Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(3):379-385
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190061
To collect data on the use of The Nutrition Risk in Critically Ill (NUTRIC) score.
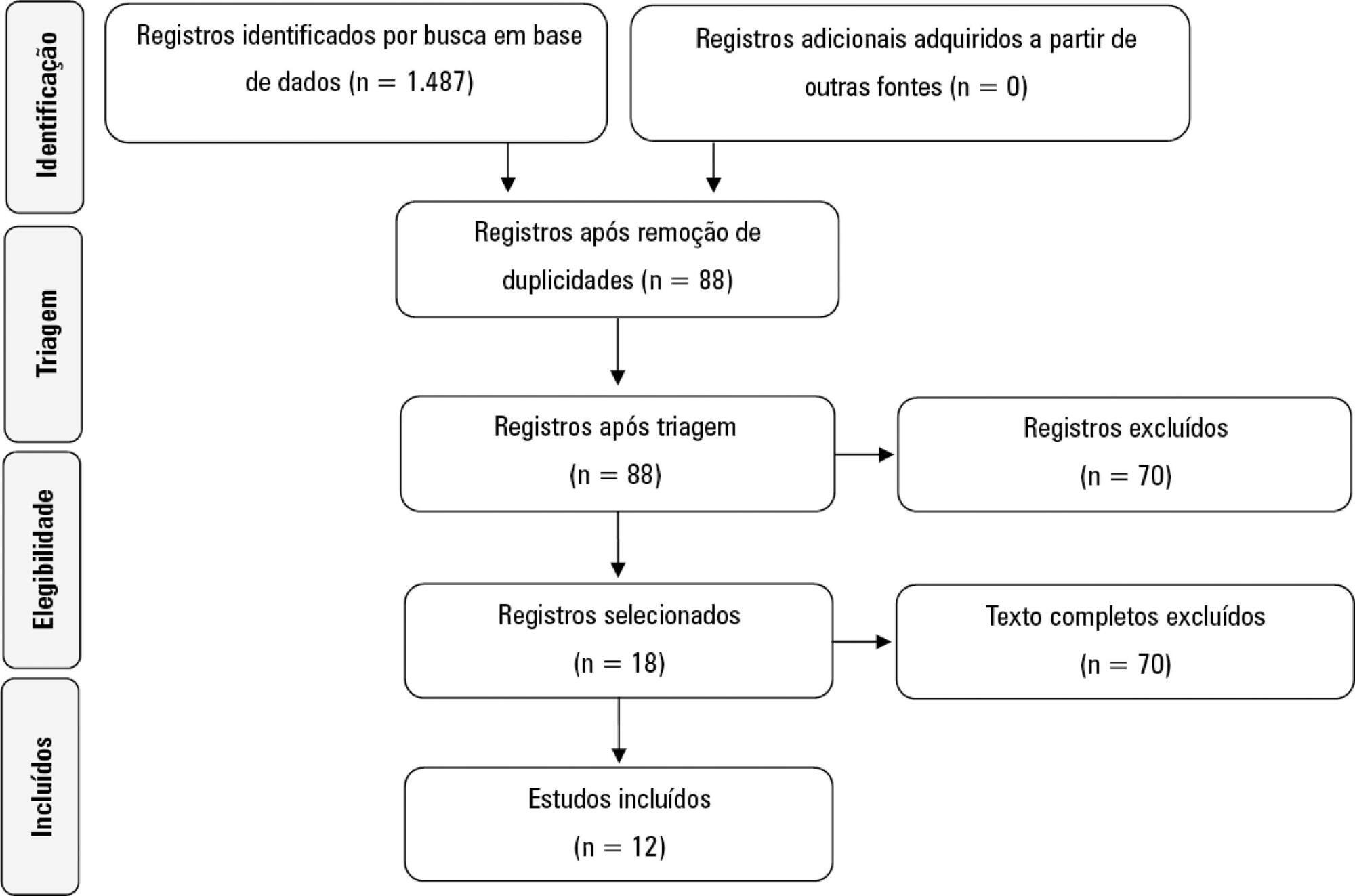
A systematic literature search was conducted in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement. Reviews, abstracts, dissertations, protocols and case reports were excluded from this review; to be included in the review, studies needed to specifically evaluate the NUTRIC score and to have been published in English, Spanish or Portuguese.
We included 12 (0.8%) studies from our search in this review. Ten studies (83.3%) were observational, 1 was a pilot study (8.3%) and 1 was a randomized control trial (8.3%). All of the included studies (100%) chose not to use IL-6 and considered a high nutritional risk cutoff point ≥ 5. There were 11 (91.7%) English language studies versus 1 (8.3%) Spanish language study. Mechanical ventilation and a high NUTRIC score were significantly correlated in four studies. The association between intensive care unit or hospital length of stay and nutritional high risk was significant in three studies. Seven studies found a statistically significant association between the NUTRIC score and mortality.
The NUTRIC score is related to clinical outcomes, such as length of hospital stay, and is appropriate for use in critically ill patients in intensive care units.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2018;30(2):160-165
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20180034
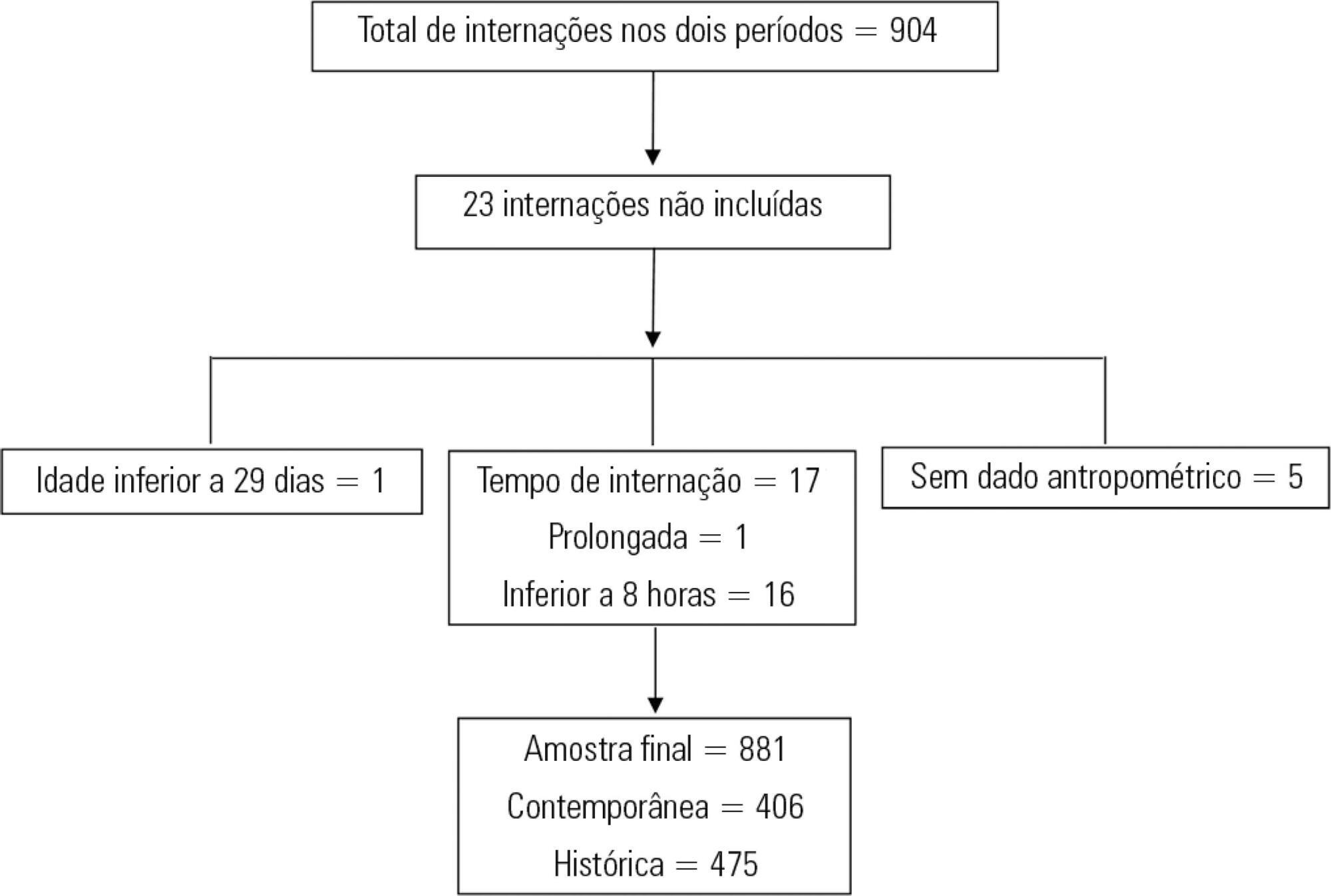
To compare the prevalence of malnutrition during two time periods in a pediatric intensive care unit.
This was a retrospective cross-sectional study of patients admitted to the pediatric intensive care unit of a university hospital during two one-year periods with an interval of four years between them. Nutritional evaluation was conducted based on weight and height measured at admission. The body mass index-for-age was the parameter chosen to evaluate nutritional status, as classified according to the World Health Organization, according to age group.
The total sample size was 881 (406 in the contemporary sample and 475 in the historical sample). There was a significant reduction in malnutrition in the contemporary sample (p = 0.03). Malnourishment in patients in the historical sample was significantly associated with mortality and length of stay, while malnourishment in patients in the contemporary sample was not associated with worse outcomes.
There was a significant reduction in malnutrition among patients in the same pediatric intensive care unit when comparing the two time periods. Our findings of a change in nutritional profile in critically ill patients corroborate the nutritional status data of children and adolescents worldwide.