Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(4):549-556
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20210083
To analyze the correlation between glycocalyx disruption measured via the serum syndecan-1 level and organ dysfunctions assessed by the PELOD-2 score and to evaluate its association with mortality in pediatric sepsis.
We performed a prospective observational study in a tertiary public hospital. Sixty-eight pediatric patients diagnosed with sepsis according to International Pediatric Sepsis Consensus Conference criteria were consecutively recruited. We performed measurements of day 1 and day 5 serum syndecan-1 levels and PELOD-2 score components. Patients were followed up to 28 days following sepsis diagnosis.
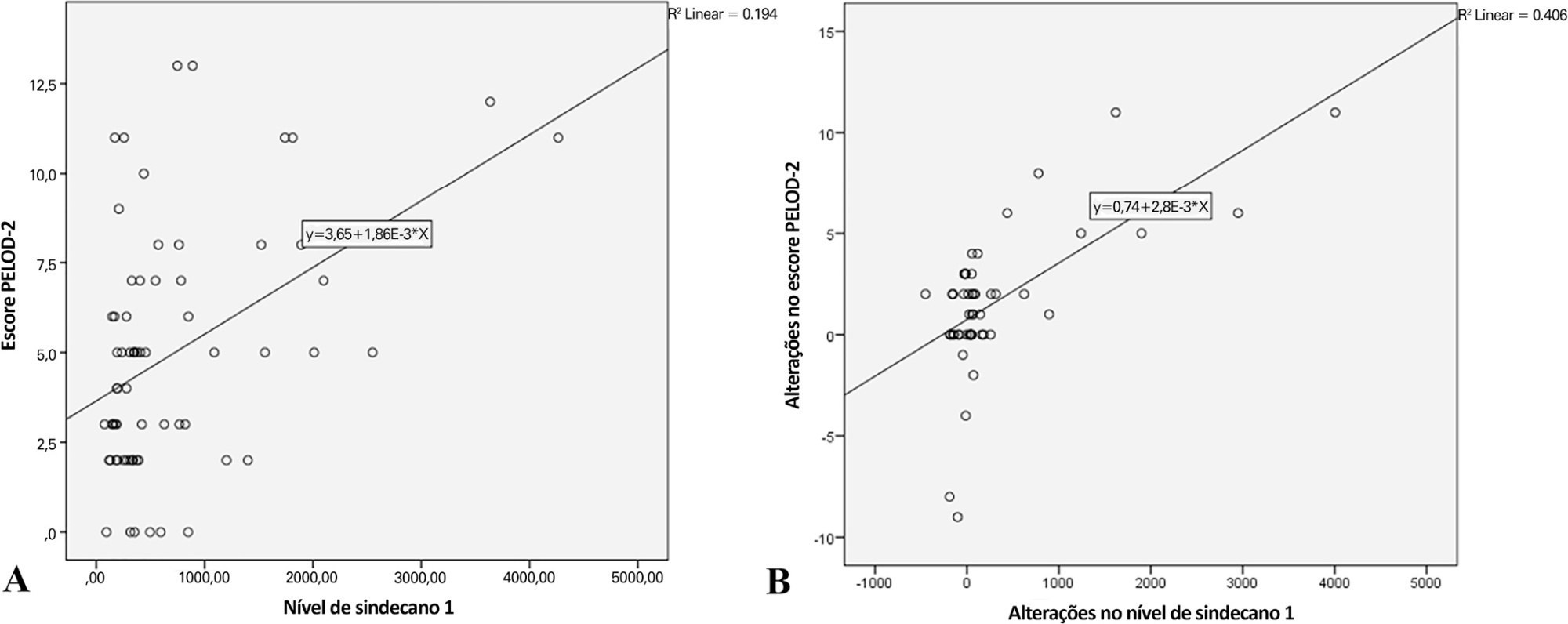
Overall, the syndecan-1 level was increased in all subjects, with a significantly higher level among septic shock patients (p = 0.01). The day 1 syndecan-1 level was positively correlated with the day 1 PELOD-2 score with a correlation coefficient of 0.35 (p = 0.003). Changes in syndecan-1 were positively correlated with changes in the PELOD-2 score, with a correlation coefficient of 0.499 (p < 0.001) during the first five days. Using the cutoff point of day 1 syndecan-1 ≥ 430ng/mL, organ dysfunction (PELOD-2 score of ≥ 8) could be predicted with an AUC of 74.3%, sensitivity of 78.6%, and specificity of 68.5% (p = 0.001).
The day 1 syndecan-1 level was correlated with the day 1 PELOD-2 score but not 28-day mortality. Organ dysfunction (PELOD-2 ≥ 8) could be predicted by the syndecan-1 level in the first 24 hours of sepsis, suggesting its significant pathophysiological involvement in sepsis-associated organ dysfunction.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2018;30(1):64-70
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20180012
To describe a cohort of patients with acute liver failure and to analyze the demographic and clinical factors associated with mortality.
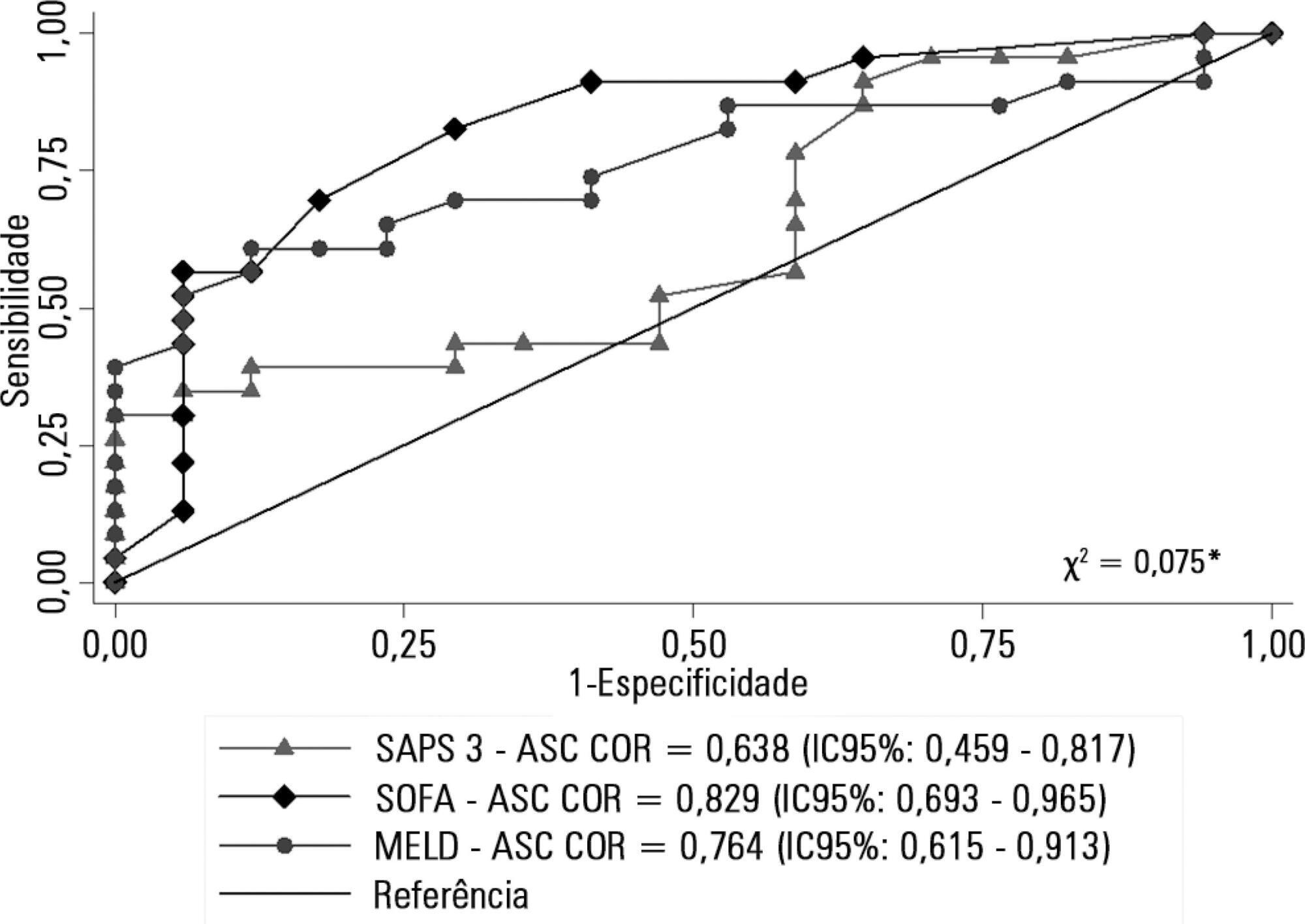
Retrospective cohort study in which all patients admitted for acute liver failure from July 28, 2012, to August 31, 2017, were included. Clinical and demographic data were collected using the Epimed System. The SAPS 3, SOFA, and MELD scores were measured. The odds ratios and 95% confidence intervals were estimated. Receiver operating characteristics curves were obtained for the prognostic scores, along with the Kaplan-Meier survival curve for the score best predicting mortality.
The majority of the 40 patients were female (77.5%), and the most frequent etiology was hepatitis B (n = 13). Only 35% of the patients underwent liver transplantation. The in-hospital mortality rate was 57.5% (95%CI: 41.5 - 73.5). Among the scores investigated, only SOFA remained associated with risk of death (OR = 1.37; 95%CI 1.11 - 1.69; p < 0.001). After SOFA stratification into < 12 and ≥ 12 points, survival was higher in patients with SOFA <12 (log-rank p < 0.001).
SOFA score in the first 24 hours was the best predictor of fatal outcome.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (116) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)