Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(3):326-332
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190041
To evaluate possible associations between nutritional risk and the clinical outcomes of critical patients admitted to an intensive care unit.
A prospective study was carried out with a cohort comprising 200 patients admitted to a university hospital intensive care unit. Nutritional risk was assessed with the NRS-2002 and NUTRIC scores. Patients with scores ≥ 5 were considered at high nutritional risk. Clinical data and outcome measures were obtained from patients' medical records. Multiple logistic regression analysis was used to calculate odds ratios and their respective 95% confidence intervals (for clinical outcomes).
This sample of critical patients had a mean age of 59.4 ± 16.5 years and 53.5% were female. The proportions at high nutritional risk according to NRS-2002 and NUTRIC were 55% and 36.5%, respectively. Multiple logistic regression models adjusted for gender and type of admission indicated that high nutritional risk assessed by the NRS-2002 was positively associated with use of mechanical ventilation (OR = 2.34; 95%CI 1.31 - 4.19; p = 0.004); presence of infection (OR = 2.21; 95%CI 1.24 - 3.94; p = 0.007), and death (OR = 1.86; 95%CI 1.01 - 3.41; p = 0.045). When evaluated by NUTRIC, nutritional risk was associated with renal replacement therapy (OR = 2.10; 95%CI 1.02 - 4.15; p = 0.040) and death (OR = 3.48; 95%CI 1.88 - 6.44; p < 0.001).
In critically ill patients, high nutritional risk was positively associated with an increased risk of clinical outcomes including hospital death.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(3):379-385
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190061
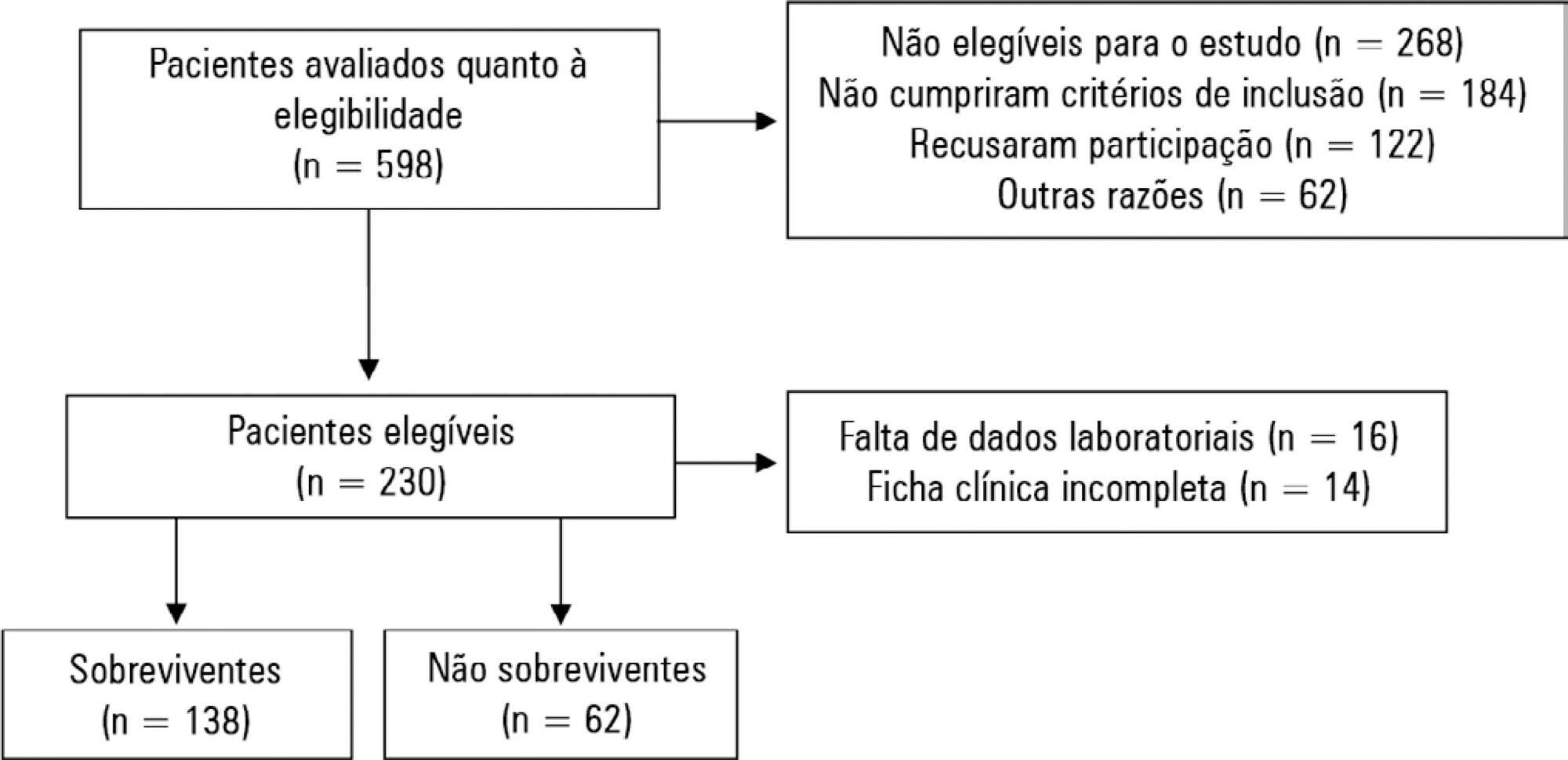
To collect data on the use of The Nutrition Risk in Critically Ill (NUTRIC) score.
A systematic literature search was conducted in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement. Reviews, abstracts, dissertations, protocols and case reports were excluded from this review; to be included in the review, studies needed to specifically evaluate the NUTRIC score and to have been published in English, Spanish or Portuguese.
We included 12 (0.8%) studies from our search in this review. Ten studies (83.3%) were observational, 1 was a pilot study (8.3%) and 1 was a randomized control trial (8.3%). All of the included studies (100%) chose not to use IL-6 and considered a high nutritional risk cutoff point ≥ 5. There were 11 (91.7%) English language studies versus 1 (8.3%) Spanish language study. Mechanical ventilation and a high NUTRIC score were significantly correlated in four studies. The association between intensive care unit or hospital length of stay and nutritional high risk was significant in three studies. Seven studies found a statistically significant association between the NUTRIC score and mortality.
The NUTRIC score is related to clinical outcomes, such as length of hospital stay, and is appropriate for use in critically ill patients in intensive care units.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(2):210-216
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190035
To evaluate the association of nutritional status and protein intake with the clinical outcomes of critically ill patients receiving enteral nutrition therapy in an intensive care unit.
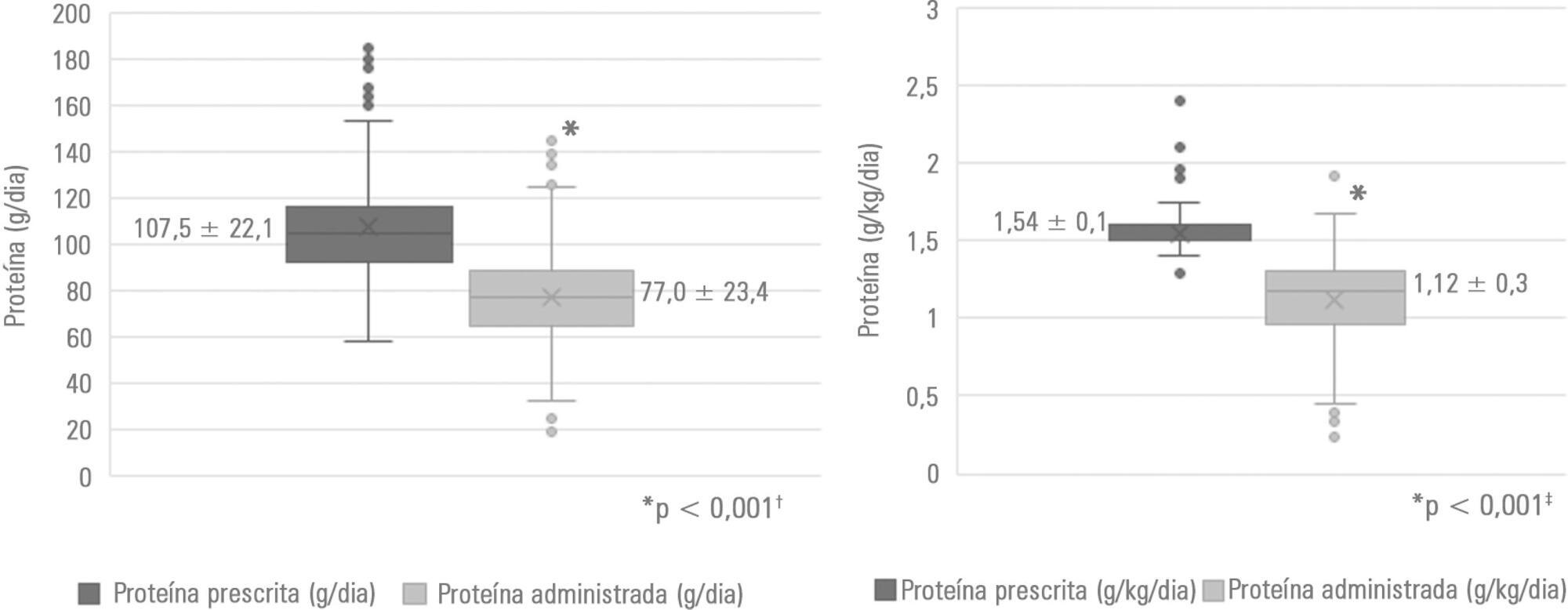
A retrospective observational analytical study was performed by collecting secondary data recorded in medical records of patients ≥ 18 years of age who were admitted to the intensive care unit and who received exclusive enteral nutrition therapy for at least 72 hours in 2017. Nutritional status was assessed by body mass index and arm circumference. For the estimation of protein requirements, the recommendation of the American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition was considered. Nutritional adequacy was assessed by the daily collection of prescribed and administered enteral formula. In the analyses, parametric and nonparametric tests were used, and significance was set at p <0.05.
Of the 188 patients evaluated, 71.3% were male. The median age of the patients was 48.5 years (31.0 - 63.75). The main clinical diagnosis was trauma (46.3%), and eutrophic was the most frequent nutritional status (54.8% according to body mass index and 46.4% according to arm circumference). Protein adequacy was not attained in 56.4% of patients, and only 46.8% reached the minimum protein recommendation. The occurrence of mortality was associated with nutritional diagnosis, body mass index (p = 0.023), arm circumference (p = 0.041) and protein adequacy (p = 0.012).
Nutritional status and protein intake were significantly associated with the clinical outcomes of critically ill patients.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2018;30(2):160-165
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20180034
To compare the prevalence of malnutrition during two time periods in a pediatric intensive care unit.
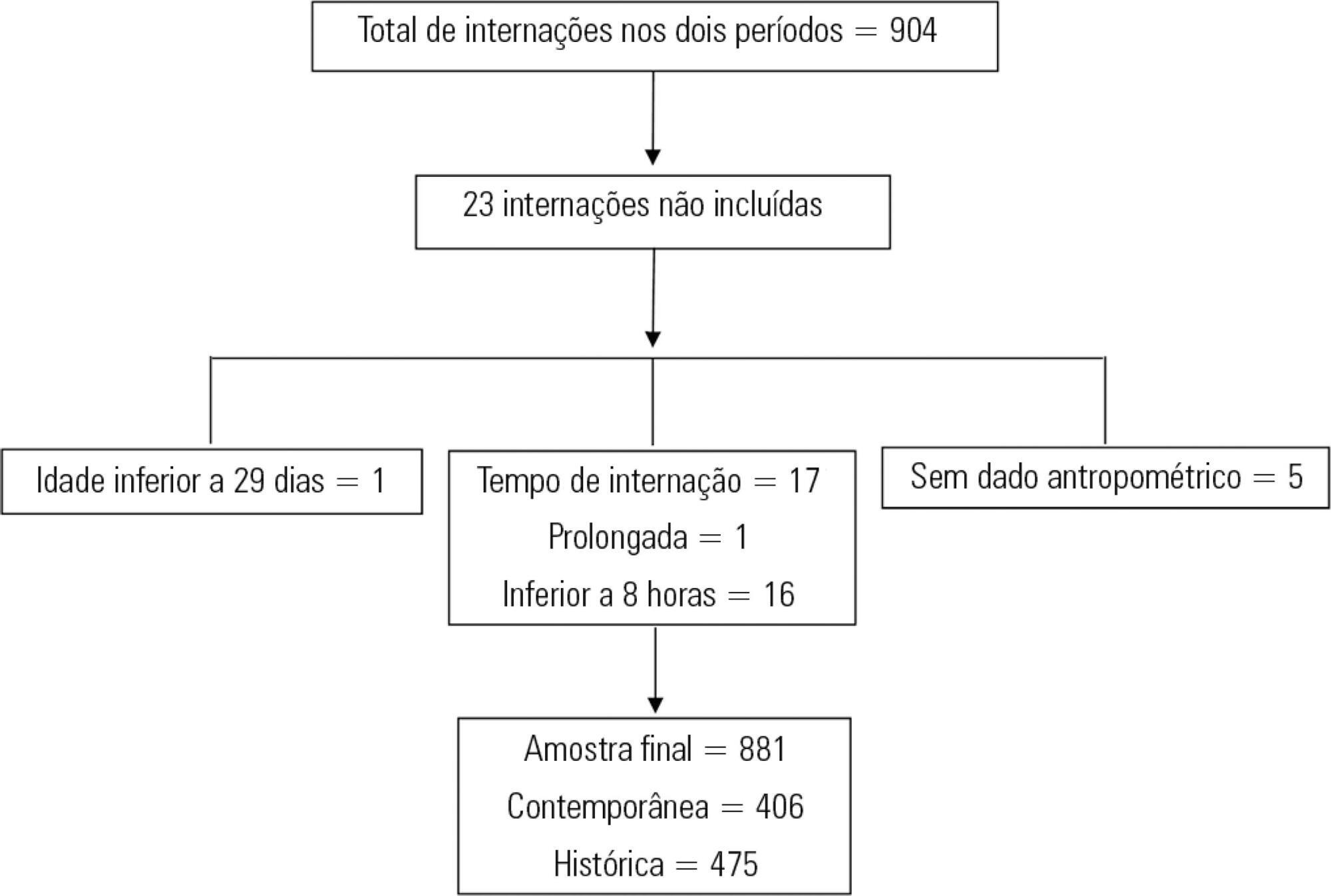
This was a retrospective cross-sectional study of patients admitted to the pediatric intensive care unit of a university hospital during two one-year periods with an interval of four years between them. Nutritional evaluation was conducted based on weight and height measured at admission. The body mass index-for-age was the parameter chosen to evaluate nutritional status, as classified according to the World Health Organization, according to age group.
The total sample size was 881 (406 in the contemporary sample and 475 in the historical sample). There was a significant reduction in malnutrition in the contemporary sample (p = 0.03). Malnourishment in patients in the historical sample was significantly associated with mortality and length of stay, while malnourishment in patients in the contemporary sample was not associated with worse outcomes.
There was a significant reduction in malnutrition among patients in the same pediatric intensive care unit when comparing the two time periods. Our findings of a change in nutritional profile in critically ill patients corroborate the nutritional status data of children and adolescents worldwide.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(3):274-283
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20150032
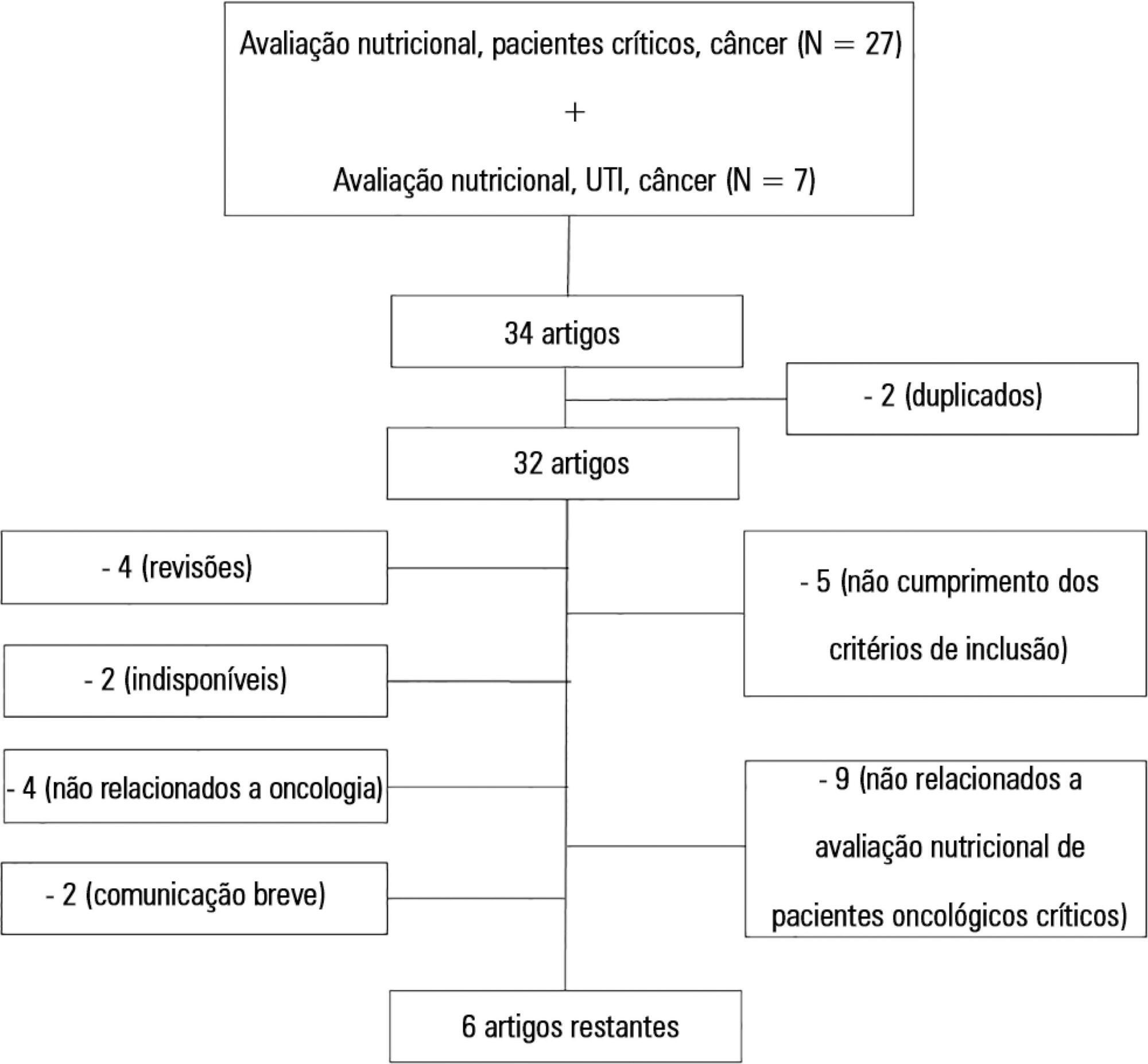
To systematically review the main methods for nutritional risk assessment used in critically ill cancer patients and present the methods that better assess risks and predict relevant clinical outcomes in this group of patients, as well as to discuss the pros and cons of these methods according to the current literature.
The study consisted of a systematic review based on analysis of manuscripts retrieved from the PubMed, LILACS and SciELO databases by searching for the key words “nutritional risk assessment”, “critically ill” and “cancer”.
Only 6 (17.7%) of 34 initially retrieved papers met the inclusion criteria and were selected for the review. The main outcomes of these studies were that resting energy expenditure was associated with undernourishment and overfeeding. The high Patient-Generated Subjective Global Assessment score was significantly associated with low food intake, weight loss and malnutrition. In terms of biochemical markers, higher levels of creatinine, albumin and urea were significantly associated with lower mortality. The worst survival was found for patients with worse Eastern Cooperative Oncologic Group - performance status, high Glasgow Prognostic Score, low albumin, high Patient-Generated Subjective Global Assessment score and high alkaline phosphatase levels. Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index values < 87 were significantly associated with mortality. A high Prognostic Inflammatory and Nutritional Index score was associated with abnormal nutritional status in critically ill cancer patients. Among the reviewed studies that examined weight and body mass index alone, no significant clinical outcome was found.
None of the methods reviewed helped to define risk among these patients. Therefore, assessment by a combination of weight loss and serum measurements, preferably in combination with other methods using scores such as Eastern Cooperative Oncologic Group - performance status, Glasgow Prognostic Score and Patient-Generated Subjective Global Assessment, is suggested given that their use is simple, feasible and useful in such cases.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2012;24(2):157-161
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2012000200010
OBJECTIVE: Because patients hospitalized in intensive care units are at risk for poor nutrition, and nutritional therapy is not always started at an appropriate time, the present study aimed to correlate nutritional status, early nutrition, and hyperglycemia with patient mortality in an intensive care unit. METHODS: This archival cohort study used the secondary database of 453 patients who stayed at least 48 hours in an intensive care unit and were assessed for 8 days of hospitalization. Patient nutritional status was defined according to the body mass index. Early nutrition was defined as an feeding energy within the first 48 hours of hospitalization, regardless of the administration route. Blood glucose levels were monitored using a glucometer. RESULTS: A majority of patients were male (54.2%), and approximately half of patients were overweight (48.4%). At the end of the first 48 hours, 69.4% of patients had received nutrition, and only 13.5% of patients still exhibited hyperglycemia. The patients who received early nutritional therapy exhibited lower a mortality risk (p = 0.002), regardless of the presence of other factors associated with mortality. CONCLUSIONS: The significant correlation between early nutritional therapy and survival emphasizes the importance of nutrition in severely ill patients. The low frequency of hyperglycemia found in this study might indicate that the prescription of nutritional therapy and the application of an insulin protocol are appropriate at institutional intensive care units.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2010;22(3):270-273
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2010000300009
OBJECTIVE: To evaluate the prevalence of gastrointestinal complications and protein-calorie adequacy in critical patients using enteral nutrition therapy. METHODS: This was a retrospective study in the intensive care unit of the Hospital das Clinicas of the Universidade Federal de Pernambuco involving analysis of nutritional records evaluating the most frequent gastrointestinal complications during the patients' hospitalization and protein-calorie supply requirements. It was considered offered, the volume and formula effectively received by the patient on the last hospitalization day. The SPSS version 13 software was used for statistical analysis. RESULTS: The sample consisted of 77 patients aged in average 54.7 ± 18.1 years who were predominantly female (54.5%). The diet offered was appropriate and all patients had some type of gastrointestinal complications, being high gastric residuals the most prevalent (39%), followed by constipation (36.4%). CONCLUSION: Despite the high prevalence of gastrointestinal complications, no mismatches were observed in protein-calorie intake. Multidisciplinary approaches to these complications should be standardized in order to provide their early resolution.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2008;20(3):286-295
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2008000300012
Considering the importance and the difficulties inherent to nutritional state assessment, as well as the results interpretation and the inexistence of specific and validated guidelines related to applied methods to the severely ill patient, the present revision aims to contribute to the analysis and recommendation of efficient methods, which are suitable to use and reliable in terms of interpretation in the context of the severely ill patient. The presence of edema and unspecific alterations in the plasmatic concentrations of proteins; altered anthropometrics variables reflecting more the rearrangement of the total body water than the nutritional state changes; inconclusive studies with electric bioimpedance; absence of data related to the application of the global subjective assessment to severely ill patients; altered biochemical markers as a consequence of the metabolic changes that, among others, indicate several method limitations to these patients. Notwithstanding the lack of studies to validate the various methods, recommendations based on clinical evidences, observation and physiopathology alterations are available. Independent from the methods, clinical observation by the health staff at all stages is mandatory. It is crucial to dedicate more efforts to identify methods and their specificity to detection, risk assessment or monitoring.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (116) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)