Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(2):251-260
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20210032
To identify predictors of coronary artery disease in survivors of cardiac arrest, to define the best timing for coronary angiography and to establish the relationship between coronary artery disease and mortality.
This was a single-center retrospective study including consecutive patients who underwent coronary angiography after cardiac arrest.
A total of 117 patients (63 ± 13 years, 77% men) were included. Most cardiac arrest incidents occurred with shockable rhythms (70.1%), and the median duration until the return of spontaneous circulation was 10 minutes. Significant coronary artery disease was found in 68.4% of patients, of whom 75% underwent percutaneous coronary intervention. ST-segment elevation (OR 6.5, 95%CI 2.2 - 19.6; p = 0.001), the presence of wall motion abnormalities (OR 22.0, 95%CI 5.7 - 84.6; p < 0.001), an left ventricular ejection fraction ≤ 40% (OR 6.2, 95%CI 1.8 - 21.8; p = 0.005) and elevated high sensitivity troponin T (OR 3.04, 95%CI 1.3 - 6.9; p = 0.008) were predictors of coronary artery disease; the latter had poor accuracy (area under the curve 0.64; p = 0.004), with an optimal cutoff of 170ng/L. Only ST-segment elevation and the presence of wall motion abnormalities were independent predictors of coronary artery disease. The duration of cardiac arrest (OR 1.015, 95%CI 1.0 - 1.05; p = 0.048) was an independent predictor of death, and shockable rhythm (OR 0.4, 95%CI 0.4 - 0.9; p = 0.031) was an independent predictor of survival. The presence of coronary artery disease and the performance of percutaneous coronary intervention had no impact on survival; it was not possible to establish the best cutoff for coronary angiography timing.
In patients with cardiac arrest, ST-segment elevation, wall motion abnormalities, left ventricular dysfunction and elevated high sensitivity troponin T were predictive of coronary artery disease. Neither coronary artery disease nor percutaneous coronary intervention significantly impacted survival.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2008;20(3):226-234
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2008000300004
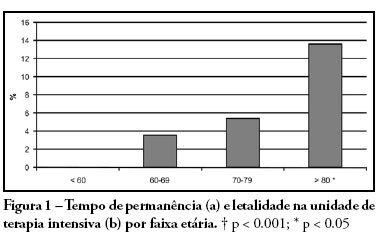
PURPOSE: Due to the increasing longevity of the and high prevalence of coronary heart disease in the aged , coronary artery bypass graft surgery has become frequent in older patients. The purpose of this study is to describe operative features, length of stay, complications and short term outcomes after coronary artery bypass graft in such patients. METHODS: From February 2005 to October 2007, 269 patients underwent coronary artery bypass graft. Demographic data, comorbidities, prognostic scores, coronary artery bypass graft elective versus urgent indication, intensive care unit length of stay, postoperative complications and intensive care unit mortality were recorded. Intra-operative characteristics, such as total surgery time, use of bypass device, on-pump time, urine output, fluid balance, use of blood products and number of grafts, were analyzed. Patients were divided in four age groups: group I (< 60 n = 68), II (60 to 69 n = 86), III (70 to 79 n = 93) IV and older than 80 years (n = 22). RESULTS: Group IV patients were more frequently submitted to coronary artery bypass graft combined with valve replacement, emergency surgery, and had longer stay in the intensive care unit (p < 0.01). The incidence of at least one postoperative complication was also higher among patients older than 80 (p < 0.001). Multivariate analysis identified age and on-pump time as independent risk factors for development of complications. Mortality increased in patients older than 70 years (p = 0.03). CONCLUSIONS: Octogenarian patients undergoing coronary artery bypass graft have longer intensive care unit length of stay, incidence of complications and mortality. Age and on-pump time were independent risk factors associated with the incidence of postoperative complications.