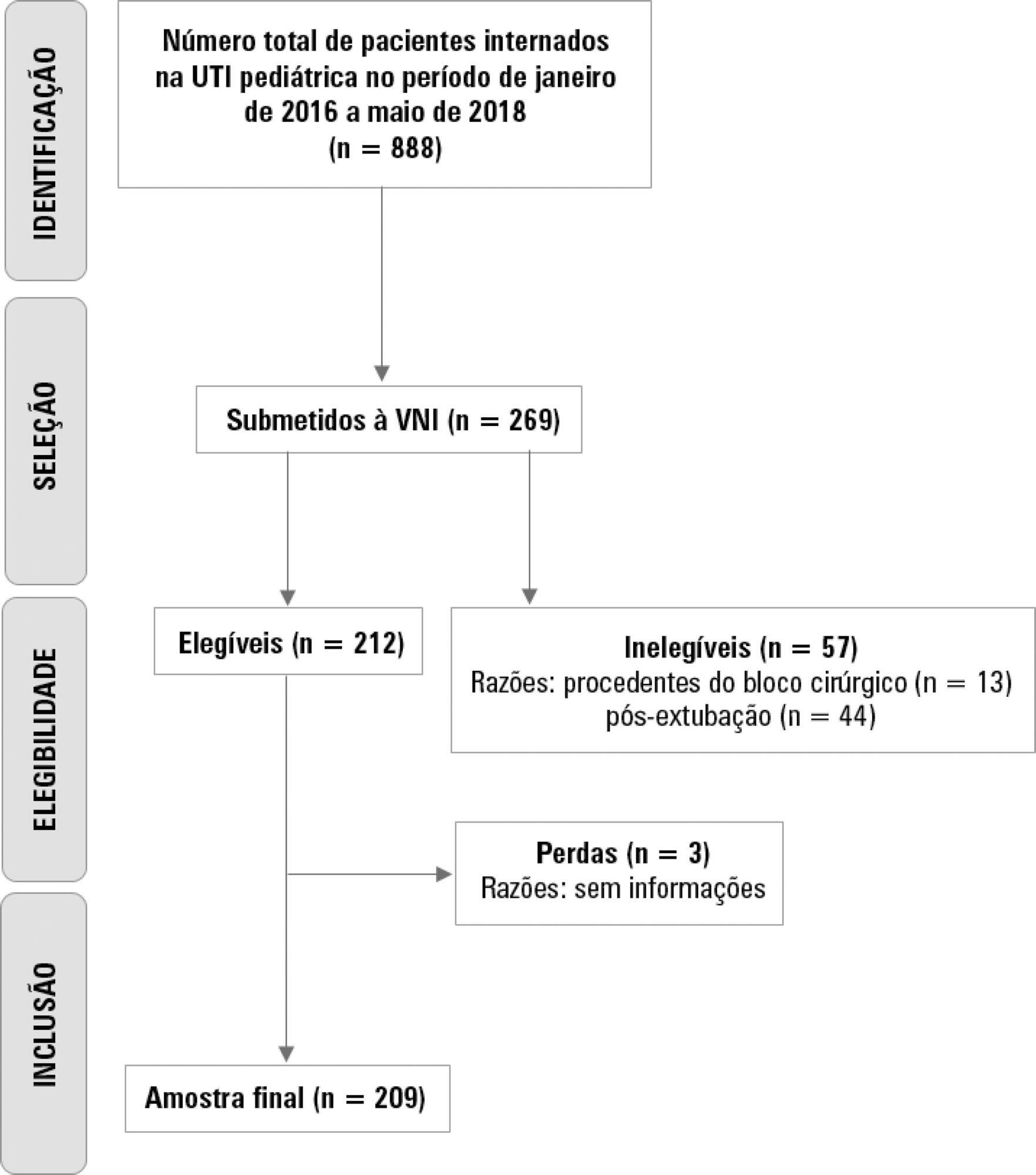
To describe the use of noninvasive ventilation to prevent tracheal intubation in children in a pediatric intensive care unit and to analyze the factors related to respiratory failure.
A retrospective cohort study was performed from January 2016 to May 2018. The study population included children aged 1 to 14 years who were subjected to noninvasive ventilation as the first therapeutic choice for acute respiratory failure. Biological, clinical and managerial data were analyzed by applying a model with the variables that obtained significance ≤ 0.20 in a bivariate analysis. Logistic regression was performed using the ENTER method. The level of significance was set at 5%.
The children had a mean age of 68.7 ± 42.3 months, 96.6% had respiratory disease as a primary diagnosis, and 15.8% had comorbidities. Of the 209 patients, noninvasive ventilation was the first option for ventilatory support in 86.6% of the patients, and the fraction of inspired oxygen was ≥ 0.40 in 47% of the cases. The lethality rate was 1.4%. The data for the use of noninvasive ventilation showed a high success rate of 95.3% (84.32 - 106). The Pediatric Risk of Mortality (PRISM) score and the length of stay in the intensive care unit were the significant clinical variables for the success or failure of noninvasive ventilation.
A high rate of effectiveness was found for the use of noninvasive ventilation for acute episodes of respiratory failure. A higher PRISM score on admission, comorbidities associated with respiratory symptoms and oxygen use ≥ 40% were independent factors related to noninvasive ventilation failure.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(3):340-346
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190049
To identify the underlying factors that affect fluid resuscitation in septic patients.
The present study was a case-control study of 181 consecutive patients admitted to a Medical Intensive Care Unit between 2012 and 2016 with a diagnosis of sepsis. Demographic, clinical, radiological and laboratory data were analyzed.
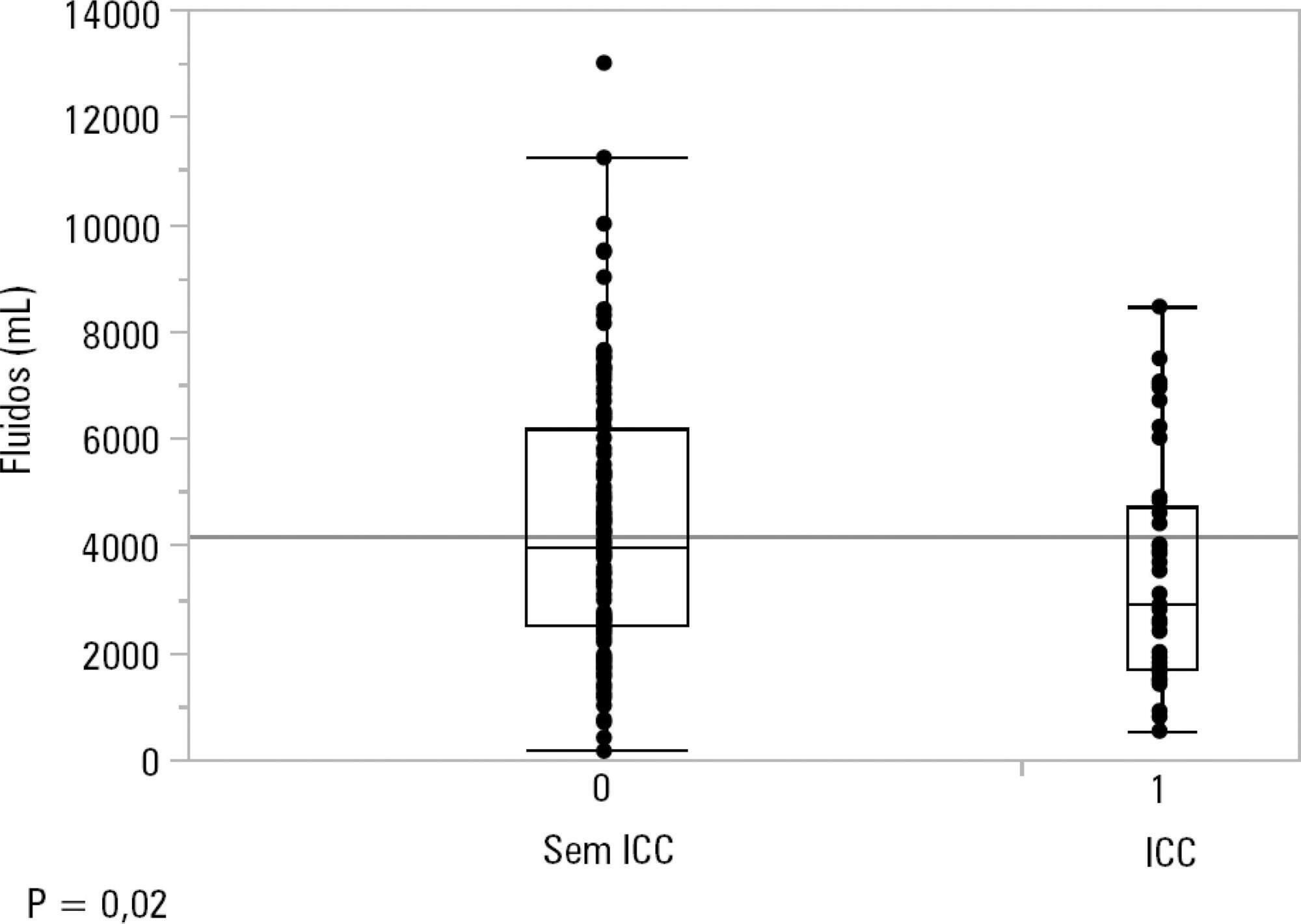
One hundred-thirty patients (72%) received ≥ 30mL/kg of IV fluids on admission. On univariate analyses, a past history of coronary artery disease and heart failure was associated with less fluid therapy. On multivariate analyses, a history of heart failure (OR = 2.31; 95%CI 1.04 - 5.14) remained significantly associated with receiving less IV fluids. Left ventricular ejection fraction, systolic/diastolic function, left ventricular hypertrophy and pulmonary hypertension were not associated with IV fluids. The amount of IV fluids was not associated with differences in mortality. During the first 24 hours, patients with a past history of heart failure received 2,900mLof IV fluids [1,688 - 4,714mL] versus 3,977mL [2,500 - 6,200mL] received by those without a history of heart failure, p = 0.02.
Septic patients with a past history of heart failure received 1L less IV fluids in the first 24 hours with no difference in mortality.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(3):347-353
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190047
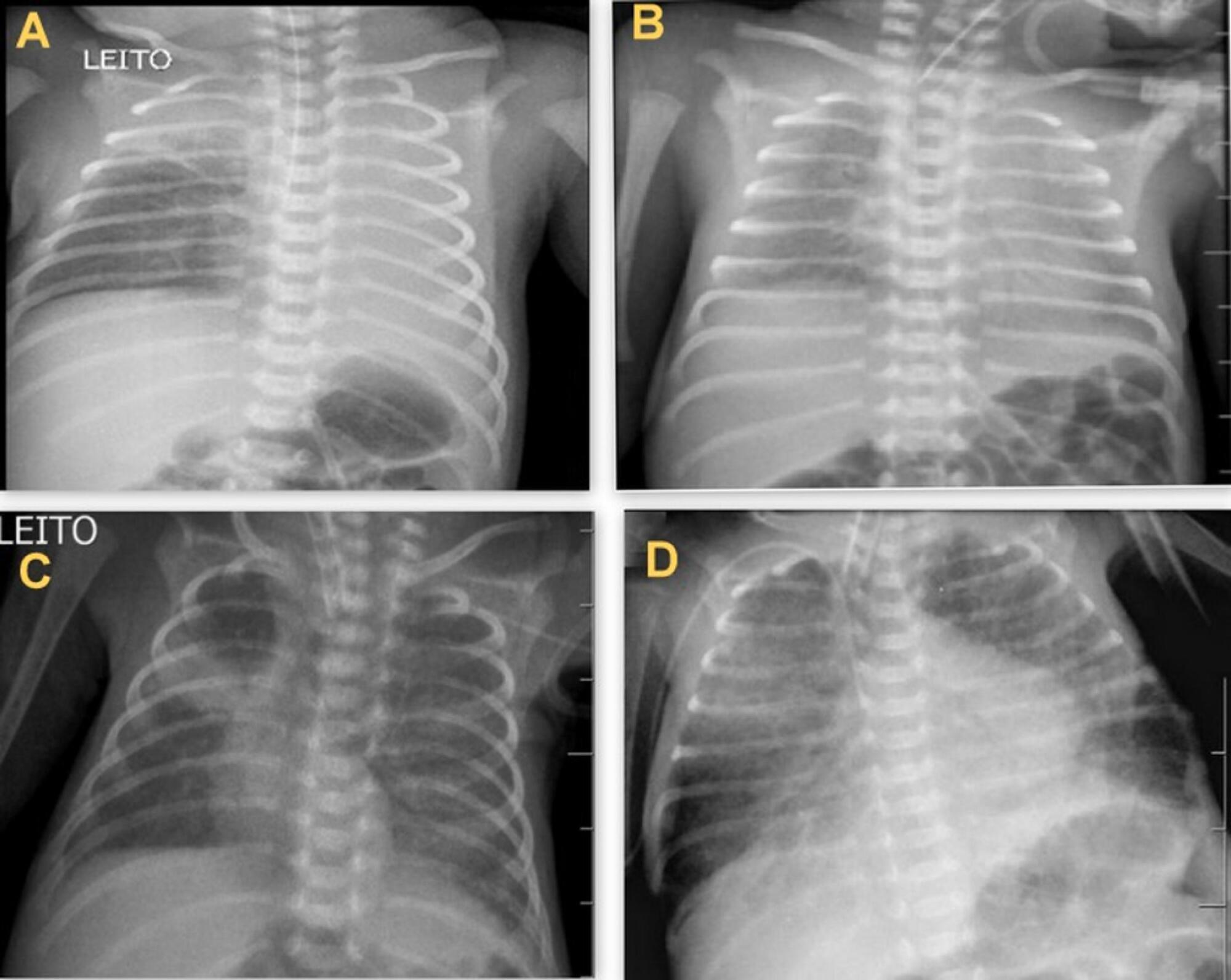
To determine the occurrence and characteristics of atelectasis, opacities, hypolucency and pulmonary infiltrates observed on chest X-rays of preterm infants in a neonatal intensive care unit.
This was a cross-sectional observational study. From August to December 2017, all chest radiographs of newborn infants were analyzed. The study included the chest radiographs of preterm neonates with gestational ages up to 36 weeks in the neonatal period that showed clear changes or suspected changes, which were confirmed after a radiologist’s report. Radiological changes were associated with possible predisposing factors.
During the study period, 450 radiographs were performed on preterm neonates, and 37 lung changes were identified and classified into 4 types: 12 (2.66%) changes were described as opacities, 11 (2.44%) were described as atelectasis, 10 (2.22%) were described as pulmonary infiltrate, and 4 (0.88%) were described as hypolucency. A higher occurrence of atelectasis was noted in the right lung (81.8%). Among the abnormal radiographs, 25 (67.6%) newborn infants were receiving invasive mechanical ventilation.
Considering the radiological report, no significance was found for the observed changes. Atelectasis was not the most frequently observed change. The predisposing factors for these changes were extreme prematurity, low weight, male sex, a poorly positioned endotracheal tube and the use of invasive mechanical ventilation.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(3):354-360
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190058
To evaluate the agreement between intensive care physicians with similar training in the use of bedside lung ultrasonography in identifying pulmonary B lines, visualized in real time, to verify the reproducibility of the method.
A total of 67 patients with some ventilatory deterioration identified within 12 hours after a pulmonary ultrasonography in the period from November 2016 to March 2017 were analyzed, and all were admitted to an intensive care unit of a private hospital in Belo Horizonte, Minas Gerais. The lung ultrasonographies were performed by three different professionals, termed A, B and C, and the time interval between each lung ultrasonography was less than 3 hours. The only visualized chest zones were the anterior and lateral, defined as right and left anterior (1) zones (Z1R and Z1L, respectively), which were delimited by the clavicle, the sternum and the horizontal line perpendicular to the xiphoid process and anterior axillary line. The right and left lateral (2) zones (Z2R and Z2L, respectively) covered the lateral area between the anterior and posterior axillary lines, with the lower limit being the same horizontal line corresponding to the height of the xiphoid process. A lung zone was considered positive for B lines upon visualization of three or more of these lines, suggesting the presence of alveolar-interstitial syndrome. Using the Kappa value, we evaluated the agreement among the four zones according to the execution of each pair of professionals (AB, AC and BC).
Approximately 80% of the areas that were visualized showed a moderate to substantial agreement, with the Kappa values ranging from 0.41 - 079 (p < 0.05; 95% CI). The highest levels of agreement occurred in the upper zones Z1R and Z1L between subgroups AC and BC, with a Kappa of approximately 0.65 (p < 0.001). In turn, Z2L showed one of the lowest agreements, with a Kappa of 0.36.
The possible limitation of an examiner-dependent effect on lung ultrasounds was not found in this study, suggesting the good reproducibility of this diagnostic modality at the bedside.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(3):361-367
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190059
To compare the impact of two fast-track strategies regarding the extubation time and removal of invasive mechanical ventilation in adults after cardiac surgery on clinical and hospital outcomes.
This was a retrospective cohort study with patients undergoing cardiac surgery. Patients were classified according to the extubation time as the Control Group (extubated 6 hours after admission to the intensive care unit, with a maximum mechanical ventilation time of 18 hours), Group 1 (extubated in the operating room after surgery) and Group 2 (extubated within 6 hours after admission to the intensive care unit). The primary outcomes analyzed were vital capacity on the first postoperative day, length of hospital stay, and length of stay in the intensive care unit. The secondary outcomes were reintubation, hospital-acquired pneumonia, sepsis, and death.
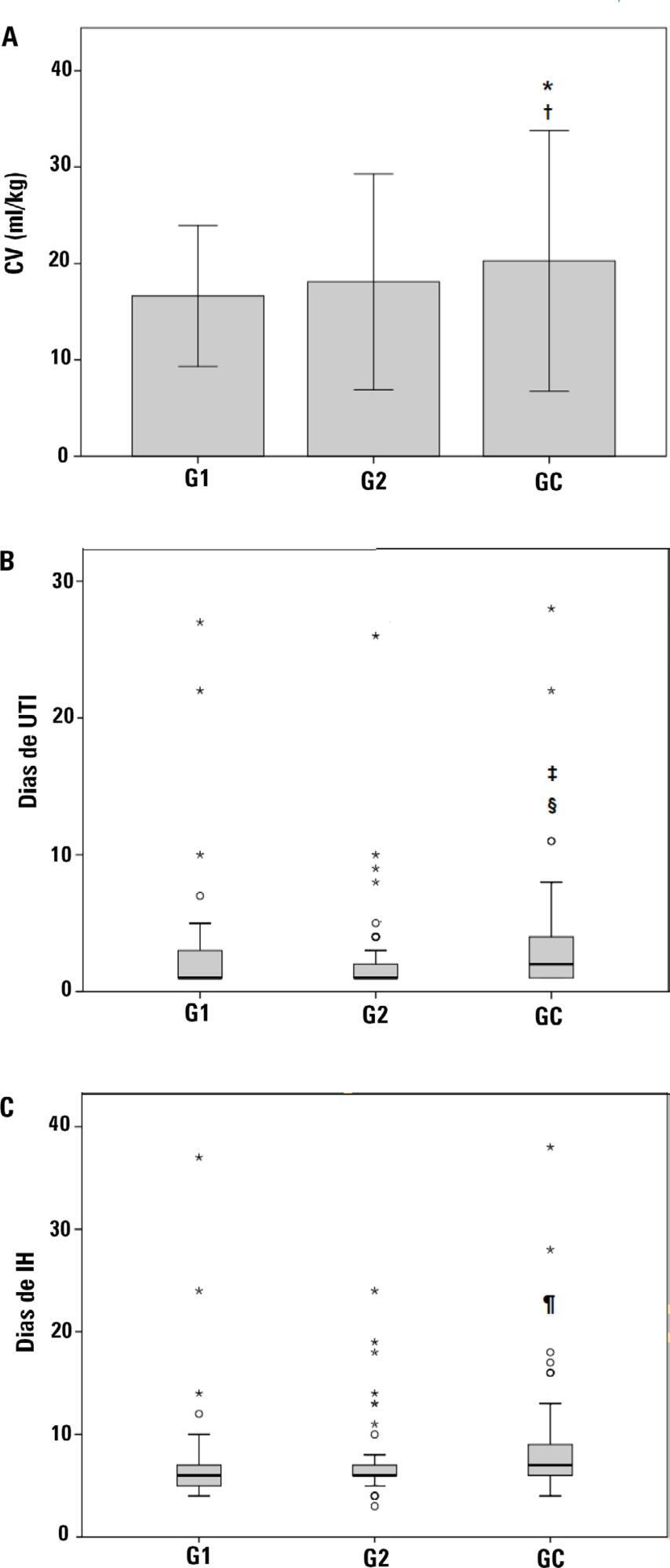
For the 223 patients evaluated, the vital capacity was lower in Groups 1 and 2 compared to the Control (p = 0.000 and p = 0.046, respectively). The length of stay in the intensive care unit was significantly lower in Groups 1 and 2 compared to the Control (p = 0.009 and p = 0.000, respectively), whereas the length of hospital stay was lower in Group 1 compared to the Control (p = 0.014). There was an association between extubation in the operating room (Group 1) with reintubation (p = 0.025) and postoperative complications (p = 0.038).
Patients undergoing fast-track management with extubation within 6 hours had shorter stays in the intensive care unit without increasing postoperative complications and death. Patients extubated in the operating room had a shorter hospital stay and a shorter stay in the intensive care unit but showed an increase in the frequency of reintubation and postoperative complications.