Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(3):410-424
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190063
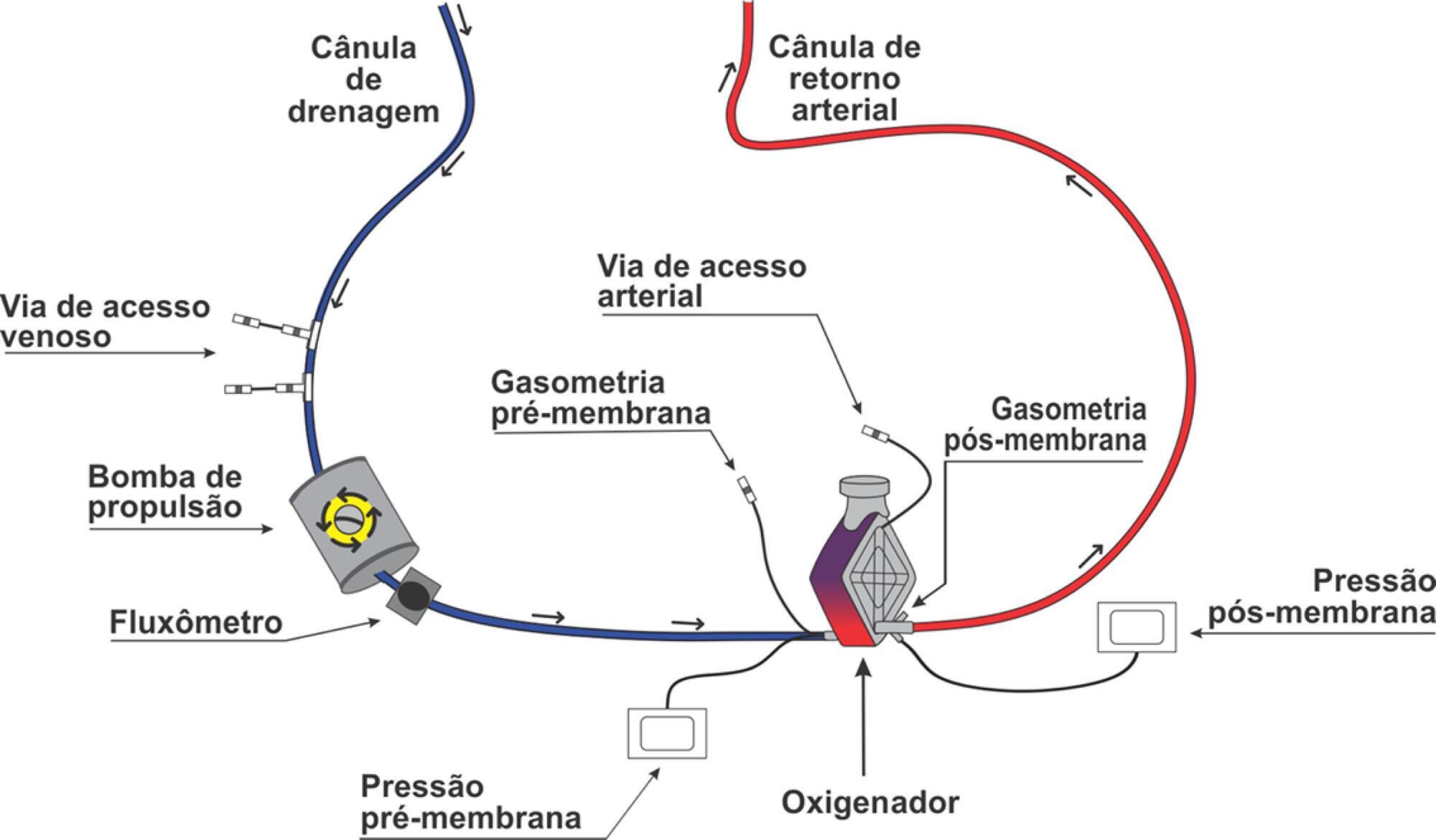
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation is a modality of extracorporeal life support that allows for temporary support in pulmonary and/or cardiac failure refractory to conventional therapy. Since the first descriptions of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, significant improvements have occurred in the device and the management of patients and, consequently, in the outcomes of critically ill patients during extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Many important studies about the use of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome refractory to conventional clinical support, under in-hospital cardiac arrest and with cardiogenic refractory shock have been published in recent years. The objective of this literature review is to present the theoretical and practical aspects of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support for respiratory and/or cardiac functions in critically ill patients.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(2):156-163
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190026
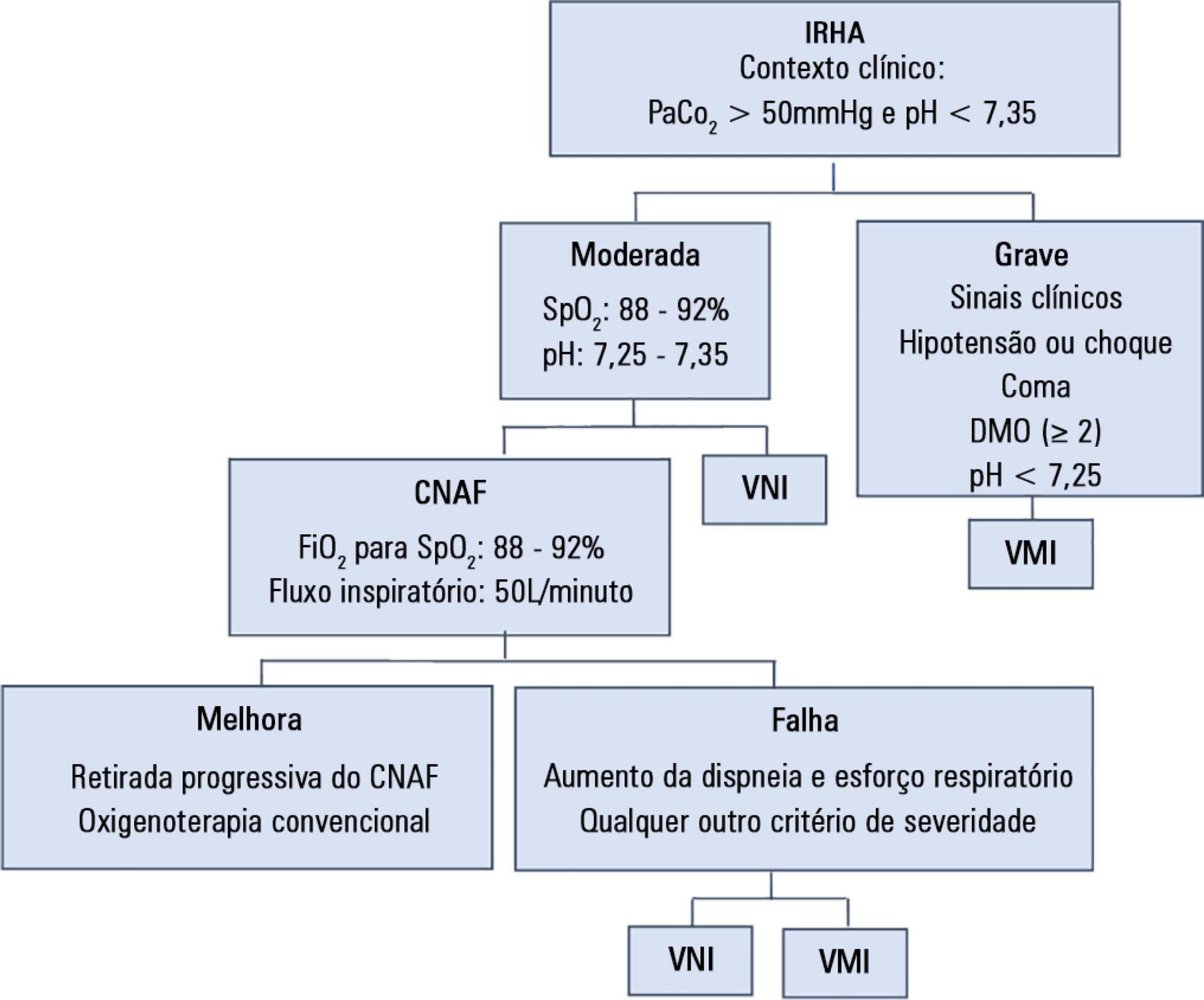
To assess the efficacy and safety of high-flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy in treating moderate hypercapnic respiratory failure in patients who cannot tolerate or have contraindications to noninvasive mechanical ventilation.
A prospective observational 13-month study involving subjects admitted to an intensive care unit with or developing moderate hypercapnic respiratory failure. Clinical and gas exchange parameters were recorded at regular intervals during the first 24 hours. The endpoints were a oxygen saturation between 88 and 92% along with a reduction in breathing effort (respiratory rate) and pH normalization (≥ 7.35). Subjects were considered nonresponders if they required ventilatory support.
Thirty subjects were treated with high-flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy. They consisted of a mixed population with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbation, acute cardiogenic pulmonary edema, and postoperative and postextubation respiratory failure. A nonsignificant improvement was observed in respiratory rate (28.0 ± 0.9 versus 24.3 ± 1.5, p = 0.22), which was apparent in the first four hours of treatment. The pH improved, although normal levels were only reached after 24 hours on high-flow nasal cannula therapy (7.28 ± 0.02 versus 7.37 ± 0.01, p = 0.02). The rate of nonresponders was 13.3% (4 subjects), of whom one needed and accepted noninvasive mechanical ventilation and three required intubation. Intensive care unit mortality was 3.3% (1 subject), and a patient died after discharge to the ward (hospital mortality of 6.6%).
High-flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy is effective for moderate hypercapnic respiratory failure as it helps normalize clinical and gas exchange levels with an acceptable rate of nonresponders who require ventilatory support.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(1):34-38
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190004
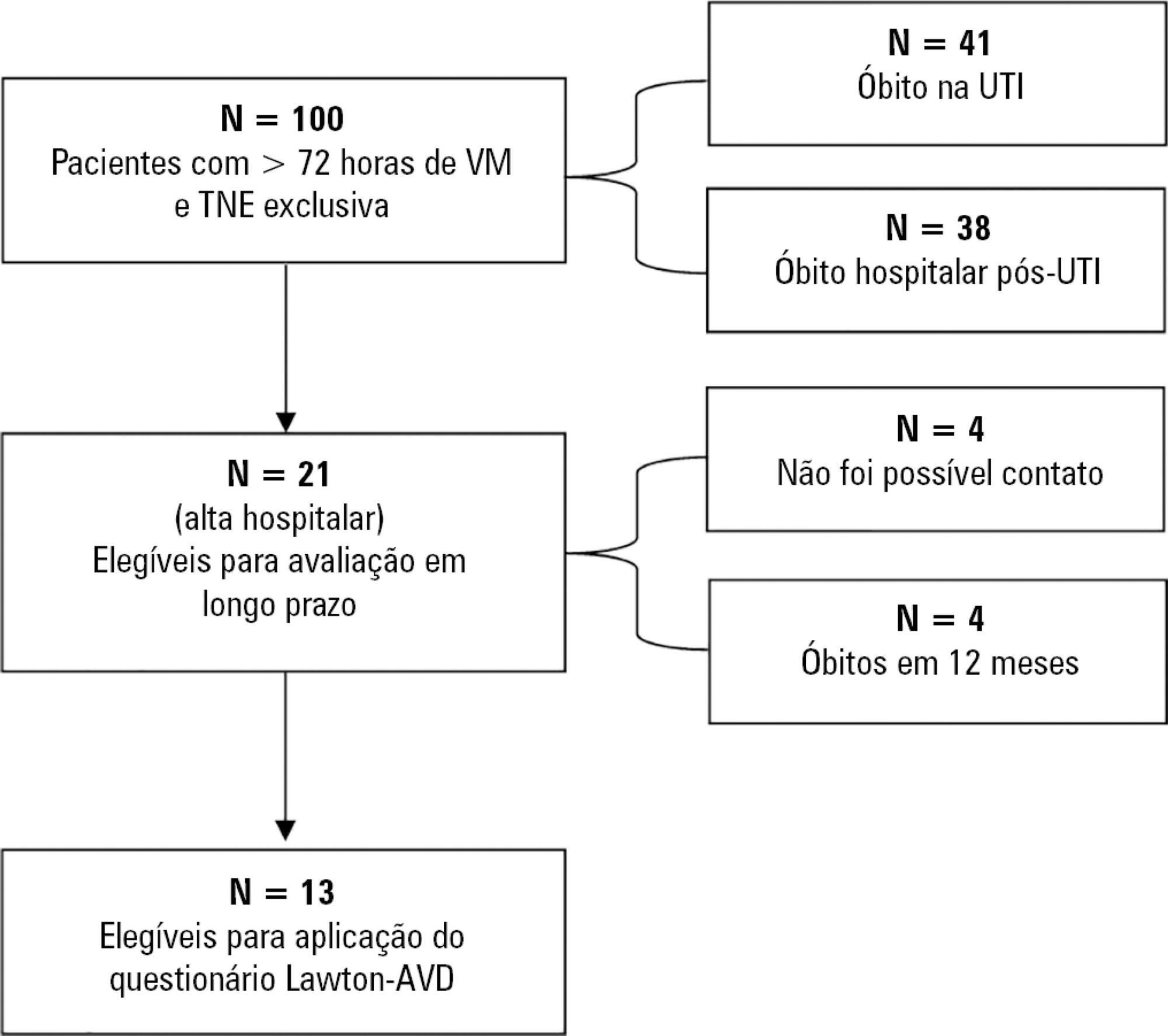
To correlate short-term (duration of mechanical ventilation and length of intensive care unit stay) and long-term (functional capacity) clinical outcomes of patients who reached nutritional adequacy ≥ 70% of predicted in the first 72 hours of hospitalization in the intensive care unit.
This was a prospective observational pilot study conducted in an 18-bed intensive care unit. A total of 100 mechanically ventilated patients receiving exclusive enteral nutritional support and receiving intensive care for more than 72 hours were included. Patients who never received enteral nutrition, those with spinal cord trauma, pregnant women, organ donors and cases of family refusal were excluded. The variables studied were nutritional adequacy ≥ 70% of predicted in the first 72 hours of hospitalization, length of intensive care unit stay, duration of mechanical ventilation and the ability to perform activities of daily living after 12 months, assessed via telephone contact using the Lawton Activities of Daily Living Scale.
The mean duration of mechanical ventilation was 18 ± 9 days, and the mean intensive care unit length of stay was 19 ± 8 days. Only 45% of the patients received more than 70% of the target nutrition in 72 hours. There was no association between nutritional adequacy and short-term (duration of mechanical ventilation, length of stay in the intensive care unit and mortality) or long-term (functional capacity and mortality) clinical outcomes.
Critically ill patients receiving caloric intake ≥ 70% in the first 72 hours of hospitalization did not present better outcomes in the short term or after 1 year.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(1):106-110
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190015
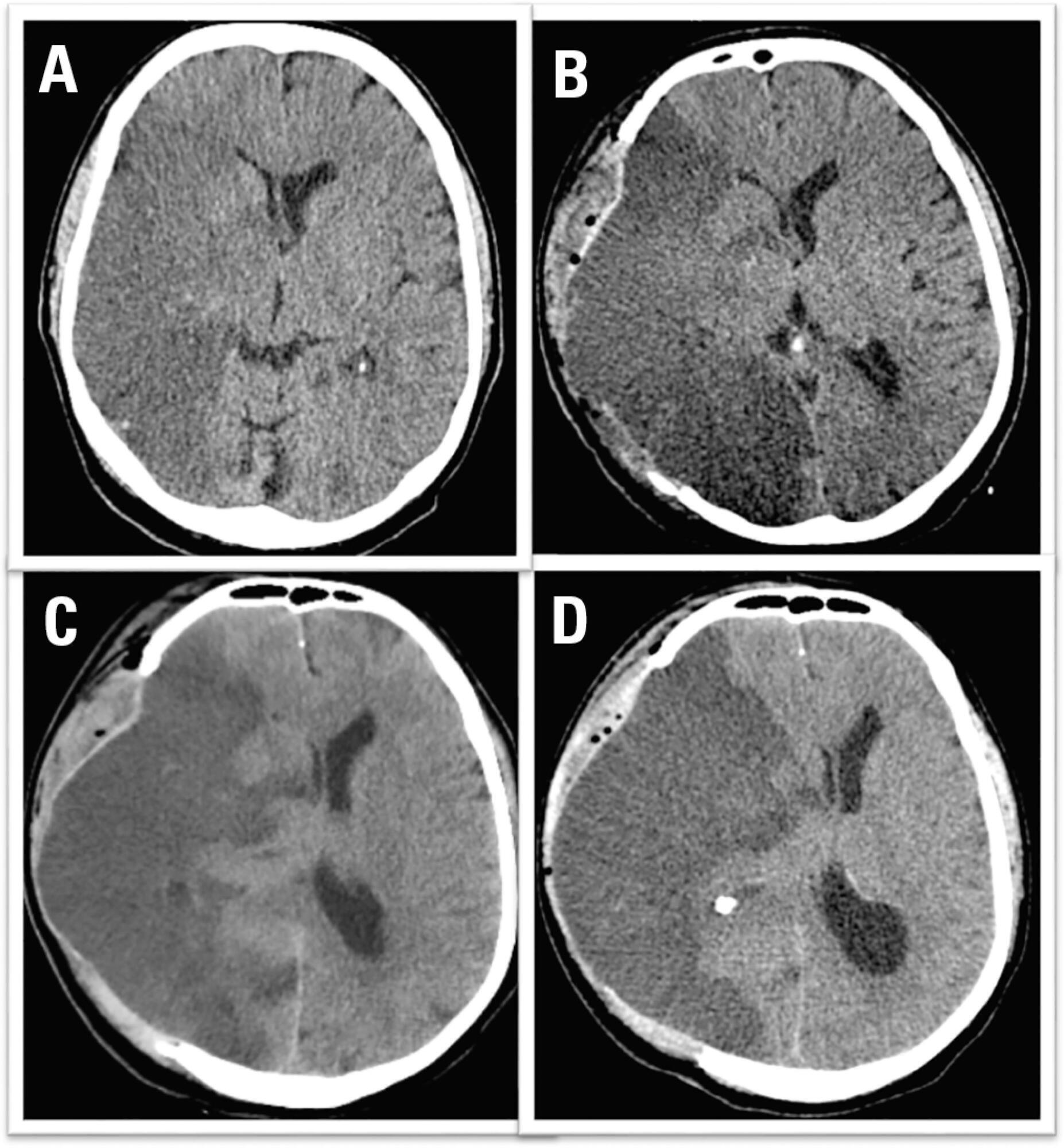
We report the case of a patient in whom brain death was suspected and associated with atelectasis and moderate to severe hypoxemia even though the patient was subjected to protective ventilation, a closed tracheal suction system, positive end-expiratory pressure, and recruitment maneuvers. Faced with the failure to obtain an adequate partial pressure of oxygen for the apnea test, we elected to place the patient in a prone position, use higher positive end-expiratory pressure, perform a new recruitment maneuver, and ventilate with a higher tidal volume (8mL/kg) without exceeding the plateau pressure of 30cmH2O. The apnea test was performed with the patient in a prone position, with continuous positive airway pressure coupled with a T-piece. The delay in diagnosis was 10 hours, and organ donation was not possible due to circulatory arrest. This report demonstrates the difficulties in obtaining higher levels of the partial pressure of oxygen for the apnea test. The delays in the diagnosis of brain death and in the organ donation process are discussed, as well as potential strategies to optimize the partial pressure of oxygen to perform the apnea test according to the current recommendations.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2018;30(3):294-300
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20180046
To determine the risk factors for extubation failure in the intensive care unit.
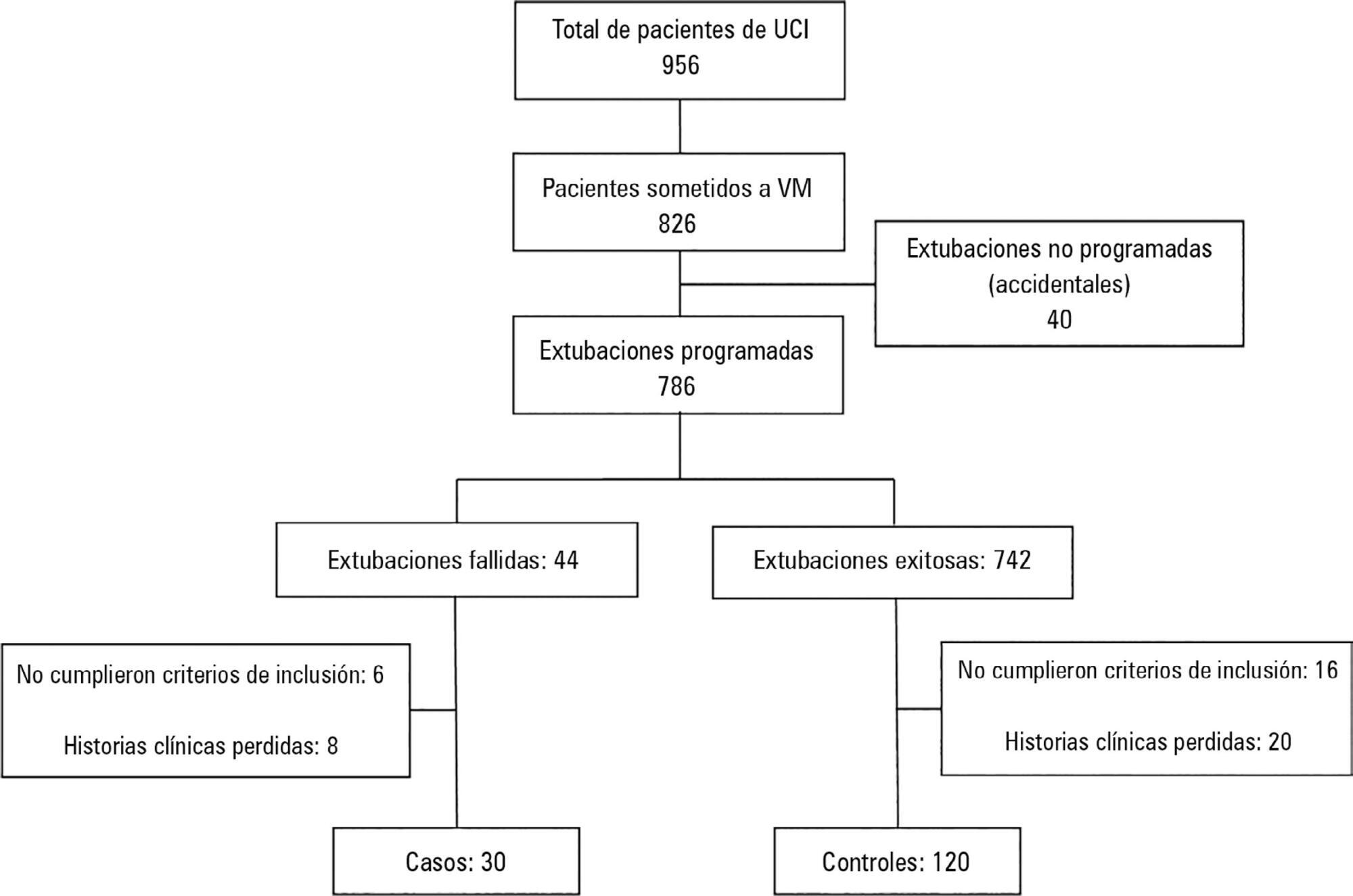
The present case-control study was conducted in an intensive care unit. Failed extubations were used as cases, while successful extubations were used as controls. Extubation failure was defined as reintubation being required within the first 48 hours of extubation.
Out of a total of 956 patients who were admitted to the intensive care unit, 826 were subjected to mechanical ventilation (86%). There were 30 failed extubations and 120 successful extubations. The proportion of failed extubations was 5.32%. The risk factors found for failed extubations were a prolonged length of mechanical ventilation of greater than 7 days (OR = 3.84, 95%CI = 1.01 - 14.56, p = 0.04), time in the intensive care unit (OR = 1.04, 95%CI = 1.00 - 1.09, p = 0.03) and the use of sedatives for longer than 5 days (OR = 4.81, 95%CI = 1.28 - 18.02; p = 0.02).
Pediatric patients on mechanical ventilation were at greater risk of failed extubation if they spent more time in the intensive care unit and if they were subjected to prolonged mechanical ventilation (longer than 7 days) or greater amounts of sedative use.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2018;30(2):208-218
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20180038
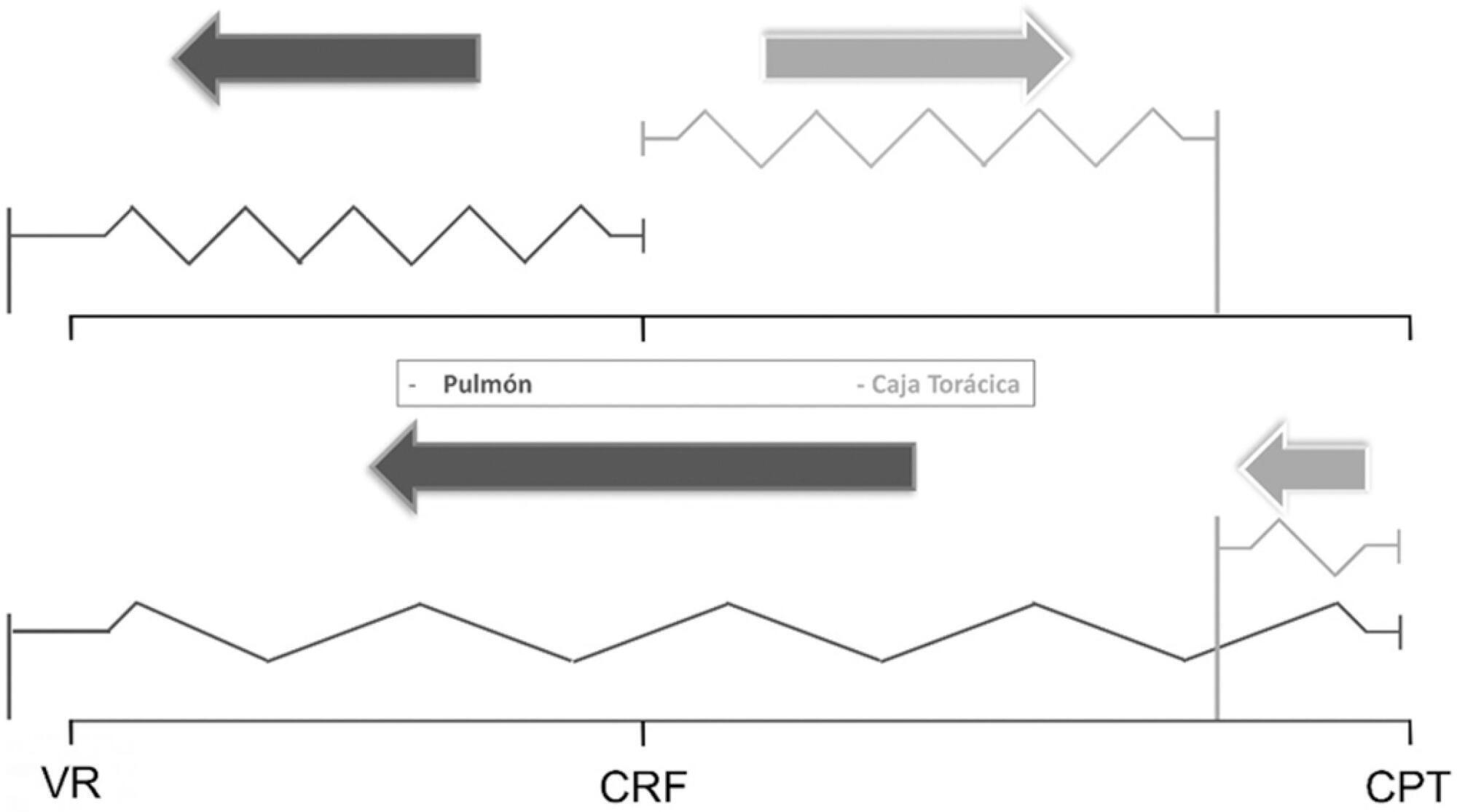
The respiratory system mechanics depend on the characteristics of the lung and chest wall and their interaction. In patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome under mechanical ventilation, the monitoring of airway plateau pressure is fundamental given its prognostic value and its capacity to assess pulmonary stress. However, its validity can be affected by changes in mechanical characteristics of the chest wall, and it provides no data to correctly titrate positive end-expiratory pressure by restoring lung volume. The chest wall effect on respiratory mechanics in acute respiratory distress syndrome has not been completely described, and it has likely been overestimated, which may lead to erroneous decision making. The load imposed by the chest wall is negligible when the respiratory system is insufflated with positive end-expiratory pressure. Under dynamic conditions, moving this structure demands a pressure change whose magnitude is related to its mechanical characteristics, and this load remains constant regardless of the volume from which it is insufflated. Thus, changes in airway pressure reflect changes in the lung mechanical conditions. Advanced monitoring could be reserved for patients with increased intra-abdominal pressure in whom a protective mechanical ventilation strategy cannot be implemented. The estimates of alveolar recruitment based on respiratory system mechanics could reflect differences in chest wall response to insufflation and not actual alveolar recruitment.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2018;30(2):187-194
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20180037
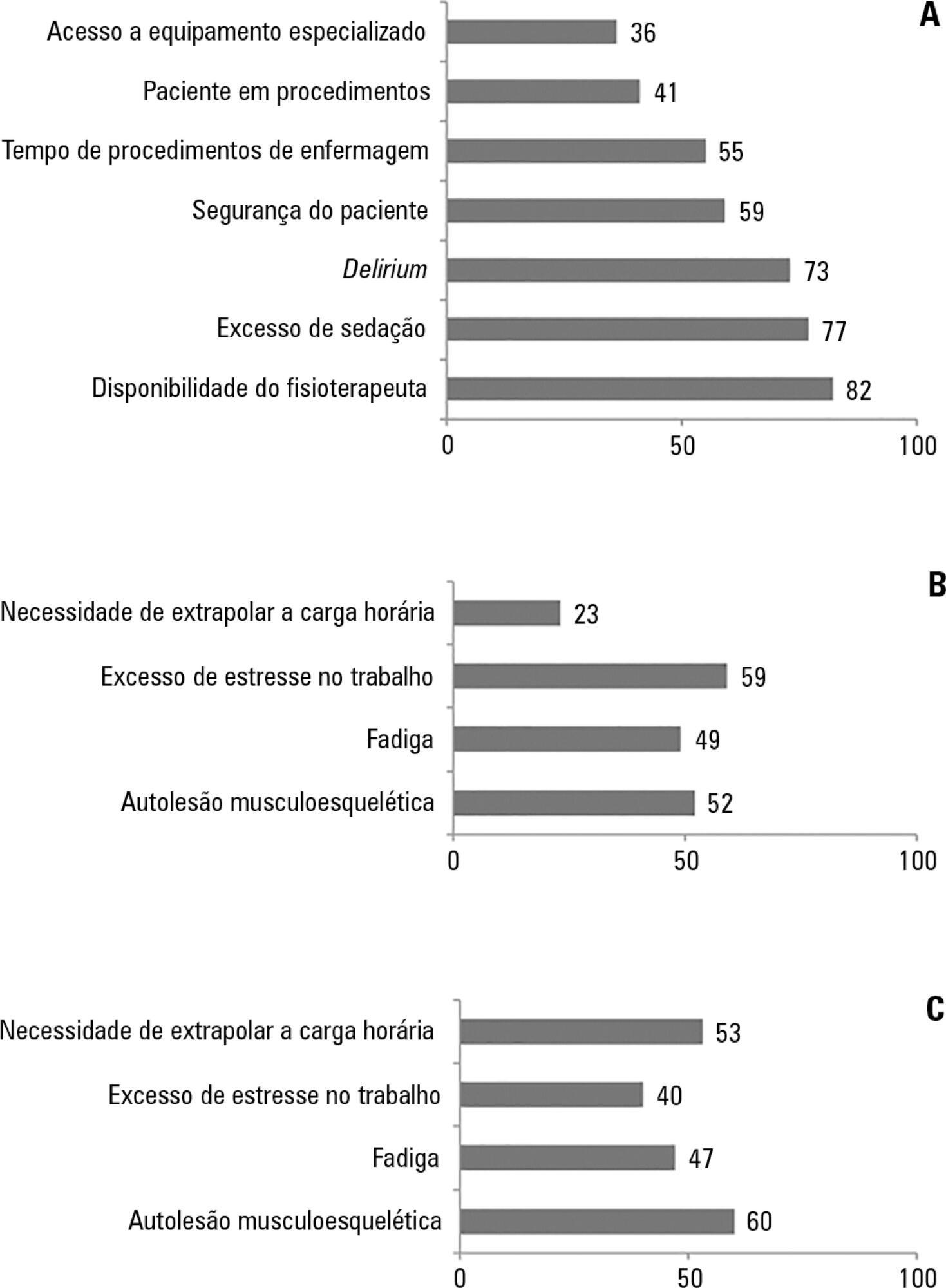
To investigate the knowledge of multi-professional staff members about the early mobilization of critically ill adult patients and identify attitudes and perceived barriers to its application.
A cross-sectional study was conducted during the second semester of 2016 with physicians, nursing professionals and physical therapists from six intensive care units at two teaching hospitals. Questions were answered on a 5-point Likert scale and analyzed as proportions of professionals who agreed or disagreed with statements. The chi-square and Fisher's exact tests were used to investigate differences in the responses according to educational/training level, previous experience with early mobilization and years of experience in intensive care units.
The questionnaire was answered by 98 out of 514 professionals (response rate: 19%). The acknowledged benefits of early mobilization were maintenance of muscle strength (53%) and shortened length of mechanical ventilation (83%). Favorable attitudes toward early mobilization included recognition that its benefits for patients under mechanical ventilation exceed the risks for both patients and staff, that early mobilization should be routinely performed via nursing and physical therapy protocols, and readiness to change the parameters of mechanical ventilation and reduce sedation to facilitate the early mobilization of patients. The main barriers mentioned were the unavailability of professionals and time to mobilize patients, excessive sedation, delirium, risk of musculoskeletal self-injury and excessive stress at work.
The participants were aware of the benefits of early mobilization and manifested attitudes favorable to its application. However, the actual performance of early mobilization was perceived as a challenge, mainly due to the lack of professionals and time, excessive sedation, delirium, risk of musculoskeletal self-injury and excessive stress at work.