Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(2):251-260
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20210032
To identify predictors of coronary artery disease in survivors of cardiac arrest, to define the best timing for coronary angiography and to establish the relationship between coronary artery disease and mortality.
This was a single-center retrospective study including consecutive patients who underwent coronary angiography after cardiac arrest.
A total of 117 patients (63 ± 13 years, 77% men) were included. Most cardiac arrest incidents occurred with shockable rhythms (70.1%), and the median duration until the return of spontaneous circulation was 10 minutes. Significant coronary artery disease was found in 68.4% of patients, of whom 75% underwent percutaneous coronary intervention. ST-segment elevation (OR 6.5, 95%CI 2.2 - 19.6; p = 0.001), the presence of wall motion abnormalities (OR 22.0, 95%CI 5.7 - 84.6; p < 0.001), an left ventricular ejection fraction ≤ 40% (OR 6.2, 95%CI 1.8 - 21.8; p = 0.005) and elevated high sensitivity troponin T (OR 3.04, 95%CI 1.3 - 6.9; p = 0.008) were predictors of coronary artery disease; the latter had poor accuracy (area under the curve 0.64; p = 0.004), with an optimal cutoff of 170ng/L. Only ST-segment elevation and the presence of wall motion abnormalities were independent predictors of coronary artery disease. The duration of cardiac arrest (OR 1.015, 95%CI 1.0 - 1.05; p = 0.048) was an independent predictor of death, and shockable rhythm (OR 0.4, 95%CI 0.4 - 0.9; p = 0.031) was an independent predictor of survival. The presence of coronary artery disease and the performance of percutaneous coronary intervention had no impact on survival; it was not possible to establish the best cutoff for coronary angiography timing.
In patients with cardiac arrest, ST-segment elevation, wall motion abnormalities, left ventricular dysfunction and elevated high sensitivity troponin T were predictive of coronary artery disease. Neither coronary artery disease nor percutaneous coronary intervention significantly impacted survival.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2014;26(4):392-396
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20140060
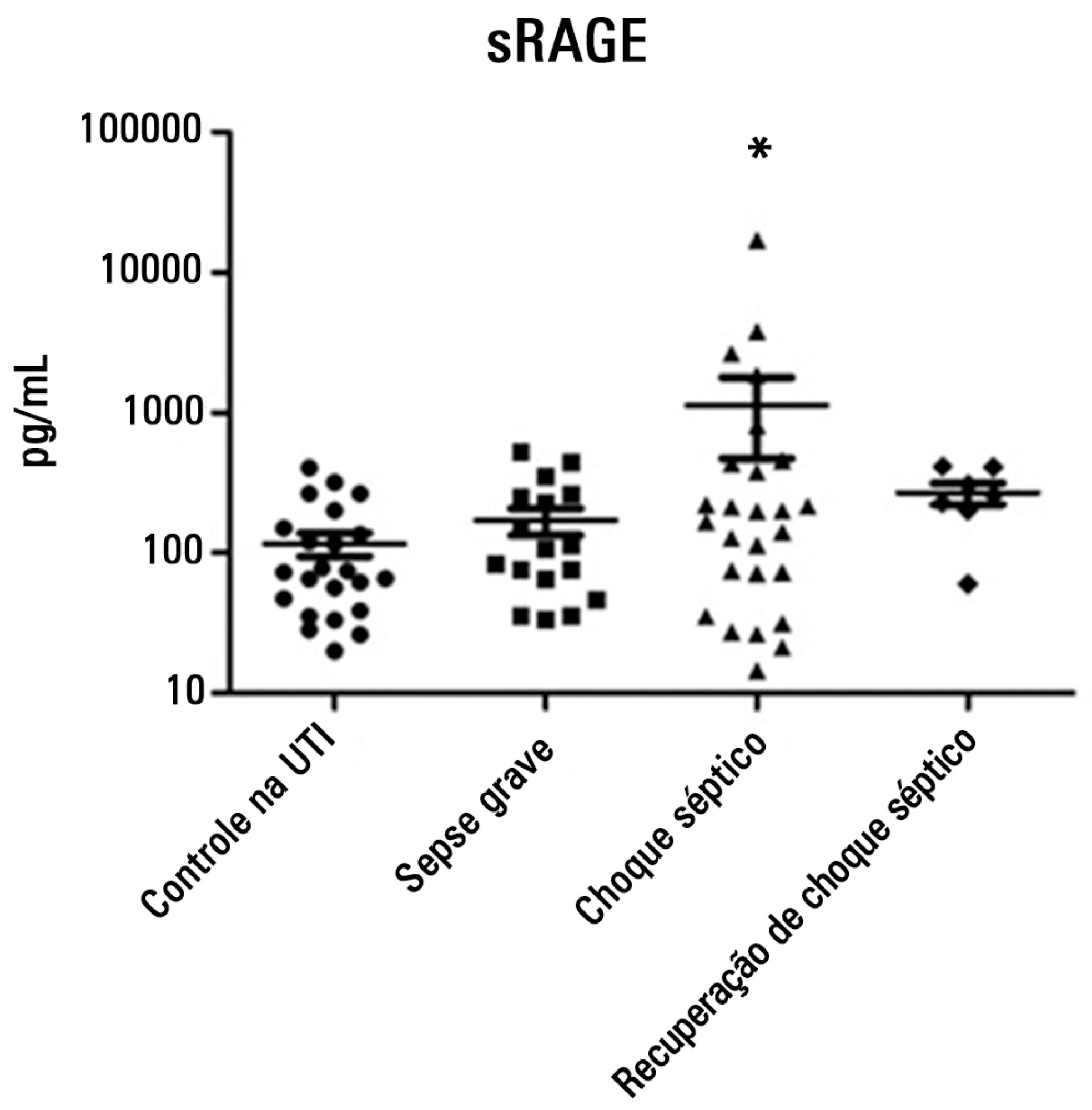
To evaluate and understand the clinical implications of the plasma levels of a soluble isoform of a receptor for advanced glycation end products (sRAGE) in different stages of sepsis.
Serum sRAGE values in patients who were divided into intensive care unit control, severe sepsis, septic shock and recovery from septic shock groups were statistically analyzed to assess quantity (Kruskal-Wallis), variability (Levine test) and correlation (Spearman rank test) with certain inflammatory mediators (IL-1 α, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IP-10, G-CSF, MCP-1, IFN-γ and TNF-α).
No changes in sRAGE levels were observed among the groups; however, the septic shock group showed differences in the variability of sRAGE compared to the other groups. A positive correlation with all the inflammatory mediators was reported in the septic shock group.
sRAGE levels are associated with worse outcomes in patients with septic shock. However, a statistical correlation analysis with other proinflammatory cytokines indicated that the pathways leading to those outcomes are different depending on the sRAGE levels. Future studies to elucidate the pathophysiological mechanisms involving sRAGE in models of sepsis are of great clinical importance for the safe handling of this biomarker.