Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2022;34(2):220-226
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20220019-en
To compare the predictive performance of residents, senior intensive care unit physicians and surrogates early during intensive care unit stays and to evaluate whether different presentations of prognostic data (probability of survival versus probability of death) influenced their performance.
We questioned surrogates and physicians in charge of critically ill patients during the first 48 hours of intensive care unit admission on the patient’s probability of hospital outcome. The question framing (i.e., probability of survival versus probability of death during hospitalization) was randomized. To evaluate the predictive performance, we compared the areas under the ROC curves (AUCs) for hospital outcome between surrogates and physicians’ categories. We also stratified the results according to randomized question framing.
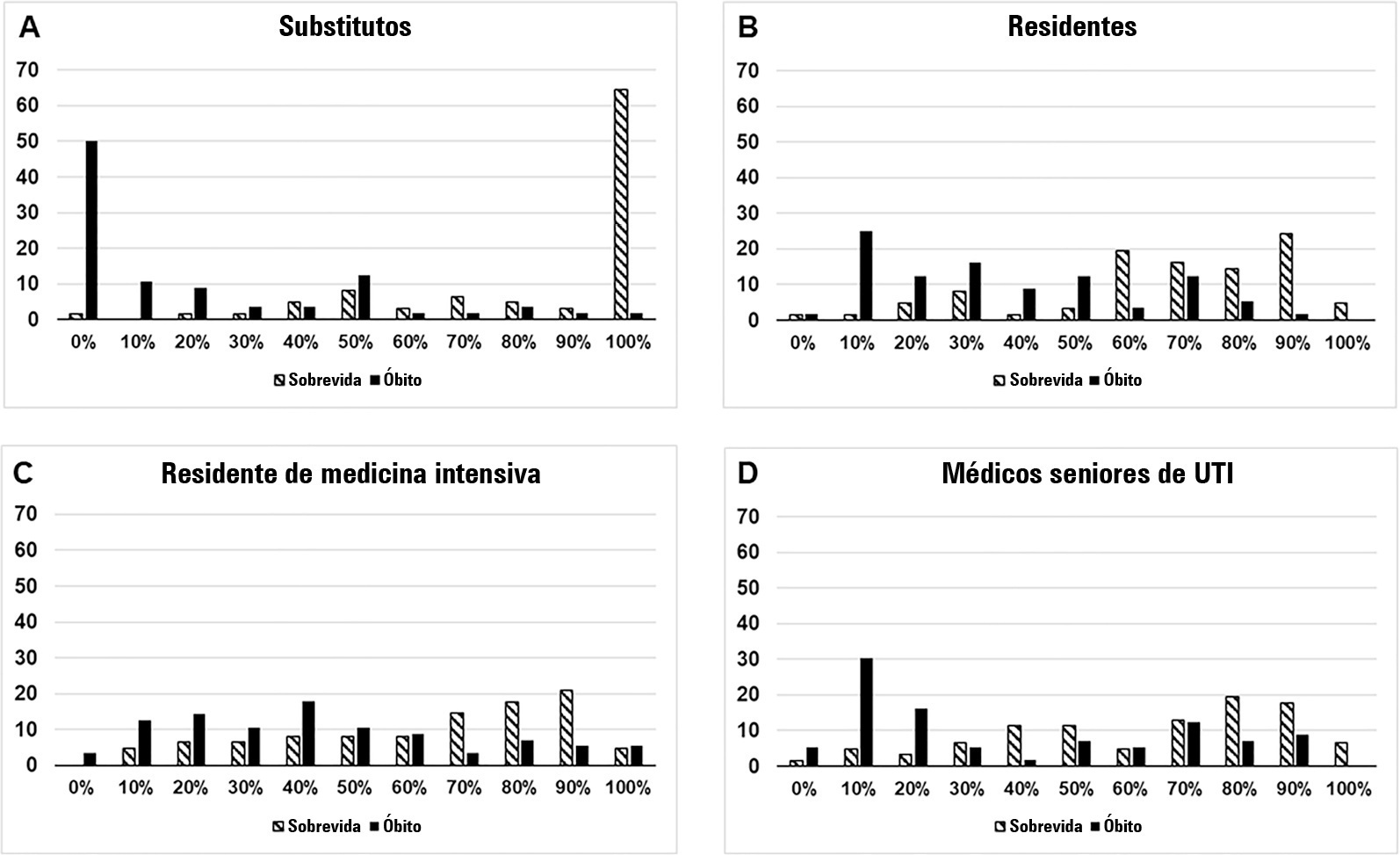
We interviewed surrogates and physicians on the hospital outcomes of 118 patients. The predictive performance of surrogate decisionmakers was significantly lower than that of physicians (AUC of 0.63 for surrogates, 0.82 for residents, 0.80 for intensive care unit fellows and 0.81 for intensive care unit senior physicians). There was no increase in predictive performance related to physicians’ experience (i.e., senior physicians did not predict outcomes better than junior physicians). Surrogate decisionmakers worsened their prediction performance when they were asked about probability of death instead of probability of survival, but there was no difference for physicians.
Different predictive performance was observed when comparing surrogate decision-makers and physicians, with no effect of experience on health care professionals’ prediction. Question framing affected the predictive performance of surrogates but not of physicians.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2022;34(2):262-271
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20220024-en
To assess euthyroid sick syndrome as a prognostic factor in patients in the intensive care unit; to detect factors that may affect mortality; and to develop an equation to calculate death probability.
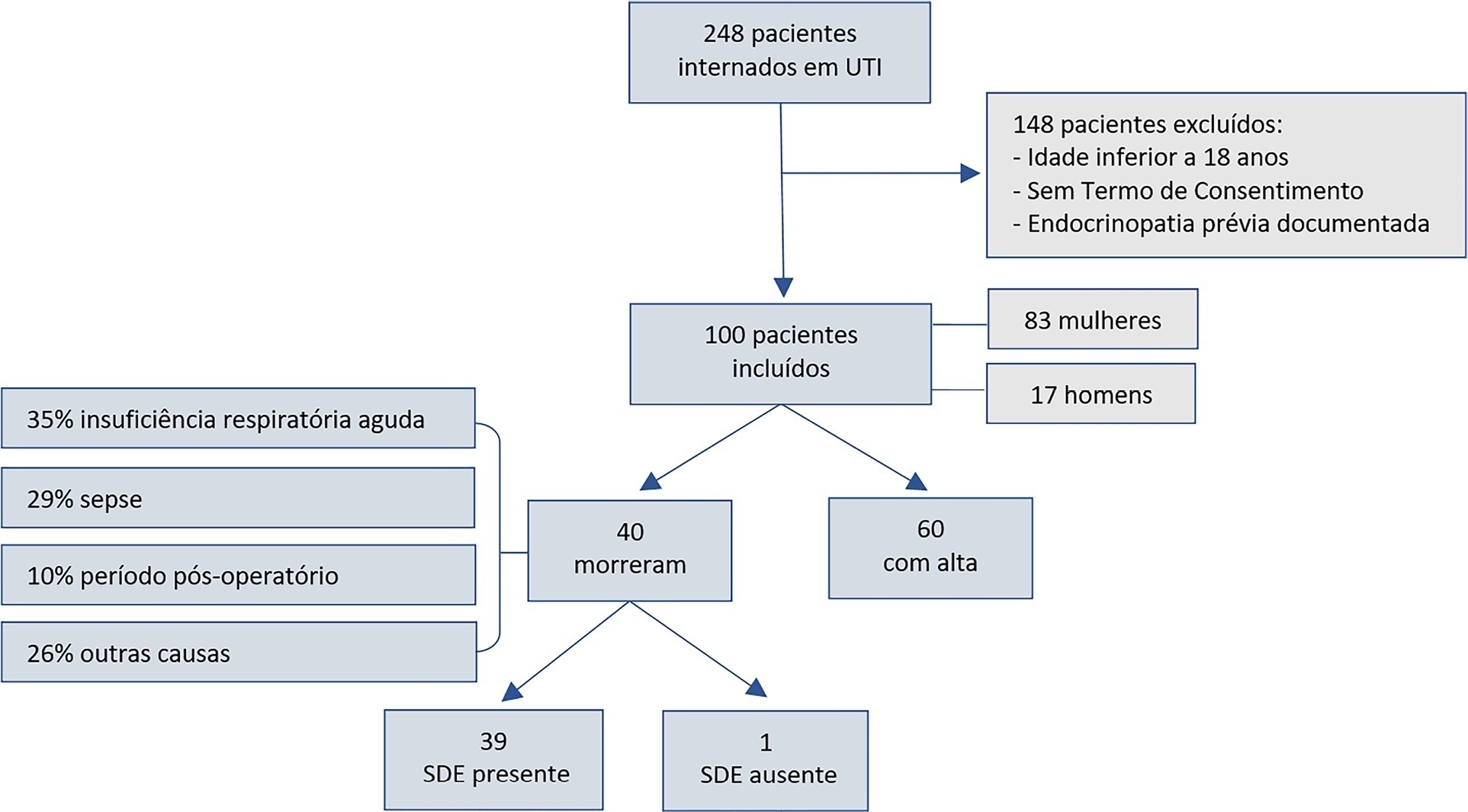
This was a longitudinal, observational, nonconcurrent cohort study developed in the intensive care unit of Fundação Santa Casa de Misericórdia do Pará. One hundred adults with no prior documented endocrinopathy were submitted to a 20mL blood sample collection for the measurement of thyroid stimulating hormone, free tetraiodothyronine, free triiodothyronine and reverse triiodothyronine.
Most patients were female, aged 20 to 29 years. Most patients who died were older (median age of 48 years), and euthyroid sick syndrome was present in 97.5% of them. Euthyroid sick syndrome was related to death, comorbidities, age and length of stay in the intensive care unit (median of 7.5 days).
The main limitation of this study is the fact that it was conducted in a reference hospital for maternal and child care; therefore, there was a greater number of female patients and, consequently, a sampling bias existed. However, opportune measurement of free and reverse triiodothyronine levels in critical patients and application of the proposed equation are suggested.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2022;34(1):124-130
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20220006-en
The current study assessed the prevalence of troponin elevation and its capacity to predict 60day mortality in COVID-19 patients in intensive care.
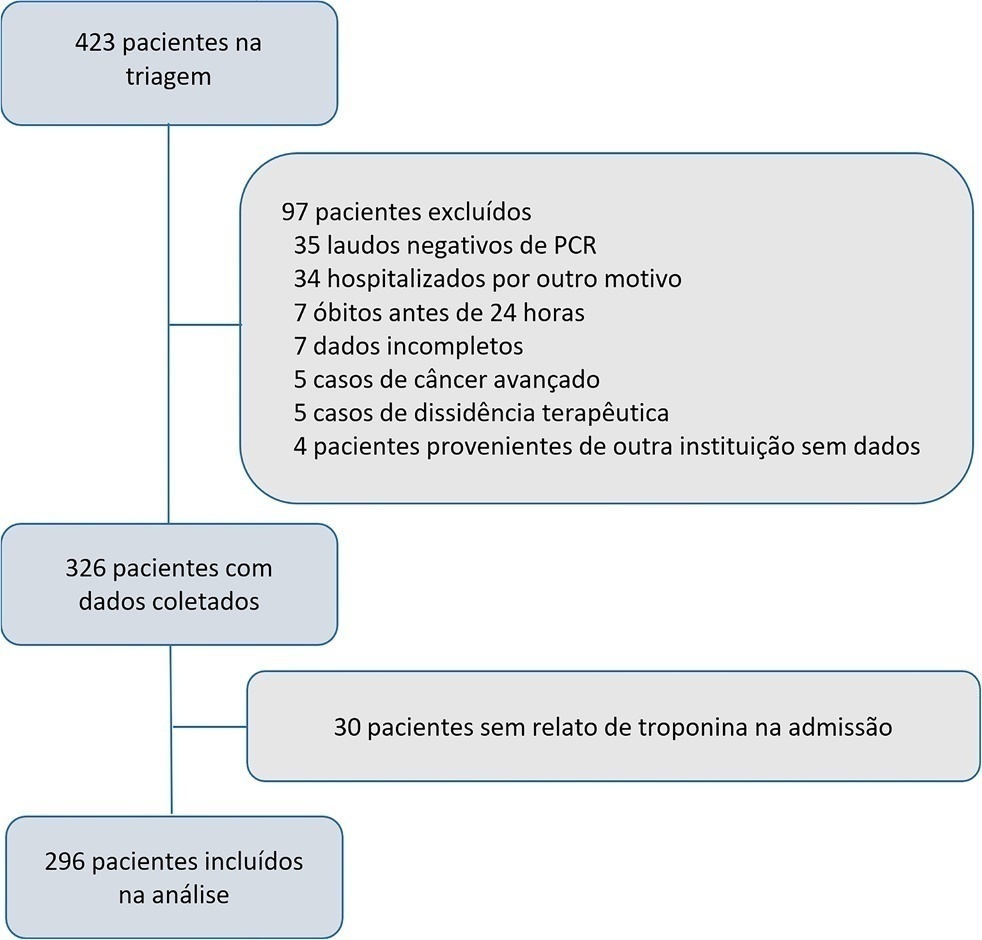
A longitudinal prospective single-center study was performed on a cohort of patients in intensive care due to a COVID-19 diagnosis confirmed using real-time test polymerase chain reaction from May to December 2020. A Receiver Operating Characteristic curve was constructed to predict death according to troponin level by calculating the area under the curve and its confidence intervals. A Cox proportional hazards model was generated to report the hazard ratios with confidence intervals of 95% and the p value for its association with 60day mortality.
A total of 296 patients were included with a 51% 60-day mortality rate. Troponin was positive in 39.9% (29.6% versus 49.7% in survivors and non-survivors, respectively). An area under the curve of 0.65 was found (95%CI: 0.59 - 0.71) to predict mortality. The Cox univariate model demonstrated a hazard ratio of 1.94 (95%CI: 1.41 - 2.67) and p < 0.001, but this relationship did not remain in the multivariate model, in which the hazard ratio was 1.387 (95%CI: 0.21 - 1.56) and the p value was 0.12.
Troponin elevation is frequently found in patients in intensive care for COVID-19. Although its levels are higher in patients who die, no relationship was found in a multivariate model, which indicates that troponin should not be used as an only prognostic marker for mortality in this population.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(4):549-556
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20210083
To analyze the correlation between glycocalyx disruption measured via the serum syndecan-1 level and organ dysfunctions assessed by the PELOD-2 score and to evaluate its association with mortality in pediatric sepsis.
We performed a prospective observational study in a tertiary public hospital. Sixty-eight pediatric patients diagnosed with sepsis according to International Pediatric Sepsis Consensus Conference criteria were consecutively recruited. We performed measurements of day 1 and day 5 serum syndecan-1 levels and PELOD-2 score components. Patients were followed up to 28 days following sepsis diagnosis.
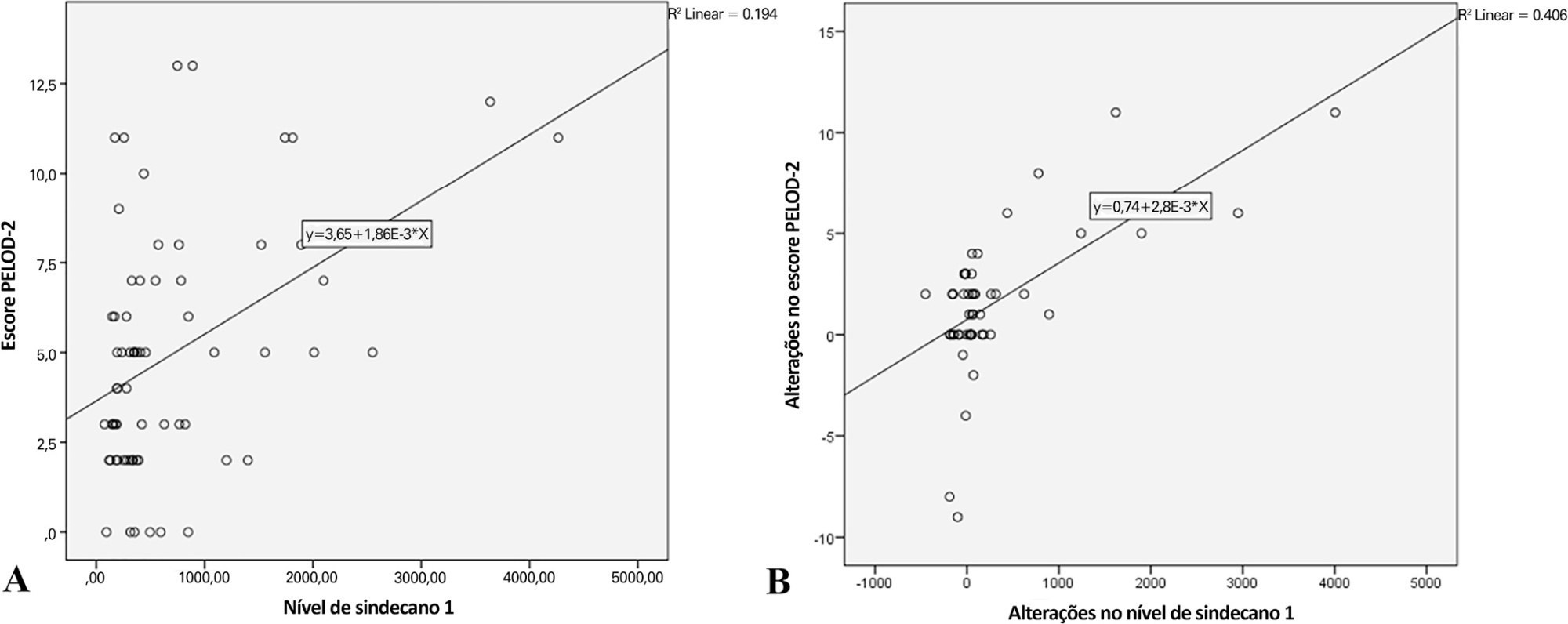
Overall, the syndecan-1 level was increased in all subjects, with a significantly higher level among septic shock patients (p = 0.01). The day 1 syndecan-1 level was positively correlated with the day 1 PELOD-2 score with a correlation coefficient of 0.35 (p = 0.003). Changes in syndecan-1 were positively correlated with changes in the PELOD-2 score, with a correlation coefficient of 0.499 (p < 0.001) during the first five days. Using the cutoff point of day 1 syndecan-1 ≥ 430ng/mL, organ dysfunction (PELOD-2 score of ≥ 8) could be predicted with an AUC of 74.3%, sensitivity of 78.6%, and specificity of 68.5% (p = 0.001).
The day 1 syndecan-1 level was correlated with the day 1 PELOD-2 score but not 28-day mortality. Organ dysfunction (PELOD-2 ≥ 8) could be predicted by the syndecan-1 level in the first 24 hours of sepsis, suggesting its significant pathophysiological involvement in sepsis-associated organ dysfunction.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(3):394-400
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20210064
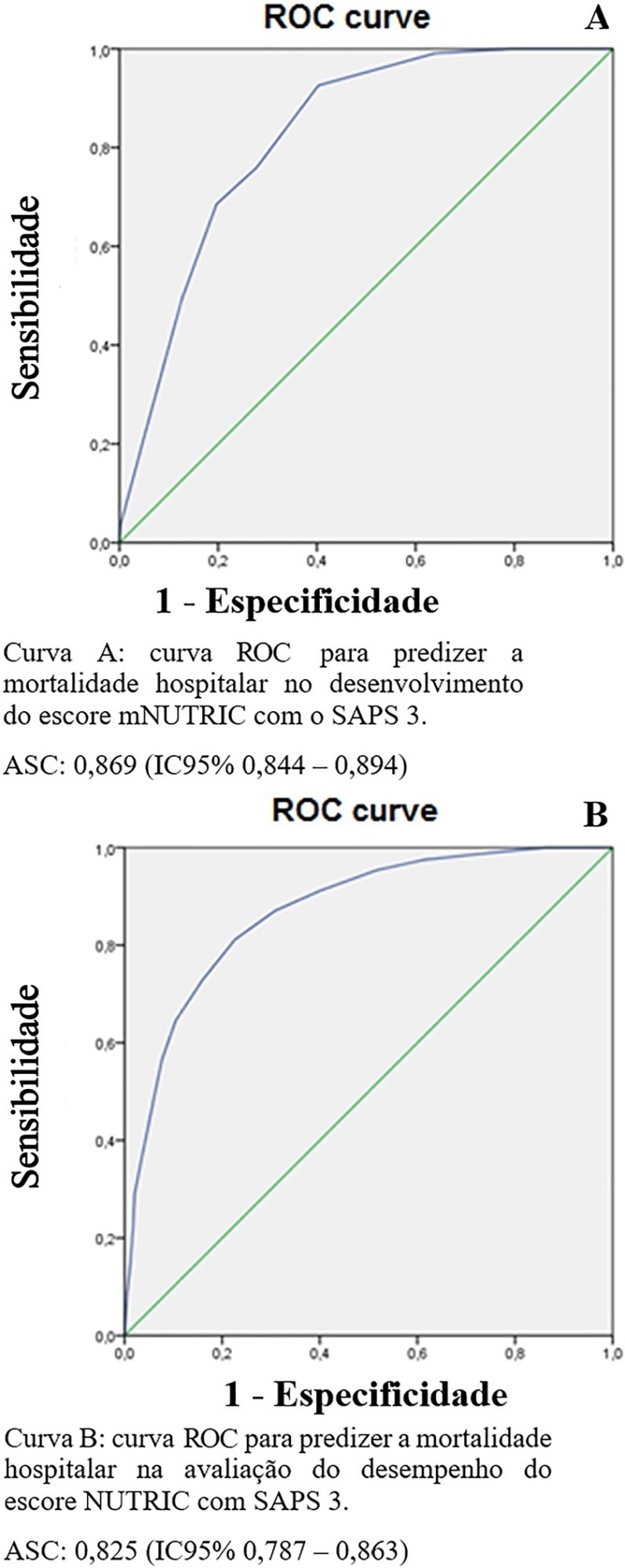
To evaluate the substitution of Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II (APACHE II) by Simplified Acute Physiology Score 3 (SAPS 3) as a severity marker in the modified version of the NUTrition RIsk in the Critically ill score (mNUTRIC); without interleukin 6) based on an analysis of its discriminative ability for in-hospital mortality prediction.
This retrospective cohort study evaluated 1,516 adult patients admitted to an intensive care unit of a private general hospital from April 2017 to January 2018. Performance evaluation included Fleiss’ Kappa and Pearson correlation analysis. The discriminative ability for estimating in-hospital mortality was assessed with the Receiver Operating Characteristic curve.
The sample was randomly divided into two-thirds for model development (n = 1,025; age 72 [57 - 83]; 52.4% male) and one-third for performance evaluation (n = 490; age 72 [57 - 83]; 50.8% male). The agreement with mNUTRIC was Kappa of 0.563 (p < 0.001), and the correlation between the instruments was Pearson correlation of 0.804 (p < 0.001). The tool showed good performance in predicting in-hospital mortality (area under the curve 0.825 [0.787 - 0.863] p < 0.001).
The substitution of APACHE II by SAPS 3 as a severity marker in the mNUTRIC score showed good performance in predicting in-hospital mortality. These data provide the first evidence regarding the validity of the substitution of APACHE II by SAPS 3 in the mNUTRIC as a marker of severity. Multicentric studies and additional analyses of nutritional adequacy parameters are required.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(2):231-242
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20210030
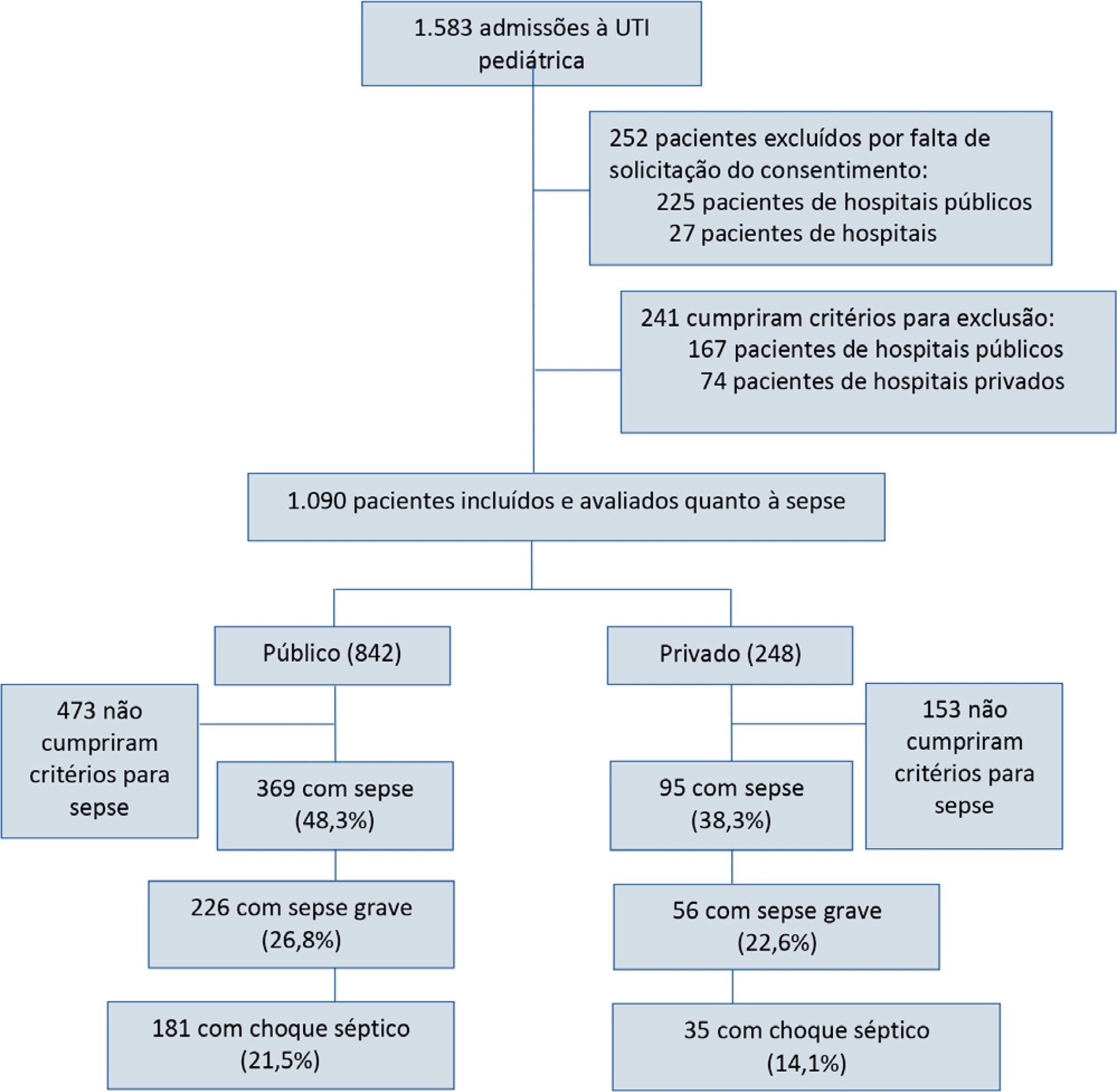
To report the prevalence and outcomes of sepsis in children admitted to public and private hospitals.
Post hoc analysis of the Latin American Pediatric Sepsis Study (LAPSES) data, a cohort study that analyzed the prevalence and outcomes of sepsis in critically ill children with sepsis on admission at 21 pediatric intensive care units in five Latin American countries.
Of the 464 sepsis patients, 369 (79.5%) were admitted to public hospitals and 95 (20.5%) to private hospitals. Compared to those admitted to private hospitals, sepsis patients admitted to public hospitals did not differ in age, sex, immunization status, hospital length of stay or type of admission but had higher rates of septic shock, higher Pediatric Risk of Mortality (PRISM), Pediatric Index of Mortality 2 (PIM 2), and Pediatric Logistic Organ Dysfunction (PELOD) scores, and higher rates of underlying diseases and maternal illiteracy. The proportion of patients admitted from pediatric wards and sepsis-related mortality were higher in public hospitals. Multivariate analysis did not show any correlation between mortality and the type of hospital, but mortality was associated with greater severity on pediatric intensive care unit admission in patients from public hospitals.
In this sample of critically ill children from five countries in Latin America, the prevalence of septic shock within the first 24 hours at admission and sepsis-related mortality were higher in public hospitals than in private hospitals. Higher sepsis-related mortality in children admitted to public pediatric intensive care units was associated with greater severity on pediatric intensive care unit admission but not with the type of hospital. New studies will be necessary to elucidate the causes of the higher prevalence and mortality of pediatric sepsis in public hospitals.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(2):261-265
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20210033
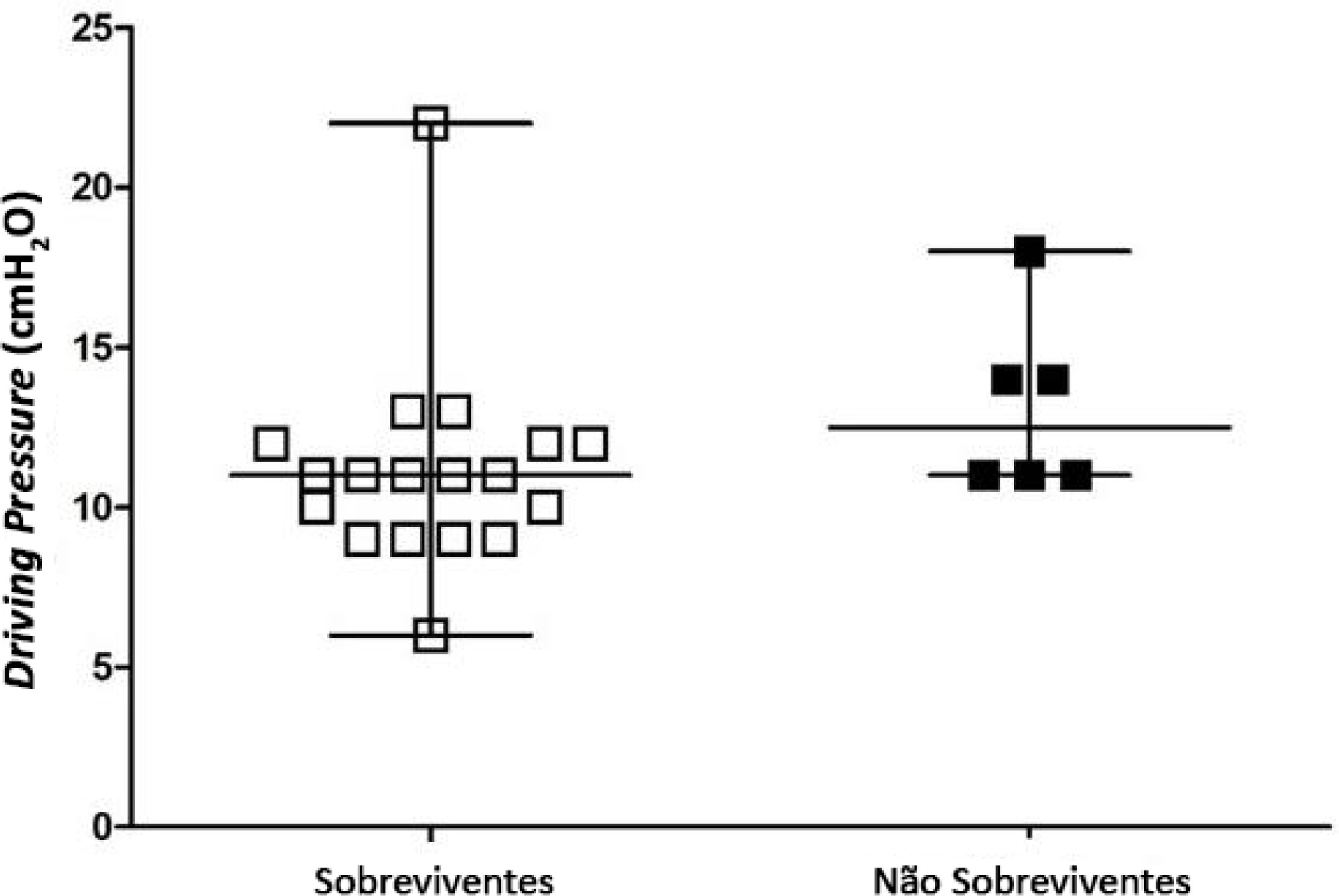
To identify the possible association between driving pressure and mechanical power values and oxygenation index on the first day of mechanical ventilation with the mortality of trauma patients without a diagnosis of acute respiratory distress syndrome.
Patients under pressure-controlled or volume-controlled ventilation were included, with data collection 24 hours after orotracheal intubation. Patient follow-up was performed for 30 days to obtain the clinical outcome. The patients were admitted to two intensive care units of the Hospital de Pronto Socorro de Porto Alegre from June to September 2019.
A total of 24 patients were evaluated. Driving pressure, mechanical power and oxygenation index were similar among patients who survived and those who died, with no statistically significant difference between groups.
Driving pressure, mechanical power and oxygenation index values obtained on the first day of mechanical ventilation were not associated with mortality of trauma patients without acute respiratory distress syndrome.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (116) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)