Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(2):141-148
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20150025
To evaluate the impact of body mass index on the short-term prognosis of non-surgical critically ill patients while controlling for performance status and comorbidities.
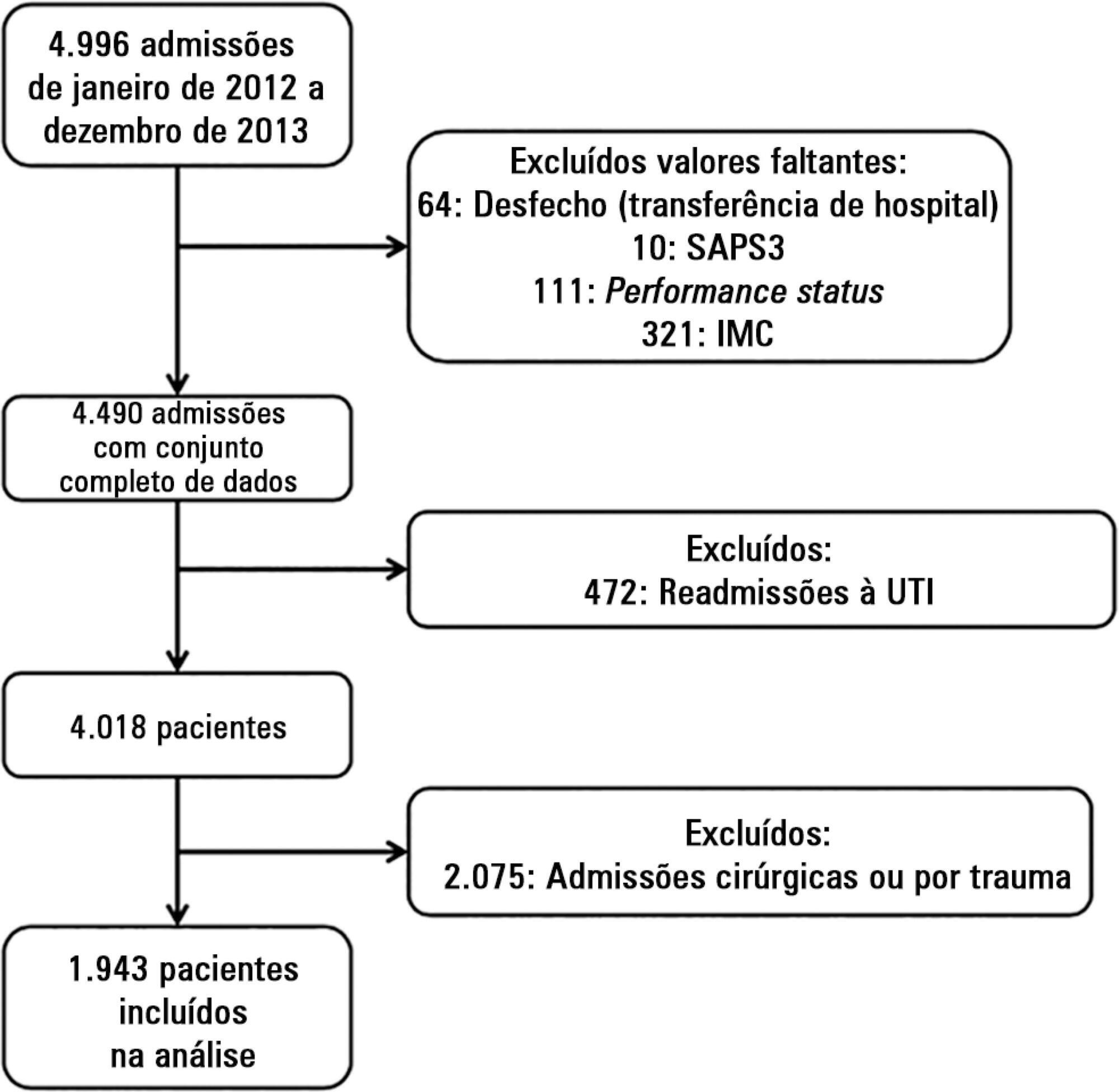
We performed a retrospective analysis on a two-year single-center database including 1943 patients. We evaluated the impact of body mass index on hospital mortality using a gradient-boosted model that also included comorbidities and was assessed by Charlson’s comorbidity index, performance status and illness severity, which was measured by the SAPS3 score. The SAPS3 score was adjusted to avoid including the same variable twice in the model. We also assessed the impact of body mass index on the length of stay in the hospital after intensive care unit admission using multiple linear regressions.
A low value (< 20kg/m2) was associated with a sharp increase in hospital mortality. Mortality tended to subsequently decrease as body mass index increased, but the impact of a high body mass index in defining mortality was low. Mortality increased as the burden of comorbidities increased and as the performance status decreased. Body mass index interacted with the impact of SAPS3 on patient outcome, but there was no significant interaction between body mass index, performance status and comorbidities. There was no apparent association between body mass index and the length of stay at the hospital after intensive care unit admission.
Body mass index does appear to influence the shortterm outcomes of critically ill medical patients, who are generally underweight. This association was independent of comorbidities and performance status.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2010;22(2):133-137
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2010000200006
STUDY OBJECTIVE: Obese patients seem to have worse outcomes and more complications during intensive care unit (ICU) stay. This study describes the clinical course, complications and prognostic factors of obese patients admitted to an intensive care unit compared to a control group of nonobese patients. DESIGN: Retrospective observational study. SETTING: A 10-bed adult intensive care unit in a university-affiliated hospital. METHODS: All patients admitted to the intensive care unit over 52 months (April 01/2005 to November 30/2008) were included. Obese patients were defined as those with a body mass index (BMI) ≥ 30 Kg/M2. Demographic and intensive care unit related data were also collected. An clinical and demographical matching group of eutrophic patients selected from the data base as comparator for mortality and morbidity outcomes. The Mann-Whitney test was used for numeric data comparisons and the Chi Square test for categorical data comparisons. RESULTS: Two hundred nineteen patients were included. The obese group (n=73) was compared to the eutrophic group (n= 146). Most of this group BMI ranged between 30 - 35 Kg/M2. Only ten patients had body mass index ≥40 Kg/M2. Significant differences between the obese and eutrophic groups were observed in median APACHE II score (16 versus 12, respectively; p<0.05) and median intensive care unit length of stay (7 versus 5 days respectively; p<0,05). No significant differences were seen regarding risk of death, mortality rate, mechanical ventilation needs, days free of mechanical ventilation and tracheostomy rates. The observed mortality was higher than the APACHE II-predicted for both groups, but the larger differences were seen for morbid obese patients (BMI ≥40 Kg/M2). CONCLUSIONS: Obesity did not increase the mortality rate, but improved intensive care unit length of stay. The current prognostic scoring systems do not include BMI, possibly underestimating the risk of death, and other quality of care indexes in obese patients. New studies could be useful to clarify how body mass index impacts the mortality rate.