Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2024;36:e20240284en
DOI 10.62675/2965-2774.20240284-en
To examine the physical function and respiratory muscle strength of patients - who recovered from critical COVID-19 – after intensive care unit discharge to the ward on Days one (D1) and seven (D7), and to investigate variables associated with functional impairment.
This was a prospective cohort study of adult patients with COVID-19 who needed invasive mechanical ventilation, non-invasive ventilation or high-flow nasal cannula and were discharged from the intensive care unit to the ward. Participants were submitted to Medical Research Council sum-score, handgrip strength, maximal inspiratory pressure, maximal expiratory pressure, and short physical performance battery tests. Participants were grouped into two groups according to their need for invasive ventilation: the Invasive Mechanical Ventilation Group (IMV Group) and the Non-Invasive Mechanical Ventilation Group (Non-IMV Group).
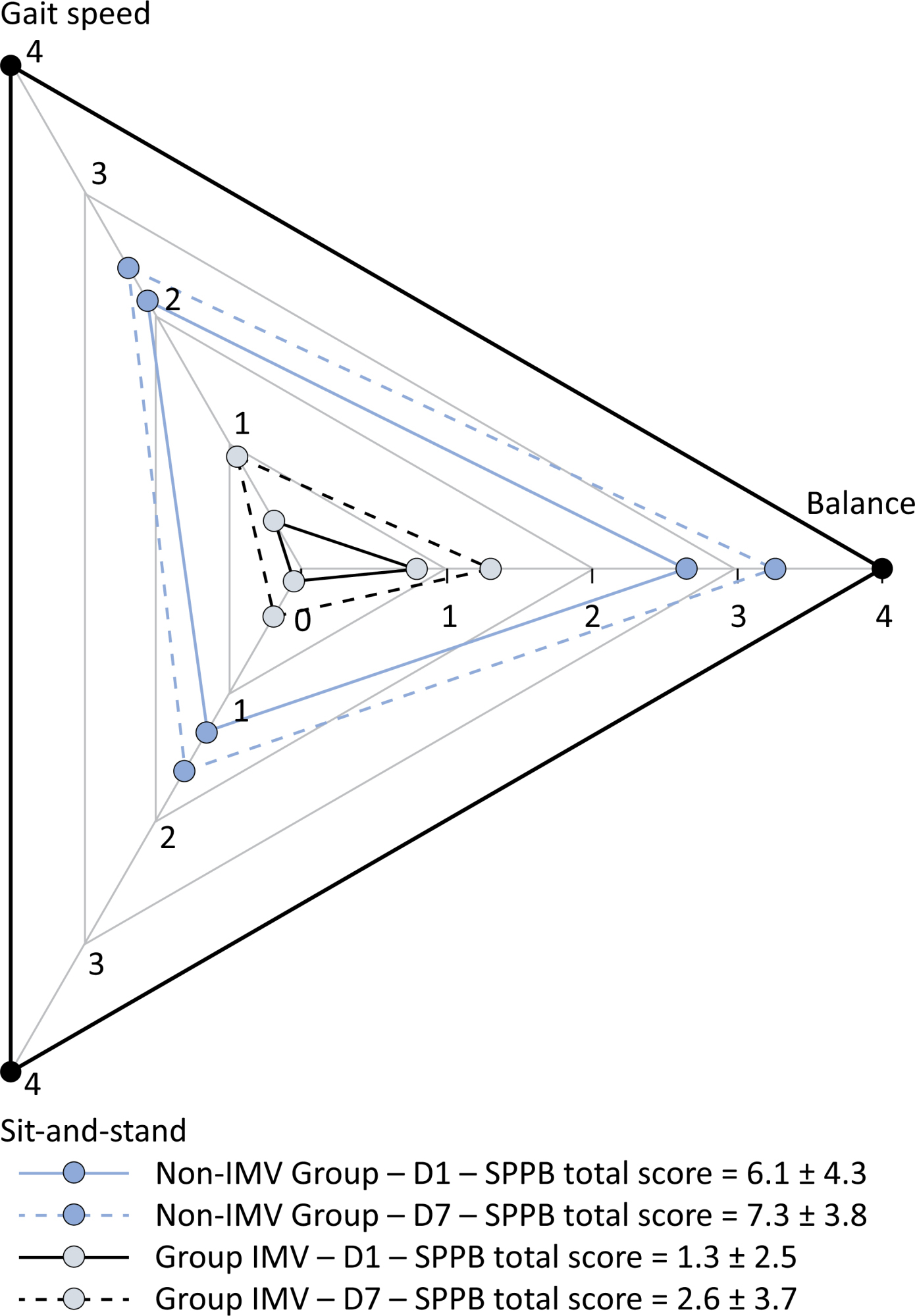
Patients in the IMV Group (n = 31) were younger and had higher Sequential Organ Failure Assessment scores than those in the Non-IMV Group (n = 33). The short physical performance battery scores (range 0 - 12) on D1 and D7 were 6.1 ± 4.3 and 7.3 ± 3.8, respectively for the Non-Invasive Mechanical Ventilation Group, and 1.3 ± 2.5 and 2.6 ± 3.7, respectively for the IMV Group. The prevalence of intensive care unit-acquired weakness on D7 was 13% for the Non-IMV Group and 72% for the IMV Group. The maximal inspiratory pressure, maximal expiratory pressure, and handgrip strength increased on D7 in both groups, but the maximal expiratory pressure and handgrip strength were still weak. Only maximal inspiratory pressure was recovered (i.e., > 80% of the predicted value) in the Non-IMV Group. Female sex, and the need and duration of invasive mechanical were independently and negatively associated with the short physical performance battery score and handgrip strength.
Patients who recovered from critical COVID-19 and who received invasive mechanical ventilation presented greater disability than those who were not invasively ventilated. However, they both showed marginal functional improvement during early recovery, regardless of the need for invasive mechanical ventilation. This might highlight the severity of disability caused by SARS-CoV-2.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2022;34(2):272-278
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20220025-en
To translate, crossculturally adapt and evaluate the clinimetric properties of the Critical Care Functional Rehabilitation Outcome Measure for evaluating the functionality of patients admitted to intensive care units in Brazil.
The process of translation and cross-cultural adaptation involved the following steps: initial translation, synthesis, back-translation, expert committee review and pretesting. The intra- and interrater reliability and agreement were analyzed between two physical therapists who evaluated the same group of patients (n = 35). The evaluations were performed by each therapist independently and blinded to the score assigned by the other professional. The qualitative analysis was performed by the review committee, and the experts adapted and synthesized the Portuguese translation of the Critical Care Functional Rehabilitation Outcome Measure.
There was agreement between the initial Brazilian translations of the Critical Care Functional Rehabilitation Outcome Measure scale. The conceptual, idiomatic, semantic and experimental equivalences between the original and translated versions were assessed, resulting in the final Brazilian version of the scale, called the Medida de Resultado da Reabilitação Funcional em Cuidados Intensivos. The evaluation of the clinimetric properties showed evidence of a high degree of agreement and reliability, as all had an intraclass correlation coefficient above 0.75. The overall intraclass correlation coefficient was 0.89.
The translated version of the Critical Care Functional Rehabilitation Outcome Measure scale for assessing the functionality of patients admitted to an intensive care unit can be used reliably in Brazil following translation and cross-cultural adaptation to Brazilian Portuguese and presents evidence of excellent interrater reliability.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (33) COVID-19 (45) Critical care (115) Critical illness (54) ICU (25) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (254) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (75) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (117) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)