Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(3):384-393
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20210055
To describe current clinical practices related to the use of high-flow nasal cannula therapy by Brazilian pediatric intensivists and compare them with those in other countries.
A questionnaire was administered to pediatric intensivists in North and South America, Asia, Europe, and Australia/New Zealand for the main study. We compared the Brazilian cohort with cohorts in the United States of America, Canada, the United Kingdom, and India
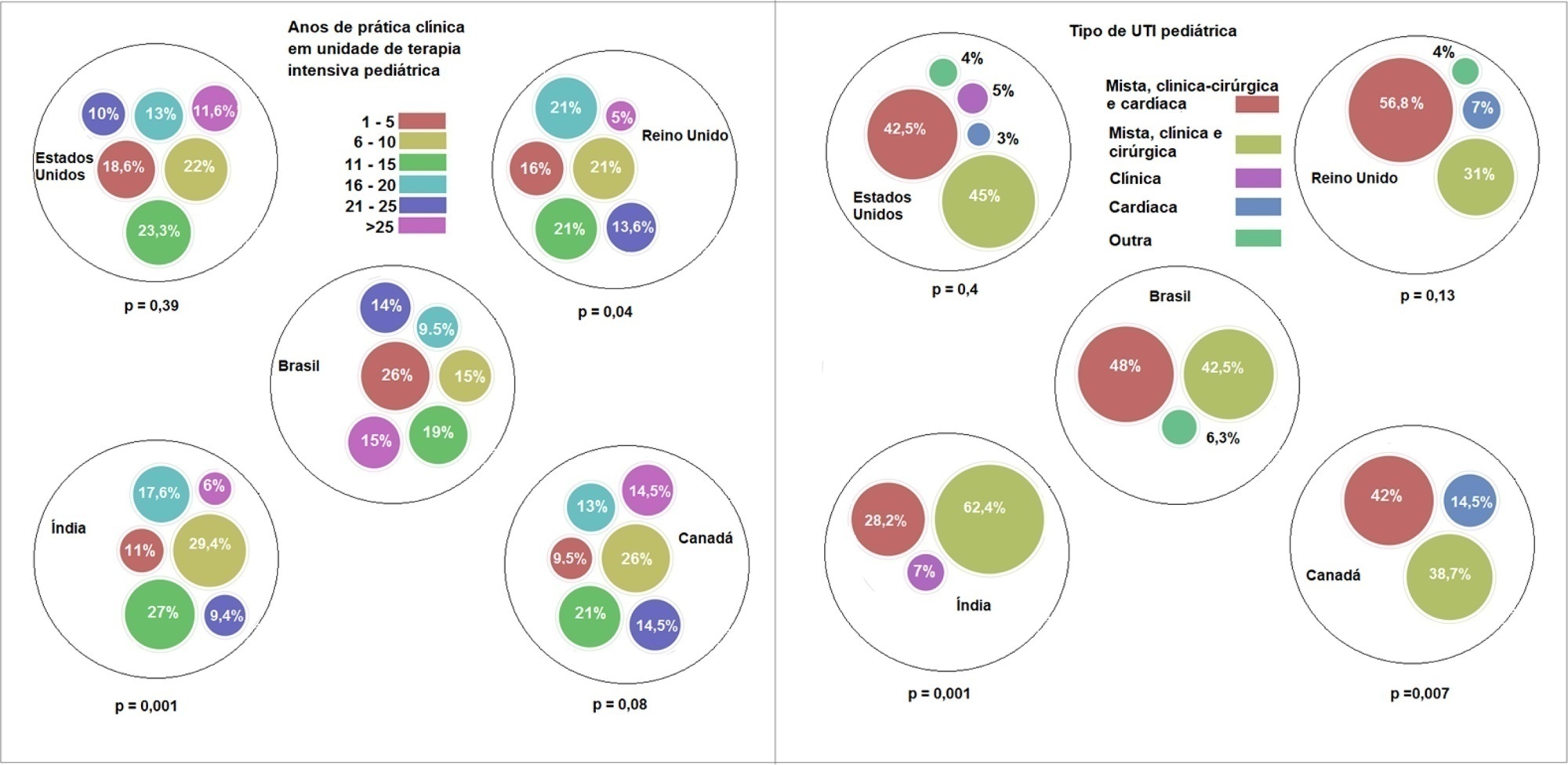
Overall, 501 physicians responded, 127 of which were in Brazil. Only 63.8% of respondents in Brazil had a high-flow nasal cannula available, in contrast to 100% of respondents in the United Kingdom, Canada, and the United States. The attending physician was responsible for the decision to start a high-flow nasal cannula according to 61.2% respondents in Brazil, 95.5% in the United Kingdom, 96.6% in the United States, 96.8% in Canada, and 84.7% in India. A total of 62% of respondents in Brazil, 96.3% in the United Kingdom, 96.6% in the United States, 96.8% in Canada, and 84.7% in India reported that the attending physician was responsible for the decision to wean or modify the high-flow nasal cannula settings. When high-flow nasal cannula therapy failed due to respiratory distress/failure, 82% of respondents in Brazil would consider a trial of noninvasive ventilation before endotracheal intubation, compared to 93% in the United Kingdom, 88% in the United States, 91.5% in Canada, and 76.8% in India. More Brazilian intensivists (6.5%) than intensivists in the United Kingdom, United States, and India (1.6% for all) affirmed using sedatives frequently with high-flow nasal cannulas.
The availability of high-flow nasal cannulas in Brazil is still not widespread. There are some divergences in clinical practices between Brazilian intensivists and their colleagues abroad, mainly in processes and decision-making about starting and weaning high-flow nasal cannula therapy.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2020;32(2):268-276
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20200043
To conduct a national survey of intensive care professionals to identify the practices for promoting sleep in adult intensive care units in Brazil and describe the professionals’ perceptions of the importance of sleep for patients.
An electronic questionnaire was distributed by the clinical research cooperation network of the Associação de Medicina Intensiva Brasileira and by the Brazilian Research in Intensive Care Network to physicians and nurses registered with the association. The questionnaire evaluated the profile of the respondents, the profile of their intensive care units, whether protocols for promoting sleep were present, the pharmacological and nonpharmacological measures typically employed in the unit, and the professionals’ perceptions regarding sleep in critically ill patients.
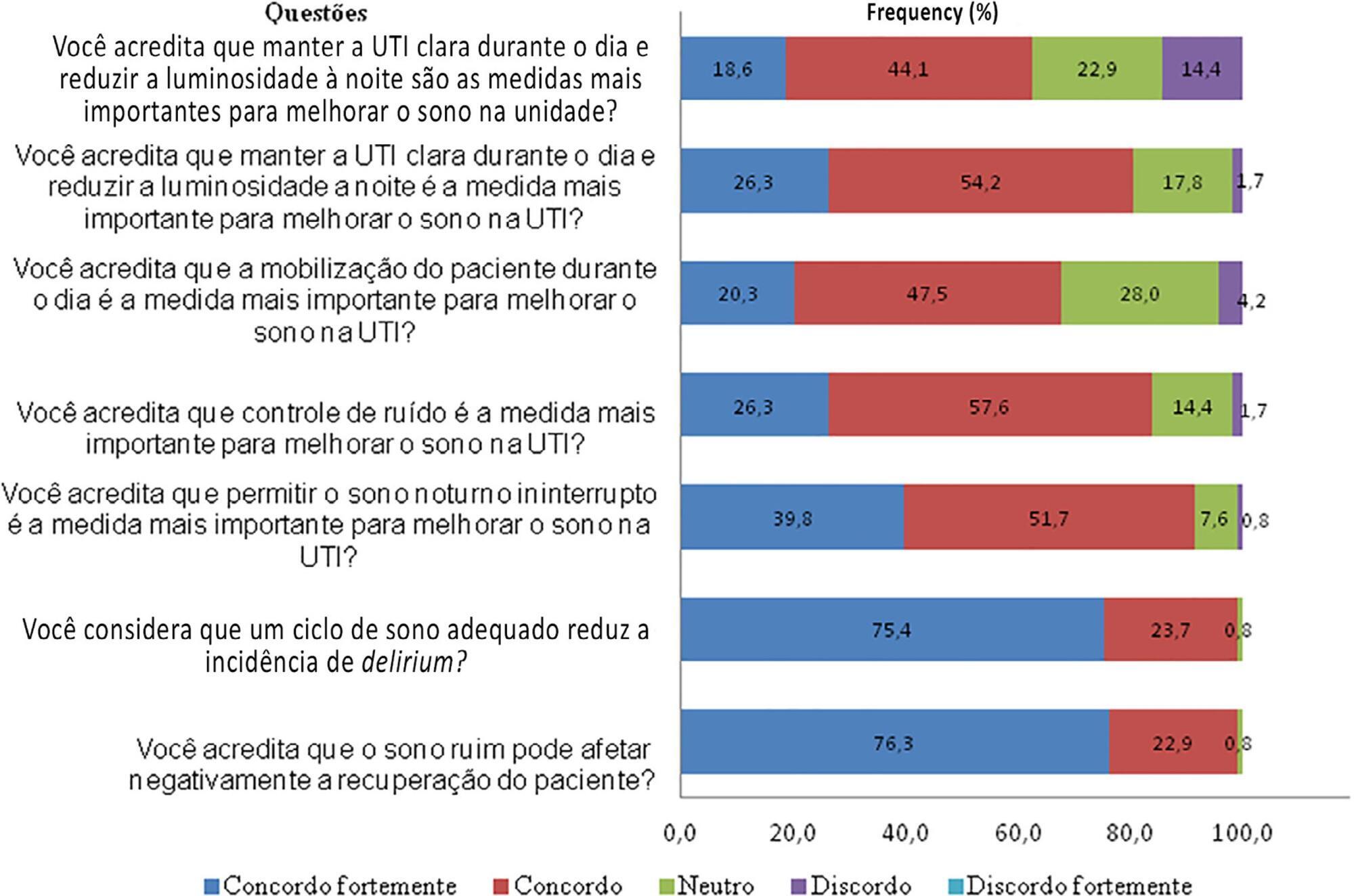
A total of 118 questionnaires were evaluated. The Southeast region of the country was the most represented (50 questionnaires, 42.4%). The majority of units had a clinical-surgical profile (93 questionnaires; 78.8%), and 26 had a continuous visitation policy (22.0%). Only 18 intensive care units (15.3%) reported having protocols for promoting sleep. The most cited measure for sleep promotion was reducing light during the night (95 questionnaires; 80.5%), which was more often performed in private intensive care units. Almost all of the responders (99%) believed that poor-quality sleep has a negative impact on patient recovery.
The responses to this Brazilian survey revealed that few intensive care units had a program for promoting sleep, although almost all participants recognized the importance of sleep in patient recovery.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2020;32(1):66-71
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20200011
To temporally assess a painful stimulus in premature infants using 3 neonatal pain scales.
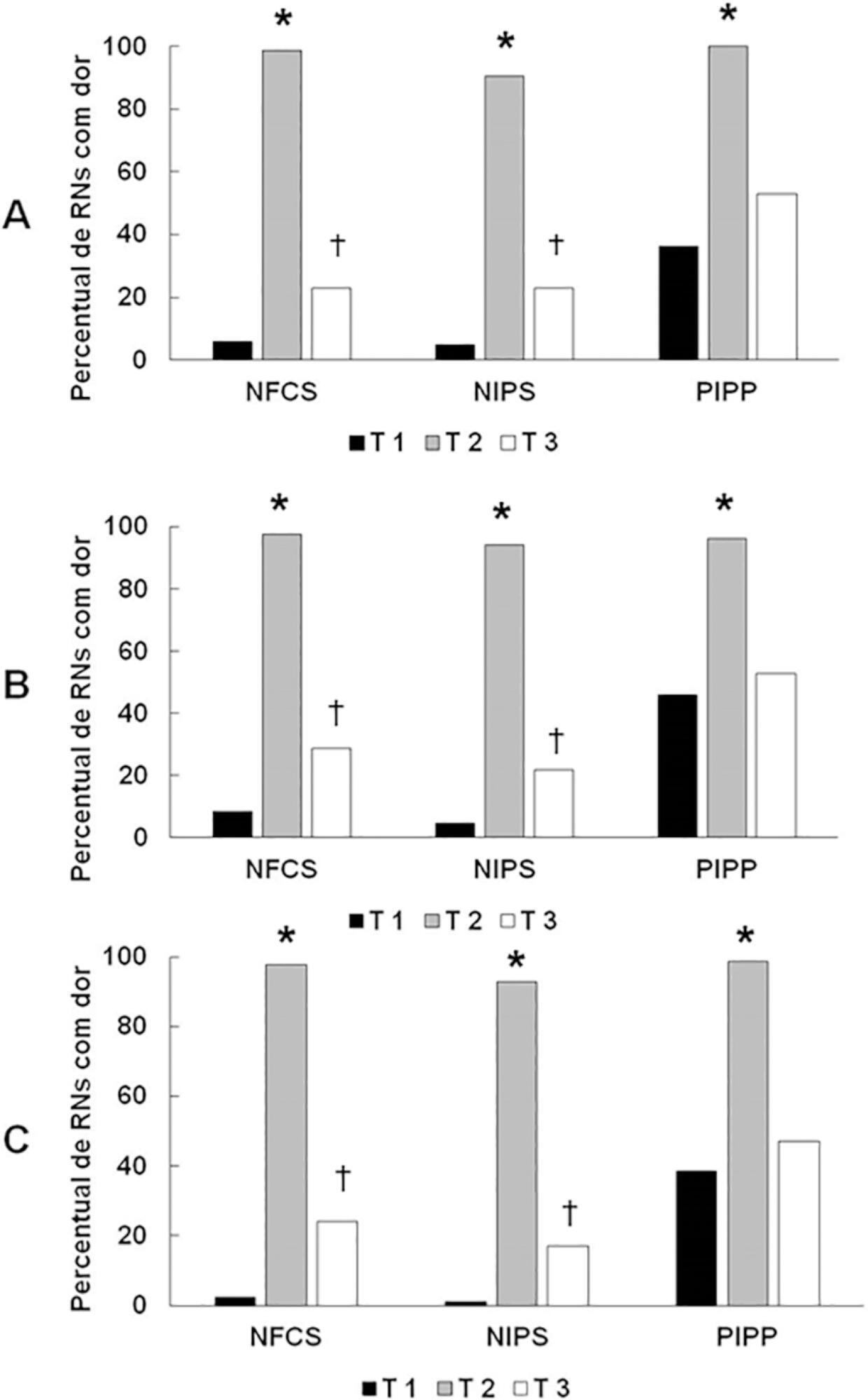
A total of 83 premature infants were observed during airway aspiration by 3 evaluators (E1, E2 and E3) using 3 pain assessment scales (Neonatal Facial Coding System - NFCS; Neonatal Infant Pain Scale - NIPS; and Premature Infant Pain Profile - PIPP) at 5 time points: T1 (before airway aspiration), T2 (during airway aspiration), T3 (1 minute after airway aspiration), T4 (3 minutes after airway aspiration), and T5 (5 minutes after airway aspiration). Light’s Kappa (agreement among examiners and among scales at each time point) and the McNemar test (comparison among time points) were used considering p < 0.05.
There was a significant difference between the 3 examiners for T1 and T2 using the 3 scales. In T3, pain was observed in 22.9%/E1, 28.9%/E2, and 24.1%/E3 according to the NFCS; 22.9%/E1, 21.7%/E2, and 16.9%/E3 according to the NIPS; and 49.4%/E1, 53.9%/E2, and 47%/E3 according to the PIPP. There was a difference between T1 and T3 using the 3 scales, except for 2 examiners for the PIPP (E2: p = 0.15/E3: p = 0.17). Comparing T4 and T5 to T1, there was no difference in the 3 scales.
Premature infants required at least 3 minutes to return to their initial state of rest (no pain).
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(3):318-325
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190057
To validate the "Checklist for Managing Critical Patients' Daily Awakening" instrument.
This was a descriptive study that used a quantitative approach for content validation using the Delphi method to obtain the consensus of experts who evaluated the instrument using a Likert scale. The validity index of each item of the instrument was calculated, with a minimum consensus parameter above 0.78.
Three Delphi rounds were required, starting with 29 experts and ending with 15 experts who were invited in person and via e-mail to participate in the study. Of the 15 items in the instrument, 13 had a content validity index > 0.78. The instrument maintained its attributes, and six items were reformulated without the need to exclude any of them. The validated items enabled the assessment of and decisions regarding the dimensions related to the level of sedation and agitation, vital signs, ventilatory parameters and pain. The instrument presented psychometric indicators with acceptable content validity.
The instrument proposed in the study exhibited content validity for most of its items and emerges as a practical strategy for the management of the daily interruption of sedation of critical patients.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2018;30(3):301-307
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20180043
To translate and cross-culturally adapt the Functional Status Scale for hospitalized children into Brazilian Portuguese.
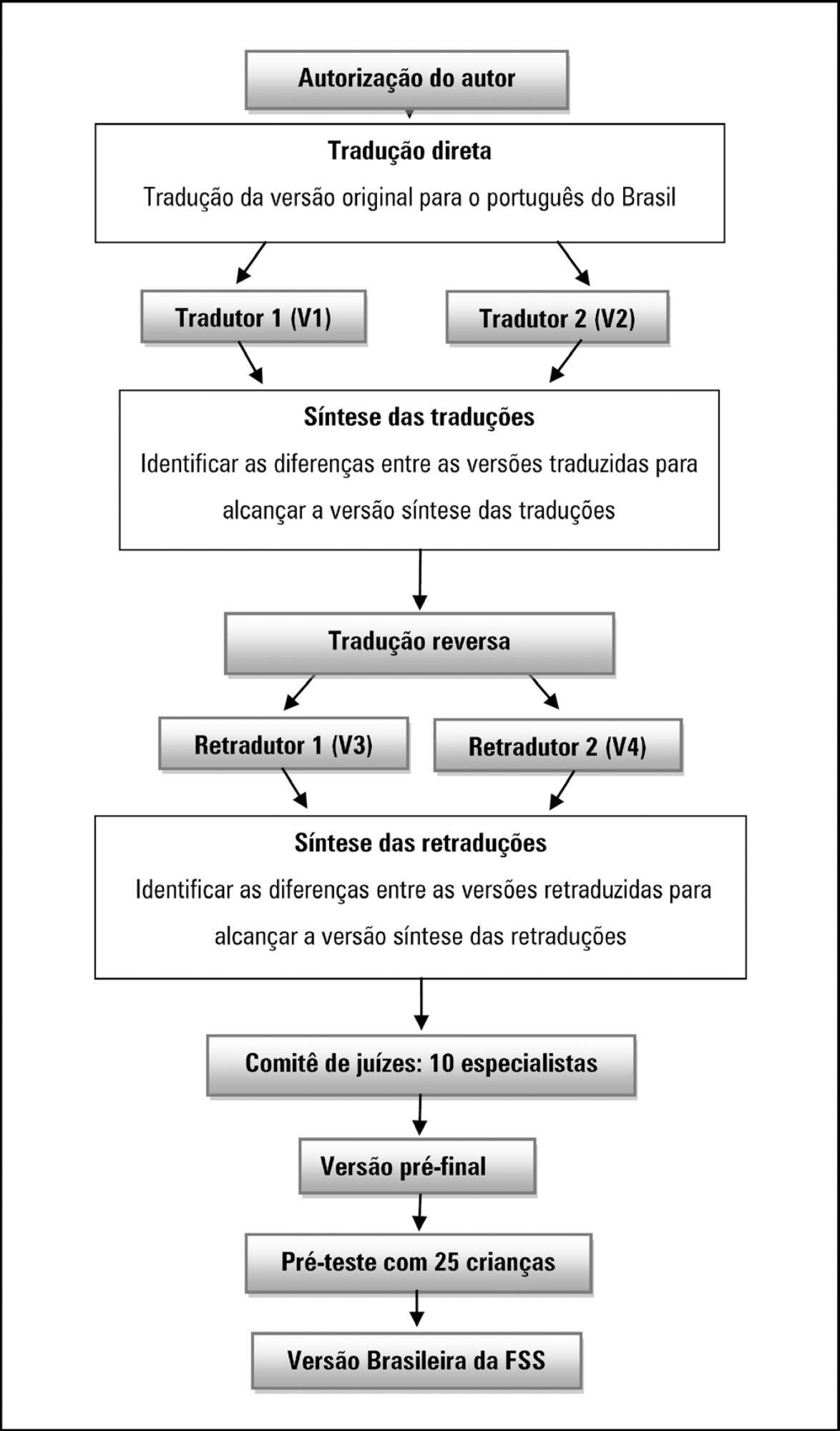
A methodological study of the translation and cross-cultural adaptation of the Functional Status Scale was conducted, according to the stages of translation, synthesis of translations, back-translation, synthesis of back-translations, expert committee analysis and pre-test with a sample of the target population. During the evaluation by the committee of experts, semantic, content and item analyses were performed.
The semantic, idiomatic, cultural and conceptual equivalences between the translated version and the original version were obtained, resulting in the Brazilian version of the Functional Status Scale. After the analysis by the expert committee, there were no problems regarding the cultural or conceptual equivalences because the items were pertinent to the Brazilian culture and few terms were modified. In the pre-test stage, the scale was applied by two evaluators to a sample of 25 children. Clarity and ease in answering the scale items were observed. Good inter-observer reliability was obtained, with an intraclass correlation coefficient of 0.85 (0.59 - 0.95).
The Functional Status Scale for pediatric use was translated and culturally adapted into Portuguese spoken in Brazil. The translated items were pertinent to the Brazilian culture and evaluated the dimensions proposed by the original instrument. Validation studies of this instrument are suggested to make it feasible for use in different regions of Brazil.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2018;30(2):195-200
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20180033
This study sought to translate the Cornell Assessment of Pediatric Delirium from English into Brazilian Portuguese and cross-culturally adapt it for use in Brazil.
Following the authorization granted by its main author, the processes of translation and cross-cultural adaptation were performed with regard to the Cornell Assessment of Pediatric Delirium in accordance with the following internationally recommended steps: translation of the original into Portuguese by two native speakers of the target language; synthesis of the translated versions; back-translation by two native speakers of the original language; review and harmonization of the back-translation; a review of the Portuguese version of the Cornell Assessment of Pediatric Delirium by an expert panel composed of specialists; pretesting including assessments of clarity, comprehensibility, and acceptability of the translated version using a sample of the target population; and finishing modifications to achieve the final version.
The translation and cross-cultural adaptation of the Cornell Assessment of Pediatric Delirium followed international recommendations. The linguistic and semantic issues that emerged during the process were discussed by the expert panel, which unanimously agreed to slight modifications. During pretesting, the Cornell Assessment of Pediatric Delirium was administered to 30 eligible children, twice per day; the final version was easy to understand, could be completed quickly, and showed a high inter-rater correlation coefficient (0.955).
The translation of the Cornell Assessment of Pediatric Delirium into Brazilian Portuguese and its cross-cultural adaptation were successful and preserved the linguistic and semantic properties of the original instrument. The Cornell Assessment of Pediatric Delirium proved to be easy to understand and could be completed quickly. Additional studies are needed to test the validity and psychometric properties of this version in Brazil.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2018;30(3):264-285
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20180058
To investigate the existing capacity for renal replacement therapy and site-specific practices for managing acute kidney injury at centers participating in the BaSICS trial.
A questionnaire was provided to the chairs of 61 intensive care units enrolled in a randomized clinical trial in Brazil. A total of 124 physicians completed the questionnaire.
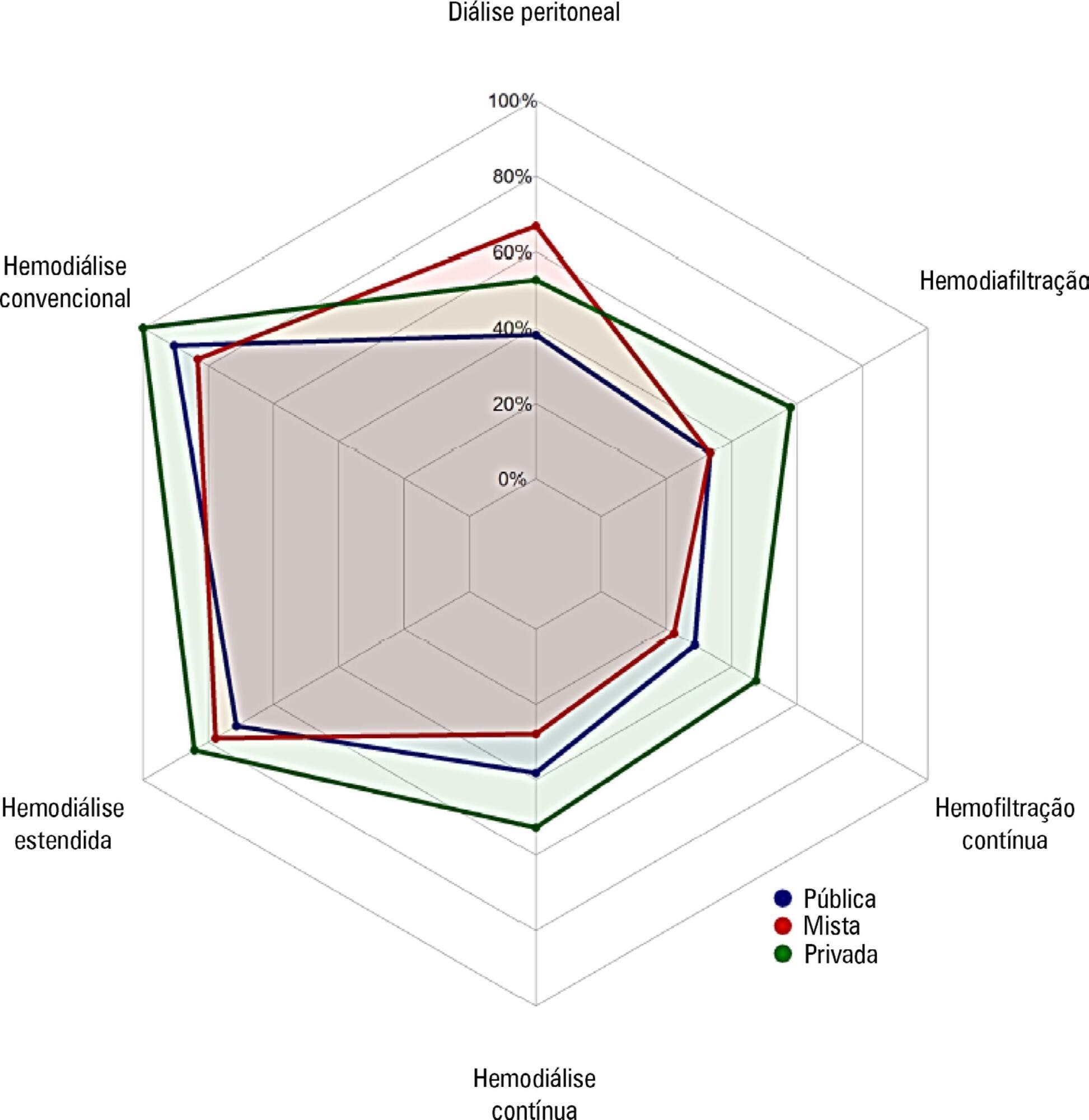
Approximately 15% of the patients admitted to the analyzed intensive care units received renal replacement therapy at the time of data collection. At least one renal replacement method was available in all of the analyzed units. Continuous methods were available more frequently at the private units than at the public units. The time from indication to onset of treatment was longer at the public units than at private units. The main obstacles to treatment initiation at public intensive care units were related to the availability of equipment and personnel, while the main bottleneck at private units was the nephrologist assessment. A considerable proportion of the participants stated that they would change their approach to renal replacement therapy if there were no limitations on the availability of methods in their units.
There was wide variation in the availability of resources for renal replacement therapy and in the management of acute kidney injury in Brazilian intensive care units. This information should be taken into account when planning clinical trials focused on this topic in Brazil.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2017;29(1):34-38
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20170006
The aim of the present study was to translate and cross-culturally adapt the Functional Status Score for the intensive care unit (FSS-ICU) into Brazilian Portuguese.
This study consisted of the following steps: translation (performed by two independent translators), synthesis of the initial translation, back-translation (by two independent translators who were unaware of the original FSS-ICU), and testing to evaluate the target audience's understanding. An Expert Committee supervised all steps and was responsible for the modifications made throughout the process and the final translated version.
The testing phase included two experienced physiotherapists who assessed a total of 30 critical care patients (mean FSS-ICU score = 25 ± 6). As the physiotherapists did not report any uncertainties or problems with interpretation affecting their performance, no additional adjustments were made to the Brazilian Portuguese version after the testing phase. Good interobserver reliability between the two assessors was obtained for each of the 5 FSS-ICU tasks and for the total FSS-ICU score (intraclass correlation coefficients ranged from 0.88 to 0.91).
The adapted version of the FSS-ICU in Brazilian Portuguese was easy to understand and apply in an intensive care unit environment.