Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2008;20(3):213-219
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2008000300002
OBJECTIVES: This study is justified by the fact that in clinical practice, changes occur in patient's positioning in the bed during hospitalization in intensive care unity, it's necessary better understanding about possible adverse effects that such changes might cause mainly on the respiratory system condition. The objective this study was to evaluate if the patients positioning in bed can to alter the pulmonary complacency. METHODS: All included patients were submitted to mechanical ventilation and were sedated and curarized respiratory system compliance was assessed in three different positioning: lateral, dorsal and sitting. After an alveolar recruitment maneuver, patients were placed to a position throughout two hours, and in the last five minutes the data was collected from the mechanical ventilator display. RESULTS: twenty eight patients were prospectively assessed. Values of respiratory system compliance in the lateral position were 37,07 ± 12,9 in the dorsal were 39,2 ± 10,5 and in the sitting 43,4 ± 9,6 mL/cmH2O. There were a statistical difference when we compared to the sitting and dorsal with lateral positioning for respiratory system compliance (p = 0.0052) and tidal volume (p < 0.001). There was a negative correlation between mean values of positive end expiratory pressure a respiratory system compliance (r = 0.59, p = 0.002). The FIO2 administered was 0.6 for the lateral positioning and 0.5 for the dorsal and sitting positioning (p = 0.049). CONCLUSIONS: That body positioning in patients restrained to a bed and submitted to invasive mechanical ventilation leads to pulmonary compliance, tidal volume and SpO2 oscillations. In the sitting position the pulmonary compliance is higher than in others positions.

Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2008;20(3):220-225
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2008000300003
OBJECTIVES: Correct cuff inflation allows appropriate ventilation, and prevents aspiration pneumonia as well as several tracheal complications. The objective of this study was to evaluate endotracheal cuff pressure and/or tracheotomy tubes at zero, 30 and 60 degrees inclination of the patient's bed head section in adult intensive care units. METHODS: A cross sectional study was carried out evaluating the cuff pressure, the expiratory tidal volume (VT) and the peak airway pressure (PP) at inclinations zero, 30 and 60 degree of the head section of the patients' bed. The 30 degree inclination was considered the standard position used as control to analyze values in the zero and 60 degree positions, which were randomly ordered. The Student's t test was used and was considered significant when p < 0.05. RESULTS: A sample of 12 women and 12 men with a mean age of 51.29 ± 19.55 years was surveyed. When inclination of the bed head section was changed from 30 to zero degrees, there was a 16.9% mean reduction of the cuff pressure and 11.8% mean increase of the PP. On the other hand, changing the position from 30 to 60 degrees caused a mean reduction of 18.8% in the cuff pressure and a mean increase of 13.3% in the PP. Findings were significant when p < 0.05. CONCLUSIONS: To prevent air leak and risk of aspiration pneumonia, adequate adjustments and monitoring of the patients cuff pressure are necessary when inclination of the bed head section is changed.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2008;20(3):226-234
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2008000300004
PURPOSE: Due to the increasing longevity of the and high prevalence of coronary heart disease in the aged , coronary artery bypass graft surgery has become frequent in older patients. The purpose of this study is to describe operative features, length of stay, complications and short term outcomes after coronary artery bypass graft in such patients. METHODS: From February 2005 to October 2007, 269 patients underwent coronary artery bypass graft. Demographic data, comorbidities, prognostic scores, coronary artery bypass graft elective versus urgent indication, intensive care unit length of stay, postoperative complications and intensive care unit mortality were recorded. Intra-operative characteristics, such as total surgery time, use of bypass device, on-pump time, urine output, fluid balance, use of blood products and number of grafts, were analyzed. Patients were divided in four age groups: group I (< 60 n = 68), II (60 to 69 n = 86), III (70 to 79 n = 93) IV and older than 80 years (n = 22). RESULTS: Group IV patients were more frequently submitted to coronary artery bypass graft combined with valve replacement, emergency surgery, and had longer stay in the intensive care unit (p < 0.01). The incidence of at least one postoperative complication was also higher among patients older than 80 (p < 0.001). Multivariate analysis identified age and on-pump time as independent risk factors for development of complications. Mortality increased in patients older than 70 years (p = 0.03). CONCLUSIONS: Octogenarian patients undergoing coronary artery bypass graft have longer intensive care unit length of stay, incidence of complications and mortality. Age and on-pump time were independent risk factors associated with the incidence of postoperative complications.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2008;20(3):235-240
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2008000300005
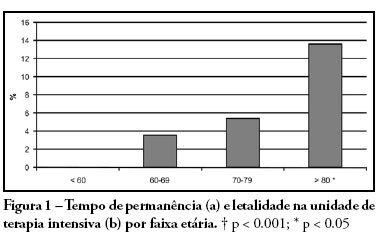
OBJECTIVES: Burnout syndrome is a response to prolonged occupational stress that involves three main dimensions: emotional exhaustion, depersonalization, and reduced personal accomplishment. The aim of this study was to describe socio-demographic characteristics of intensive care unit physicians and evaluate factors associated to the presence of Burnout syndrome in this population. METHODS: A cross-sectional study was performed to evaluate physicians who have worked in intensive care units from the city of Salvador (Bahia - Brazil) with a minimum weekly workload of 12-hour. An anonymous self-reported questionnaire was used and it was divided into two parts: socio-demographic characteristics and evaluation of Burnout syndrome through Maslach Burnout Inventory. RESULTS: We studied 297 physicians and most of them were male (70%). The mean age and time of graduation were, respectively, 34.2 and 9 years. High levels of emotional exhaustion, depersonalization, and reduced personal accomplishment were found in respectively, 47.5%, 24.6% and 28.3%. The prevalence of Burnout syndrome, considered as high level in at least one dimension, was of 63.3%. This prevalence was statistically lower in physicians specialized on intensive care, those with more than nine years of graduation and those who intend to continue working in intensive care units for more than 10 years. The prevalence was higher in the doctors with more than 24-hours of uninterrupted intensive care work per week. CONCLUSIONS: Burnout syndrome was common among intensive care physicians and it was more frequent in the youngest doctors, with higher workload and without specialization on intensive care.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2008;20(3):241-248
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2008000300006
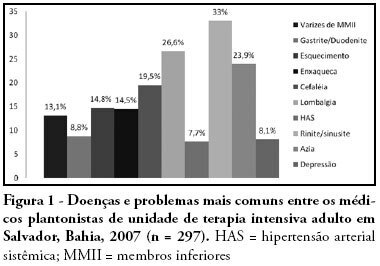
OBJECTIVES: Sepsis is the main cause of death in the intensive care unit. New preventive measures for nosocomial infections have been researched, such as pre, pro and symbiotic usage, due to its immunoregulatory properties. The objective was to evaluate the effect of administration of pre, pro and symbiotic on gastrointestinal and inferior airway colonization and on nosocomial infections, particularly ventilator-associated pneumonia. METHODS: Patients who were admitted to the intensive care unit at Hospital Universitário Clementino Fraga Filho between November 2004 and September 2006 and mechanically ventilated were randomized in one of four groups: control (n = 16), prebiotic (n = 10), probiotic (n = 12) or symbiotic (n = 11). Treatment was administered for fourteen days. Outcomes measured were: a) Colonization of the gastrointestinal tract and trachea; b) incidence of nosocomial infections, particularly ventilator associated pneumonia; c) duration of mechanical ventilation, length of stay in the intensive care unit, duration of hospitalization, mortality rates, and d) development of organ dysfunction. RESULTS: Forty-nine patients were evaluated. intensive care unit's mortality was 34% and in-hospital mortality was 53%, APACHE II median was 20 (13 -25). The groups were matched at admission. There was no difference between the groups in relation to the incidence of ventilator associated pneumonia or nosocomial infection. There was a non-significant increase in the proportion of enterobacteria in the trachea at the seventh day in the pre and probiotic groups compared to control. There was a non-significant decrease in the number of bacteria found in the stomach in the pre, pro and symbiotic group at day 7. No significant difference, in regards to the remaining measured parameters, could be found. CONCLUSIONS: Probiotic therapy was not efficient in the prevention of nosocomial infection but there was a tendency to reduction in tracheal colonization by non-fermenting bacteria.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2008;20(3):249-253
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2008000300007
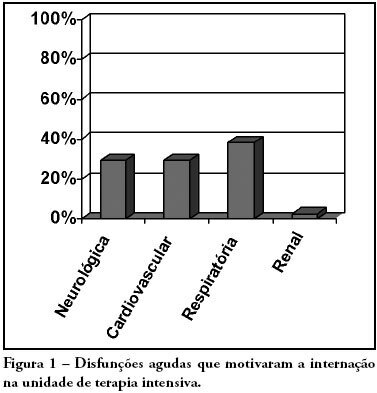
OBJECTIVES: Due to the high incidence in our service, we did object on this study describe the features and outcome of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) admitted to the intensive care unit of Walter Cantídio University Hospital METHODS: Patients were restrospectively characterized according to demography parameters, time of diagnosis of SLE, organ dysfunction and laboratorial parameters at admission, supportive therapies during their stay, length of stay in the hospital before admission, length of stay in the unit, readmission to the unit and outcome. We also evaluated Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity (SLEDAI) score, Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II (APACHE II) score, expected mortality and standardized mortality ratio. RESULTS: From November 2003 to October 2006, 1,052 patients were admitted to the intensive care unit. Fifty patients had SLE and were included in this retrospective study. Of the 50 patients with SLE admitted to the ICU, 88.2% were female. The mean age was 30.3 ± 12.8 years. The median time of diagnosis of SLE was 67 months. The most common organ dysfunctions were renal (70.6%), cardiovascular (61.8%), respiratory (55.9%) and neurological (55.9%). The main reasons for admission to the ICU were respiratory (38.2%), cardiologic (29.4%) and neurological (29.4%) dysfunctions. Among the intensive care therapies, 44.1% of the patients needed blood products, 41.2% vasopressor agents and 35.3% mechanical ventilation, 23.5% dialysis. The mean SLEDAI score was 15.0 ± 12.2. The mean APACHE II score was 19.3 ± 6.8, with a predicted mortality rate of 37.6%. The actual mortality rate in ICU was 29.4%, with 8.8% before 48 hours. The standardized mortality ratio was 0.78. Patients with APACHE II > 18, with more than 3 acute organ involvements, leukopenia (< 4000 cells/mm3) and gastrointestinal or metabolic involvement had higher mortality in the intensive care unit. CONCLUSION: Although the severity of patients at admission to the ICU, demonstrated by APACHE II and the acute dysfunctions, the outcomes of analysed patients sugest susceptibility to the therapy.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2008;20(3):254-260
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2008000300008
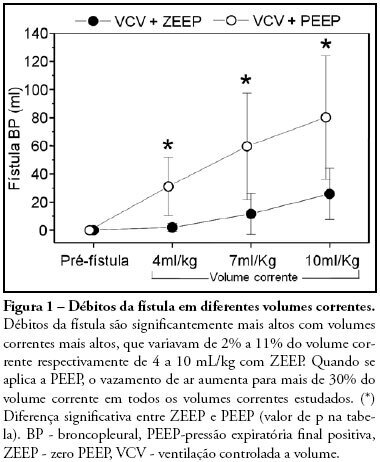
OBJECTIVES: The present study was designed to identify the effect of positive end expiratory pressure (PEEP) and the ideal pulmonary tidal volume to ventilate animals with a surgically produced bronchopleural fistula, aiming to reduce fistula output without affecting gas exchange. METHODS: Hemodynamic and respiratory assessment of gas exchange was obtained in five, healthy, young, mechanically ventilated Large White pigs under volume controlled ventilation with FiO2 of 0.4 and an inspiration:expiration ratio of 1:2, keeping respiratory rate at 22 cpm. A bronchopleural fistula was produced by resection of the lingula. Underwater seal drainage was installed and the thorax was hermetically closed. Gas exchange and fistula output were measured with the animals ventilated sequentially with tidal volumes of 4 ml/kg, 7 ml/kg and 10 ml/Kg alternating zero of positive end expiratory pressure (ZEEP) and PEEP of 10 cmH2O, always in the same order. RESULTS: These findings are attributed to reduced alveolar ventilation and ventilation/perfusion abnormalities and were attenuated with larger tidal volumes. PEEP increases air leak, even with low volume (of 2.0 ± 2.8mL to 31 ± 20.7mL; p= 0.006) and decreases alveolar ventilation in all tidal volumes. Alveolar ventilation improved with larger tidal volumes, but increased fistula output (10 mL/kg - 25.8 ± 18.3mL to 80.2 ± 43.9mL; p=0.0010). Low tidal volumes result in hypercapnia (ZEEP - Toneloto MGC, Terzi RGG, Silva WA, Moraes AC, Moreira MM 83.7± 6.9 mmHg and with PEEP 10 - 93 ± 10.1mmHg) and severely decreased arterial oxygen saturation, about of 84%. CONCLUSIONS: The tidal volume of 7 ml/Kg with ZEEP was considered the best tidal volume because, despite moderate hypercapnia, arterial oxygen saturation is sustained around 90%, alveolar ventilation improves and the fistula output is reduced when compared with a tidal volume of 10ml/Kg. A low tidal volume results in hypercapnia and severe desaturation. Finally, at any tidal volume, PEEP increases the fistula leak and decreases alveolar ventilation.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2008;20(3):261-266
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2008000300009
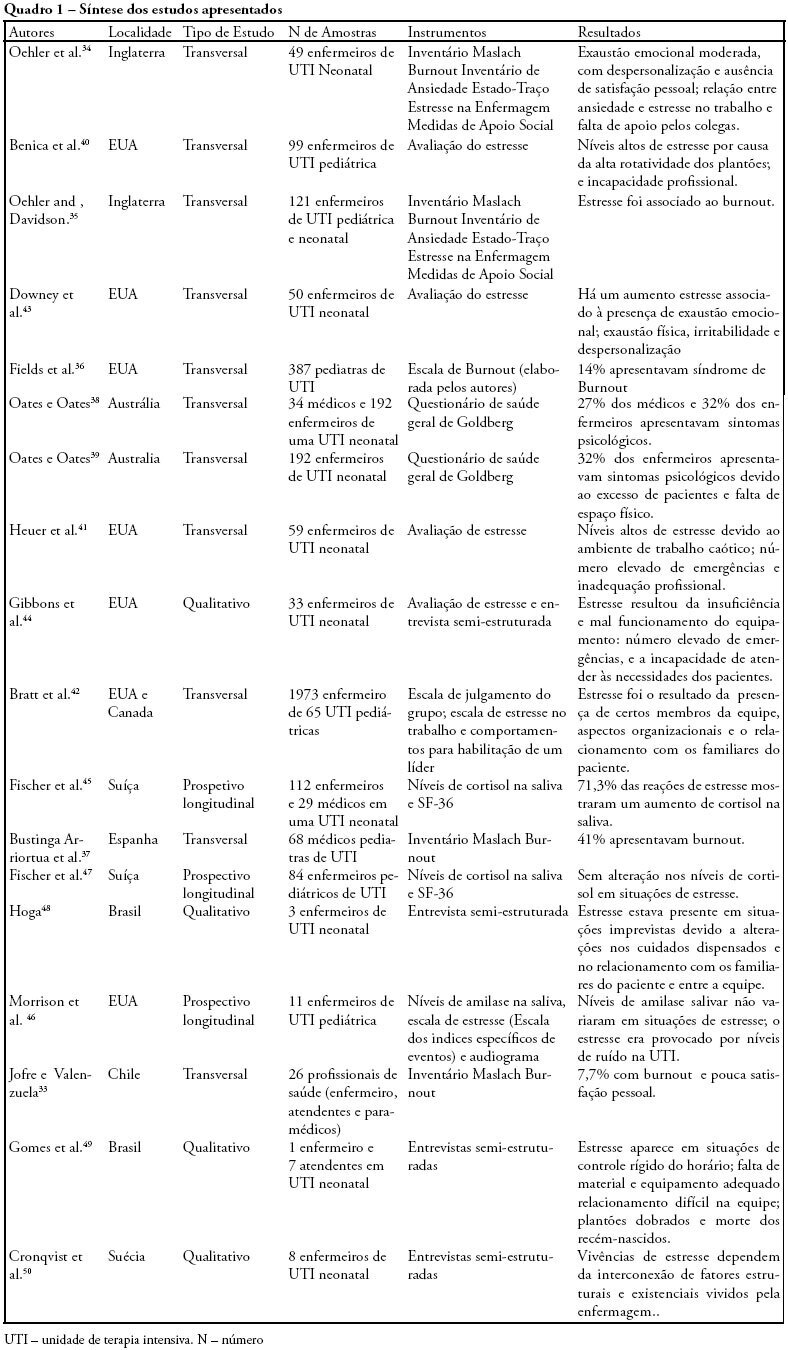
OBJECTIVES: Bibliographic review on occupational stress and burnout presence in physicians and nurses that work in pediatric and neonatal intensive care units. METHODS: The articles were selected from the MedLine, LILACS and SciElo data base using the key words: stress, burnout, physicians, nursing, intensive care unit, pediatric intensive care unit and neonatal intensive care unit. The studied period ranged from 1990 to 2007. RESULTS: Health professionals who work in pediatric and neonatal intensive care units are strong candidates for developing stress, psychological alterations and burnout syndrome. Researches on this subject identified important alterations suffered by these physicians and nurses, such as: work overload, burnout, desires of giving up their jobs, high levels of cortisol, among other alterations. CONCLUSIONS: Professionals, who work in pediatric and neonatal intensive care units, due to the specificity of their job, are liable to develop occupational stress, and consequently burnout. These results suggest the need for further research with the objective of developing preventive measures and intervention models.