Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2022;34(3):380-385
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20220224-en
To determine the incidence of postintensive care syndrome in a cohort of critically ill patients admitted to the intensive care unit and to identify risk factors related to its development in the physical, cognitive and mental health areas.
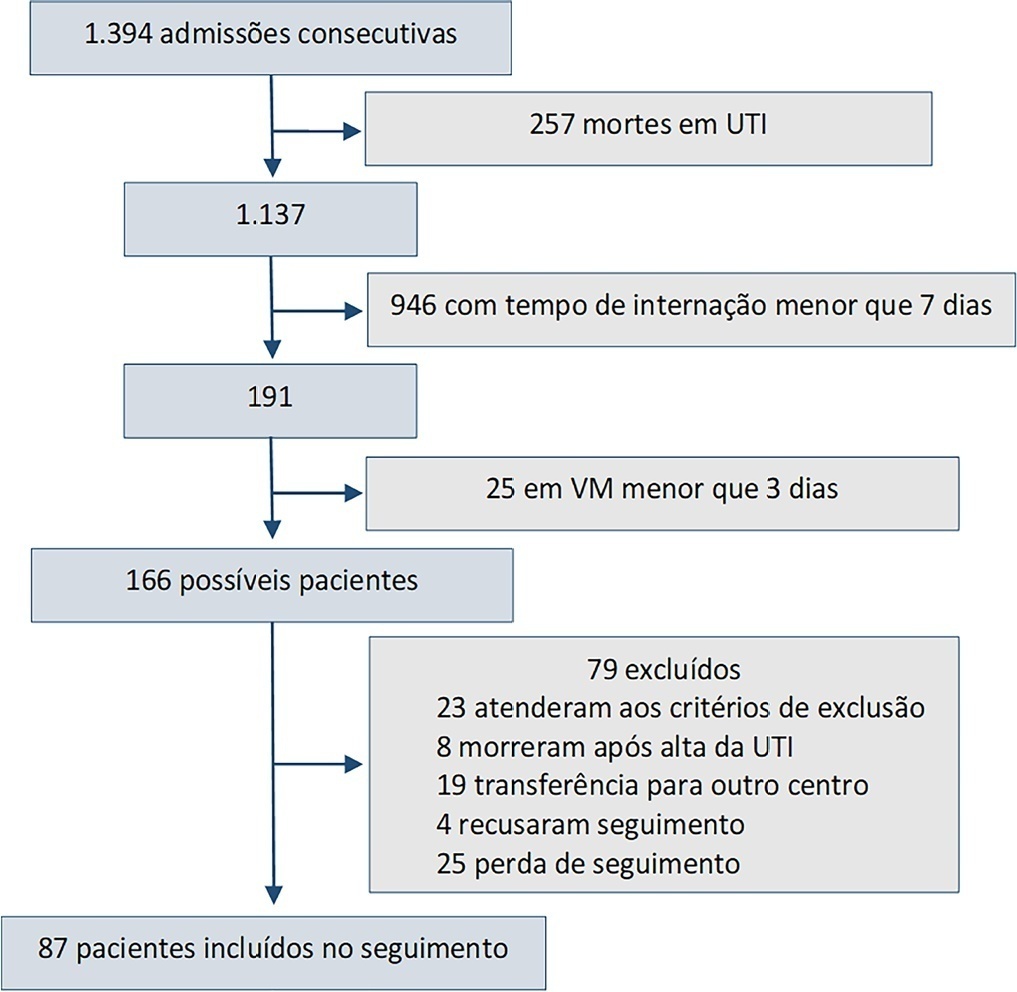
This was a prospective observational cohort study developed in the intensive care unit of a university hospital. Patients with intensive care unit stays equal to or longer than one week and the need for mechanical ventilation for more than 3 days, shock or delirium were included in the study. Demographic variables, reasons for admission, diagnoses, sedation, type of mechanical ventilation used, complications and length of stay were recorded. A univariate analysis was performed to identify risk factors related to postintensive care syndrome. The scales used for the assessment of the different spheres were Barthel, Pfeiffer, Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale and Impact of Event Scale-6. The main variables of interest were postintensive care syndrome incidence overall and by domains. Risk factors were examined in each of the health domains (physical, cognitive and mental health).
Eighty-seven patients were included. The mean Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II score was 16.5. The mean number of intensive care unit days was 17. The incidence of global postintensive care syndrome was 56.3% (n = 49, 95%CI 45.8 - 66.2%). The incidence of postintensive care syndrome in each of the spheres was 32.1% (physical), 11.5% (cognitive), and 36.6% (mental health).
The incidence of postintensive care syndrome is 56.3%. The mental health sphere is the most frequently involved. The risk factors are different depending on the area considered.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(1):111-118
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20210012
To evaluate the incidence of hypothermia in patients undergoing continuous renal replacement therapy in the intensive care unit. As secondary objectives, we determined associated factors and compared the occurrence of hypothermia between two modalities of continuous renal replacement therapy.
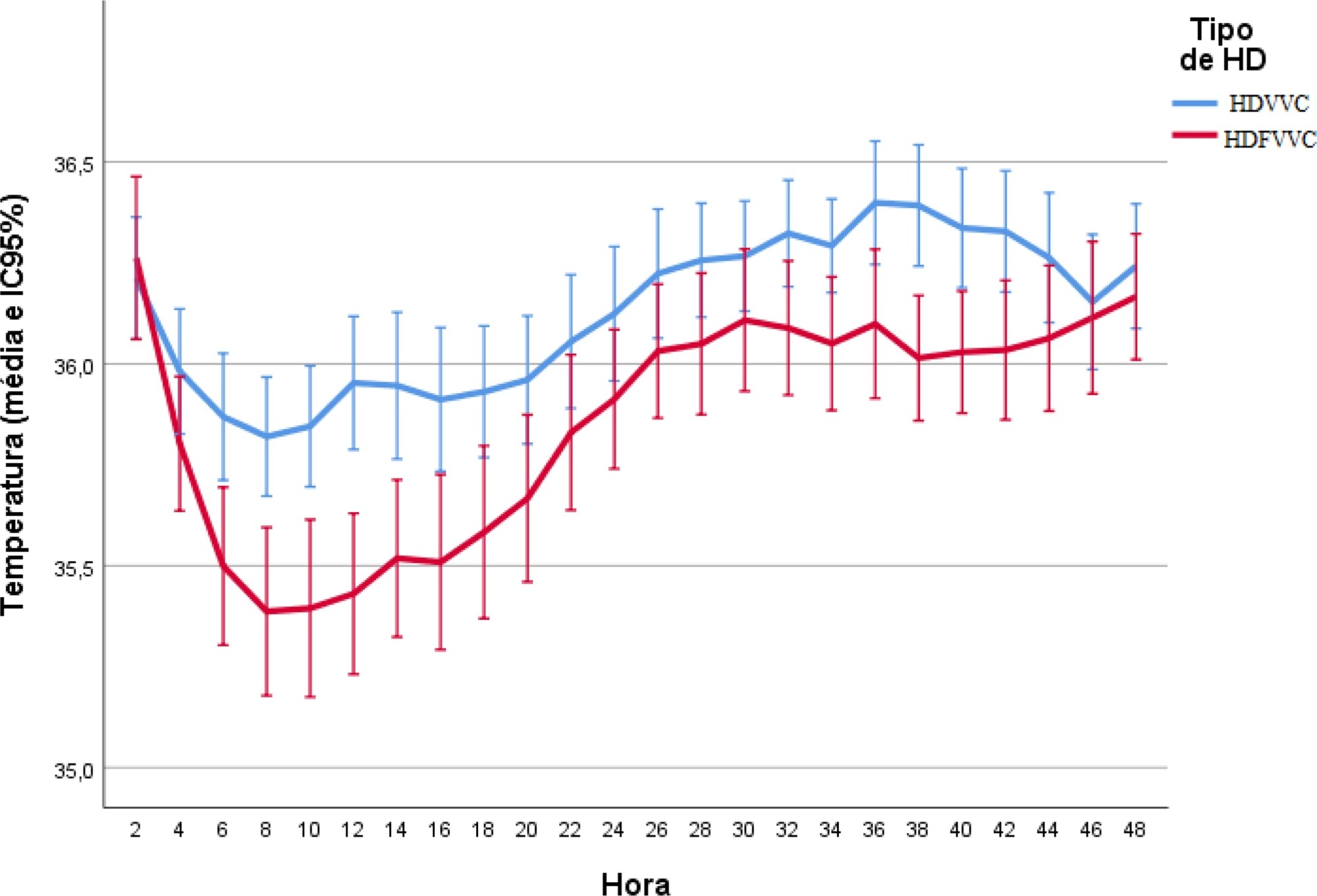
A prospective cohort study was conducted with adult patients who were admitted to a clinical-surgical intensive care unit and underwent continuous renal replacement therapy in a high-complexity public university hospital in southern Brazil from April 2017 to July 2018. Hypothermia was defined as a body temperature ≤ 35ºC. The patients included in the study were followed for the first 48 hours of continuous renal replacement therapy. The researchers collected data from medical records and continuous renal replacement therapy records.
A total of 186 patients were equally distributed between two types of continuous renal replacement therapy: hemodialysis and hemodiafiltration. The incidence of hypothermia was 52.7% and was higher in patients admitted for shock (relative risk of 2.11; 95%CI 1.21 - 3.69; p = 0.009) and in those who underwent hemodiafiltration with heating in the return line (relative risk of 1.50; 95%CI 1.13 - 1.99; p = 0.005).
Hypothermia in critically ill patients with continuous renal replacement therapy is frequent, and the intensive care team should be attentive, especially when there are associated risk factors.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2018;30(2):166-173
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20180022
To assess the predictors of de novo atrial fibrillation in patients in a non-cardiac intensive care unit.
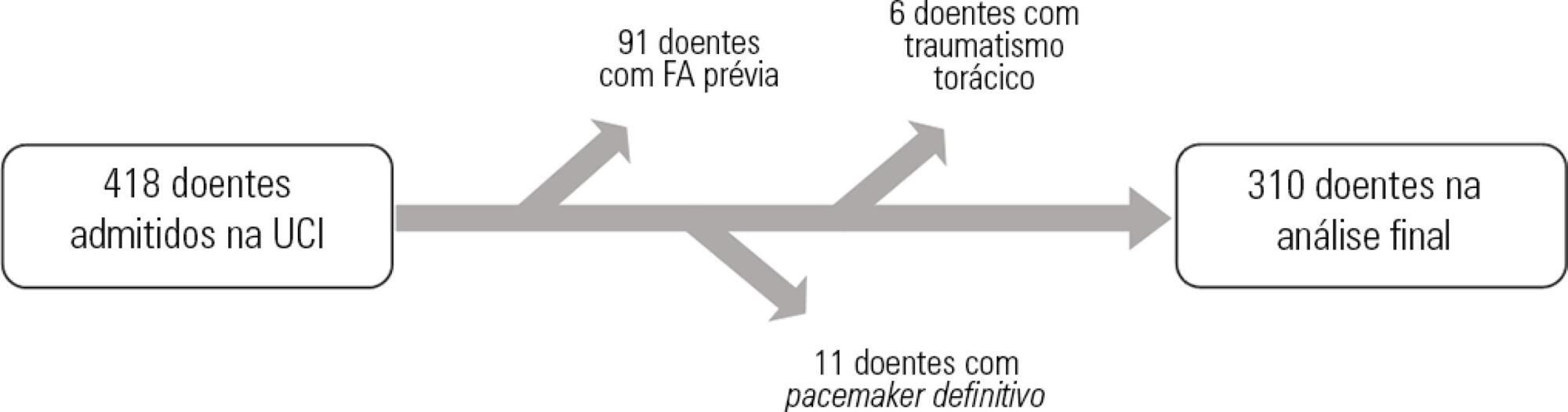
A total of 418 hospitalized patients were analyzed between January and September 2016 in a non-cardiac intensive care unit. Clinical characteristics, interventions, and biochemical markers were recorded during hospitalization. In-hospital mortality and length of hospital stay in the intensive care unit were also evaluated.
A total of 310 patients were included. The mean age of the patients was 61.0 ± 18.3 years, 49.4% were male, and 23.5% presented de novo atrial fibrillation. The multivariate model identified previous stroke (OR = 10.09; p = 0.016) and elevated levels of pro-B type natriuretic peptide (proBNP, OR = 1.28 for each 1,000pg/mL increment; p = 0.004) as independent predictors of de novo atrial fibrillation. Analysis of the proBNP receiver operating characteristic curve for prediction of de novo atrial fibrillation revealed an area under the curve of 0.816 (p < 0.001), with a sensitivity of 65.2% and a specificity of 82% for proBNP > 5,666pg/mL. There were no differences in mortality (p = 0.370), but the lengths of hospital stay (p = 0.002) and stay in the intensive care unit (p = 0.031) were higher in patients with de novo atrial fibrillation.
A history of previous stroke and elevated proBNP during hospitalization were independent predictors of de novo atrial fibrillation in the polyvalent intensive care unit. The proBNP is a useful and easy- and quick-access tool in the stratification of atrial fibrillation risk.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2013;25(4):290-296
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20130050
Acute kidney injury is a common complication in critically ill patients, and the RIFLE, AKIN and KDIGO criteria are used to classify these patients. The present study's aim was to compare these criteria as predictors of mortality in critically ill patients.
Prospective cohort study using medical records as the source of data. All patients admitted to the intensive care unit were included. The exclusion criteria were hospitalization for less than 24 hours and death. Patients were followed until discharge or death. Student's t test, chi-squared analysis, a multivariate logistic regression and ROC curves were used for the data analysis.
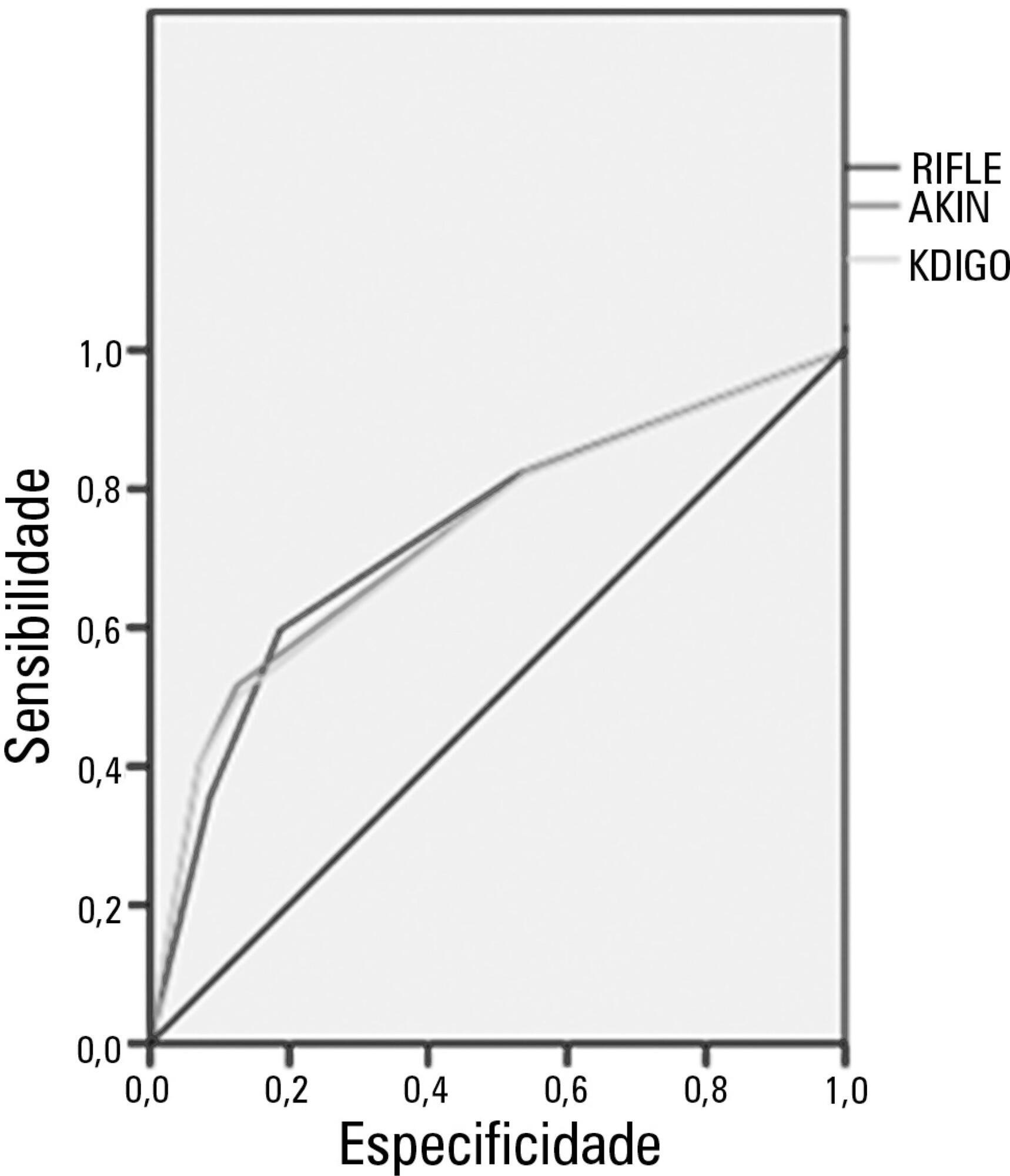
The mean patient age was 64 years old, and the majority of patients were women of African descent. According to RIFLE, the mortality rates were 17.74%, 22.58%, 24.19% and 35.48% for patients without acute kidney injury (AKI) in stages of Risk, Injury and Failure, respectively. For AKIN, the mortality rates were 17.74%, 29.03%, 12.90% and 40.32% for patients without AKI and at stage I, stage II and stage III, respectively. For KDIGO 2012, the mortality rates were 17.74%, 29.03%, 11.29% and 41.94% for patients without AKI and at stage I, stage II and stage III, respectively. All three classification systems showed similar ROC curves for mortality.
The RIFLE, AKIN and KDIGO criteria were good tools for predicting mortality in critically ill patients with no significant difference between them.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2012;24(3):230-235
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2012000300005
OBJECTIVE: This study established the incidence and primary causes of unplanned extubation in newborns in the neonatal intensive care units of the Hospital Sofia Feldman, Belo Horizonte (Minas Gerais). METHODS: This retrospective study was conducted between July 1, 2009 and April 30, 2010. Unplanned extubations and their primary causes were assessed using an adverse events form. The following variables were assessed: gender, corrected age, present weight, duration of mechanical ventilation time, and motives/causes of the event on the day of the unplanned extubation event. RESULTS: Fifty-four unplanned extubations occurred, which corresponded to an incidence of 1.0 event/100 days of mechanical ventilation. This rate was higher among newborns with a corrected age of 30 to 36 weeks and weight < 1,000 g. The primary causes of unplanned extubations included patient agitation, inappropriate handling of patients during the performance of procedures, and inappropriate fixation and positioning of the endotracheal tube. CONCLUSION: The incidence of unplanned extubation in the investigated neonatal intensive care units was low during the study period compared to previously reported data. Nevertheless, the assessment of the quality of procedures, the continuous follow-up of newborns, and the monitoring of the causes of extubation are required to further reduce this incidence.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2011;23(3):321-326
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2011000300010
OBJECTIVE:To compare the clinical features and outcomes of patients with and without acute kidney injury in an intensive care unit of a tertiary university hospital and to identify acute kidney injury and mortality risk factors. METHODS: This was a prospective observational study of a cohort including 564 patients followed during their stay in the intensive care unit of Hospital das Clinicas da Faculdade de Medicina de Botucatu (Botucatu, São Paulo, Brazil) between May 2008 and May 2010. Patients were allocated to two different groups: with (G1) and without (G2) acute kidney injury. RESULTS: The incidence of acute kidney injury was 25.5%. The groups were different with respect to the reason for admission to the intensive care unit (sepsis, G1: 41.6% versus G2: 24.1%; P < 0.0001; neurosurgery, postoperative G1: 13.8% versus G2: 38.1%; P < 0.0001); age (G1: 56.8 ± 15.9 vs. G2: 49.8 ± 17.8 years; P < 0.0001); Acute Physiological Chronic Health Evaluation (APACHE) II score (G1: 21.9 ± 6.9 versus G2: 14.1 ± 4.6; P < 0.0001); use of mechanical ventilation (G1: 89.2% vs. G2: 69.1%; P < 0.0001) and use of vasoactive drugs (G1: 78.3% vs. G2: 56.1%; P < 0.0001). Higher rates of diabetes mellitus, congestive heart failure, chronic renal disease and use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs were more frequent in acute kidney injury patients (28.2% vs. 19.7%, P = 0.03; 23.6 vs. 11.6%, P = 0.0002; 21.5% vs. 11.5%, P < 0.0001 and 23.5% vs. 71.%, P < 0.0001, for G1 versus G2, respectively). Length of hospital stay and mortality were also higher for acute kidney injury patients (G1: 6.6 ± 2.7 days versus G2: 12.9 ±5.6 days, P < 0.0001 and G1: 62.5% versus G2: 16.4%, P < 0.0001). Multivariate analysis identified the following as risk factors for acute kidney injury: age above 55 years, APACHE II score above 16, baseline creatinine above 1.2 and use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (odds ratio (OR) = 1.36, 95% confidence interval (95%CI): 1.22 - 1.85; OR = 1.2, 95%CI: 1.11 - 1.33; OR = 5.2, 95%CI: 2.3 - 11.6 and OR = 2.15, 95%CI: 1.1 - 4.2, respectively). Acute kidney injury was independently associated with longer hospital stay and increased mortality (OR = 1.18, 95%CI: 1.05 - 1.26 and OR = 1.24, 95%CI: 1.09 - 1.99, respectively). Analysis of the survival curve 30 days after admission showed 83.3% mortality for acute kidney injury patients and 45.2% for non-acute kidney injury patients (P < 0.0001). CONCLUSION: The incidence of acute kidney injury was high in this intensive care unit; the independent risk factors associated with acute kidney injury were age > 55 years, APACHE II > 16, baseline serum creatinine > 1.2 and use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Acute kidney injury is an independent risk factor for longer intensive care unit stay and mortality.
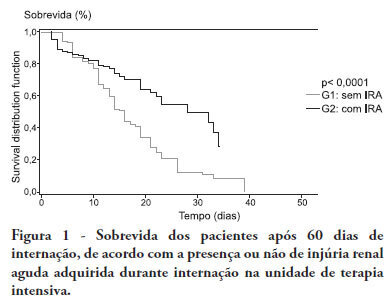
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2010;22(1):11-18
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2010000100004
OBJECTIVE: This study aimed to evaluate the outcome of cirrhotic patients admitted to Intensive Care Unit. METHODS: We conducted a prospective cohort of cirrhotic patients admitted to two intensive care unit between June 1999 to September 2004. We collected demographic, comorbid conditions, diagnosis, vital signs, laboratory data, prognostic scores and evolution in intensive care unit and hospital. The patients were divided in groups: non surgical, non liver surgery, surgery for portal hypertension, liver surgery, liver transplantation, and urgent surgery. RESULTS: We studied 304 patients, which 190 (62.5%) were male. The median of age was 54 (47-61) years. The mortality rate in intensive care unit and hospital were 29.3 and 39.8%, respectively, more elevated than in the other patients admitted critically ill patients (19.6 and 28.3%; p<0.001). Non surgical patients and those submitted to urgent surgery presented high mortality rate in the intensive care unit (64.3 and 65.4%) and in the hospital (80.4 and 76.9%). The variables related to hospital mortality were [Odds ratio (confidence interval 95%)]: mean arterial pressure [0.985 (0.974-0.997)]; mechanical ventilation in the first 24 h [4.080 (1.990-8.364)]; confirmed infection in the first 24 h [7.899 (2.814-22.175)]; acute renal failure [5.509 (1.708-17.766)] and APACHE II score (points) [1.078 (1.017-1.143)]. CONCLUSIONS: Cirrhotic patients had higher mortality rate compared to non cirrhotic critically ill patients. Those admitted after urgent surgery and non surgical had higher mortality rate.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (33) COVID-19 (45) Critical care (115) Critical illness (54) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (254) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (75) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (117) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98) Septic shock (25)