Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2024;36:e20240005en
DOI 10.62675/2965-2774.20240005-en
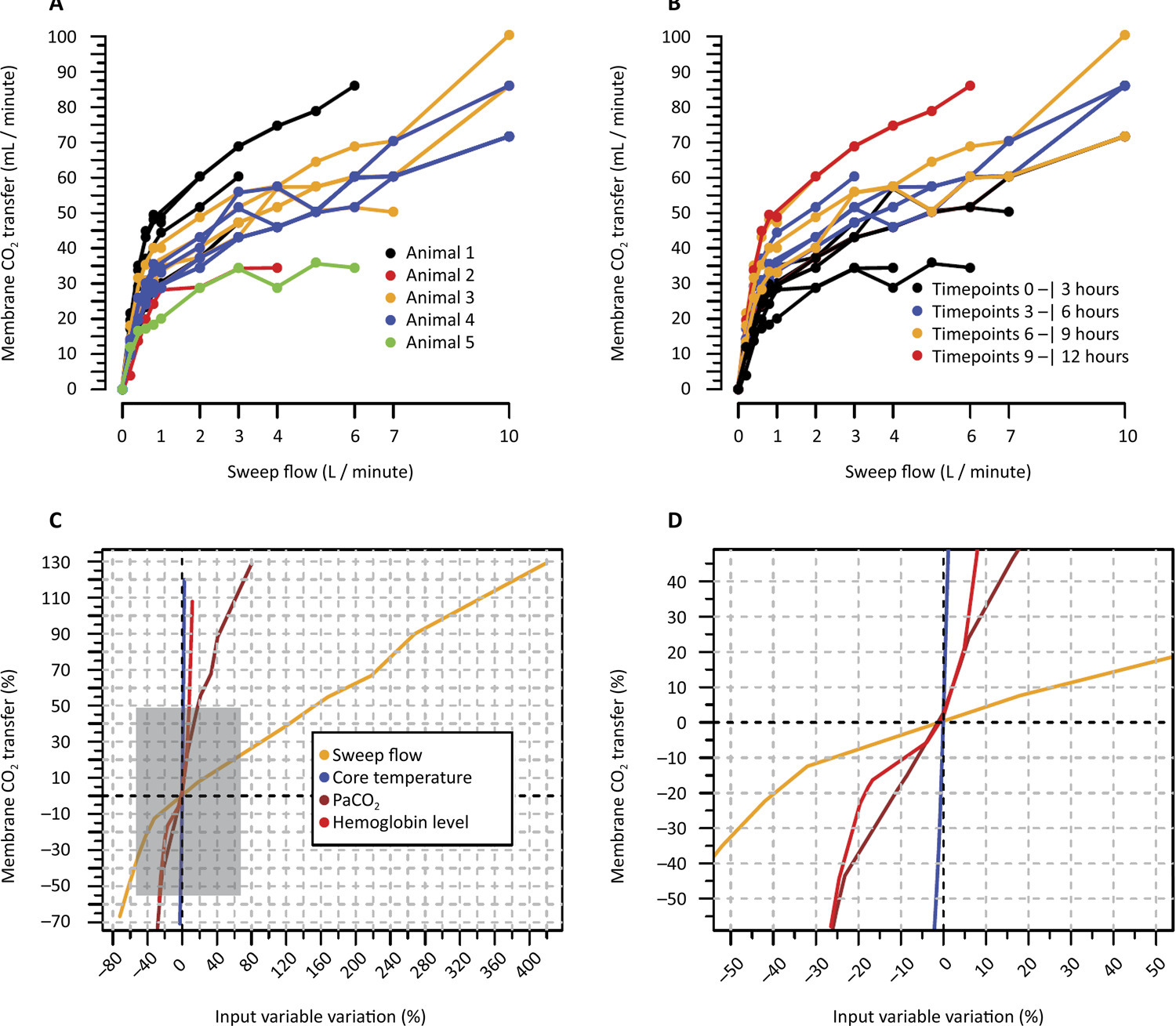
To investigate the factors influencing carbon dioxide transfer in a system that integrates an oxygenation membrane in series with high-bicarbonate continuous veno-venous hemodialysis in hypercapnic animals.
In an experimental setting, we induced severe acute kidney injury and hypercapnia in five female Landrace pigs. Subsequently, we initiated high (40mEq/L) bicarbonate continuous veno-venous hemodialysis with an oxygenation membrane in series to maintain a pH above 7.25. At intervals of 1 hour, 6 hours, and 12 hours following the initiation of continuous veno-venous hemodialysis, we performed standardized sweep gas flow titration to quantify carbon dioxide transfer. We evaluated factors associated with carbon dioxide transfer through the membrane lung with a mixed linear model.
A total of 20 sweep gas flow titration procedures were conducted, yielding 84 measurements of carbon dioxide transfer. Multivariate analysis revealed associations among the following (coefficients ± standard errors): core temperature (+7.8 ± 1.6 °C, p < 0.001), premembrane partial pressure of carbon dioxide (+0.2 ± 0.1/mmHg, p < 0.001), hemoglobin level (+3.5 ± 0.6/g/dL, p < 0.001), sweep gas flow (+6.2 ± 0.2/L/minute, p < 0.001), and arterial oxygen saturation (-0.5 ± 0.2%, p = 0.019). Among these variables, and within the physiological ranges evaluated, sweep gas flow was the primary modifiable factor influencing the efficacy of low-blood-flow carbon dioxide removal.
Sweep gas flow is the main carbon dioxide removal-related variable during continuous veno-venous hemodialysis with a high bicarbonate level coupled with an oxygenator. Other carbon dioxide transfer modulating variables included the hemoglobin level, arterial oxygen saturation, partial pressure of carbon dioxide and core temperature. These results should be interpreted as exploratory to inform other well-designed experimental or clinical studies.
Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2024;36:e20240253en
DOI 10.62675/2965-2774.20240253-en
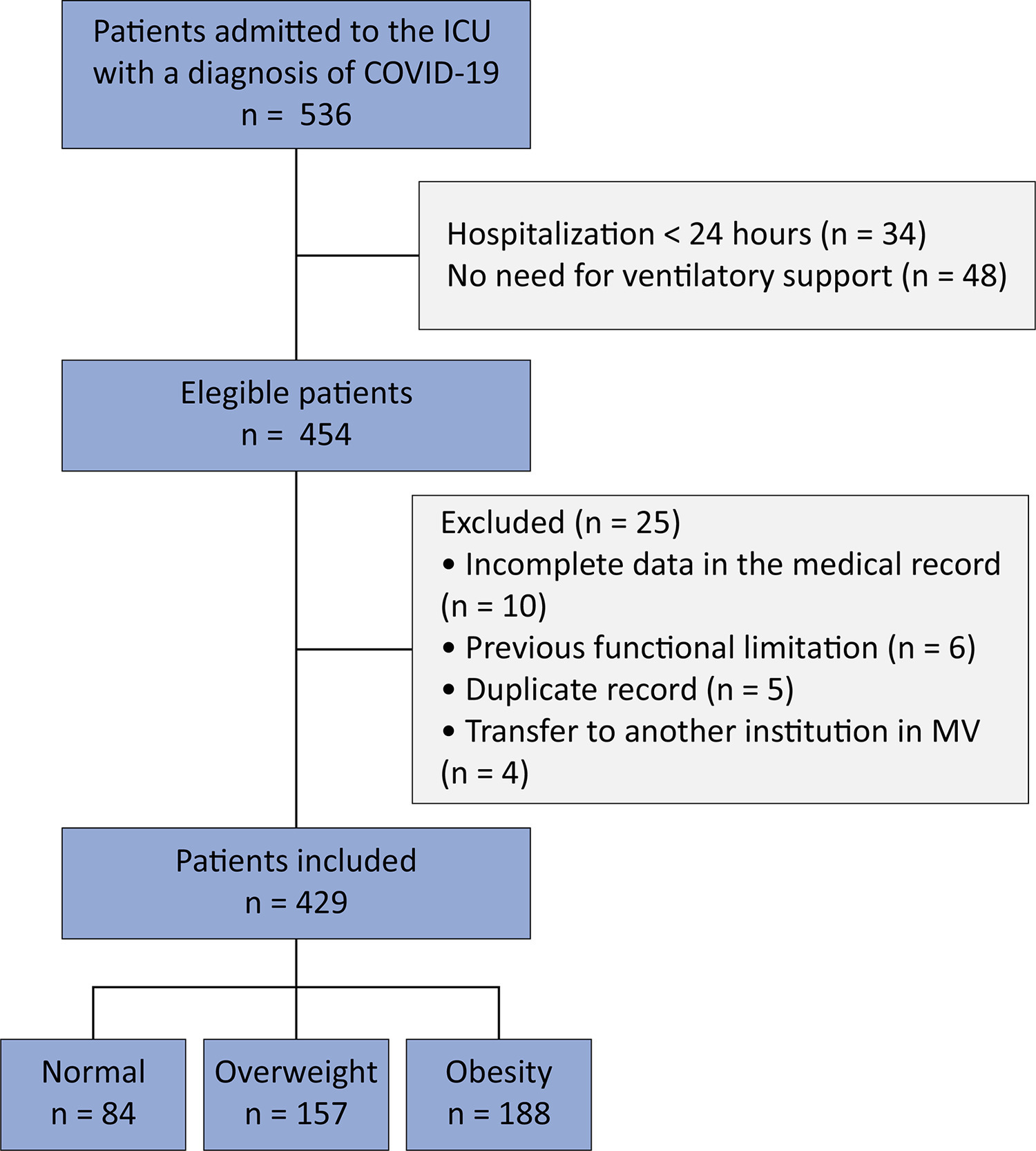
To identify the influence of obesity on mortality, time to weaning from mechanical ventilation and mobility at intensive care unit discharge in patients with COVID-19.
This retrospective cohort study was carried out between March and August 2020. All adult patients admitted to the intensive care unit in need of ventilatory support and confirmed to have COVID-19 were included. The outcomes included mortality, time on mechanical ventilation, and mobility at intensive care unit discharge.
Four hundred and twenty-nine patients were included, 36.6% of whom were overweight and 43.8% of whom were obese. Compared with normal body mass index patients, overweight and obese patients had lower mortality (p = 0.002) and longer intensive care unit survival (log-rank p < 0.001). Compared with patients with a normal body mass index, overweight patients had a 36% lower risk of death (p = 0.04), while patients with obesity presented a 23% lower risk (p < 0.001). There was no association between obesity and time on mechanical ventilation. The level of mobility at intensive care unit discharge did not differ between groups and showed a moderate inverse correlation with length of stay in the intensive care unit (r = -0.461; p < 0.001).
Overweight and obese patients had lower mortality and higher intensive care unit survival rates. The duration of mechanical ventilation and mobility level at intensive care unit discharge did not differ between the groups.
Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2024;36:e20240203en
DOI 10.62675/2965-2774.20240203-en
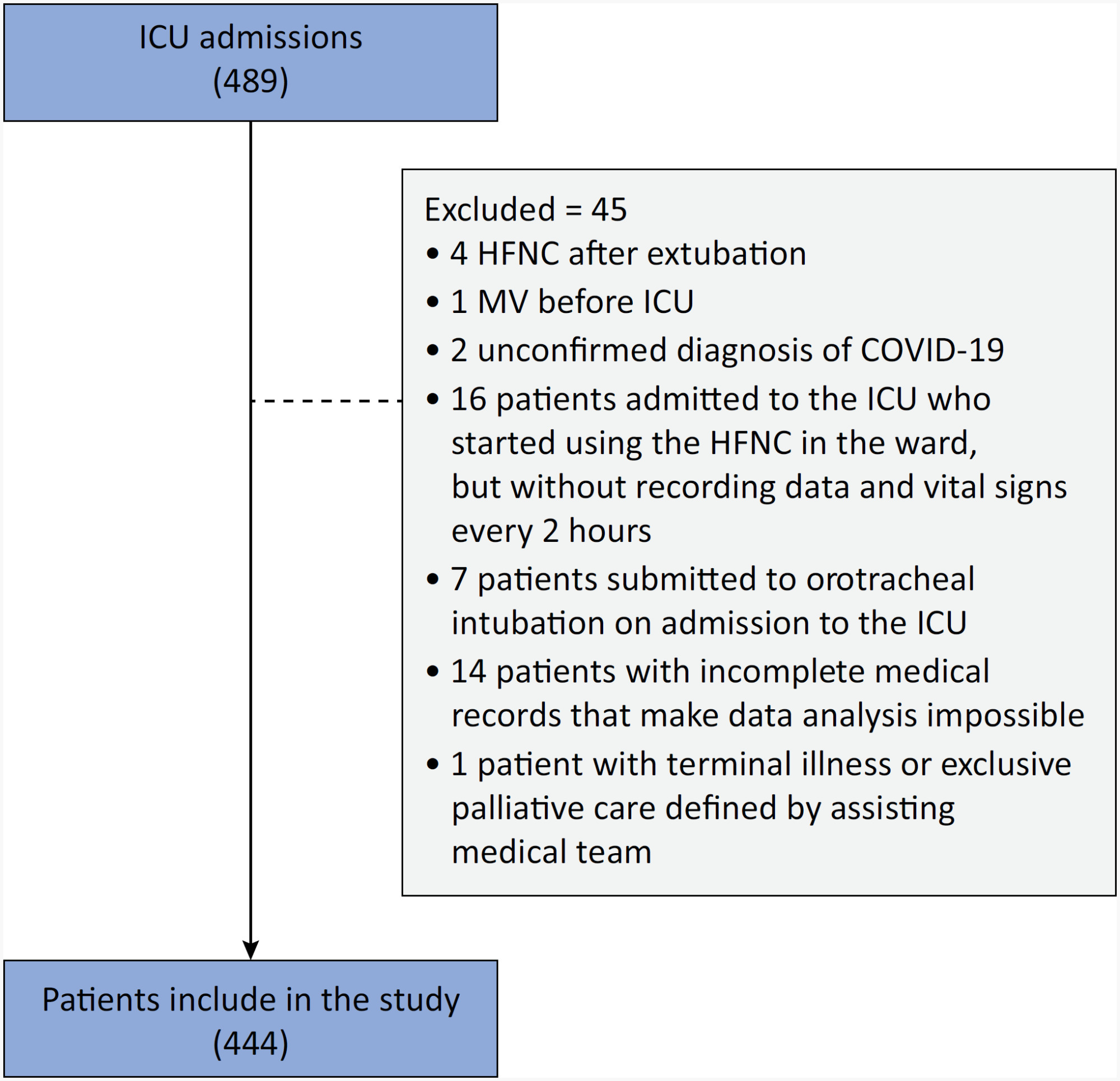
To assess whether the respiratory oxygenation index (ROX index) measured after the start of high-flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy can help identify the need for intubation in patients with acute respiratory failure due to coronavirus disease 2019.
This retrospective, observational, multicenter study was conducted at the intensive care units of six Brazilian hospitals from March to December 2020. The primary outcome was the need for intubation up to 7 days after starting the high-flow nasal cannula.
A total of 444 patients were included in the study, and 261 (58.7%) were subjected to intubation. An analysis of the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) showed that the ability to discriminate between successful and failed high-flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy within 7 days was greater for the ROX index measured at 24 hours (AUROC 0.80; 95%CI 0.76 - 0.84). The median interval between high-flow nasal cannula initiation and intubation was 24 hours (24 - 72), and the most accurate predictor of intubation obtained before 24 hours was the ROX index measured at 12 hours (AUROC 0.75; 95%CI 0.70 - 0.79). Kaplan-Meier curves revealed a greater probability of intubation within 7 days in patients with a ROX index ≤ 5.54 at 12 hours (hazard ratio 3.07; 95%CI 2.24 - 4.20) and ≤ 5.96 at 24 hours (hazard ratio 5.15; 95%CI 3.65 - 7.27).
The ROX index can aid in the early identification of patients with acute respiratory failure due to COVID-19 who will progress to the failure of high-flow nasal cannula supportive therapy and the need for intubation.
Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2024;36:e20240229en
DOI 10.62675/2965-2774.20240229-en
To compare two methods for defining and classifying the severity of pediatric acute respiratory distress syndrome: the Berlin classification, which uses the relationship between the partial pressure of oxygen and the fraction of inspired oxygen, and the classification of the Pediatric Acute Lung Injury Consensus Conference, which uses the oxygenation index.
This was a prospective study of patients aged 0 - 18 years with a diagnosis of acute respiratory distress syndrome who were invasively mechanically ventilated and provided one to three arterial blood gas samples, totaling 140 valid measurements. These measures were evaluated for correlation using the Spearman test and agreement using the kappa coefficient between the two classifications, initially using the general population of the study and then subdividing it into patients with and without bronchospasm and those with and without the use of neuromuscular blockers. The effect of these two factors (bronchospasm and neuromuscular blocking agent) separately and together on both classifications was also assessed using two-way analysis of variance.
In the general population, who were 54 patients aged 0 - 18 years a strong negative correlation was found by Spearman’s test (ρ -0.91; p < 0.001), and strong agreement was found by the kappa coefficient (0.62; p < 0.001) in the comparison between Berlin and Pediatric Acute Lung Injury Consensus Conference. In the populations with and without bronchospasm and who did and did not use neuromuscular blockers, the correlation coefficients were similar to those of the general population, though among patients not using neuromuscular blockers, there was greater agreement between the classifications than for patients using neuromuscular blockers (kappa 0.67 versus 0.56, p < 0.001 for both). Neuromuscular blockers had a significant effect on the relationship between the partial pressure of oxygen and the fraction of inspired oxygen (analysis of variance; F: 12.9; p < 0.001) and the oxygenation index (analysis of variance; F: 8.3; p = 0.004).
There was a strong correlation and agreement between the two classifications in the general population and in the subgroups studied. Use of neuromuscular blockers had a significant effect on the severity of acute respiratory distress syndrome.
Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2024;36:e20240246en
DOI 10.62675/2965-2774.20240246-en
To discuss the strengths and limitations of ventilator-free days and to provide a comprehensive discussion of the different analytic methods for analyzing and interpreting this outcome.
Using simulations, the power of different analytical methods was assessed, namely: quantile (median) regression, cumulative logistic regression, generalized pairwise comparison, conditional approach and truncated approach. Overall, 3,000 simulations of a two-arm trial with n = 300 per arm were computed using a two-sided alternative hypothesis and a type I error rate of α = 0.05.
When considering power, median regression did not perform well in studies where the treatment effect was mainly driven by mortality. Median regression performed better in situations with a weak effect on mortality but a strong effect on duration, duration only, and moderate mortality and duration. Cumulative logistic regression was found to produce similar power to the Wilcoxon rank-sum test across all scenarios, being the best strategy for the scenarios of moderate mortality and duration, weak mortality and strong duration, and duration only.
In this study, we describe the relative power of new methods for analyzing ventilator-free days in critical care research. Our data provide validation and guidance for the use of the cumulative logistic model, median regression, generalized pairwise comparisons, and the conditional and truncated approach in specific scenarios.
Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2024;36:e20240196en
DOI 10.62675/2965-2774.20240196-en
To provide insights into the potential benefits of goal-directed therapy guided by FloTrac in reducing postoperative complications and improving outcomes.
We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials to evaluate goal-directed therapy guided by FloTrac in major surgery, comparing goal-directed therapy with usual care or invasive monitoring in cardiac and noncardiac surgery subgroups. The quality of the articles and evidence were evaluated with a risk of bias tool and GRADE.
We included 29 randomized controlled trials with 3,468 patients. Goal-directed therapy significantly reduced the duration of hospital stay (mean difference -1.43 days; 95%CI 2.07 to -0.79; I2 81%), intensive care unit stay (mean difference -0.77 days; 95%CI -1.18 to -0.36; I2 93%), and mechanical ventilation (mean difference -2.48 hours, 95%CI -4.10 to -0.86, I2 63%). There was no statistically significant difference in mortality, myocardial infarction, acute kidney injury or hypotension, but goal-directed therapy significantly reduced the risk of heart failure or pulmonary edema (RR 0.46; 95%CI 0.23 - 0.92; I2 0%).
Goal-directed therapy guided by the FloTrac sensor improved clinical outcomes and shortened the length of stay in the hospital and intensive care unit in patients undergoing major surgery. Further research can validate these results using specific protocols and better understand the potential benefits of FloTrac beyond these outcomes.
Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2024;36:e20240208en
DOI 10.62675/2965-2774.20240208-en
To evaluate the association between driving pressure and tidal volume based on predicted body weight and mortality in a cohort of patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome caused by COVID-19.
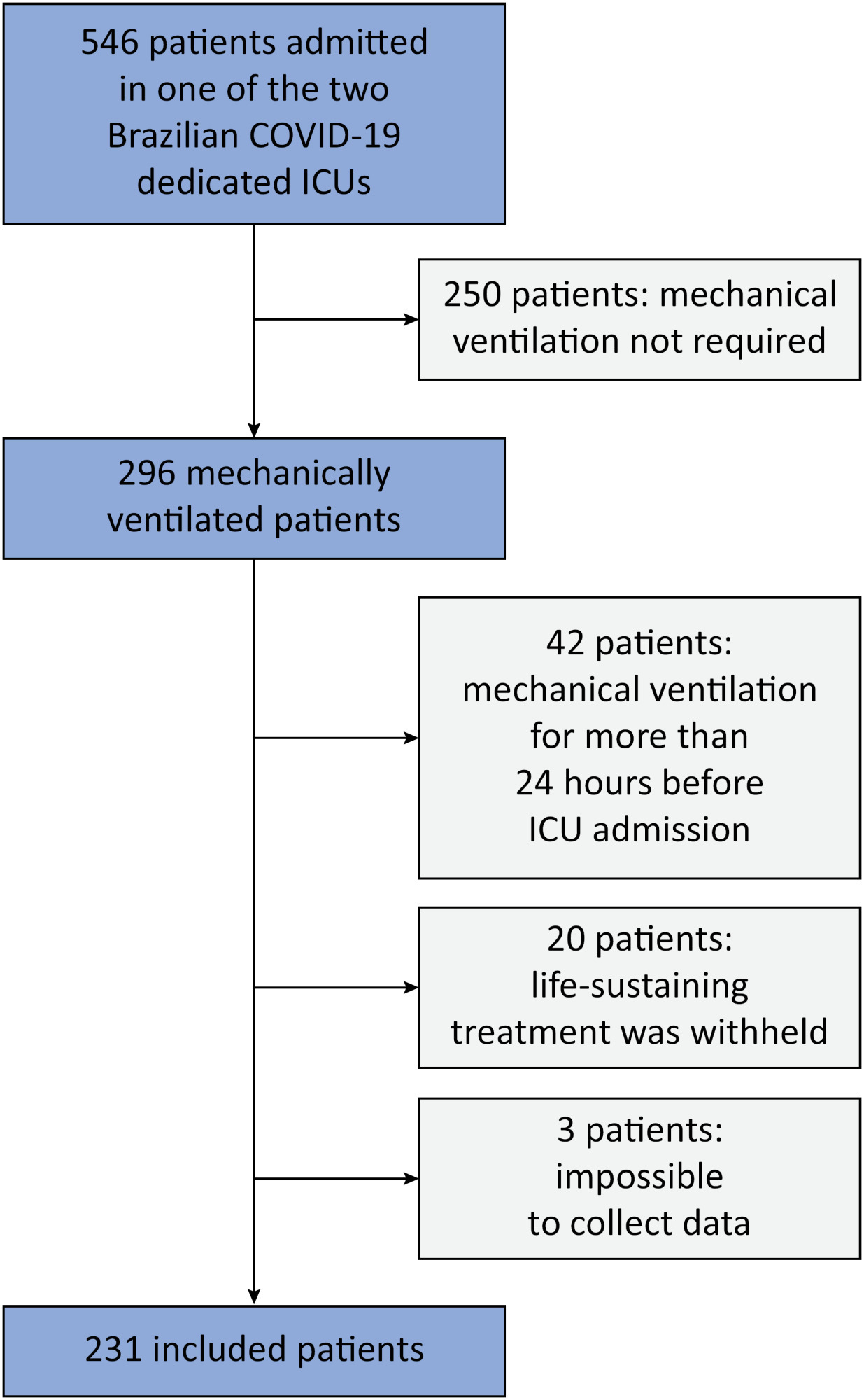
This was a prospective, observational study that included patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome due to COVID-19 admitted to two intensive care units. We performed multivariable analyses to determine whether driving pressure and tidal volume/kg predicted body weight on the first day of mechanical ventilation, as independent variables, are associated with hospital mortality.
We included 231 patients. The mean age was 64 (53 - 74) years, and the mean Simplified Acute and Physiology Score 3 score was 45 (39 - 54). The hospital mortality rate was 51.9%. Driving pressure was independently associated with hospital mortality (odds ratio 1.21, 95%CI 1.04 - 1.41 for each cm H2O increase in driving pressure, p = 0.01). Based on a double stratification analysis, we found that for the same level of tidal volume/kg predicted body weight, the risk of hospital death increased with increasing driving pressure. However, changes in tidal volume/kg predicted body weight were not associated with mortality when they did not lead to an increase in driving pressure.
In patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome caused by COVID-19, exposure to higher driving pressure, as opposed to higher tidal volume/kg predicted body weight, is associated with greater mortality. These results suggest that driving pressure might be a primary target for lung-protective mechanical ventilation in these patients.
Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2024;36:e20240284en
DOI 10.62675/2965-2774.20240284-en
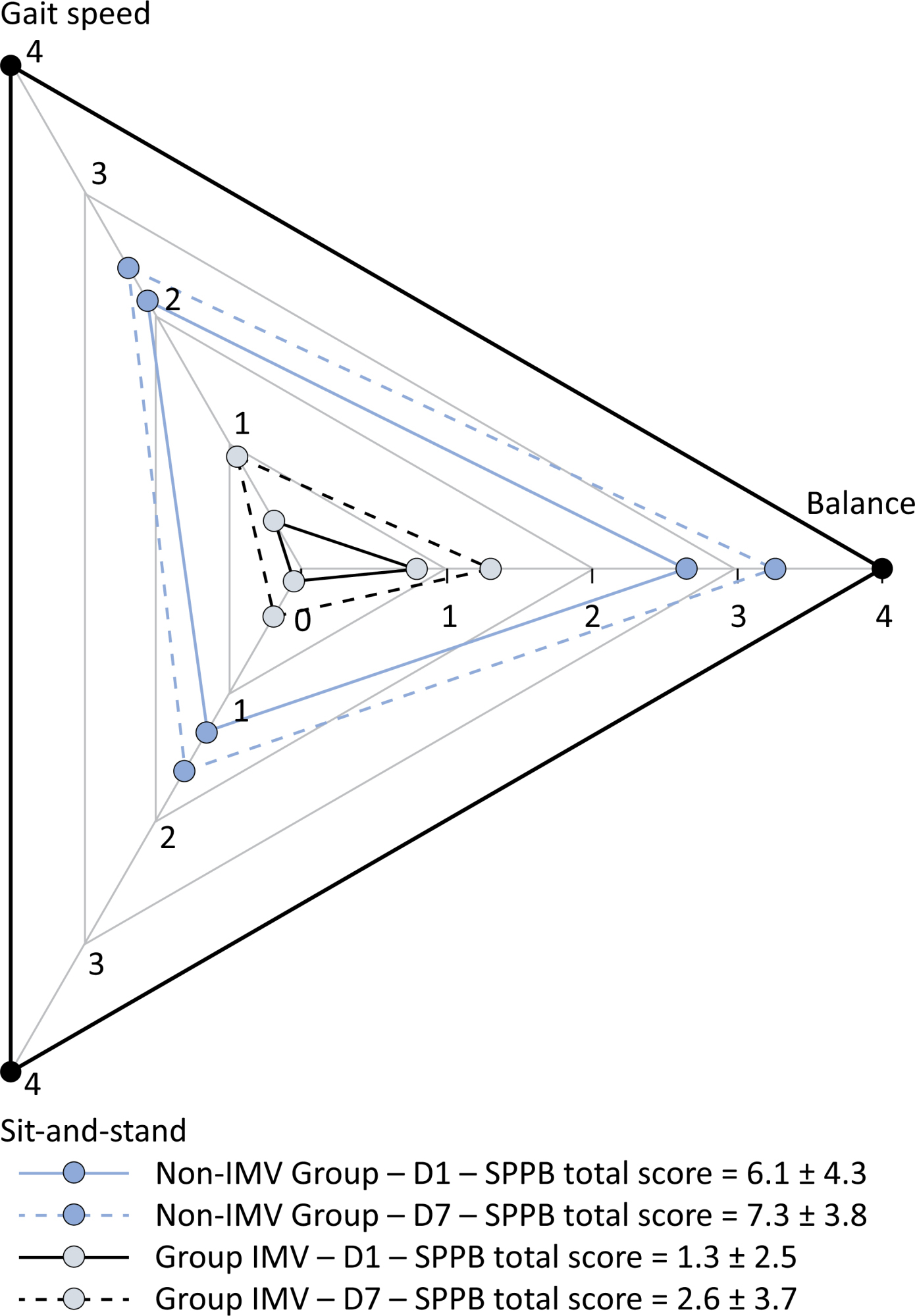
To examine the physical function and respiratory muscle strength of patients - who recovered from critical COVID-19 – after intensive care unit discharge to the ward on Days one (D1) and seven (D7), and to investigate variables associated with functional impairment.
This was a prospective cohort study of adult patients with COVID-19 who needed invasive mechanical ventilation, non-invasive ventilation or high-flow nasal cannula and were discharged from the intensive care unit to the ward. Participants were submitted to Medical Research Council sum-score, handgrip strength, maximal inspiratory pressure, maximal expiratory pressure, and short physical performance battery tests. Participants were grouped into two groups according to their need for invasive ventilation: the Invasive Mechanical Ventilation Group (IMV Group) and the Non-Invasive Mechanical Ventilation Group (Non-IMV Group).
Patients in the IMV Group (n = 31) were younger and had higher Sequential Organ Failure Assessment scores than those in the Non-IMV Group (n = 33). The short physical performance battery scores (range 0 - 12) on D1 and D7 were 6.1 ± 4.3 and 7.3 ± 3.8, respectively for the Non-Invasive Mechanical Ventilation Group, and 1.3 ± 2.5 and 2.6 ± 3.7, respectively for the IMV Group. The prevalence of intensive care unit-acquired weakness on D7 was 13% for the Non-IMV Group and 72% for the IMV Group. The maximal inspiratory pressure, maximal expiratory pressure, and handgrip strength increased on D7 in both groups, but the maximal expiratory pressure and handgrip strength were still weak. Only maximal inspiratory pressure was recovered (i.e., > 80% of the predicted value) in the Non-IMV Group. Female sex, and the need and duration of invasive mechanical were independently and negatively associated with the short physical performance battery score and handgrip strength.
Patients who recovered from critical COVID-19 and who received invasive mechanical ventilation presented greater disability than those who were not invasively ventilated. However, they both showed marginal functional improvement during early recovery, regardless of the need for invasive mechanical ventilation. This might highlight the severity of disability caused by SARS-CoV-2.