Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(1):10-17
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20150004
We aimed to evaluate the cumulative fluid balance during the period of shock and determine what happens to fluid balance in the 7 days following recovery from shock.
A prospective and observational study in septic shock patients. Patients with a mean arterial pressure ≥ 65mmHg and lactate < 2.0mEq/L were included < 12 hours after weaning from vasopressor, and this day was considered day 1. The daily fluid balance was registered during and for seven days after recovery from shock. Patients were divided into two groups according to the full cohort’s median cumulative fluid balance during the period of shock: Group 1 ≤ 4.4L (n = 20) and Group 2 > 4.4L (n = 20).
We enrolled 40 patients in the study. On study day 1, the cumulative fluid balance was 1.1 [0.6 - 3.4] L in Group 1 and 9.0 [6.7 - 13.8] L in Group 2. On study day 7, the cumulative fluid balance was 8.0 [4.5 - 12.4] L in Group 1 and 14.7 [12.7 - 20.6] L in Group 2 (p < 0.001 for both). Afterwards, recovery of shock fluid balance continued to increase in both groups. Group 2 had a more prolonged length of stay in the intensive care unit and hospital compared to Group 1.
In conclusion, positive fluid balances are frequently seen in patients with septic shock and may be related to worse outcomes. During the shock period, even though the fluid balance was previously positive, it becomes more positive. After recovery from shock, the fluid balance continues to increase. The group with a more positive fluid balance group spent more time in the intensive care unit and hospital.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(1):18-25
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20150005
To evaluate and compare stressors identified by patients of a coronary intensive care unit with those perceived by patients of a general postoperative intensive care unit.
This cross-sectional and descriptive study was conducted in the coronary intensive care and general postoperative intensive care units of a private hospital. In total, 60 patients participated in the study, 30 in each intensive care unit. The stressor scale was used in the intensive care units to identify the stressors. The mean score of each item of the scale was calculated followed by the total stress score. The differences between groups were considered significant when p < 0.05.
The mean ages of patients were 55.63 ± 13.58 years in the coronary intensive care unit and 53.60 ± 17.47 years in the general postoperative intensive care unit. For patients in the coronary intensive care unit, the main stressors were “being in pain”, “being unable to fulfill family roles” and “being bored”. For patients in the general postoperative intensive care unit, the main stressors were “being in pain”, “being unable to fulfill family roles” and “not being able to communicate”. The mean total stress scores were 104.20 ± 30.95 in the coronary intensive care unit and 116.66 ± 23.72 (p = 0.085) in the general postoperative intensive care unit. When each stressor was compared separately, significant differences were noted only between three items. “Having nurses constantly doing things around your bed” was more stressful to the patients in the general postoperative intensive care unit than to those in the coronary intensive care unit (p = 0.013). Conversely, “hearing unfamiliar sounds and noises” and “hearing people talk about you” were the most stressful items for the patients in the coronary intensive care unit (p = 0.046 and 0.005, respectively).
The perception of major stressors and the total stress score were similar between patients in the coronary intensive care and general postoperative intensive care units.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(1):26-35
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20150006
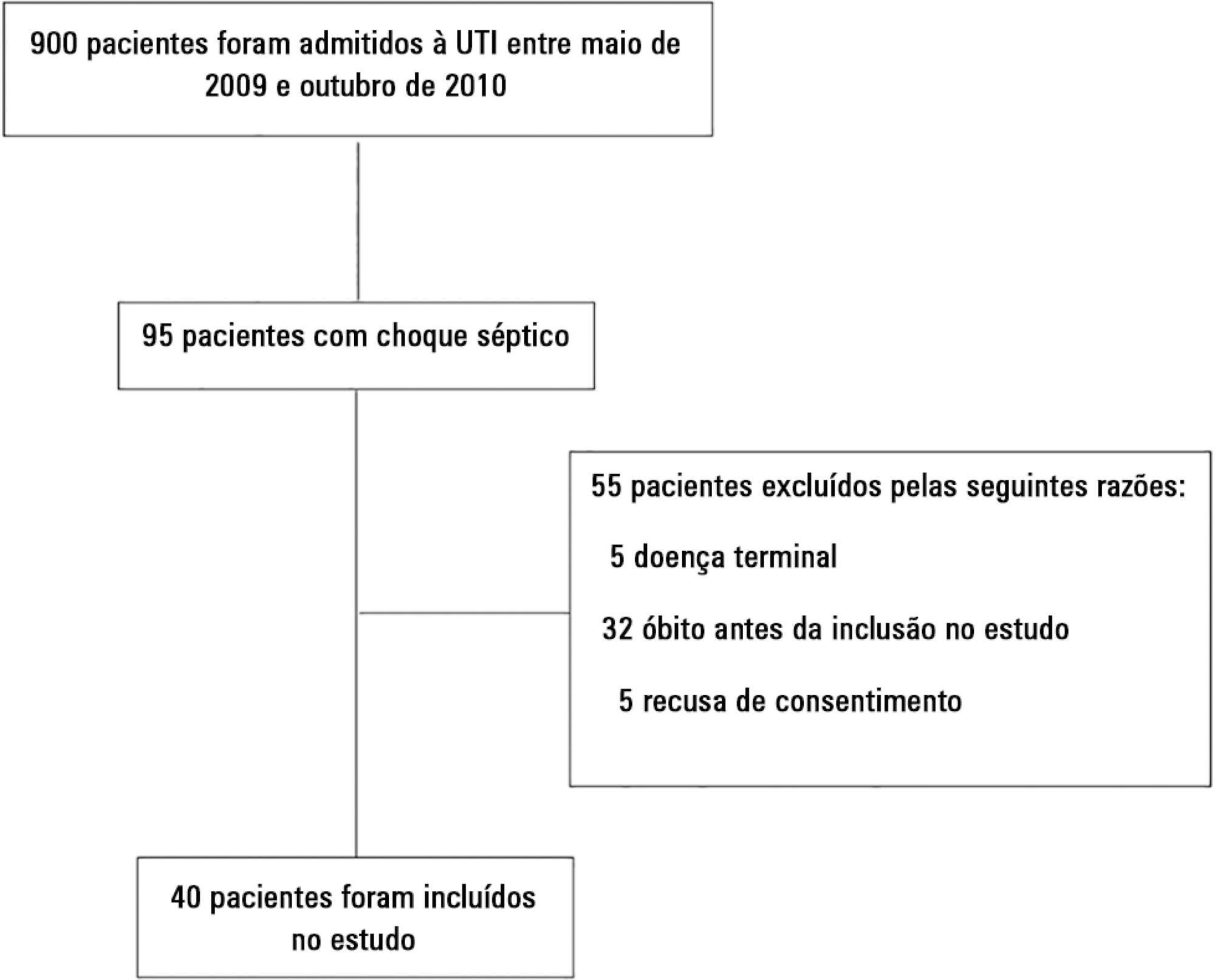
The number of patients who require prolonged mechanical ventilation increased during the last decade, which generated a large population of chronically ill patients. This study established the incidence of prolonged mechanical ventilation in four intensive care units and reported different characteristics, hospital outcomes, and the impact of costs and services of prolonged mechanical ventilation patients (mechanical ventilation dependency ≥ 21 days) compared with non-prolonged mechanical ventilation patients (mechanical ventilation dependency < 21 days).
This study was a multicenter cohort study of all patients who were admitted to four intensive care units. The main outcome measures were length of stay in the intensive care unit, hospital, complications during intensive care unit stay, and intensive care unit and hospital mortality.
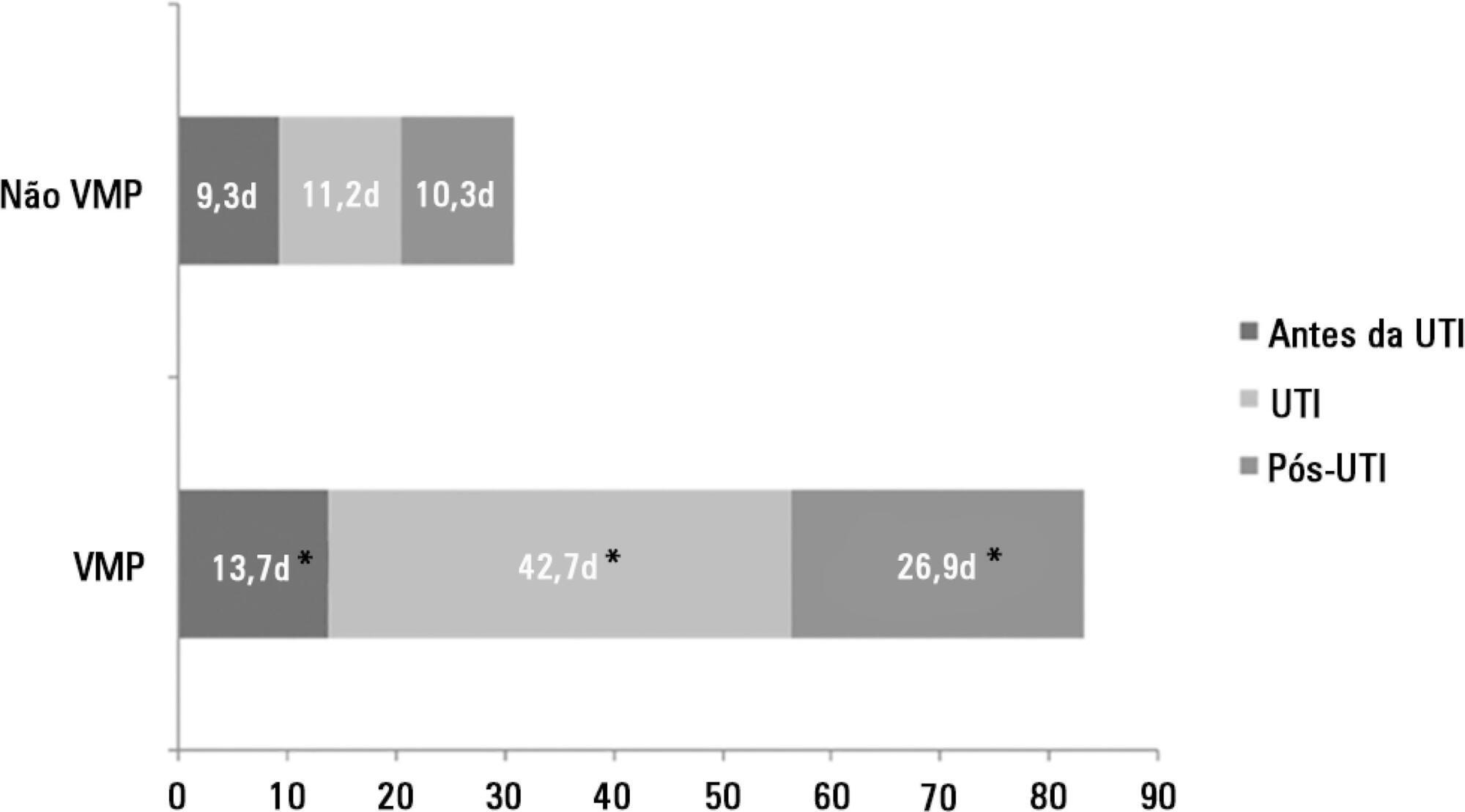
There were 5,287 admissions to the intensive care units during study period. Some of these patients (41.5%) needed ventilatory support (n = 2,197), and 218 of the patients met criteria for prolonged mechanical ventilation (9.9%). Some complications developed during intensive care unit stay, such as muscle weakness, pressure ulcers, bacterial nosocomial sepsis, candidemia, pulmonary embolism, and hyperactive delirium, were associated with a significantly higher risk of prolonged mechanical ventilation. Prolonged mechanical ventilation patients had a significant increase in intensive care unit mortality (absolute difference = 14.2%, p < 0.001) and hospital mortality (absolute difference = 19.1%, p < 0.001). The prolonged mechanical ventilation group spent more days in the hospital after intensive care unit discharge (26.9 ± 29.3 versus 10.3 ± 20.4 days, p < 0.001) with higher costs.
The classification of chronically critically ill patients according to the definition of prolonged mechanical ventilation adopted by our study (mechanical ventilation dependency ≥ 21 days) identified patients with a high risk for complications during intensive care unit stay, longer intensive care unit and hospital stays, high death rates, and higher costs.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(1):36-43
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20150007
To evaluate the immediate effects of red blood cell transfusion on central venous oxygen saturation and lactate levels in septic shock patients with different transfusion triggers.
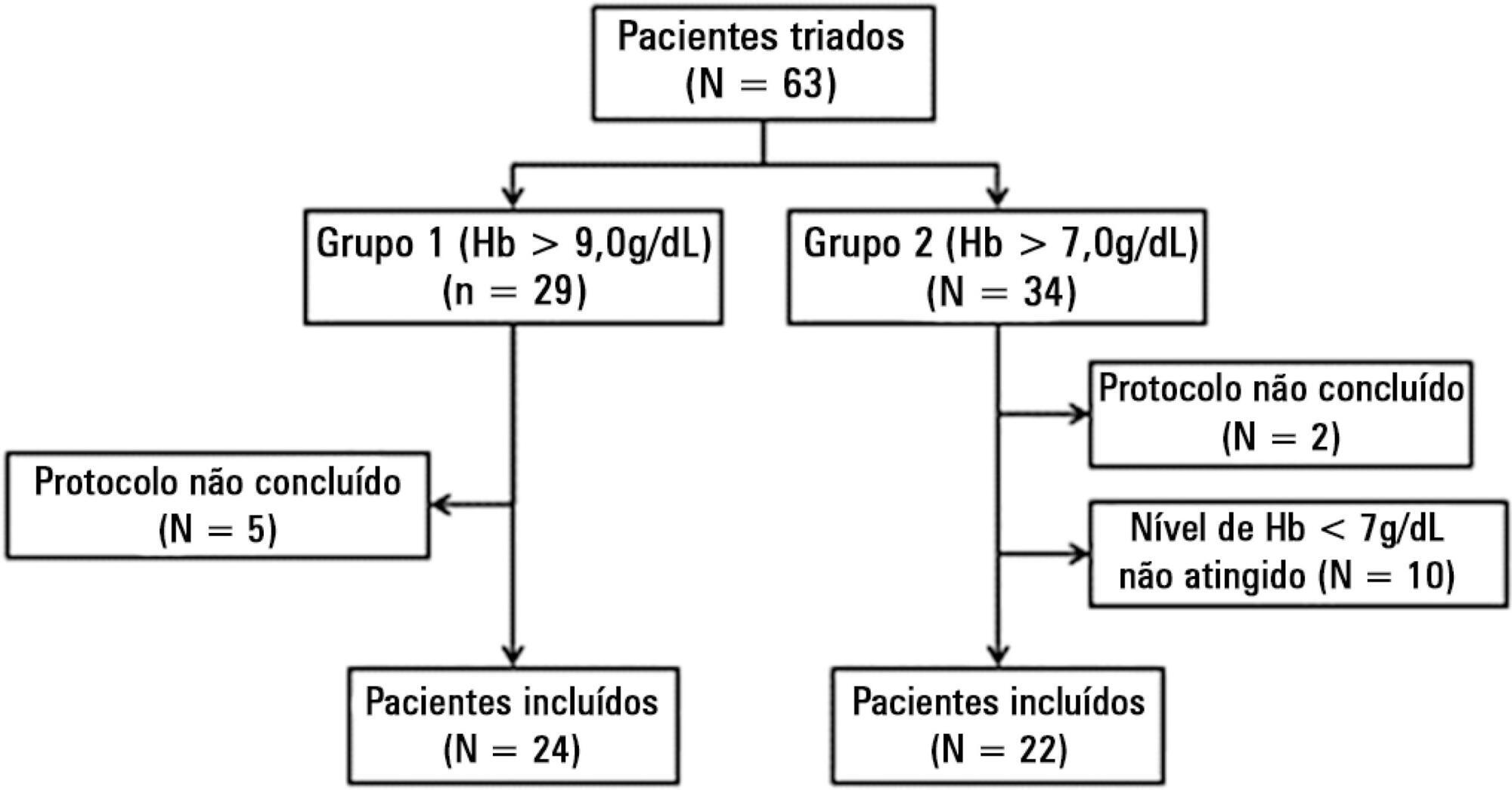
We included patients with a diagnosis of septic shock within the last 48 hours and hemoglobin levels below 9.0g/dL Patients were randomized for immediate transfusion with hemoglobin concentrations maintained above 9.0g/dL (Group Hb9) or to withhold transfusion unless hemoglobin felt bellow 7.0g/dL (Group Hb7). Hemoglobin, lactate, central venous oxygen saturation levels were determined before and one hour after each transfusion.
We included 46 patients and 74 transfusions. Patients in Group Hb7 had a significant reduction in median lactate from 2.44 (2.00 - 3.22) mMol/L to 2.21 (1.80 - 2.79) mMol/L, p = 0.005, which was not observed in Group Hb9 [1.90 (1.80 - 2.65) mMol/L to 2.00 (1.70 - 2.41) mMol/L, p = 0.23]. Central venous oxygen saturation levels increased in Group Hb7 [68.0 (64.0 - 72.0)% to 72.0 (69.0 - 75.0)%, p < 0.0001] but not in Group Hb9 [72.0 (69.0 - 74.0)% to 72.0 (71.0 - 73.0)%, p = 0.98]. Patients with elevated lactate or central venous oxygen saturation < 70% at baseline had a significant increase in these variables, regardless of baseline hemoglobin levels. Patients with normal values did not show a decrease in either group.
Red blood cell transfusion increased central venous oxygen saturation and decreased lactate levels in patients with hypoperfusion regardless of their baseline hemoglobin levels. Transfusion did not appear to impair these variables in patients without hypoperfusion.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(2):105-112
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20150020
The European Surgical Outcomes Study described mortality following in-patient surgery. Several factors were identified that were able to predict poor outcomes in a multivariate analysis. These included age, procedure urgency, severity and type and the American Association of Anaesthesia score. This study describes in greater detail the relationship between the American Association of Anaesthesia score and postoperative mortality.
Patients in this 7-day cohort study were enrolled in April 2011. Consecutive patients aged 16 years and older undergoing inpatient non-cardiac surgery with a recorded American Association of Anaesthesia score in 498 hospitals across 28 European nations were included and followed up for a maximum of 60 days. The primary endpoint was in-hospital mortality. Decision tree analysis with the CHAID (SPSS) system was used to delineate nodes associated with mortality.
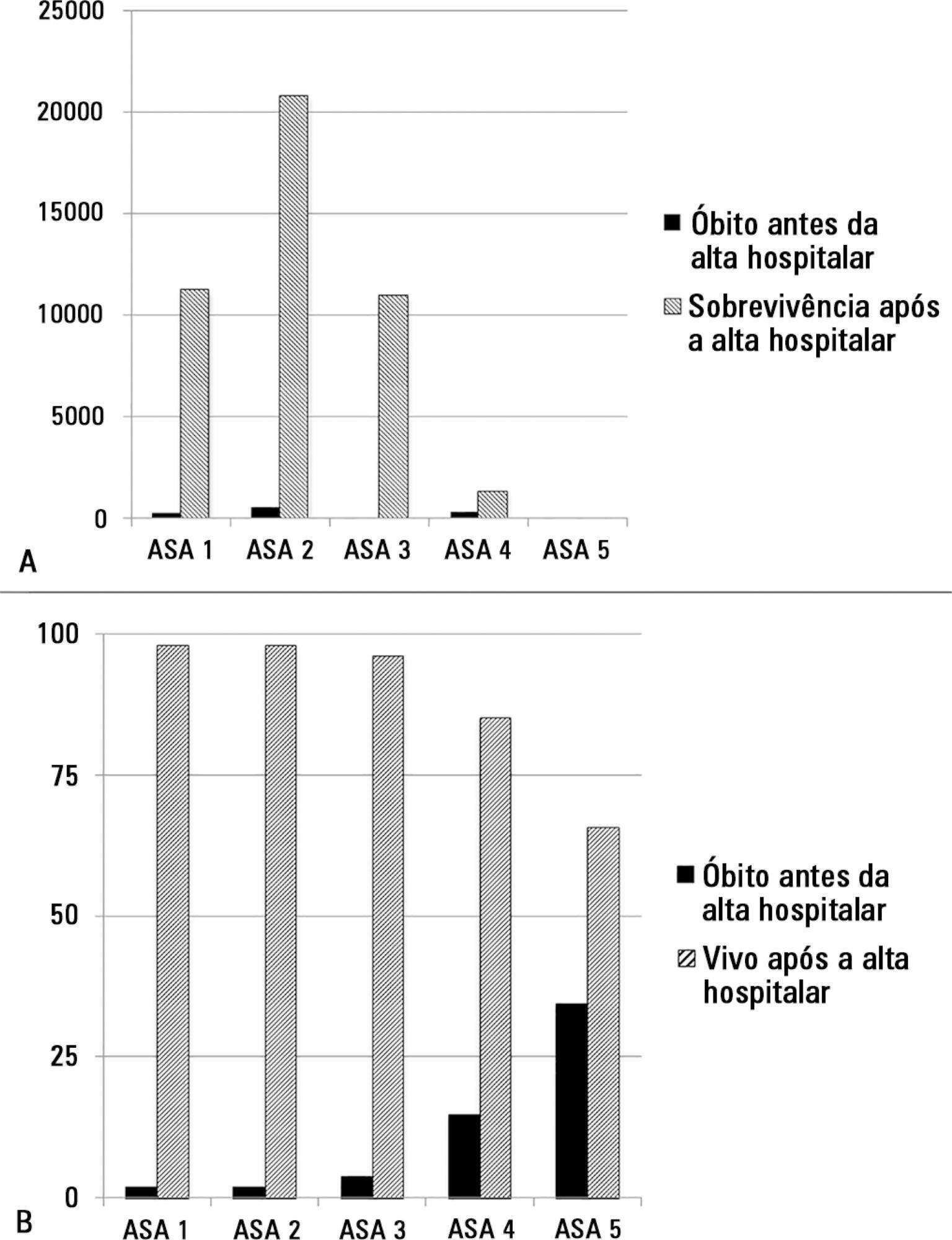
The study enrolled 46,539 patients. Due to missing values, 873 patients were excluded, resulting in the analysis of 45,666 patients. Increasing American Association of Anaesthesia scores were associated with increased admission rates to intensive care and higher mortality rates. Despite a progressive relationship with mortality, discrimination was poor, with an area under the ROC curve of 0.658 (95% CI 0.642 - 0.6775). Using regression trees (CHAID), we identified four discrete American Association of Anaesthesia nodes associated with mortality, with American Association of Anaesthesia 1 and American Association of Anaesthesia 2 compressed into the same node.
The American Association of Anaesthesia score can be used to determine higher risk groups of surgical patients, but clinicians cannot use the score to discriminate between grades 1 and 2. Overall, the discriminatory power of the model was less than acceptable for widespread use.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(2):113-118
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20150021
To analyze the clinical characteristics, complications and factors associated with the prognosis of severe traumatic brain injury among patients who undergo a decompressive craniectomy.
Retrospective study of patients seen in an intensive care unit with severe traumatic brain injury in whom a decompressive craniectomy was performed between the years 2003 and 2012. Patients were followed until their discharge from the intensive care unit. Their clinical-tomographic characteristics, complications, and factors associated with prognosis (univariate and multivariate analysis) were analyzed.
A total of 64 patients were studied. Primary and lateral decompressive craniectomies were performed for the majority of patients. A high incidence of complications was found (78% neurological and 52% nonneurological). A total of 42 patients (66%) presented poor outcomes, and 22 (34%) had good neurological outcomes. Of the patients who survived, 61% had good neurological outcomes. In the univariate analysis, the factors significantly associated with poor neurological outcome were postdecompressive craniectomy intracranial hypertension, greater severity and worse neurological state at admission. In the multivariate analysis, only postcraniectomy intracranial hypertension was significantly associated with a poor outcome.
This study involved a very severe and difficult to manage group of patients with high morbimortality. Intracranial hypertension was a main factor of poor outcome in this population.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(2):119-124
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20150022
To evaluate the efficacy and safety of percutaneous tracheostomy by means of single-step dilation with fiber optic bronchoscopy assistance in critical care patients under mechanical ventilation.
Between the years 2004 and 2014, 512 patients with indication of tracheostomy according to clinical criteria, were prospectively and consecutively included in our study. One-third of them were high-risk patients. Demographic variables, APACHE II score, and days on mechanical ventilation prior to percutaneous tracheostomy were recorded. The efficacy of the procedure was evaluated according to an execution success rate and based on the necessity of switching to an open surgical technique. Safety was evaluated according to post-operative and operative complication rates.
The mean age of the group was 64 ± 18 years (203 women and 309 males). The mean APACHE II score was 21 ± 3. Patients remained an average of 11 ± 3 days on mechanical ventilation before percutaneous tracheostomy was performed. All procedures were successfully completed without the need to switch to an open surgical technique. Eighteen patients (3.5%) presented procedure complications. Five patients experienced transient desaturation, 4 presented low blood pressure related to sedation, and 9 presented minor bleeding, but none required a transfusion. No serious complications or deaths associated with the procedure were recorded. Eleven patients (2.1%) presented post-operative complications. Seven presented minor and transitory bleeding of the percutaneous tracheostomy stoma, 2 suffered displacement of the tracheostomy cannula, and 2 developed a superficial infection of the stoma.
Percutaneous tracheostomy using the single-step dilation technique with fiber optic bronchoscopy assistance seems to be effective and safe in critically ill patients under mechanical ventilation when performed by experienced intensive care specialists using a standardized procedure.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(2):125-133
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20150023
To evaluate the prevalence of burnout syndrome among nursing workers in intensive care units and establish associations with psychosocial factors.
This descriptive study evaluated 130 professionals, including nurses, nursing technicians, and nursing assistants, who performed their activities in intensive care and coronary care units in 2 large hospitals in the city of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Data were collected in 2011 using a self-reported questionnaire. The Maslach Burnout Inventory was used to evaluate the burnout syndrome dimensions, and the Self Reporting Questionnaire was used to evaluate common mental disorders.
The prevalence of burnout syndrome was 55.3% (n = 72). In the quadrants of the demand-control model, low-strain workers exhibited a prevalence of 64.5% of suspected cases of burnout, whereas high-strain workers exhibited a prevalence of 72.5% of suspected cases (p = 0.006). The prevalence of suspected cases of common mental disorders was 27.7%; of these, 80.6% were associated with burnout syndrome (< 0.0001). The multivariate analysis adjusted for gender, age, educational level, weekly work duration, income, and thoughts about work during free time indicated that the categories associated with intermediate stress levels - active work (OR = 0.26; 95%CI = 0.09 - 0.69) and passive work (OR = 0.22; 95%CI = 0.07 - 0.63) - were protective factors for burnout syndrome.
Psychosocial factors were associated with the development of burnout syndrome in this group. These results underscore the need for the development of further studies aimed at intervention and the prevention of the syndrome.