Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(2):276-281
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20210035
To evaluate serum uteroglobin-related protein 1 expression early after smoke inhalation injuries and its association with the severity of inhalation injury in burned patients.
Smoke or chemical inhalation injury is associated with morbidity and mortality. The consequences of inhalation result from an inflammatory response. Uteroglobin-related protein 1 is an anti-inflammatory protein and may improve lung inflammation. We hypothesized that uteroglobin-related protein 1 levels could reflect disease severity and predict outcome in patients with inhalation injury. Sixteen patients diagnosed with acute respiratory distress syndrome secondary to smoke inhalation injury were prospectively included in the study. Plasma was collected upon intensive care unit admission and within 24 hours of the inhalation injury. Bronchoscopies were carried out in all patients to assess the severity of inhalation injury within 72 hours. Uteroglobin-related protein 1 plasma levels were determined in duplicate with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
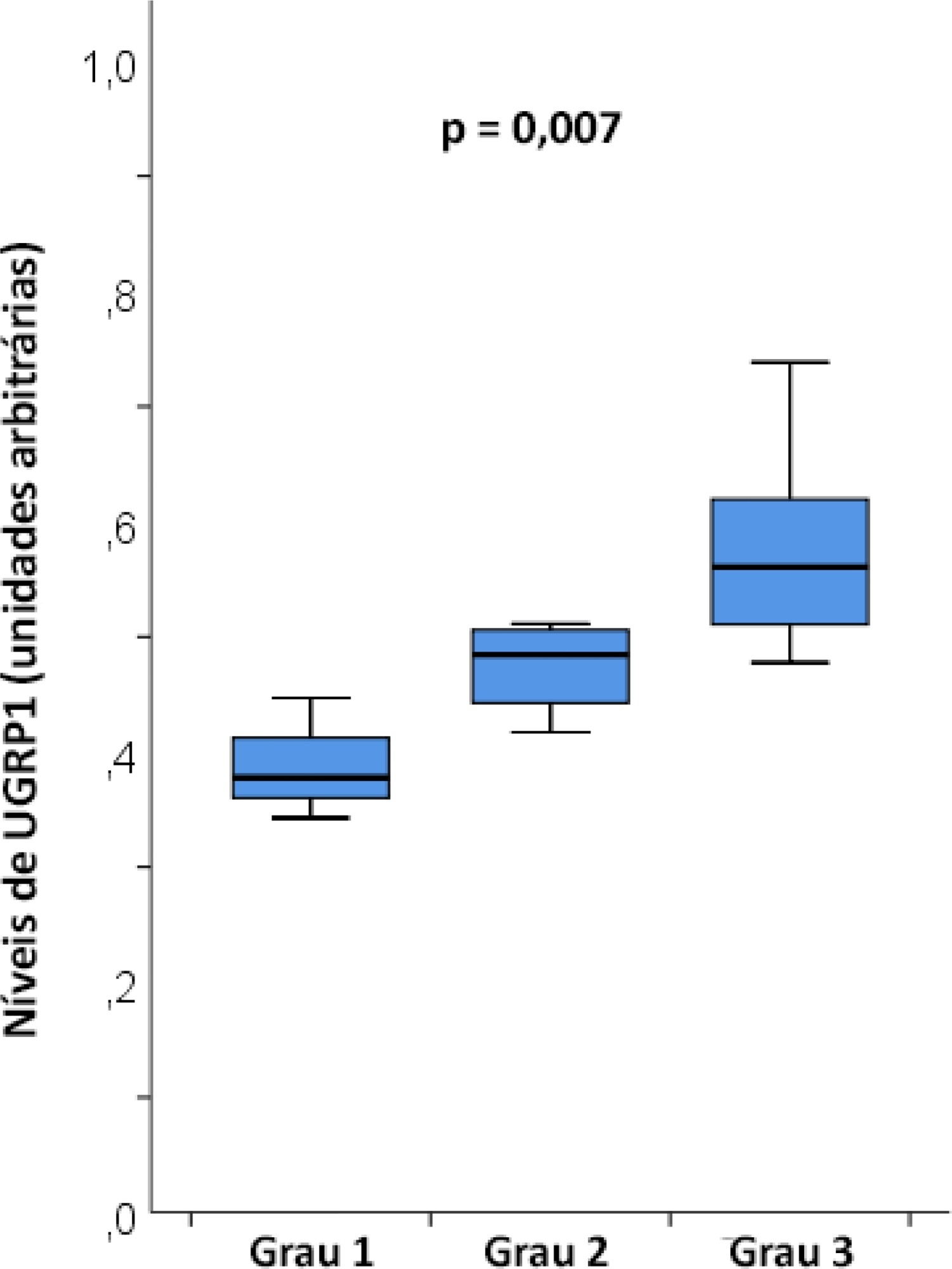
The mean age was 23 ± 5 years, and the inhalation injury distribution was as follows: three of grade 1, four of grade 2, and nine of grade 3. The level of uteroglobin-related protein 1 was related to inhalation severity (grade 1: 0.389 ± 0.053 arbitrary units versus grade 2: 0.474 ± 0.0423 arbitrary units versus grade 3: 0.580 ± 0.094 arbitrary units; p = 0.007).
Plasma levels of uteroglobin-related protein 1 are associated with the degree of lung inhalation injury.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2020;32(4):542-550
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20200091
To assess whether preoperative versus intraoperative insertion of an intra-aortic balloon pump is associated with lower 30-day mortality or reduced length of hospital stay among patients who had an intra-aortic balloon pump inserted for cardiac surgery.
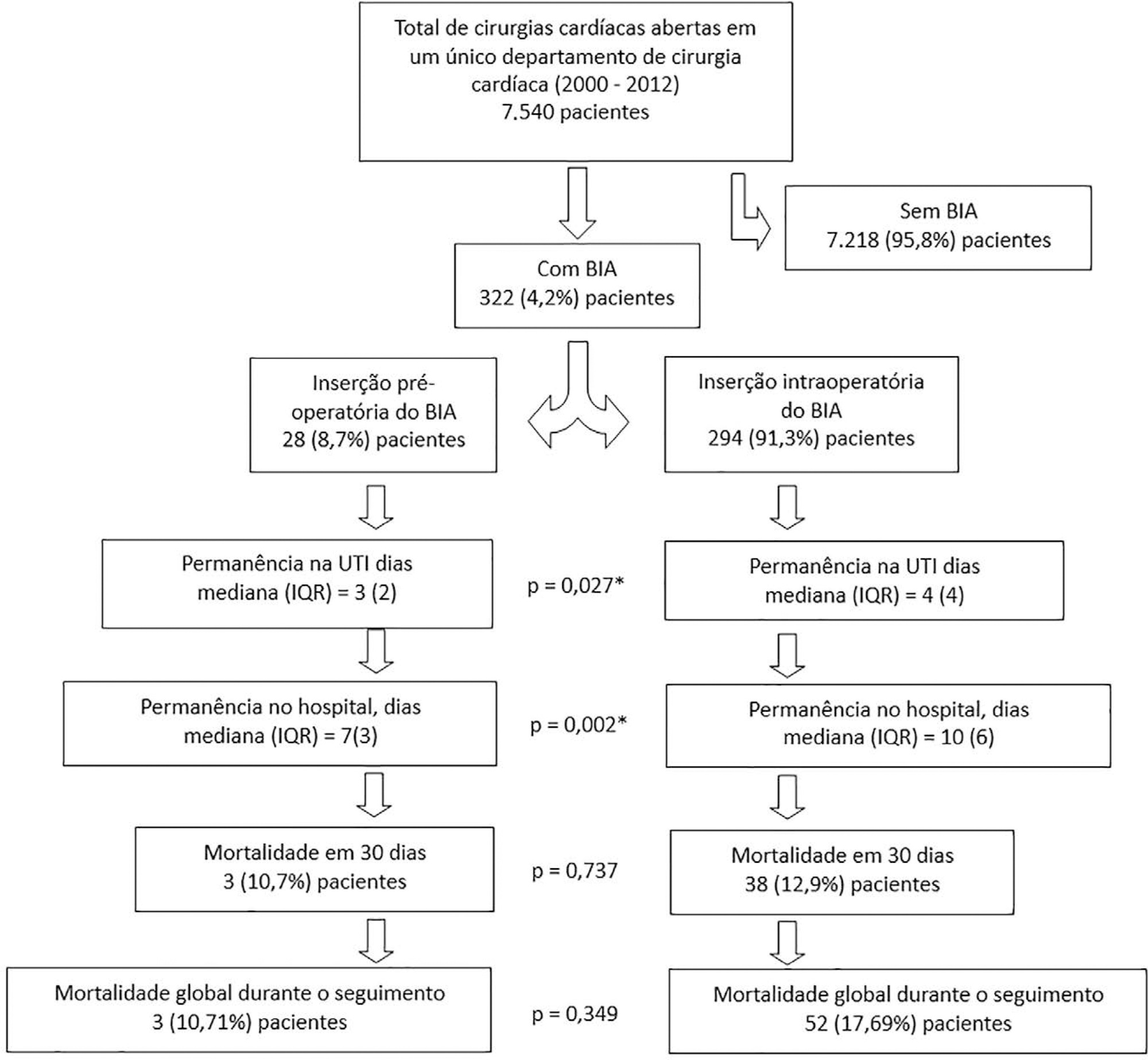
This was an observational study of patients who had an intra-aortic balloon pump inserted in the preoperative or intraoperative period of cardiac surgery in our department between 2000 and 2012. We assessed the association between preoperative versus intraoperative insertion of an intra-aortic balloon pump and 30-day mortality in a multivariable logistic regression analysis, including preoperative New York Heart Association class, postoperative atrial fibrillation, reoperation, postoperative creatinine and isolated coronary bypass grafting as cofactors. We used a multivariate linear model to assess whether a preoperative versus intraoperative intra-aortic balloon pump was associated with length of postoperative hospital stay, adjusting for reoperation, isolated coronary bypass grafting, heart valve surgery, sex, age, cardiopulmonary bypass time, aortic cross-clamp time, preoperative patients’ status (elective, urgency or emergency surgery) and preoperative myocardial infarction.
Overall, 7,540 consecutive patients underwent open heart surgery in our department, and an intra-aortic balloon pump was inserted pre- or intraoperatively in 322 (4.2%) patients. The mean age was 67 ± 10.2 years old, the 30-day mortality was 12.7%, and the median length of hospital stay was 9 days (7 - 13). Preoperative versus intraoperative intra-aortic balloon pump insertion did not affect the incidence of 30-day mortality (adjusted OR = 0.69; 95% CI, 0.15 - 3.12; p = 0.63) and length of postoperative hospital stay (β = 5.3; 95%CI, -1.6 to 12.8; p = 0.13).
Preoperative insertion of an intra-aortic balloon pump was not associated with a lower 30-day mortality or reduced length of postoperative hospital stay compared to intraoperative insertion.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2020;32(4):578-584
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20200096
To determine the concordance of mortality risk classification through the use of the Pediatric Index of Mortality (PIM) 2 and 3.
Through a retrospective cohort, we evaluated patients admitted to the pediatric intensive care unit between April 2016 and December 2018. We calculated the mortality risk with the PIM 2 and 3. Analyses were carried out to determine the concordance between the risk classification obtained with both scales using unweighted and linearly weighted kappa.
A total of 722 subjects were included, and 66.6% had a chronic condition. The overall mortality was 3.7%. The global kappa concordance coefficient for classifying patients according to risk with the PIM 2 and 3 was moderate at 0.48 (95%CI 0.43 - 0.53). After linear weighting, concordance was substantial at 0.64 (95%CI 0.59 - 0.69). For cardiac surgery patients, concordance for risk classification was fair at 0.30 (95%CI 0.21 - 0.39), and after linear weighting, concordance was only moderate at 0.49 (95%CI 0.39 - 0.59). The PIM 3 assigned a lower risk than the PIM 2 in 44.8% of patients in this subgroup.
Our study proves that the PIM 2 and 3 are not clinically equivalent and should not be used interchangeably for quality evaluation across pediatric intensive care units. Validation studies must be performed before using the PIM 2 or PIM 3 in specific settings.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2020;32(2):229-234
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20200041
To depict the clinical presentation and outcomes of a cohort of critically ill patients with esophageal cancer.
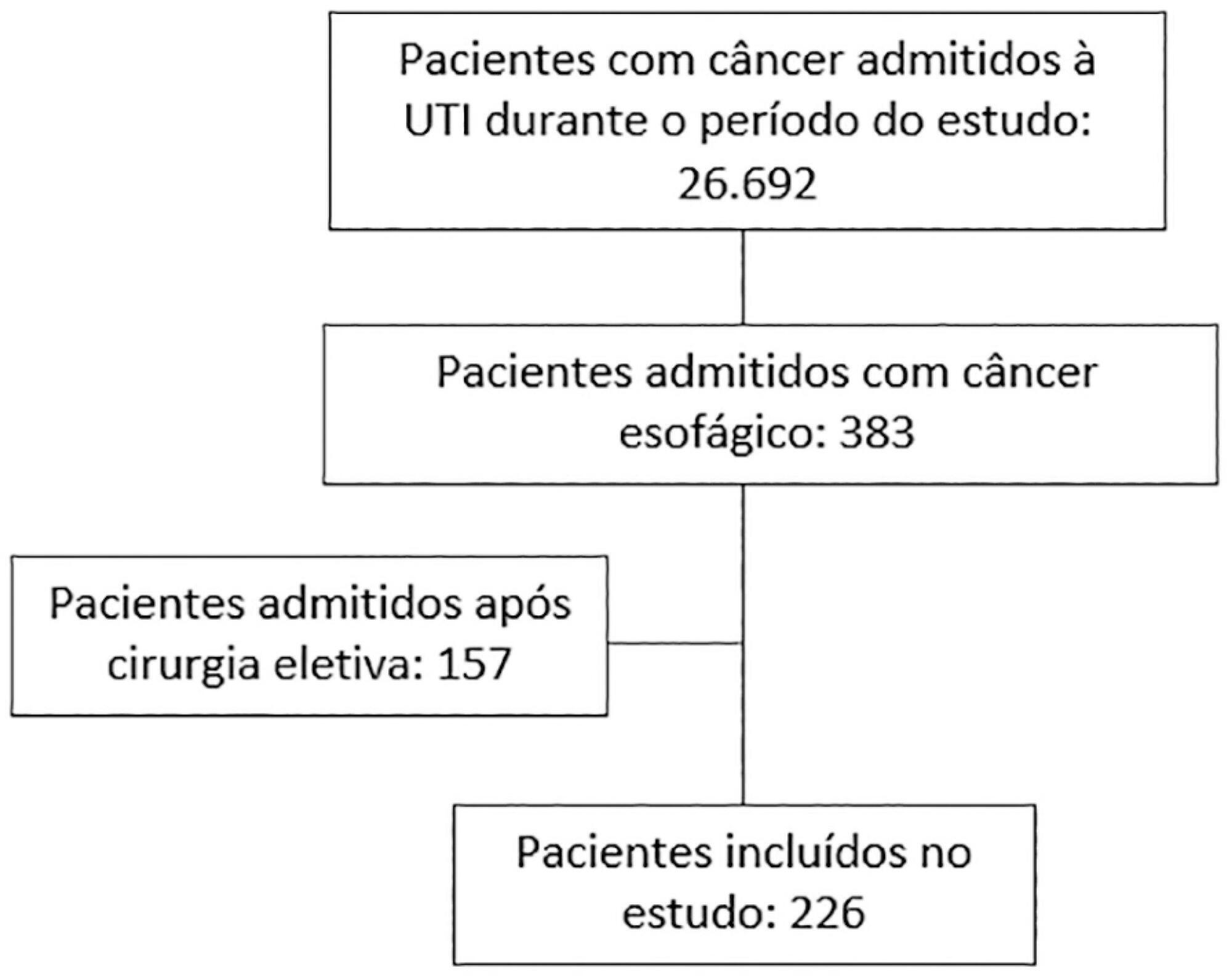
We carried out a multicenter retrospective study that included patients with esophageal cancer admitted to intensive care units with acute illness between September 2009 and December 2017. We collected the demographic and clinical characteristics of all included patients, as well as organ-support measures and hospital outcomes. We performed logistic regression analysis to identify independent factors associated with in-hospital mortality.
Of 226 patients included in the study, 131 (58.0%) patients died before hospital discharge. Squamous cell carcinoma was more frequent than adenocarcinoma, and 124 (54.9%) patients had metastatic cancer. The main reasons for admission were sepsis/septic shock and acute respiratory failure. Mechanical ventilation (OR = 6.18; 95%CI 2.86 - 13.35) and metastatic disease (OR = 7.10; 95%CI 3.35 - 15.05) were independently associated with in-hospital mortality.
In this cohort of patients with esophageal cancer admitted to intensive care units with acute illness, the in-hospital mortality rate was very high. The requirement for invasive mechanical ventilation and metastatic disease were independent prognostic factors and should be considered in discussions about the short-term outcomes of these patients.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2020;32(2):284-294
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20200045
To identify the relationship of patient-ventilator asynchrony with the level of sedation and hemogasometric and clinical results.
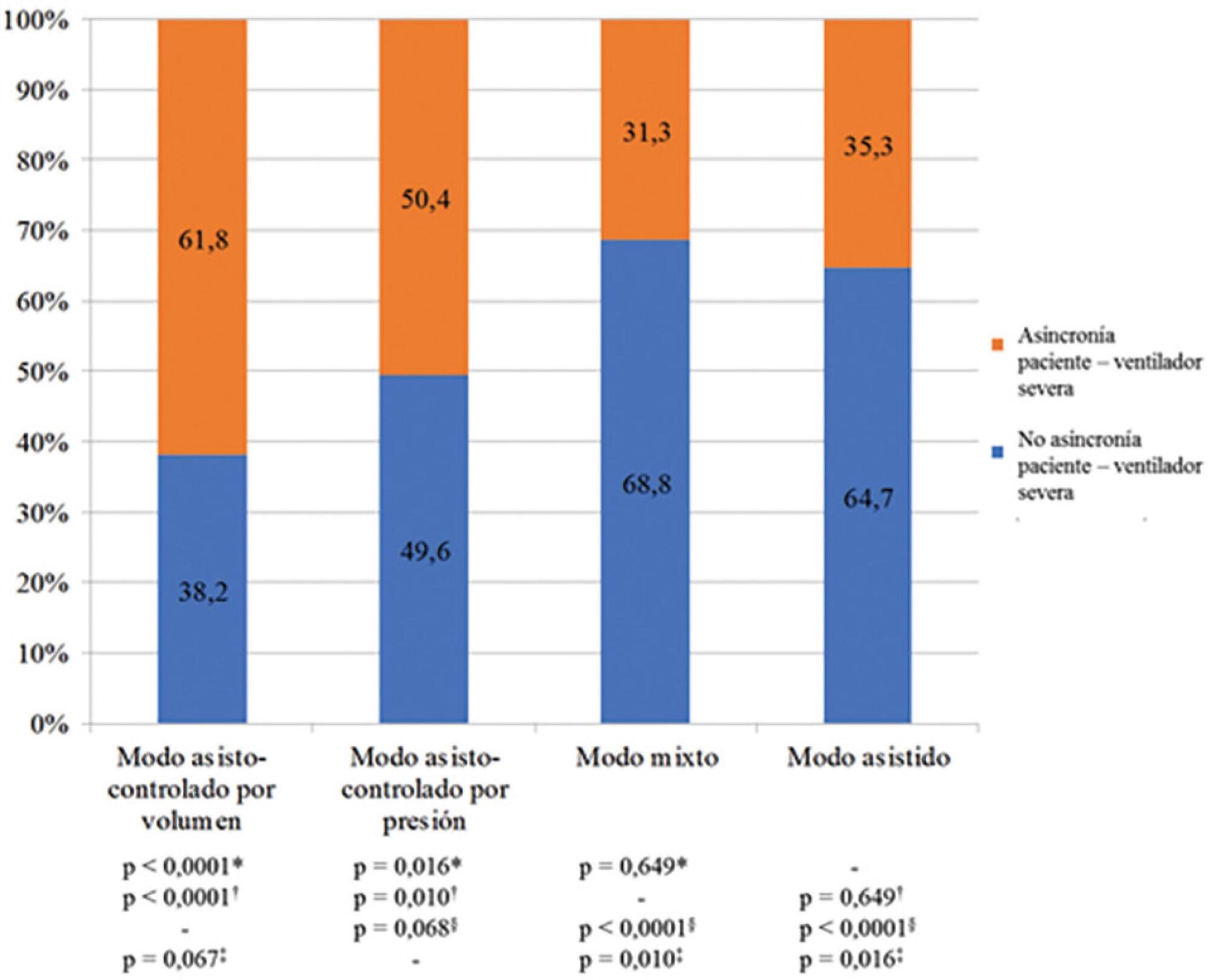
This was a prospective study of 122 patients admitted to the intensive care unit who underwent > 24 hours of invasive mechanical ventilation with inspiratory effort. In the first 7 days of ventilation, patient-ventilator asynchrony was evaluated daily for 30 minutes. Severe patient-ventilator asynchrony was defined as an asynchrony index > 10%.
A total of 339,652 respiratory cycles were evaluated in 504 observations. The mean asynchrony index was 37.8% (standard deviation 14.1 - 61.5%). The prevalence of severe patient-ventilator asynchrony was 46.6%. The most frequent patient-ventilator asynchronies were ineffective trigger (13.3%), autotrigger (15.3%), insufficient flow (13.5%), and delayed cycling (13.7%). Severe patient-ventilator asynchrony was related to the level of sedation (ineffective trigger: p = 0.020; insufficient flow: p = 0.016; premature cycling: p = 0.023) and the use of midazolam (p = 0.020). Severe patient-ventilator asynchrony was also associated with hemogasometric changes. The persistence of severe patient-ventilator asynchrony was an independent risk factor for failure of the spontaneous breathing test, ventilation time, ventilator-associated pneumonia, organ dysfunction, mortality in the intensive care unit, and length of stay in the intensive care unit.
Patient-ventilator asynchrony is a frequent disorder in critically ill patients with inspiratory effort. The patient’s interaction with the ventilator should be optimized to improve hemogasometric parameters and clinical results. Further studies are required to confirm these results.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2020;32(2):224-228
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20200030
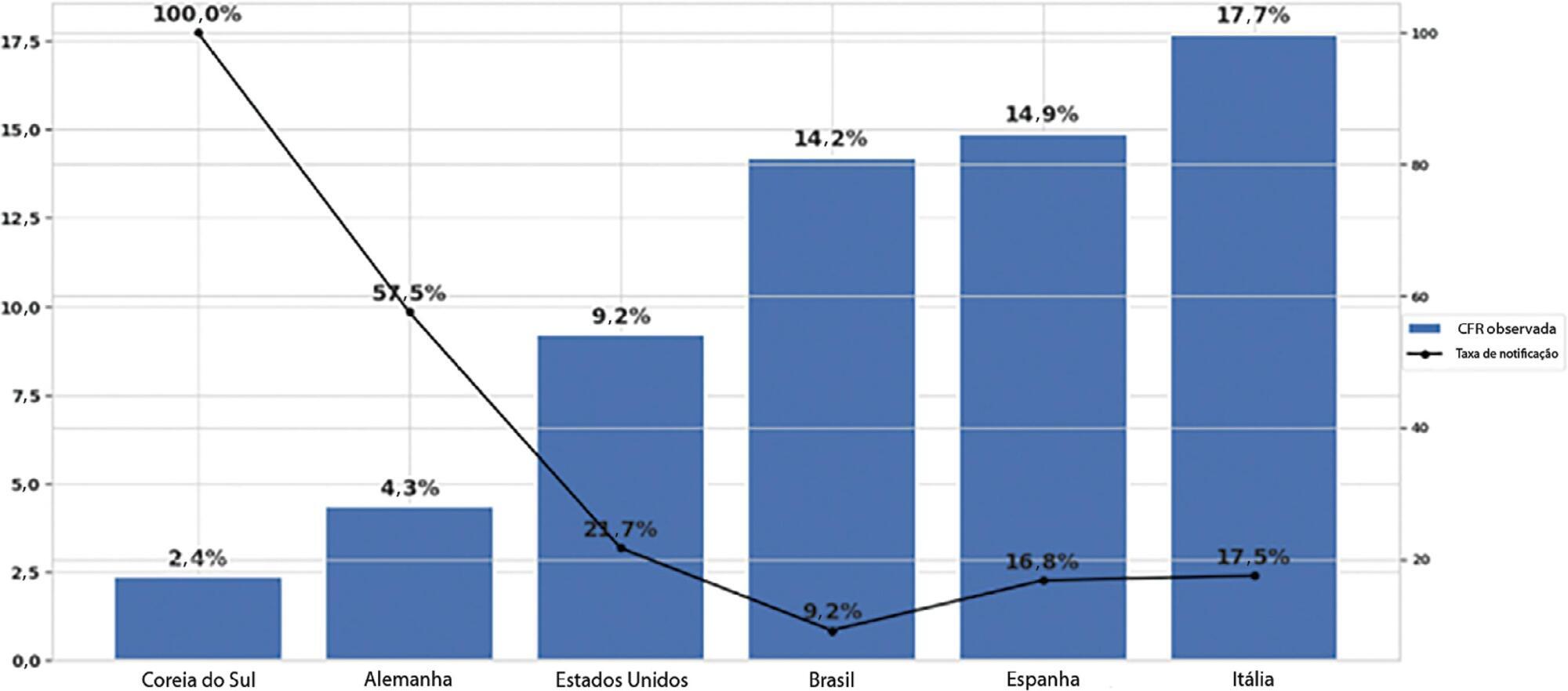
To estimate the reporting rates of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) cases for Brazil as a whole and states.
We estimated the actual number of COVID-19 cases using the reported number of deaths in Brazil and each state, and the expected case-fatality ratio from the World Health Organization. Brazil’s expected case-fatality ratio was also adjusted by the population’s age pyramid. Therefore, the notification rate can be defined as the number of confirmed cases (notified by the Ministry of Health) divided by the number of expected cases (estimated from the number of deaths).
The reporting rate for COVID-19 in Brazil was estimated at 9.2% (95%CI 8.8% - 9.5%), with all the states presenting rates below 30%. São Paulo and Rio de Janeiro, the most populated states in Brazil, showed small reporting rates (8.9% and 7.2%, respectively). The highest reporting rate occurred in Roraima (31.7%) and the lowest in Paraiba (3.4%).
The results indicated that the reporting of confirmed cases in Brazil is much lower as compared to other countries we analyzed. Therefore, decision-makers, including the government, fail to know the actual dimension of the pandemic, which may interfere with the determination of control measures.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2020;32(1):99-107
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20200015
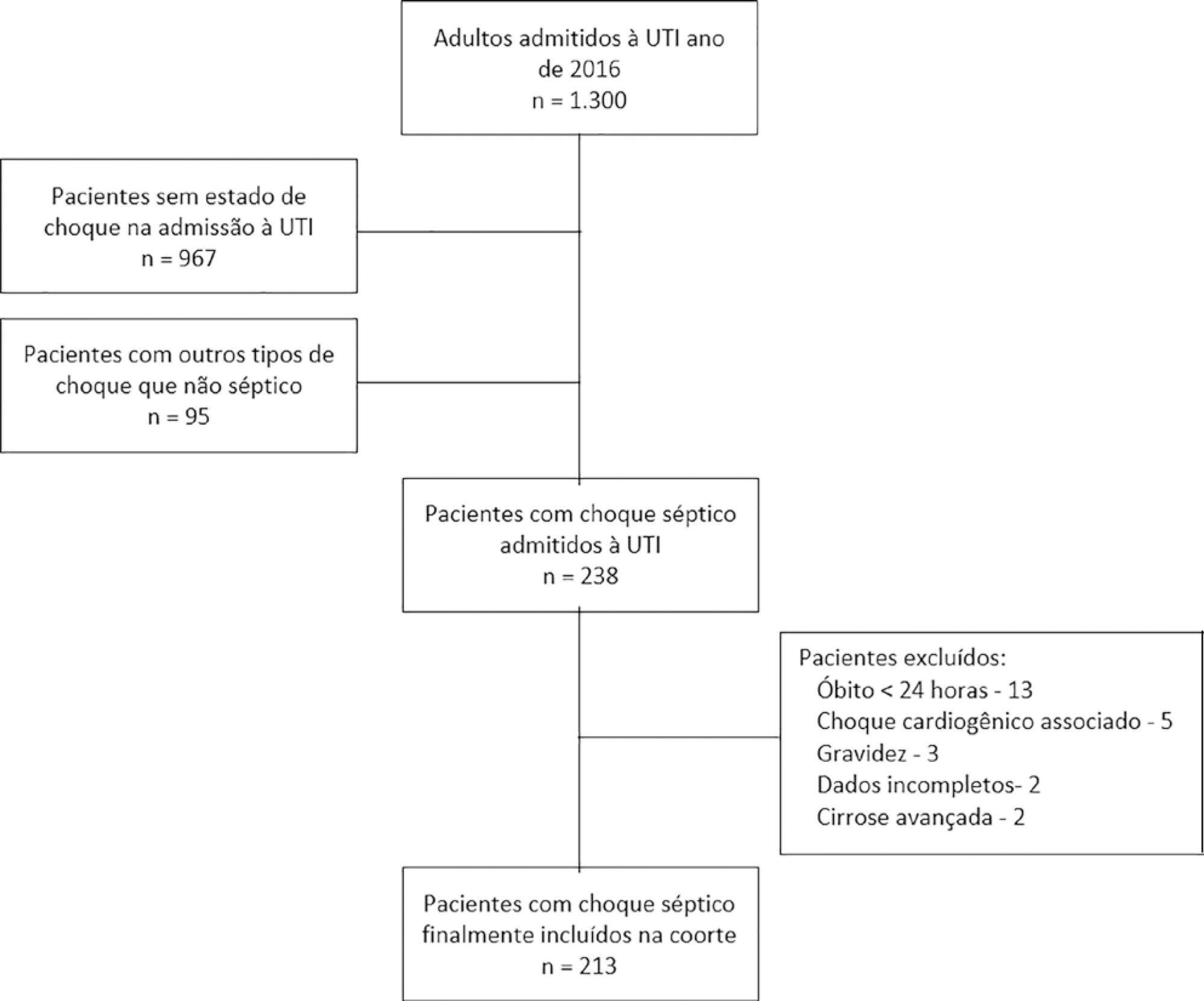
To assess whether fluid overload in fluid therapy is a prognostic factor for patients with septic shock when adjusted for lactate clearance goals.
This was a retrospective cohort study conducted at a level IV care hospital in Bogotá, Colombia. A cohort of patients with septic shock was assembled. Their characteristics and fluid balance were documented. The patients were stratified by exposure levels according to the magnitude of fluid overload by body weight after 24 hours of therapy. Mortality was determined at 30 days, and an unconditional logistic regression model was created, adjusting for confounders. The statistical significance was established at p ≤ 0.05.
There were 213 patients with septic shock, and 60.8% had a lactate clearance ≥ 50% after treatment. Ninety-seven (46%) patients developed fluid overload ≥ 5%, and only 30 (13%) developed overload ≥ 10%. Patients exhibiting fluid overload ≥ 5% received an average of 6227mL of crystalloids (SD ± 5838mL) in 24 hours, compared to 3978mL (SD ± 3728mL) among unexposed patients (p = 0.000). The patients who developed fluid overload were treated with mechanical ventilation (70.7% versus 50.8%) (p = 0.003), albumin (74.7% versus 55.2%) (p = 0.003) and corticosteroids (53.5% versus 35.0%) (p = 0.006) more frequently than those who did not develop fluid overload. In the multivariable analysis, cumulative fluid balance was not associated with mortality (OR 1.03; 95%CI 0.89 - 1.20).
Adjusting for the severity of the condition and adequate lactate clearance, cumulative fluid balance was not associated with increased mortality in this Latin American cohort of septic patients.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (116) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)