Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2014;26(4):392-396
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20140060
To evaluate and understand the clinical implications of the plasma levels of a soluble isoform of a receptor for advanced glycation end products (sRAGE) in different stages of sepsis.
Serum sRAGE values in patients who were divided into intensive care unit control, severe sepsis, septic shock and recovery from septic shock groups were statistically analyzed to assess quantity (Kruskal-Wallis), variability (Levine test) and correlation (Spearman rank test) with certain inflammatory mediators (IL-1 α, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IP-10, G-CSF, MCP-1, IFN-γ and TNF-α).
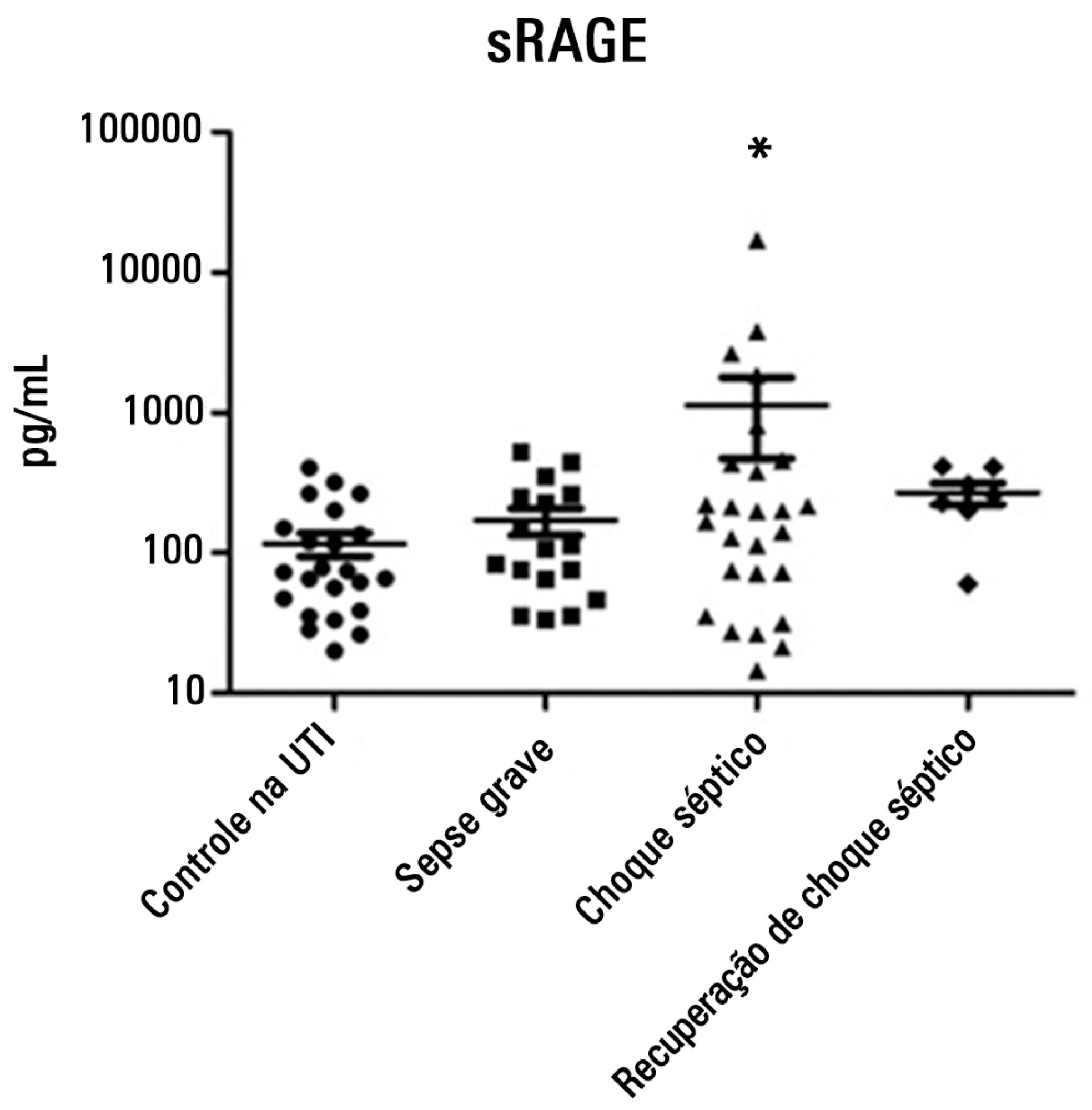
No changes in sRAGE levels were observed among the groups; however, the septic shock group showed differences in the variability of sRAGE compared to the other groups. A positive correlation with all the inflammatory mediators was reported in the septic shock group.
sRAGE levels are associated with worse outcomes in patients with septic shock. However, a statistical correlation analysis with other proinflammatory cytokines indicated that the pathways leading to those outcomes are different depending on the sRAGE levels. Future studies to elucidate the pathophysiological mechanisms involving sRAGE in models of sepsis are of great clinical importance for the safe handling of this biomarker.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2014;26(3):305-312
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20140043
The number of studies investigating circulating nucleic acids as potential biomarkers has increased in recent years. The detection of such biomarkers is a minimally invasive alternative for the diagnosis and prognosis of various clinical conditions. The value of circulating DNA levels as a predictive biomarker has been demonstrated in patients suffering from numerous acute pathologies that have a high risk of intensive care needs and in-hospital deaths. The mechanism by which circulating DNA levels increase in patients with these conditions remains unclear. In this review, we focused on the potential use of this biomarker for prognosis prediction in critically ill and trauma patients. The literature review was performed by searching MedLine using PubMed in the English language.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2013;25(1):6-11
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2013000100003
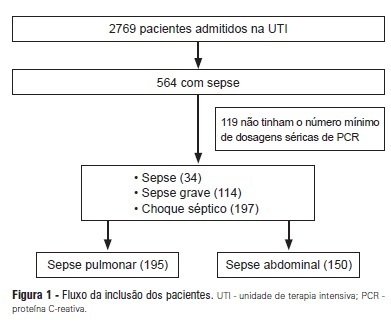
OBJECTIVES: To evaluate the C-reactive protein serum levels in patients with pulmonary and abdominal sepsis during the first five days of sepsis progression. METHODS: The present investigation was a retrospective cohort study conducted at the university hospital with 345 patients who were admitted to the intensive care unit and diagnosed with sepsis of pulmonary or abdominal origin. Serum C-reactive protein concentrations were measured by the turbidimetric immunoassay. For analysis of C-reactive protein, day 1 was defined as the day on which the patient was clinically diagnosed with sepsis. RESULTS: Thirty-four patients with sepsis (9.8%), 114 patients with severe sepsis (33.0%), and 197 patients with septic shock (57.2%) were evaluated. The age of the patients was 56.4±19.8 years. The serum C-reactive protein concentrations were higher on the day of sepsis diagnosis in the group with abdominal infection compared with the group with pulmonary sepsis (17.8±10.1 mg/dL versus 14.9±11.1 mg/dL, p=0.025) and remained significantly higher during the first five days of sepsis progression. CONCLUSION: The serum C-reactive protein concentrations were significantly higher in the patients with abdominal sepsis compared with the patients with pulmonary sepsis during the first five days of sepsis progression.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2013;25(1):56-62
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2013000100011
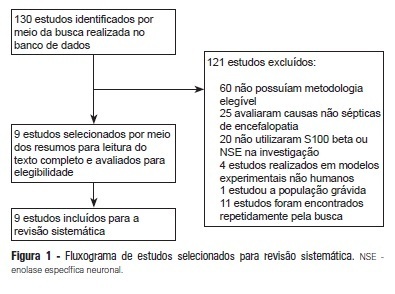
OBJECTIVE: The aim of this study was to systematically review the importance of neuron-specific enolase and S100 beta for diagnosing and monitoring septic encephalopathy. METHODS: A PubMed database search was performed to identify studies that evaluated S100 beta and neuron-specific enolase serum levels in patients with sepsis and that were published between January 2000 and April 2012. Only human studies that employed an additional method of neurological assessment were selected. RESULTS: Nine studies were identified, seven of which associated high concentrations of S100 beta and neuron-specific enolase with the development of septic encephalopathy. Four studies also associated these concentrations with increased mortality. However, two studies did not find such an association when they evaluated S100 beta levels, and one of these studies did not observe a correlation between neuron-specific enolase and septic encephalopathy. CONCLUSION: S100 beta and neuron-specific enolase are promising biomarkers for diagnosing and monitoring patients with septic encephalopathy, but more research is necessary.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2009;21(1):25-31
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2009000100004
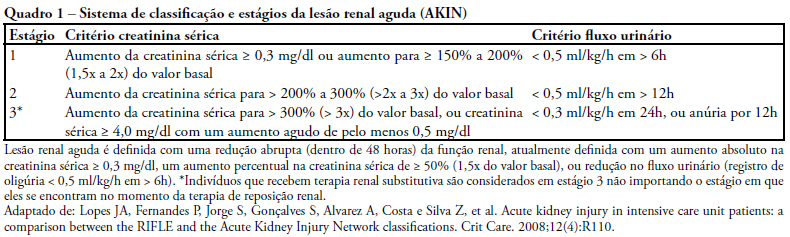
OBJECTIVES: To identify the frequency of the Acute Kidney Injury and to compare the application of the AKIN classification with the separate use of the serum creatinine in the postoperative period of cardiac surgery. METHODS: This study was prospectively developed in a teaching and specialized research hospital in cardiology of the public health system of the state of São Paulo. Forty-four patients submitted to the elective cardiac surgery since the immediate post-surgical period up to the 2nd post-surgical period were followed. RESULTS: It was possible to verify that from the forty-four patients, 75% were hypertensive, 27% were diabetic and mostly were male (64%), with an average age of 55+16 years old. It was observed that advanced age and the elevated body mass index shows a significant correlation to renal dysfunction (p<0, 05). According to the AKIN classification, the urinary flow criterion identified more renal dysfunction than creatinine criterion. It was verified that the renal dysfunction occurred more frequently in the postsurgery period and the majority (82%) from the 63,6% of the patients which were submitted to the revascularization of the myocardium surgery. CONCLUSION: The majority of patients (75%) evolved initially with renal dysfunction signaled it mainly by the urinary flow criterion from the AKIN classification, a higher number compared to the separated creatinine. This fact confirms that the serum creatinine association with the urinary flow has a higher discriminatory performance for the early identification of this syndrome comparatively with the routinely use of the isolated creatinine.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2008;20(4):411-421
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2008000400015
Trauma is the leading cause of death of people from 1 to 44 years of age. Traumatic brain injury is the main determinant for mortality and morbidity caused by trauma. Outcome prediction is one of the major problems related to severe traumatic brain injury because clinical evaluation has an unreliable predictive value and complicates identification of patients with higher risk of developing secondary lesions and fatal outcome. That is why, there is considerable interest in development of biomarkers that reflect the severity of brain injury and correlate with mortality and functional outcome. Proteins S100B and neuron specific enolases are among the markers most studied for this purpose, however some studies are investigating glial fibrillary acidic protein, creatinine phospokinase, isoenzime B, myelin basic protein, plasma desoxiribonucleic acid, heat shock protein 70, von Willebrand factor, metalloproteinases and brain-derived neurotrophic factor, among others. Evidence suggests that inflammation, oxidative stress, excitotoxicity, neuroendocrine responses and apoptosis play an important role in the development of secondary lesions. Markers involved in these processes are being studied in traumatic brain injury. We reviewed these biomarkers, some of which present promising results for future clinical application.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (115) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)