Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2014;26(2):122-129
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20140018
To investigate the relationship between sedation and the memories reported by patients subjected to mechanical ventilation following discharge from the intensive care unit.
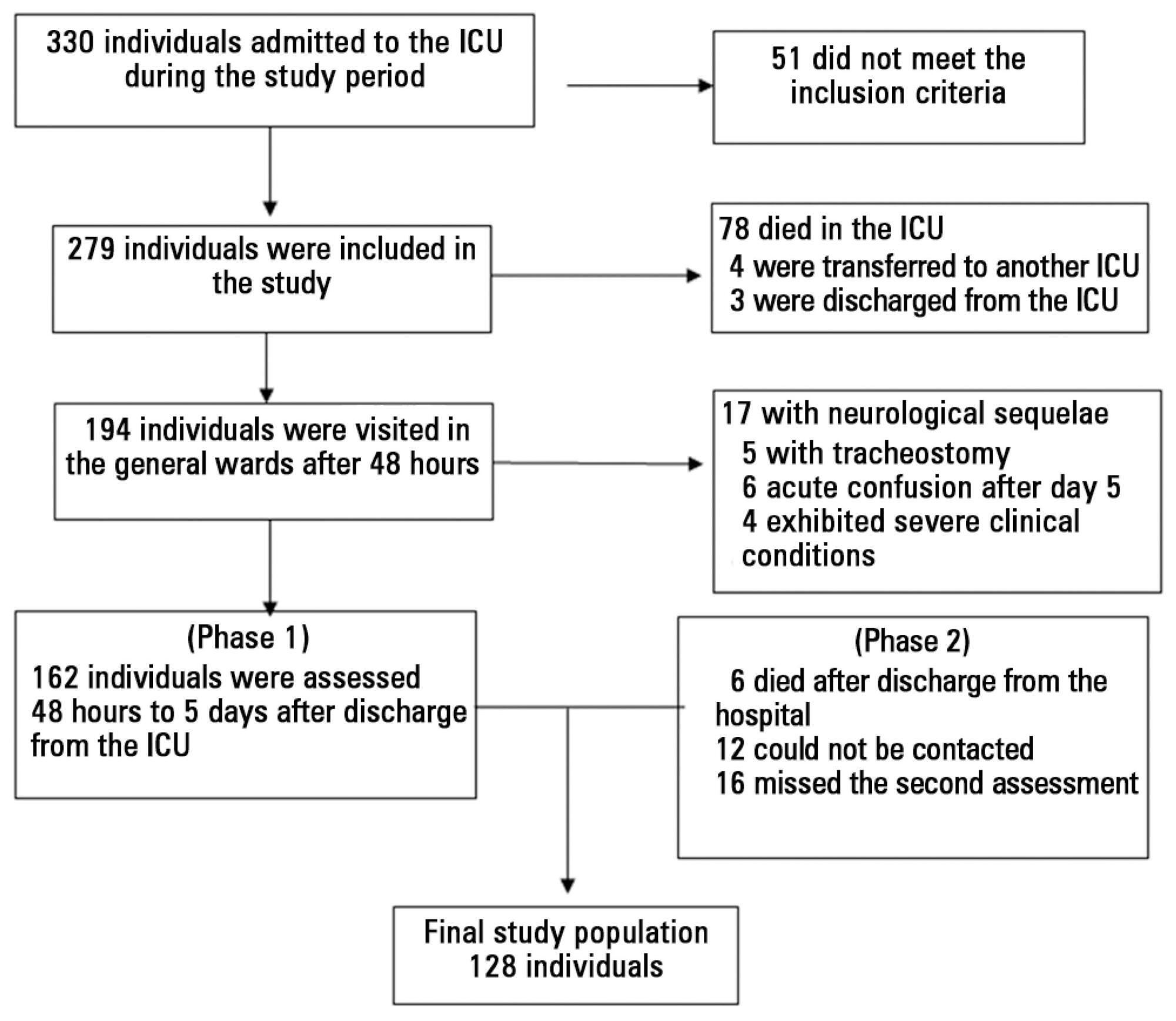
This prospective, observational, cohort study was conducted with individuals subjected to mechanical ventilation who remained in the intensive care unit for more than 24 hours. Clinical statistics and sedation records were extracted from the participants' clinical records; the data relative to the participants' memories were collected using a specific validated instrument. Assessment was performed three months after discharge from the intensive care unit.
A total of 128 individuals were assessed, most of whom (84.4%) reported recollections from their stay in the intensive care unit as predominantly a combination of real and illusory events. The participants subjected to sedation (67.2%) at deep levels (Richmond Agitation-Sedation Scale [RASS] -4 and -5) for more than two days and those with psychomotor agitation (33.6%) exhibited greater susceptibility to occurrence of illusory memories (p>0.001).
The probability of the occurrence of illusory memories was greater among the participants who were subjected to deep sedation. Sedation seems to be an additional factor that contributed to the occurrence of illusory memories in severely ill individuals subjected to mechanical ventilation.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2014;26(2):130-136
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20140019
To assess the performance of central venous oxygen saturation, lactate, base deficit, and C-reactive protein levels and SOFA and SWIFT scores on the day of discharge from the intensive care unit as predictors of patient readmission to the intensive care unit.
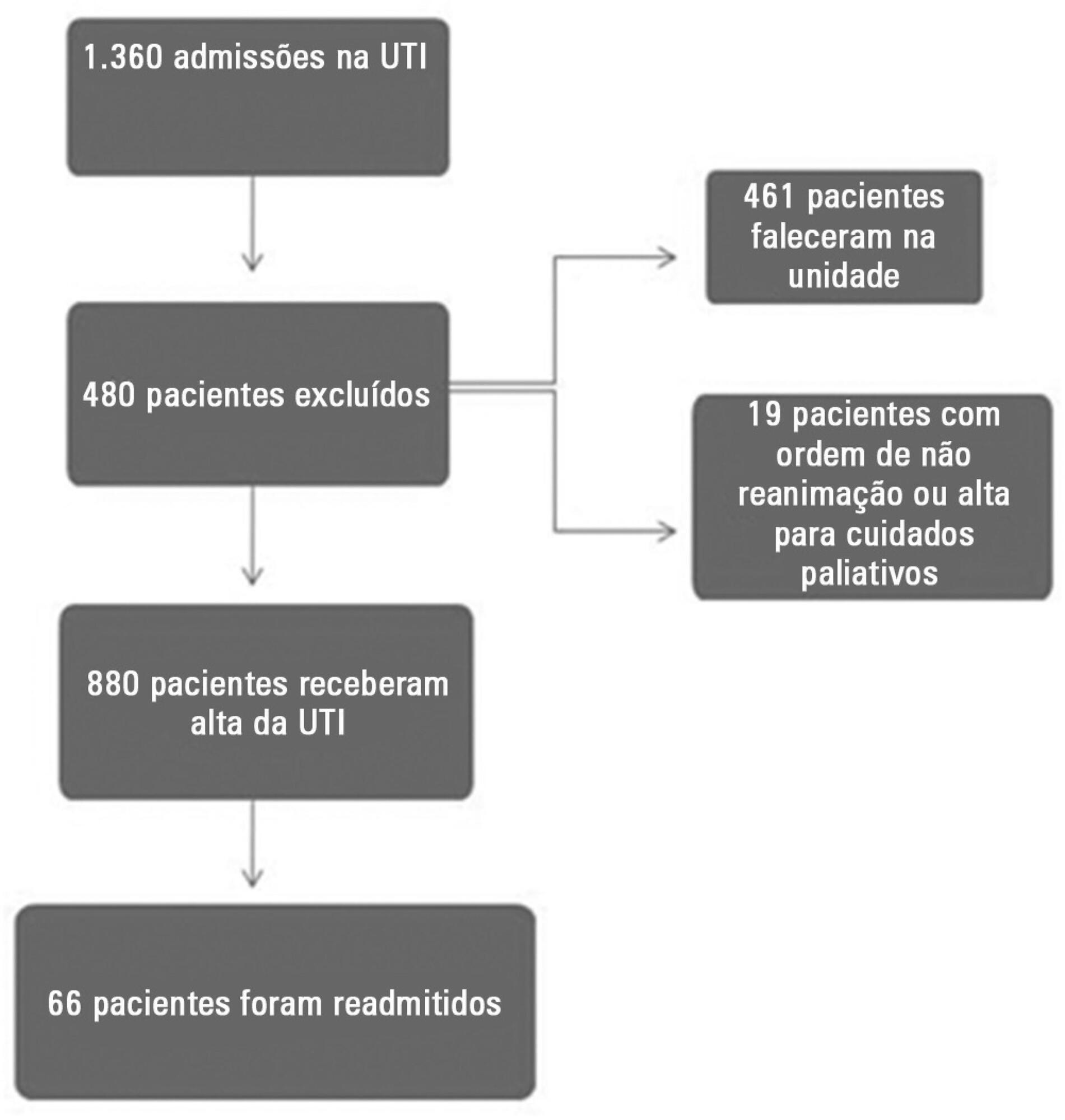
This prospective and observational study collected data from 1,360 patients who were admitted consecutively to a clinical-surgical intensive care unit from August 2011 to August 2012. The clinical characteristics and laboratory data of readmitted and non-readmitted patients after discharge from the intensive care unit were compared. Using a multivariate analysis, the risk factors independently associated with readmission were identified.
The C-reactive protein, central venous oxygen saturation, base deficit, and lactate levels and the SWIFT and SOFA scores did not correlate with the readmission of critically ill patients. Increased age and contact isolation because of multidrug-resistant organisms were identified as risk factors that were independently associated with readmission in this study group.
Inflammatory and perfusion parameters were not associated with patient readmission. Increased age and contact isolation because of multidrug-resistant organisms were identified as predictors of readmission to the intensive care unit.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2014;26(2):137-142
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20140020
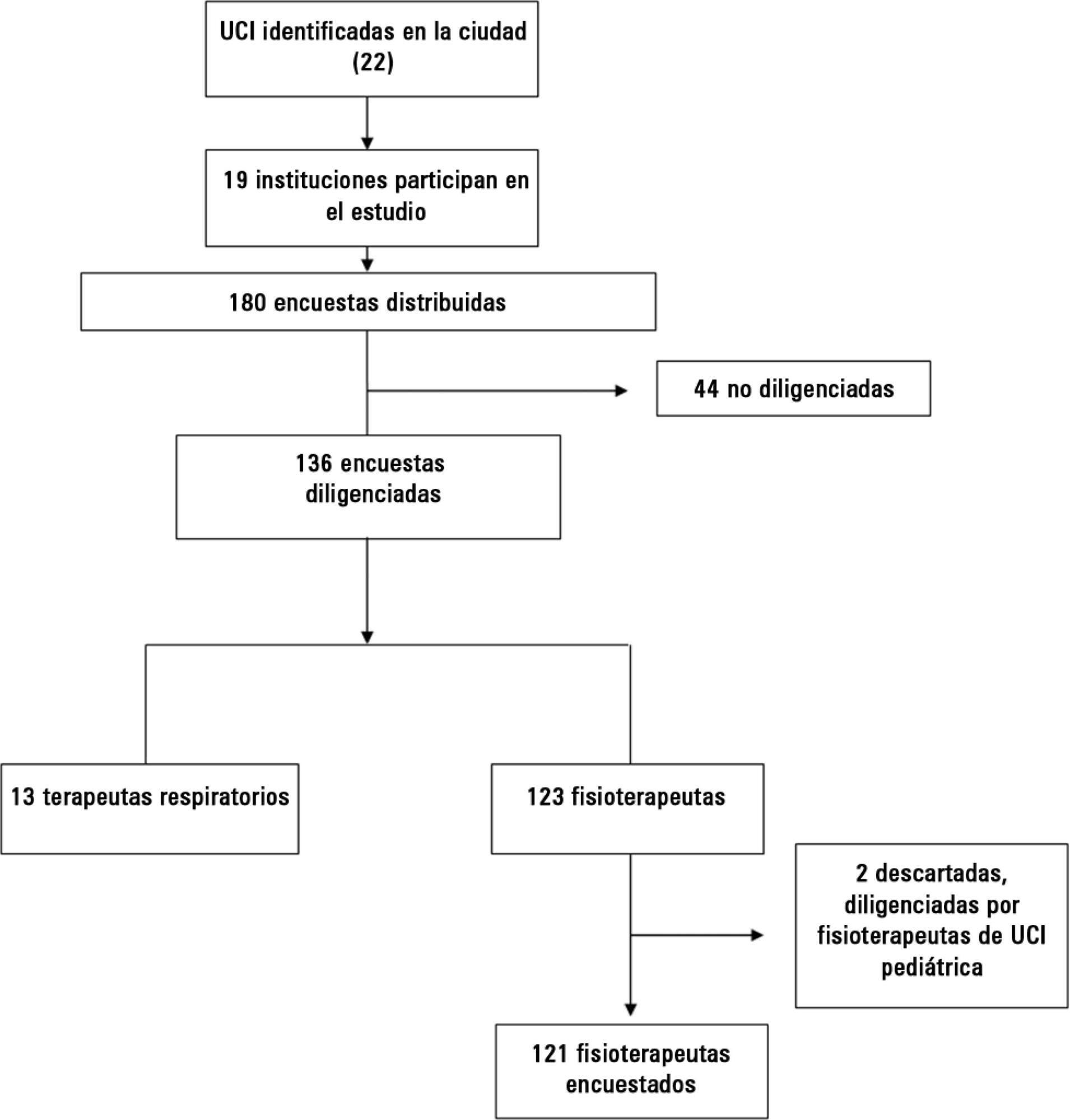
Early weaning from mechanical ventilation is one of the primary goals in managing critically ill patients. There are various techniques and measurement parameters for such weaning. The objective of this study was to describe the practices of ventilatory weaning in adult intensive care units in the city of Cali.
A survey of 32 questions (some multiple choice) evaluating weaning practices was distributed to physiotherapists and respiratory therapists working in intensive care units, to be answered anonymously.
The most common strategy for the parameter set was the combination of continuous positive airway pressure with pressure support (78%), with a large variability in pressure levels, the most common range being 6 to 8cmH2O. The most common weaning parameters were as follows: tidal volume (92.6%), respiratory rate (93.3%) and oxygen saturation (90.4%). The most common waiting time for registration of the parameters was >15 minutes (40%). The measurements were preferably obtained from the ventilator display.
The methods and measurement parameters of ventilatory weaning vary greatly. The most commonly used method was continuous positive airway pressure with more pressure support and the most commonly used weaning parameters were the measured tidal volume and respiratory rate.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2014;26(2):143-147
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20140021
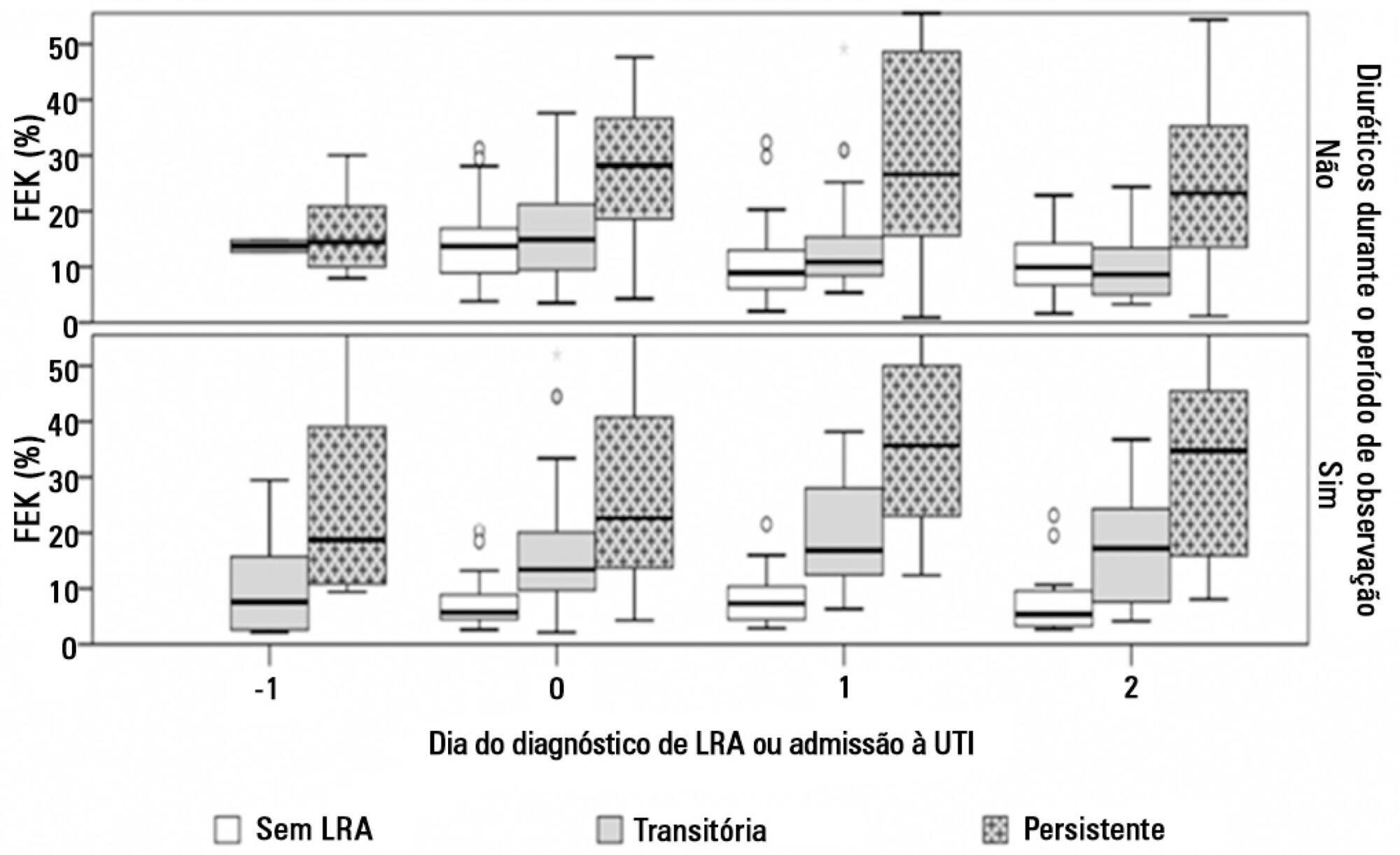
To evaluate the behavior of fractional excretion of potassium in the course of acute kidney injury in critically ill patients.
As part of a larger study in which we have evaluated blood and urinary parameters in the course of acute kidney injury, 168 patients were included. Blood and urine samples were collected daily until the removal of the urinary catheter or the initiation of renal replacement therapy. We describe the evolution of fractional excretion of potassium based on whether acute kidney injury was diagnosed, its duration (transient or persistent) and its severity (creatinine-based Acute Kidney Injury Network - AKIN stage). The diagnostic performance of fractional excretion of potassium in predicting the duration of acute kidney injury and the need for renal replacement therapy on the day of acute kidney injury diagnosis was also evaluated.
Fractional excretion of potassium was significantly higher in persistent acute kidney injury compared to transient acute kidney injury on the day of acute kidney injury diagnosis (24.8 vs. 13.8%, p<0.001). Both groups had the median fractional excretion of potassium increasing in the two days preceding the acute kidney injury diagnosis. Patients without acute kidney injury had stable low fractional excretion of potassium values. The fractional excretion of potassium was fairly accurate in predicting persistent acute kidney injury (area under the curve: 0.712; 95% confidence interval: 0.614-0.811; p<0.001) on the day of acute kidney injury diagnosis. The area under the curve was 0.663 (95% confidence interval: 0.523-0.803; p=0.03) for renal replacement therapy. The fractional excretion of potassium increased with maximum AKIN stage reached, in both transient and persistent acute kidney injury.
Sequential fractional excretion of potassium assessment appears to be useful in critically ill patients at risk for acute kidney injury.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2014;26(2):148-154
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20140022
Patients with traumatic brain injury are particularly susceptible to sepsis, which may exacerbate the systemic inflammatory response and lead to organ dysfunction. The influence of clinical variables on the mortality of intensive care unit patients with traumatic brain injury and sepsis was investigated.
The present investigation was a retrospective study involving 175 patients with traumatic brain injury who were treated in a period of 1 year at a reference hospital for trauma and who had sepsis, severe sepsis, or septic shock. Demographic and clinical data were obtained, and the SOFA score was calculated at the time sepsis was found and after 72 hours.
There was a predominance of young men with severe traumatic brain injury, multiple head injuries, sepsis with a pulmonary focus, prolonged hospital stay, and high mortality (37.7%). Circulatory and respiratory failure had a high incidence, but renal and coagulation failure were less frequent, and liver failure was not observed. After logistic regression, the presence of septic shock and respiratory failure 72 hours after the sepsis diagnosis was associated with higher mortality, with an odds ratio of 7.56 (95%CI=2.04-27.31, p=0.0024) and 6.62 (95%CI=1.93-22.78, p=0.0027), respectively. In addition, there was a higher mortality among patients who had no organ failure on D1 but who developed the condition after 72 hours of sepsis and in those patients who already had organ failure at the time sepsis was diagnosed and remained in this condition after 72 hours.
Septic shock and progressive organ (particularly respiratory) dysfunction increases the mortality of patients with traumatic brain injury and sepsis.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2014;26(2):155-162
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20140023
To determine the factors that influence the adequacy of enteral nutritional therapy in an intensive care unit.
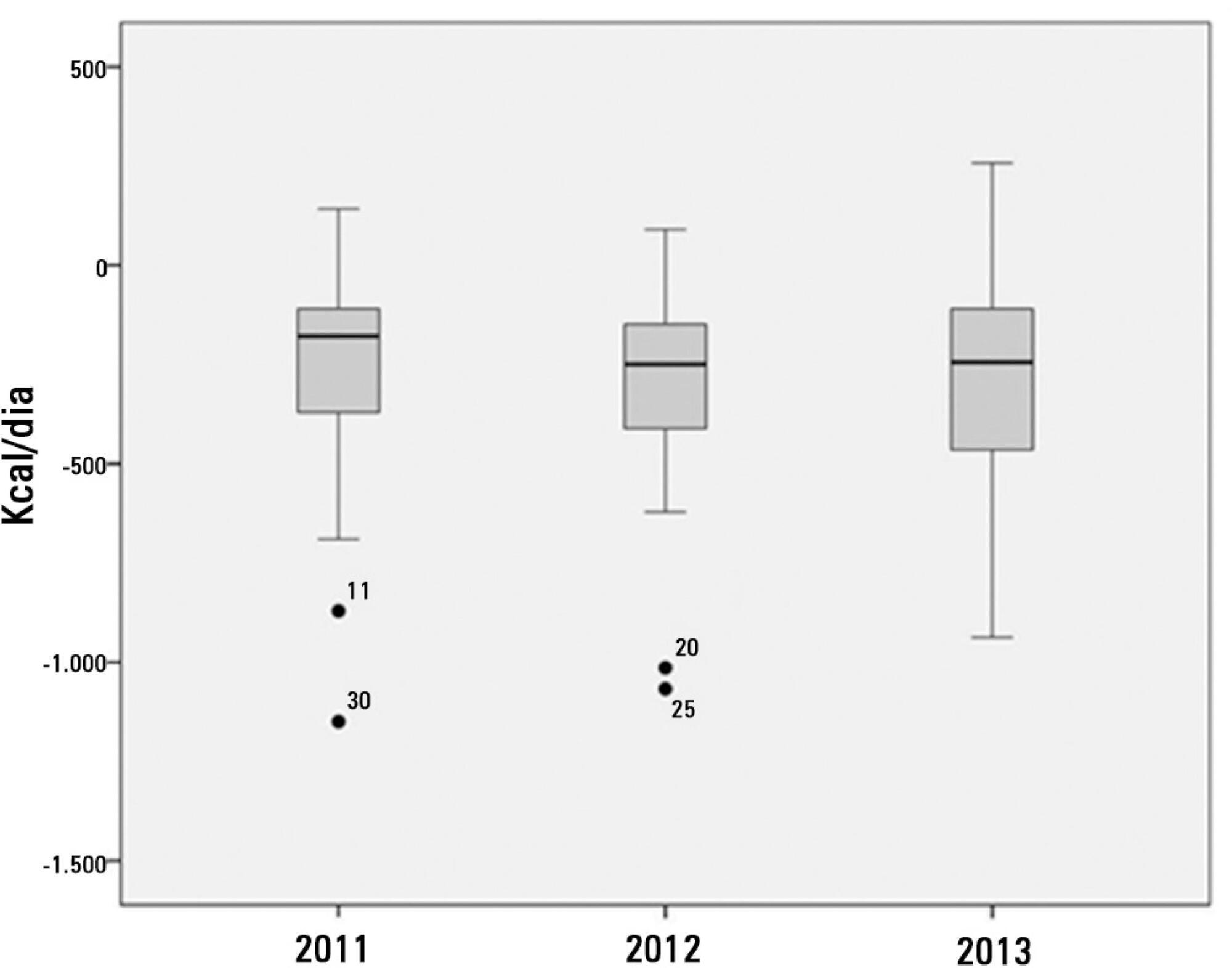
This prospective observational study was conducted in an intensive care unit between 2010 and 2012. Patients >18 years of age underwent exclusive enteral nutritional therapy for ≥72 hours. The energy and protein requirements were calculated according to the ICU protocols. The data regarding enteral nutrition, the causes of non-compliance, and the biochemical test results were collected daily.
Ninety-three patients admitted to the intensive care unit were evaluated. Among these patients, 82% underwent early enteral nutritional therapy, and 80% reached the nutritional goal in <36 hours. In addition, 81.6%±15.4% of the enteral nutrition volume was infused, with an adequacy of 82.2%±16.0% for calories, 82.2%±15.9% for proteins, and a mean energy balance of -289.9±277.1kcal/day. A negative correlation of C-reactive protein with the volume infused and the energy and protein balance was observed. In contrast, a positive correlation was found between C-reactive protein and the time required to reach nutritional goals. Extubation was the main cause for interrupting the enteral nutritional therapy (29.9% of the interruption hours), and the patients >60 years of age exhibited a lower percentage of recovery of the oral route compared with the younger patients (p=0.014).
Early enteral nutritional therapy and the adequacy for both energy and protein of the nutritional volume infused were in accordance with the established guidelines. Possible inadequacies of energy and protein balance appeared to be associated with an acute inflammatory response, which was characterized by elevated C-reactive protein levels. The main cause of interruption of the enteral nutritional therapy was the time spent in extubation.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2014;26(2):163-168
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20140024
To compare the effectiveness of the alveolar recruitment maneuver and the breath stacking technique with respect to lung mechanics and gas exchange in patients with acute lung injury.
Thirty patients were distributed into two groups: Group 1 - breath stacking; and Group 2 - alveolar recruitment maneuver. After undergoing conventional physical therapy, all patients received both treatments with an interval of 1 day between them. In the first group, the breath stacking technique was used initially, and subsequently, the alveolar recruitment maneuver was applied. Group 2 patients were initially subjected to alveolar recruitment, followed by the breath stacking technique. Measurements of lung compliance and airway resistance were evaluated before and after the use of both techniques. Gas analyses were collected before and after the techniques were used to evaluate oxygenation and gas exchange.
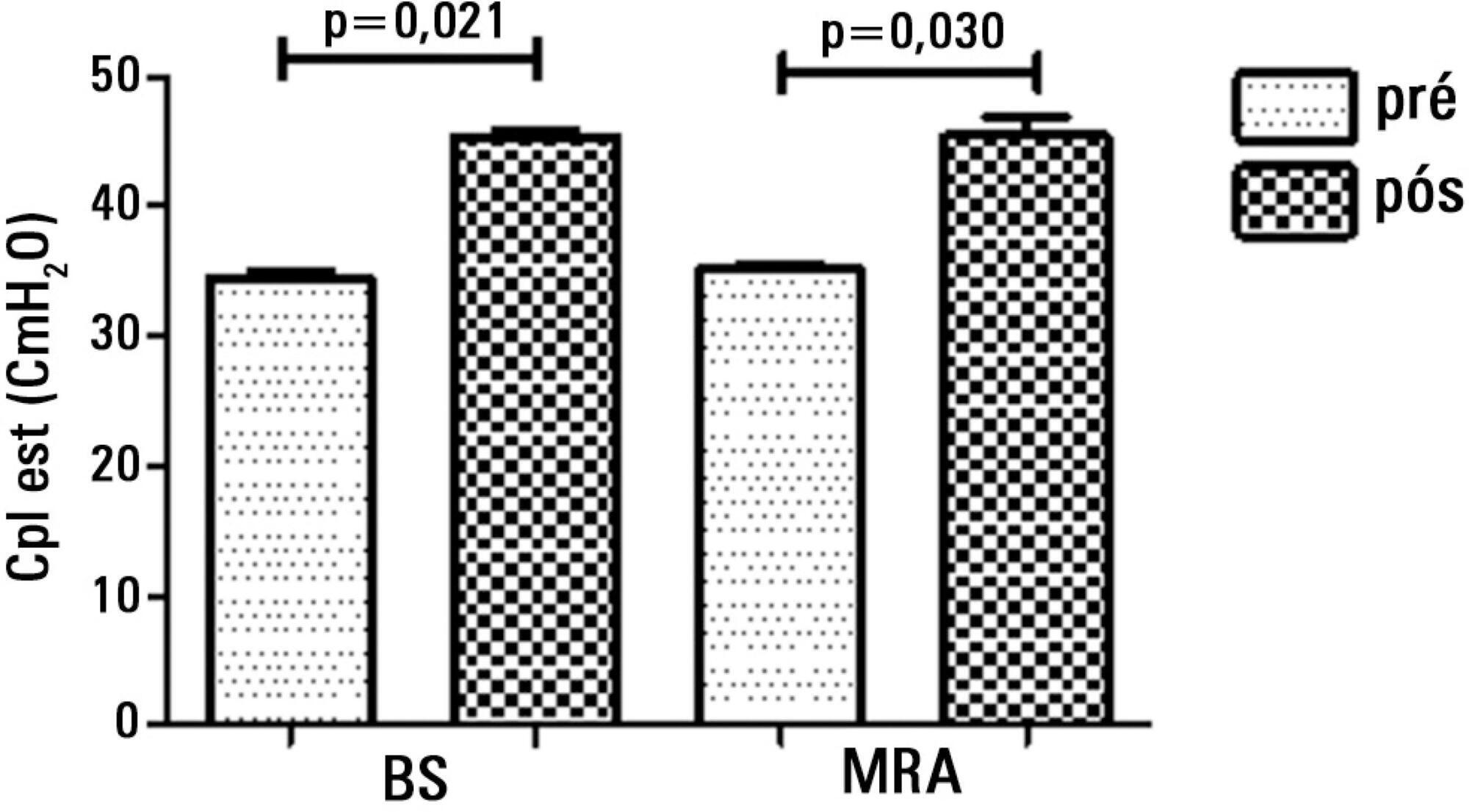
Both groups had a significant increase in static compliance after breath stacking (p=0.021) and alveolar recruitment (p=0.03), but with no significant differences between the groups (p=0.95). The dynamic compliance did not increase for the breath stacking (p=0.22) and alveolar recruitment (p=0.074) groups, with no significant difference between the groups (p=0.11). The airway resistance did not decrease for either groups, i.e., breath stacking (p=0.91) and alveolar recruitment (p=0.82), with no significant difference between the groups (p=0.39). The partial pressure of oxygen increased significantly after breath stacking (p=0.013) and alveolar recruitment (p=0.04), but there was no significant difference between the groups (p=0.073). The alveolar-arterial O2 difference decreased for both groups after the breath stacking (p=0.025) and alveolar recruitment (p=0.03) interventions, and there was no significant difference between the groups (p=0.81).
Our data suggest that the breath stacking and alveolar recruitment techniques are effective in improving the lung mechanics and gas exchange in patients with acute lung injury.