Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2014;26(4):347-354
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20140053
To assess the diagnostic and prognostic efficacy of urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in patients admitted to an intensive care unit.
Longitudinal, prospective cohort study conducted in a cardiology intensive care unit. The participants were divided into groups with and without acute kidney injury and were followed from admission to the intensive care unit until hospital discharge or death. Serum creatinine, urine output and urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin were measured 24 and 48 hours after admission.
A total of 83 patients admitted to the intensive care unit for clinical reasons were assessed, most being male (57.8%). The participants were divided into groups without acute kidney injury (N=18), with acute kidney injury (N=28) and with severe acute kidney injury (N=37). Chronic diseases, mechanical ventilation and renal replacement therapy were more common in the groups with acute kidney injury and severe acute kidney injury, and those groups exhibited longer intensive care unit stay and hospital stay and higher mortality. Serum creatinine did not change significantly in the group with acute kidney injury within the first 24 hours of admission to the intensive care unit, although, urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin was high in the groups with acute kidney injury and severe acute kidney injury (p<0.001). Increased urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin was associated with death.
An increase in urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin precedes variations in serum creatinine in patients with acute kidney injury and may be associated with death.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2009;21(4):359-368
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2009000400005
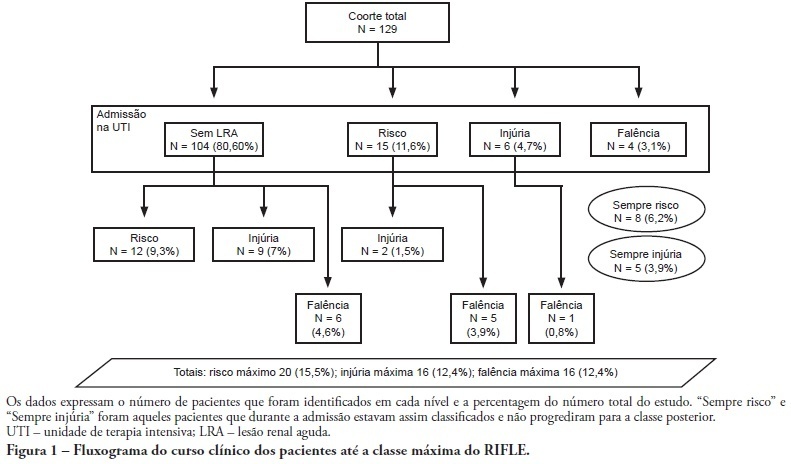
OBJECTIVE: To correlate the RIFLE classification with mortality and length of stay both in the intensive care unit and hospital. METHODS: A prospective, observational, longitudinal cohort study, approved by the Institution's Ethics Committee. Data were collected for all patients staying longer than 24 hours in the intensive care unit of Hospital Universitário Polydoro Ernani de São Thiago - Universidade Federal de Santa Catarina from September 2007 to March 2008, followed-up either until discharge or death. Patients were divided in two groups: with or without acute kidney injury. The acute kidney injury group was additionally divided according to the RIFLE and sub-divided according to the maximal score in Risk, Injury of Failure. Loss and End-stage classes were not included in the study. APACHE II and SOFA were also evaluated. The t Student and Chi-Square tests were used. A P<0.05 was considered statistically significant. RESULTS: The sample included 129 patients, 52 (40.3%) with acute kidney injury according to RIFLE. Patients were more severely ill in this group, with higher APACHE and SOFA scores (P<0.05). Compared to the without kidney injury group, the kidney injury severity caused increased intensive care unity (Risk 25%; Injury 37.5%; Failure 62.5%) and in-hospital (Risk 50%; Injury 37.5%; Failure 62.5%) mortality, and longer intensive care unit stay (P<0.05). CONCLUSION: The RIFLE system, according to the severity class, was a marker for risk of increased intensive care unit and in-hospital mortality, and longer intensive care unit stay. No relationship with in-hospital length of stay was found.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2009;21(1):25-31
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2009000100004
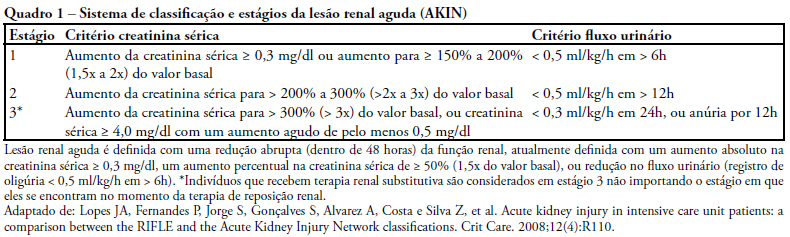
OBJECTIVES: To identify the frequency of the Acute Kidney Injury and to compare the application of the AKIN classification with the separate use of the serum creatinine in the postoperative period of cardiac surgery. METHODS: This study was prospectively developed in a teaching and specialized research hospital in cardiology of the public health system of the state of São Paulo. Forty-four patients submitted to the elective cardiac surgery since the immediate post-surgical period up to the 2nd post-surgical period were followed. RESULTS: It was possible to verify that from the forty-four patients, 75% were hypertensive, 27% were diabetic and mostly were male (64%), with an average age of 55+16 years old. It was observed that advanced age and the elevated body mass index shows a significant correlation to renal dysfunction (p<0, 05). According to the AKIN classification, the urinary flow criterion identified more renal dysfunction than creatinine criterion. It was verified that the renal dysfunction occurred more frequently in the postsurgery period and the majority (82%) from the 63,6% of the patients which were submitted to the revascularization of the myocardium surgery. CONCLUSION: The majority of patients (75%) evolved initially with renal dysfunction signaled it mainly by the urinary flow criterion from the AKIN classification, a higher number compared to the separated creatinine. This fact confirms that the serum creatinine association with the urinary flow has a higher discriminatory performance for the early identification of this syndrome comparatively with the routinely use of the isolated creatinine.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2008;20(4):385-393
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2008000400011
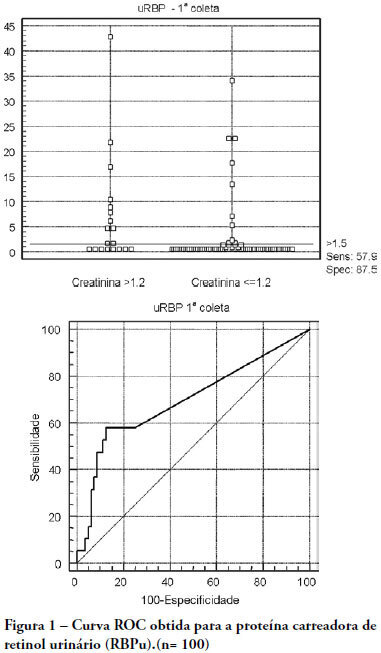
OBJECTIVES: The early assessment of renal dysfunction using common markers does not provide either a sensitive or specific indication of renal dysfunction in critically ill patients. More specific and sensitive markers are desirable for the early detection of an initial renal pathophysiological process. Urinary retinol-binding protein could be an alternative method to early evaluation of renal function in these patients. METHODS: This study followed-up 100 critical care patients and assessed their clinical and laboratory variables, including plasma creatinine and urinary retinol-binding ratio, and demographic variables. RESULTS: The sample was characterized by geriatric (63.4±15.6 years), male (68%), being 53% surgical patients. Statistical analysis showed association between plasma creatinine and the following variables: gender (p-0.026), age (p-0.038), use of vasoactive drugs (p-0.003), proteinuria (p-0.025), Acute Physiological Chronic Health Evaluation (APACHE) II score (p-0.000), urea (p-0.000), potassium (p-0.003) and estimated creatinine clearance (p-0.000). Urinary retinol-binding protein was correlated with more variables: weight, use of invasive ventilation (p-0.000), use of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (p-0.018), use of vasoactive drugs (p-0.021), high temperature (>37.5ºC) (p-0.005), proteinuria (p-0.000), bilirubinuria (p-0.004), urinary flow (p-0.019), minimal diastolic pressure (p-0.032), minimal systolic pressure (p-0.029), APACHE II (p-0.000), creatinine (p-0.001), urea (p-0.001), estimated creatinine clearance (p-0.000). Urinary retinol-binding protein also tended to associate with previous renal disease, vasculopathy and neoplasm. Sodium excretion fraction correlated with plasma creatinine and urinary retinol-binding protein in univariate analysis. CONCLUSIONS: Urinary retinol-binding protein might be considered in clinical practice as a better marker regarding diagnostic performance in patients at risk of developing acute kidney injury, when compared with other markers routinely used. Moreover, urinary retinol-binding protein has other features of a good diagnostic test - it is a practical and non-invasive method.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (33) COVID-19 (45) Critical care (115) Critical illness (54) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (254) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (75) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (117) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98) Septic shock (25)