Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(2):320-324
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20210041
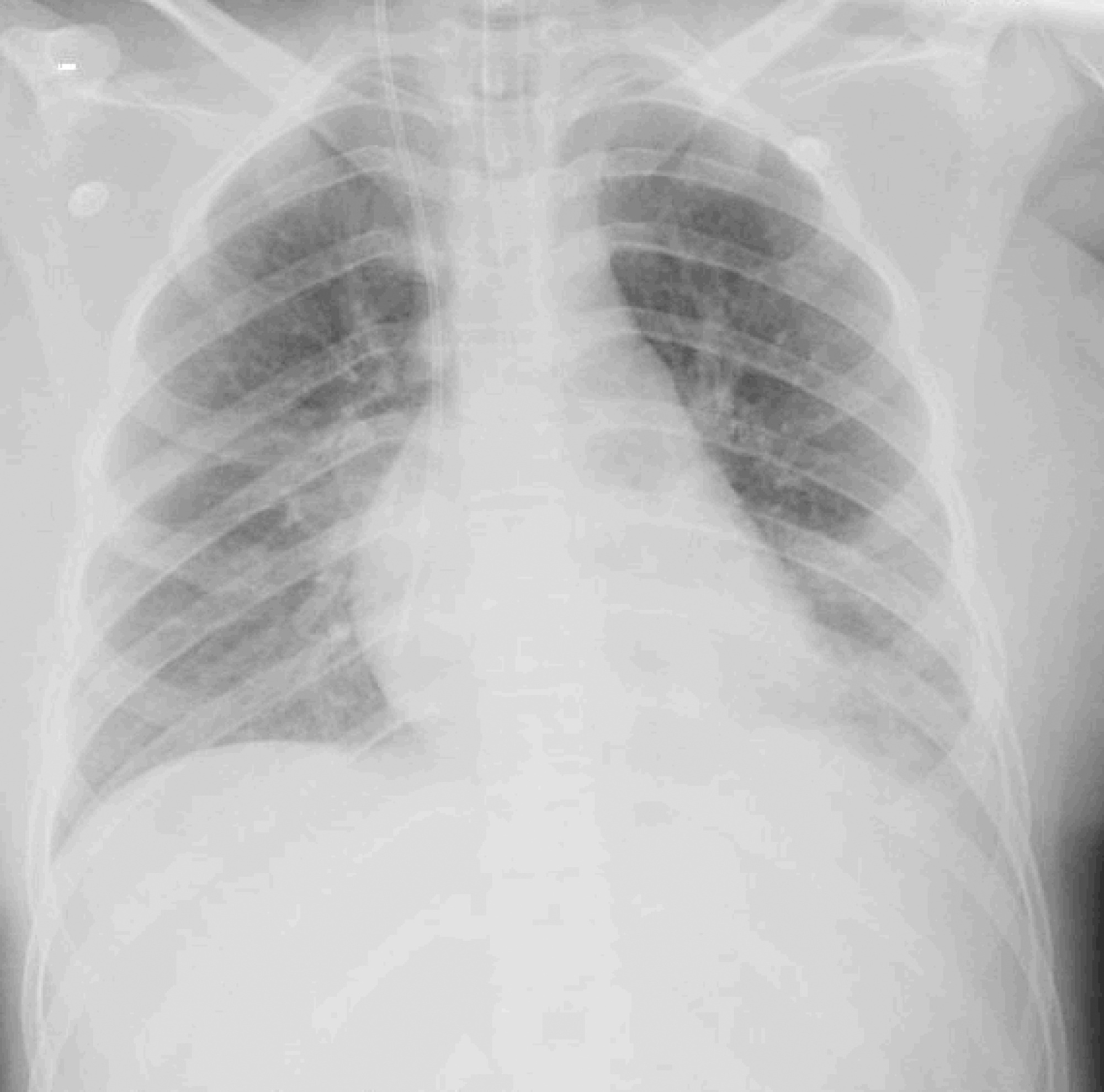
We report a case of Influenza B infection and Kawasaki disease in an adolescent, diagnosed during the COVID-19 pandemic. An asthmatic female adolescent presented with fever and flu-like symptoms for 7 days and was admitted with acute respiratory failure requiring mechanical ventilation. She progressed with hemodynamic instability responsive to vasoactive drugs. Antibiotic therapy and support measures were introduced, showing progressive hemodynamics and respiratory improvement, however with persistent fever and increased inflammatory markers. During the hospitalization, she developed bilateral non-purulent conjunctivitis, hand and feet desquamation, strawberry tongue, and cervical adenopathy, and was diagnosed with Kawasaki disease. She was prescribed intravenous immunoglobulin and, due to the refractory clinical conditions, corticosteroid therapy was added; 24 hours later, the patient was afebrile. No coronary changes were found. A full viral panel including COVID-19 C-reactive protein and serology could only isolate the Influenza B virus. During the hospitalization, she was diagnosed with pulmonary thromboembolism; coagulopathies were investigated, and she was diagnosed with heterozygous factor V Leiden mutation. There is a potential association between Kawasaki disease and infection with Influenza B or with other viruses such as coronavirus. Therefore, this association should be considered in pediatric patients, adolescents included, with prolonged febrile conditions.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(1):68-74
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20210006
To analyze whether changes in medical care due to the application of COVID-19 protocols affected clinical outcomes in patients without COVID-19 during the pandemic.
This was a retrospective, observational cohort study carried out in a thirty-eight-bed surgical and medical intensive care unit of a high complexity private hospital. Patients with respiratory failure admitted to the intensive care unit during March and April 2020 and the same months in 2019 were selected. We compared interventions and outcomes of patients without COVID-19 during the pandemic with patients admitted in 2019. The main variables analyzed were intensive care unit respiratory management, number of chest tomography scans and bronchoalveolar lavages, intensive care unit complications, and status at hospital discharge.
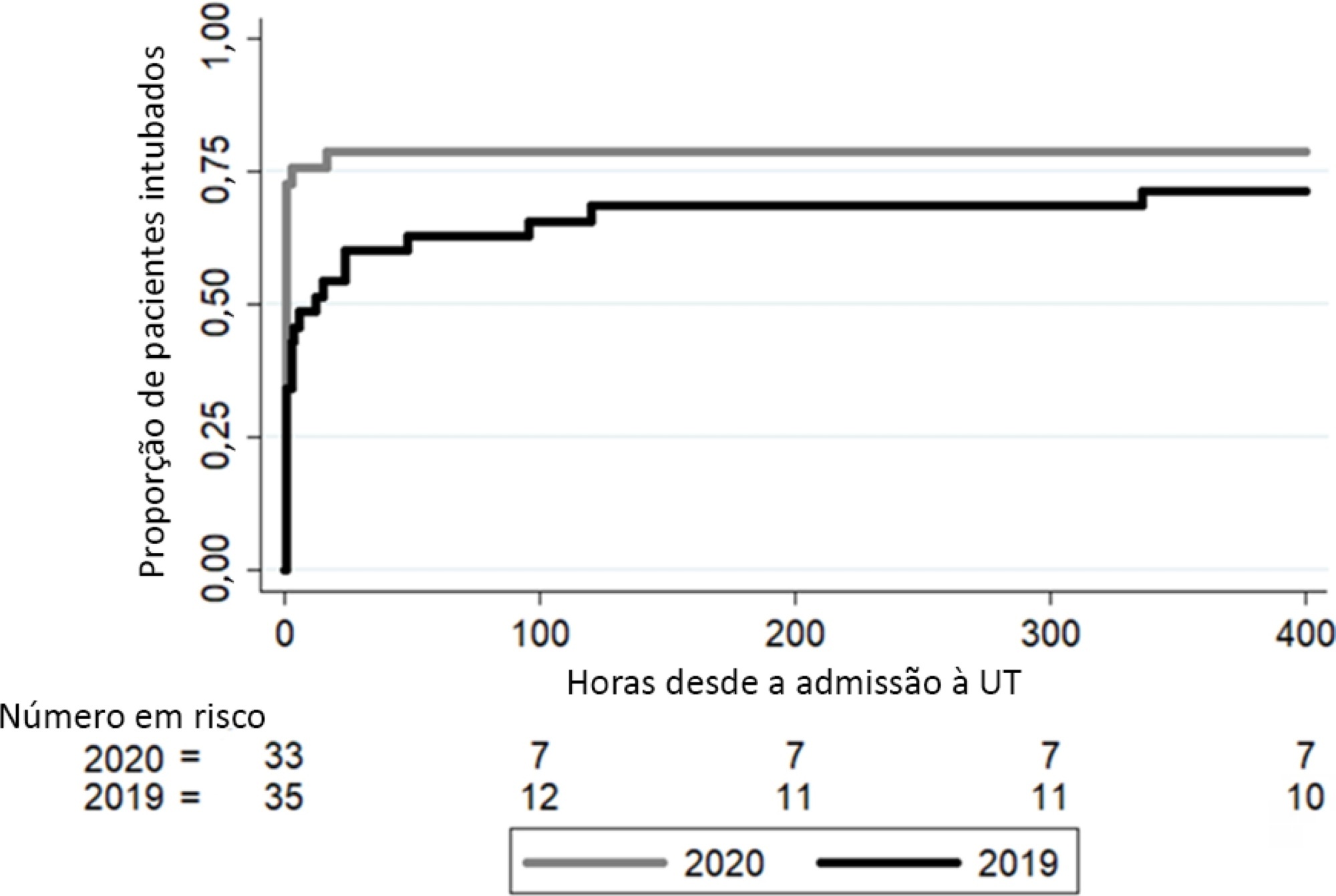
In 2020, a significant reduction in the use of a high-flow nasal cannula was observed: 14 (42%) in 2019 compared to 1 (3%) in 2020. Additionally, in 2020, a significant increase was observed in the number of patients under mechanical ventilation admitted to the intensive care unit from the emergency department, 23 (69%) compared to 11 (31%) in 2019. Nevertheless, the number of patients with mechanical ventilation after 5 days of admission was similar in both years: 24 (69%) in 2019 and 26 (79%) in 2020.
Intensive care unit protocols based on international recommendations for the COVID-19 pandemic have produced a change in non-COVID-19 patient management. We observed a reduction in the use of a high-flow nasal cannula and an increased number of tracheal intubations in the emergency department. However, no changes in the percentage of intubated patients in the intensive care unit, the number of mechanical ventilation days or the length of stay in intensive care unit.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2020;32(2):319-325
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20200032
The apnea test, which involves disconnection from the mechanical ventilator, presents risks during the determination of brain death, especially in hypoxemic patients. We describe the performance of the apnea test without disconnection from the mechanical ventilator in two patients. The first case involved an 8-year-old boy admitted with severe hypoxemia due to pneumonia. He presented with cardiorespiratory arrest, followed by unresponsive coma due to hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Two clinical exams revealed the absence of brainstem reflexes, and transcranial Doppler ultrasound revealed brain circulatory arrest. Three attempts were made to perform the apnea test, which were interrupted by hypoxemia; therefore, the apnea test was performed without disconnection from the mechanical ventilator, adjusting the continuous airway pressure to 10cmH2O and the inspired fraction of oxygen to 100%. The oxygen saturation was maintained at 100% for 10 minutes. Posttest blood gas analysis results were as follows: pH, 6.90; partial pressure of oxygen, 284.0mmHg; partial pressure of carbon dioxide, 94.0mmHg; and oxygen saturation, 100%. The second case involved a 43-year-old woman admitted with subarachnoid hemorrhage (Hunt-Hess V and Fisher IV). Two clinical exams revealed unresponsive coma and absence of all brainstem reflexes. Brain scintigraphy showed no radioisotope uptake into the brain parenchyma. The first attempt at the apnea test was stopped after 5 minutes due to hypothermia (34.9°C). After rewarming, the apnea test was repeated without disconnection from the mechanical ventilator, showing maintenance of the functional residual volume with electrical bioimpedance. Posttest blood gas analysis results were as follows: pH, 7.01; partial pressure of oxygen, 232.0mmHg; partial pressure of carbon dioxide, 66.9mmHg; and oxygen saturation, 99.0%. The apnea test without disconnection from the mechanical ventilator allowed the preservation of oxygenation in both cases. The use of continuous airway pressure during the apnea test seems to be a safe alternative in order to maintain alveolar recruitment and oxygenation during brain death determination.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(3):333-339
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190045
To describe the use of noninvasive ventilation to prevent tracheal intubation in children in a pediatric intensive care unit and to analyze the factors related to respiratory failure.
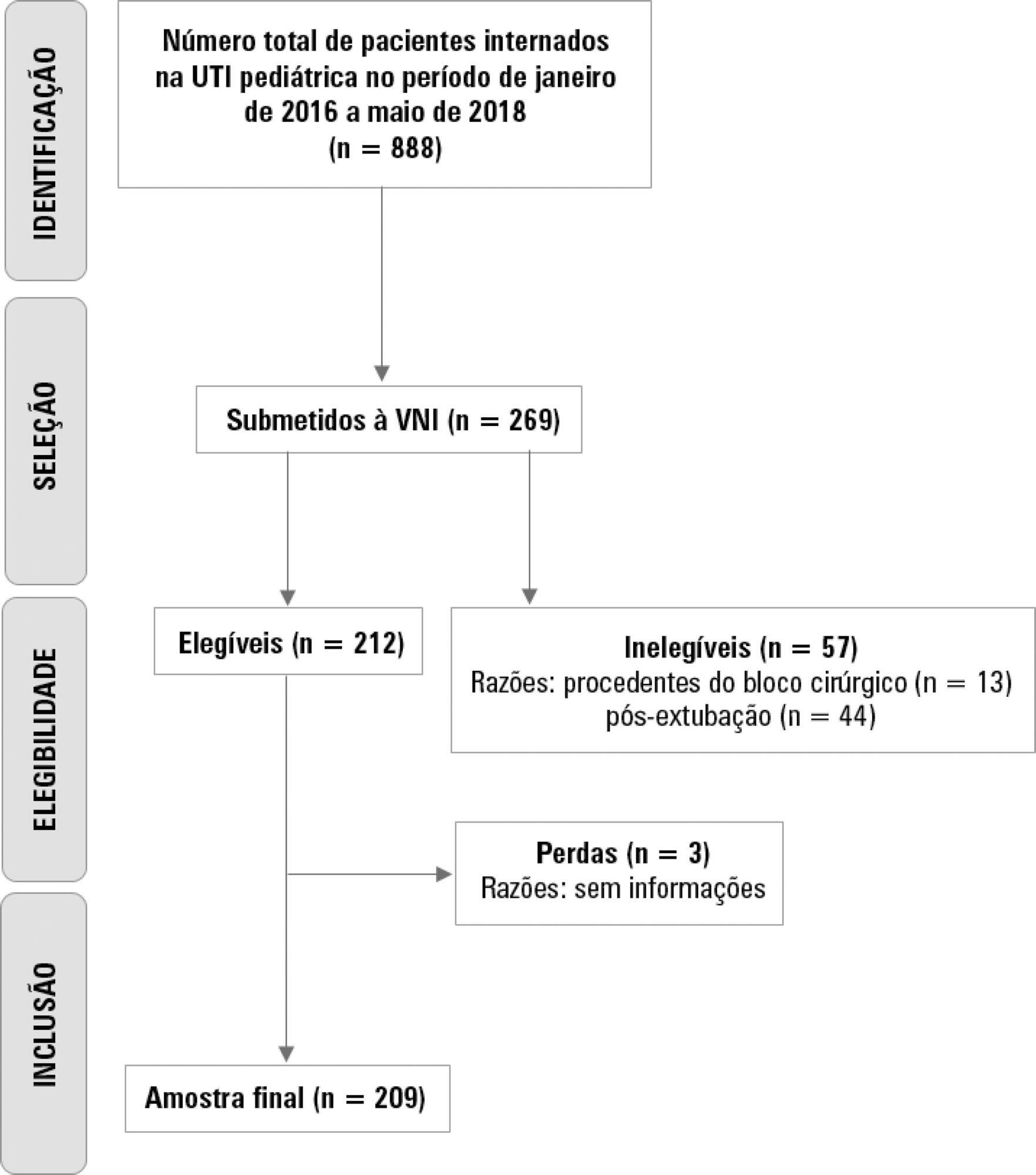
A retrospective cohort study was performed from January 2016 to May 2018. The study population included children aged 1 to 14 years who were subjected to noninvasive ventilation as the first therapeutic choice for acute respiratory failure. Biological, clinical and managerial data were analyzed by applying a model with the variables that obtained significance ≤ 0.20 in a bivariate analysis. Logistic regression was performed using the ENTER method. The level of significance was set at 5%.
The children had a mean age of 68.7 ± 42.3 months, 96.6% had respiratory disease as a primary diagnosis, and 15.8% had comorbidities. Of the 209 patients, noninvasive ventilation was the first option for ventilatory support in 86.6% of the patients, and the fraction of inspired oxygen was ≥ 0.40 in 47% of the cases. The lethality rate was 1.4%. The data for the use of noninvasive ventilation showed a high success rate of 95.3% (84.32 - 106). The Pediatric Risk of Mortality (PRISM) score and the length of stay in the intensive care unit were the significant clinical variables for the success or failure of noninvasive ventilation.
A high rate of effectiveness was found for the use of noninvasive ventilation for acute episodes of respiratory failure. A higher PRISM score on admission, comorbidities associated with respiratory symptoms and oxygen use ≥ 40% were independent factors related to noninvasive ventilation failure.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(3):410-424
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190063
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation is a modality of extracorporeal life support that allows for temporary support in pulmonary and/or cardiac failure refractory to conventional therapy. Since the first descriptions of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, significant improvements have occurred in the device and the management of patients and, consequently, in the outcomes of critically ill patients during extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Many important studies about the use of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome refractory to conventional clinical support, under in-hospital cardiac arrest and with cardiogenic refractory shock have been published in recent years. The objective of this literature review is to present the theoretical and practical aspects of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support for respiratory and/or cardiac functions in critically ill patients.
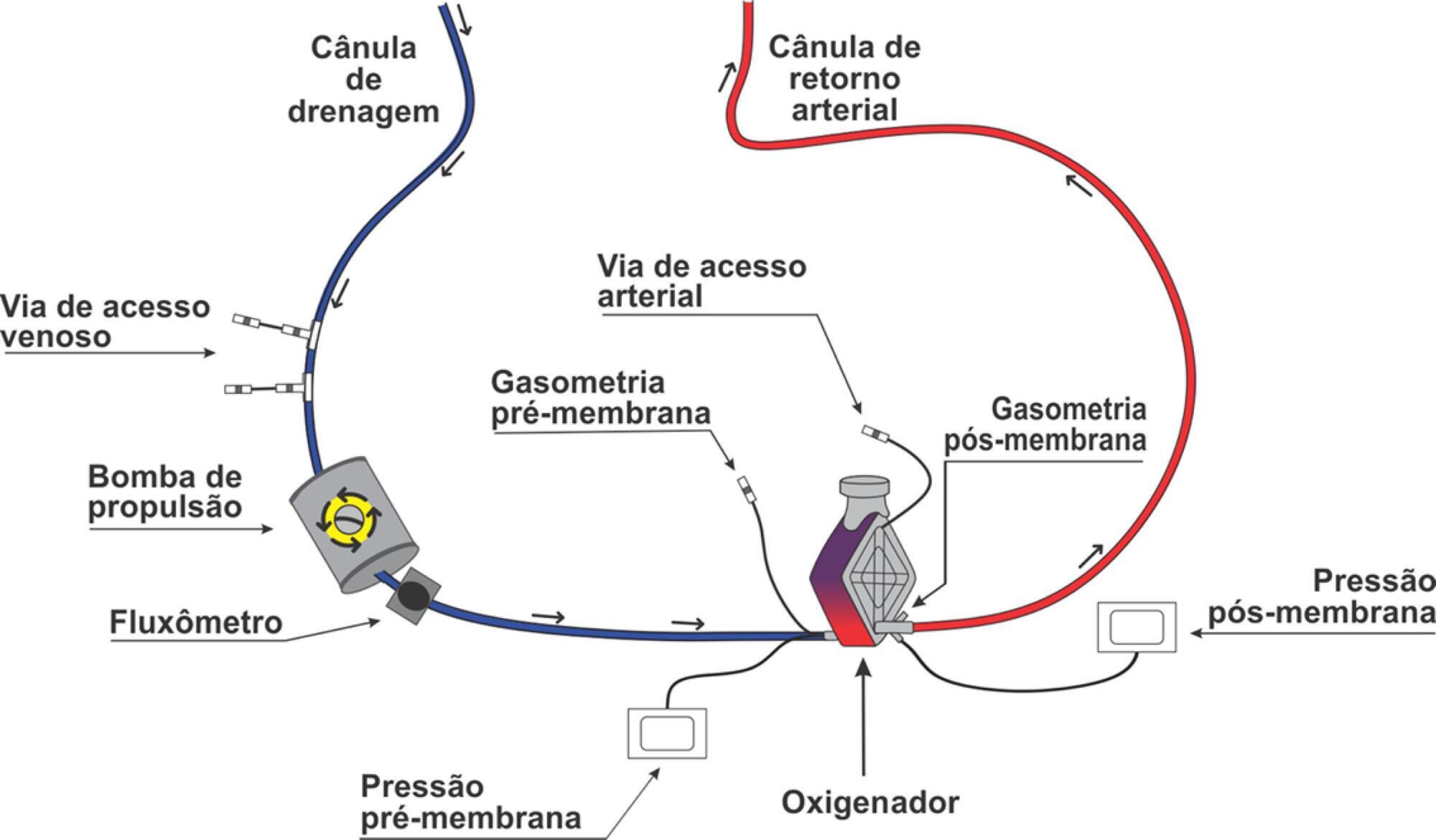
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2018;30(1):127-130
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20180019
In the 2014 - 2015 season, most influenza infections were due to A (H3N2) viruses. More than two-thirds of circulating A (H3N2) viruses are antigenically and genetically different (drifted) from the A (H3N2) vaccine component of 2014 - 2015 northern and southern Hemisphere seasonal influenza vaccines. The purpose of this paper is to report a case of seasonal influenza A non-H1N1 infection that occurred in June 2015 in an adult cystic fibrosis patient with severe lung disease previously vaccinated with the anti-flu trivalent vaccine. The patient evolved to respiratory and renal failure (without rhabdomyolysis) and was placed under mechanical ventilation and hemodialysis. The clinical outcome was positive after 39 days of hospital stay. In addition, the patient was clinically stable after 18 months of follow-up. With the recent advances in critical care medicine and in cystic fibrosis treatment, survival with advanced pulmonary disease in cystic fibrosis presents new questions and potential problems, which are still being formulated.
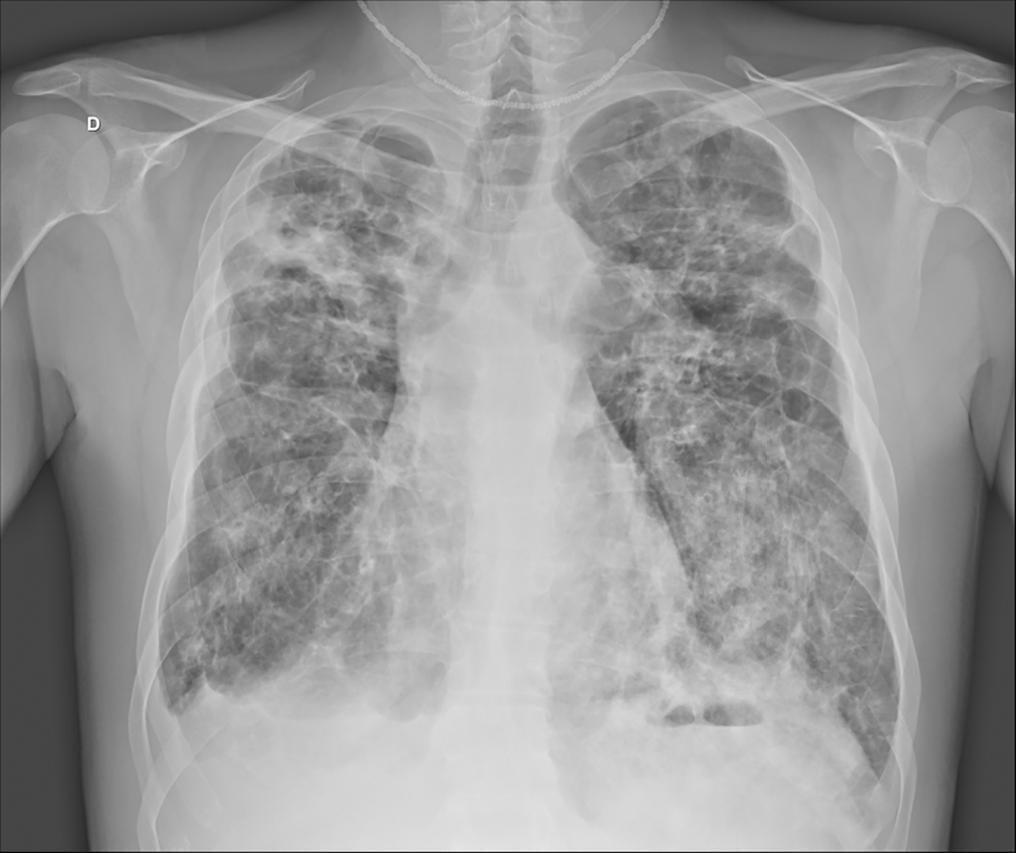
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2018;30(3):317-326
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20180052
To characterize the transport of severely ill patients with extracorporeal respiratory or cardiovascular support.
A series of 18 patients in the state of São Paulo, Brazil is described. All patients were consecutively evaluated by a multidisciplinary team at the hospital of origin. The patients were rescued, and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support was provided on site. The patients were then transported to referral hospitals for extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support. Data were retrieved from a prospectively collected database.
From 2011 to 2017, 18 patients aged 29 (25 - 31) years with a SAPS 3 of 84 (68 - 92) and main primary diagnosis of leptospirosis and influenza A (H1N1) virus were transported to three referral hospitals in São Paulo. A median distance of 39 (15 - 82) km was traveled on each rescue mission during a period of 360 (308 - 431) min. A median of one (0 - 2) nurse, three (2 - 3) physicians, and one (0 - 1) physical therapist was present per rescue. Seventeen rescues were made by ambulance, and one rescue was made by helicopter. The observed complications were interruption in the energy supply to the pump in two cases (11%) and oxygen saturation < 70% in two cases. Thirteen patients (72%) survived and were discharged from the hospital. Among the nonsurvivors, there were two cases of brain death, two cases of multiple organ dysfunction syndrome, and one case of irreversible pulmonary fibrosis.
Transportation with extracorporeal support occurred without serious complications, and the hospital survival rate was high.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (116) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)