Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(4):490-496
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190086
To evaluate the concordance between the modified NUTRIC and NUTRIC with C-reactive protein instruments in identifying nutritional risk patients and predicting mortality in critically ill patients. The risk of death in patient groups was also investigated according to nutritional risk and malnutrition detected by subjective global assessment.
A cohort study of patients admitted to an intensive care unit. Nutritional risk was assessed by modified NUTRIC and a version of NUTRIC with C-reactive protein. Subjective global assessment was applied to diagnose malnutrition. Kappa statistics were calculated, and an ROC curve was constructed considering modified NUTRIC as a reference. The predictive validity was assessed considering mortality in 28 days (whether in the intensive care unit or after discharge) as the outcome.
A total of 130 patients were studied (63.05 ± 16.46 years, 53.8% males). According to NUTRIC with C-reactive protein, 34.4% were classified as having a high score, while 28.5% of patients had this classification with modified NUTRIC. According to SGA 48.1% of patients were malnourished. There was excellent agreement between modified NUTRIC and NUTRIC with C-reactive protein (Kappa = 0.88, p < 0.001). The area under the ROC curve was equal to 0.942 (0.881 - 1.000) for NUTRIC with C-reactive protein. The risk of death within 28 days was increased in patients with high modified NUTRIC (HR = 1.827; 95%CI 1.029 - 3.244; p = 0.040) and NUTRIC with C-reactive protein (HR = 2.685; 95%CI 1.423 - 5.064; p = 0.002) scores. A high risk of death was observed in patients with high nutritional risk and malnutrition, independent of the version of the NUTRIC score applied.
An excellent agreement between modified NUTRIC and NUTRIC with C-reactive protein was observed. In addition, combining NUTRIC and subjective global assessment may increase the accuracy of predicting mortality in critically ill patients.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2011;23(4):492-498
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2011000400015
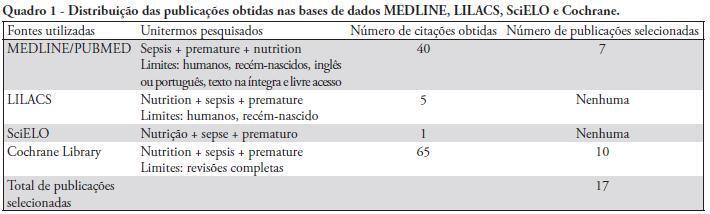
This article reviews the current understanding of enteral and parenteral nutrition therapy in preterm infants, with an emphasis on very low birth weight babies. The protective effects of nutrition therapy against neonatal sepsis and necrotizing enterocolitis are discussed. Different methods of feeding preterm infants are evaluated. Special attention is given to the problems of very low birth weight babies and the protective effects of nutrition to counteract complications, especially infection. The preferential use of breast milk for enteral nutrition, the management of protein and energy offers, the use of early and minimal enteral nutrition, the early introduction of parenteral nutrition (within the first 24 hours of life) and the use of immunonutrients that are appropriately supported by a sufficient number of studies can provide good adjuvant therapy guidelines to prevent neonatal sepsis and necrotizing enterocolitis. However, we conclude that additional multicenter, randomized controlled studies are necessary to clarify the protective role of nutrition in preterm infants. Appropriate nutrition is not only effective in treating and preventing infective complications, but it also promotes neurodevelopment and prevents future harmful consequences.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (116) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)