Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2013;25(4):290-296
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20130050
Acute kidney injury is a common complication in critically ill patients, and the RIFLE, AKIN and KDIGO criteria are used to classify these patients. The present study's aim was to compare these criteria as predictors of mortality in critically ill patients.
Prospective cohort study using medical records as the source of data. All patients admitted to the intensive care unit were included. The exclusion criteria were hospitalization for less than 24 hours and death. Patients were followed until discharge or death. Student's t test, chi-squared analysis, a multivariate logistic regression and ROC curves were used for the data analysis.
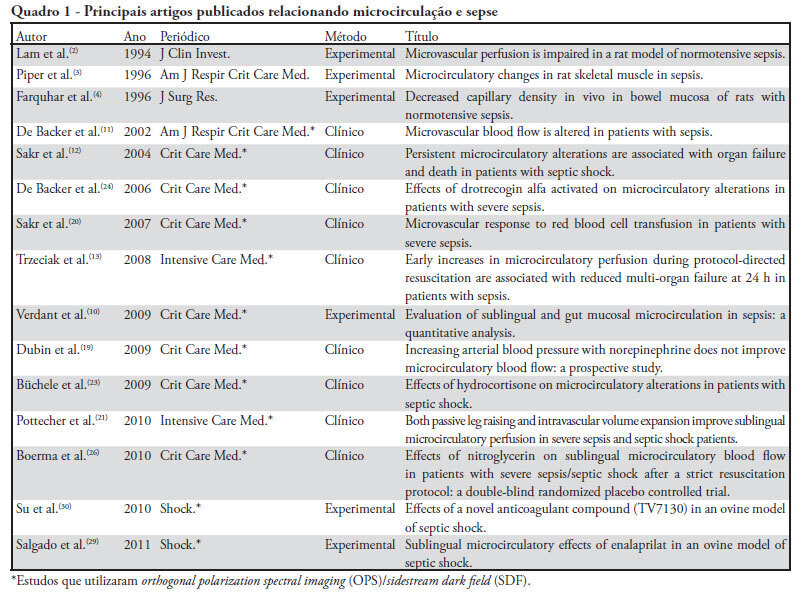
The mean patient age was 64 years old, and the majority of patients were women of African descent. According to RIFLE, the mortality rates were 17.74%, 22.58%, 24.19% and 35.48% for patients without acute kidney injury (AKI) in stages of Risk, Injury and Failure, respectively. For AKIN, the mortality rates were 17.74%, 29.03%, 12.90% and 40.32% for patients without AKI and at stage I, stage II and stage III, respectively. For KDIGO 2012, the mortality rates were 17.74%, 29.03%, 11.29% and 41.94% for patients without AKI and at stage I, stage II and stage III, respectively. All three classification systems showed similar ROC curves for mortality.
The RIFLE, AKIN and KDIGO criteria were good tools for predicting mortality in critically ill patients with no significant difference between them.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2012;24(3):263-269
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2012000300010
OBJECTIVE: This study evaluated the relationship between nutritional intake and protein and caloric requirements and observed clinical outcomes on the 7th day of intensive care unit stay. METHODS: This was a retrospective cohort study of 126 patients who were admitted to the intensive care unit for >7 days. The patients were categorized according to the adequacy of energy and protein intake in relation to requirements (a >60% Adequate Intake Group and a <60% Inadequate Intake Group). The length of stay, ventilator free time and mortality in the intensive care unit and hospital were evaluated. RESULTS: Enteral nutrition was used in 95.6% of the 126 included patients, and nutrition was initiated 41 hours after admission to the intensive care unit. The adequacy of intake was 84% for energy and 72.5% for protein. No differences in the length of stay [16 (11-23) versus 15 (11-21) days, p=0.862], ventilator free time [2 (0-7) versus 3 (0-6) days, p=0.985] or mortality in the intensive care unit [12 (41.4%) versus 38 (39.1%), p=0.831] and hospital [15 (51.7%) versus 44 (45.4%), p=0.348] were observed between the adequate and inadequate energy intake groups, respectively. Similar results in protein intake and the length of hospital stay [15 (12-21) versus 15 (11-21) days, p=0.996], ventilator free time [2 (0-7) versus 3 (0-6) days, p=0.846], and mortality in the intensive care unit [15 (28.3%) versus 35 (47.9%), p=0.536)] and hospital [18 (52.9%) versus 41 (44.6%), p=0.262] were observed between groups. CONCLUSION: The results did not establish that energy and protein intakes of greater or less than 60% of nutritional requirements were reliable dividers of clinical outcomes.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2012;24(3):246-251
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2012000300007
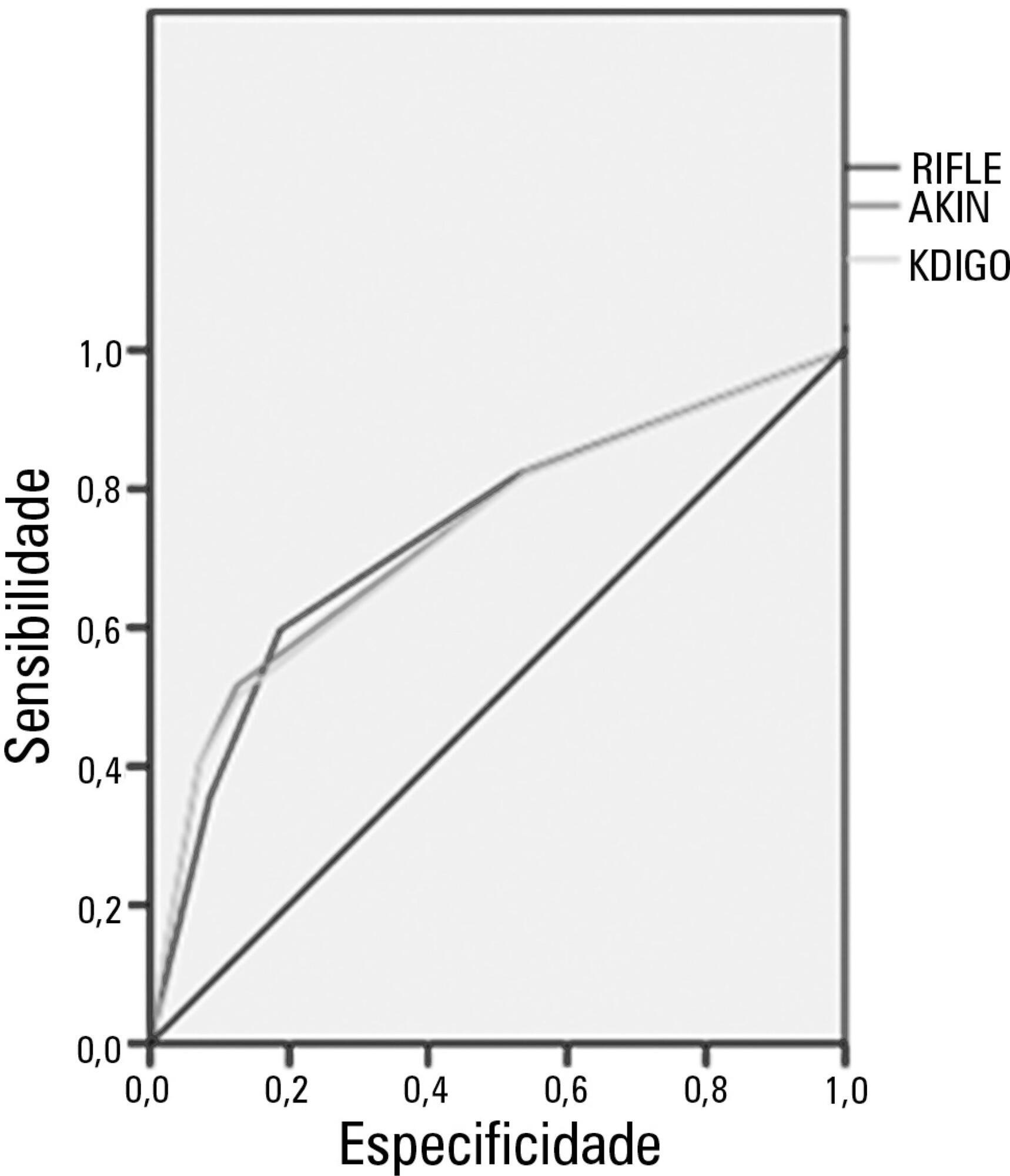
OBJECTIVE: This study compared the general and specific severity indices to assess the prognosis of severe acute pancreatitis at a polyvalent intensive care unit. METHODS: This retrospective study included 108 patients who were diagnosed with severe acute pancreatitis from July 1, 1999 to March 31, 2012. Their demographic and clinical data were collected, and the following severity indices were calculated: Ranson, Osborne, Blamey and Imrie, Balthazar, POP, APACHE II, SAPS II, and SOFA. The discriminative power of these indices with regard to mortality at the intensive care unit and hospital was assessed using the area under the ROC curve. RESULTS: The demographic data of the surviving and deceased patients did not significantly differ at baseline. The mortality rates were 27% and 39% at the intensive care unit and hospital, respectively. The severity indices that exhibited the greatest discriminative power with regard to mortality at the intensive care unit and hospital were the POP 0, POP 24, SOFA (at admission, 24 hours, 48 hours, and discharge), SAPS II, and APACHE II. CONCLUSION: The POP performed better than the other indices (aROC>0.8) at admission and 24 hours later (as originally described). The general physiological dysfunction indices also exhibited reasonable discriminative power (aROC=0.75-0.8), which was unlike the remaining pancreatitis specific indices, whose discriminative power was lower.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2012;24(2):143-150
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2012000200008
OBJECTIVE: To determine the prevalence of infections in Brazilian intensive care units and the associated mortality by analyzing the data obtained in the Extended Prevalence of Infection in Intensive Care (EPIC II) study. METHODS: EPIC II was a multicenter, international, cross-sectional prospective study of infection prevalence. It described the demographic, physiological, bacteriological, and therapeutic characteristics, outcome up to the 60th day, prevalence of infection, and mortality of all the patients admitted to the participating ICUs between zero hour and midnight on May 8, 2007. A total of 14,414 patients were included in the original study. Of these 14,414 patients, 1,235 were Brazilian and were hospitalized in 90 Brazilian ICUs. They represent the focus of this study. RESULTS: Among these 1,235 Brazilian patients, 61,6% had an infection on the day of the trial, and the lungs were the main site of infection (71.2%). Half of the patients had positive cultures, predominantly gram-negative bacilli (72%). On the day of the study, the median SOFA score was 5 (3-8) and the median SAPS II score was 36 (26-47). The infected patients had SOFA scores significantly higher than those of the non-infected patients 6 (4-9) and 3 (2-6), respectively). The overall ICU mortality rate was 28.4%: 37.6% in the infected patients, and 13.2% in the non-infected patients (p<0.001). Similarly, the in-hospital mortality rate was 34.2%, with a higher rate in the infected than in the non-infected patients (44.2% vs. 17.7%) (p<0.001). In the multivariate analysis, the main factors associated with infection incidence were emergency surgery (OR 2.89, 95%CI [1.72-4.86], p<0.001), mechanical ventilation (OR 2.06, 95% CI [1.5-2.82], p<0.001), and the SAPS II score (OR 1.04, 95% CI [1.03-1.06], p<0.001). The main factors related to mortality were ICC functional class III/ IV (OR 3.0, 95% CI [1.51-5.98], p<0.01), diabetes mellitus (OR 0.48, 95% CI [0.25-0.95], p<0.03), cirrhosis (OR 4.62, 95% CI [1.47-14,5], p<0.01), male gender (OR 0.68, 95% CI [0.46-1.0], p<0.05), mechanical ventilation (OR 1.87, 95% CI [1.19-2.95], p<0.01), hemodialysis (OR 1.98, 95% CI [1.05-3.75], p<0.03), and the SAPS II score (OR 1.08, 95% CI [1.06-1.10], p<0.001). CONCLUSION: The present study revealed a higher prevalence of infections in Brazilian ICUs than has been previously reported. There was a clear association between infection and mortality.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2011;23(3):304-311
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2011000300008
OBJECTIVES: Ascending aortic dissection has a poor prognosis if it is not promptly corrected surgically. Even with surgical correction, postoperative management is feared because of its complicated course. Our aim was to describe the incidence of postoperative complications and identify the 1 and 6-month mortality rate of our ascending aortic dissection surgical cohort. Secondarily, a comparison was made between ascending aortic dissection patients and paired-matched patients who received urgent coronary artery bypass graft surgery. METHODS: A retrospective analysis of a prospectively-collected database from February 2005 through June 2008 revealed 12 ascending aortic dissection and 10 elective ascending aortic aneurysm repair patients. These patients were analyzed for demographic and perioperative characteristics. Ascending aortic dissection patients were compared to paired-matched coronary artery bypass graft surgery patients according to age (± 3 years), gender, elective/urgent procedure and surgical team. The main outcome was in-hospital morbidity, defined by postoperative complications, intensive care unit admission and hospital length of stay. RESULTS: Twenty-two patients received operations to correct ascending aortic dissections and ascending aortic aneurysms, while 246 patients received coronary artery bypass graft surgeries. Ascending aortic dissection patients were notably similar to ascending aortic aneurysm brackets, except for longer mechanical ventilation times and lengths of stay in the hospital. After matching coronary artery bypass graft surgery patients to an ascending aortic dissection group, the following significantly worse results were found for the Aorta group: higher incidence of postoperative complications (91% vs. 45%, p=0.03), and longer hospital length of stay (19 [11-41] vs. 12.5 [8.5-13] days, p=0.05). No difference in mortality was found at the 1-month (8.3%) or 6-month (16.6%) postoperative care date. CONCLUSION: Ascending aortic dissection correction is associated with an increased incidence of postoperative complications and an increased hospital length of stay, but 1 and 6-month mortality is similar to that of paired-matched coronary artery bypass graft surgery patients.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2011;23(3):312-320
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2011000300009
OBJECTIVE: To evaluate associations between post-operative complications in patients who survive surgery and in-hospital deaths and lengths of hospital stays of patients who undergo coronary artery bypass graft surgery METHODS: Patients who underwent coronary artery bypass graft surgery and survived the operating theater were randomly selected. Information on complications and hospital lengths of stay until hospital discharge or death were retrospectively collected based on medical records and declarations of death. These aspects were estimated according to the presence of complications, frequency of complications, mortality, relative risk and attributable population risk. Mean hospital lengths of stay were compared using Wald's statistics. RESULTS: Medical records indicating deaths in the operating theater were excluded, and 86.9% of the included records reported complications; the greatest loss of information (43.9%) was related to kidney failure. Hyperglycemia was estimated as the most frequent complication (74.6%), with an attributable risk of 31.6%. The population's attributable risks were greater than 60% for low cardiac output (77.0%), kidney failure (64.3%) and cardiorespiratory failure (60.4%). Twelve different situations were identified for paired combinations of significant differences between average post-operative hospitalization times and complications, according to the outcome of discharge or death. CONCLUSION: Several complications were identified during the postoperative period of coronary artery bypass graft surgery, with different frequencies and impacts on mortality. Control of the myocardium at the risk of ischemia, hemodynamic stabilization and volume replacement strategies may be effective for controlling mortality rates and shortening hospital lengths of stay.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2011;23(3):321-326
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2011000300010
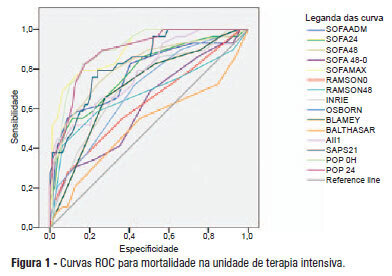
OBJECTIVE:To compare the clinical features and outcomes of patients with and without acute kidney injury in an intensive care unit of a tertiary university hospital and to identify acute kidney injury and mortality risk factors. METHODS: This was a prospective observational study of a cohort including 564 patients followed during their stay in the intensive care unit of Hospital das Clinicas da Faculdade de Medicina de Botucatu (Botucatu, São Paulo, Brazil) between May 2008 and May 2010. Patients were allocated to two different groups: with (G1) and without (G2) acute kidney injury. RESULTS: The incidence of acute kidney injury was 25.5%. The groups were different with respect to the reason for admission to the intensive care unit (sepsis, G1: 41.6% versus G2: 24.1%; P < 0.0001; neurosurgery, postoperative G1: 13.8% versus G2: 38.1%; P < 0.0001); age (G1: 56.8 ± 15.9 vs. G2: 49.8 ± 17.8 years; P < 0.0001); Acute Physiological Chronic Health Evaluation (APACHE) II score (G1: 21.9 ± 6.9 versus G2: 14.1 ± 4.6; P < 0.0001); use of mechanical ventilation (G1: 89.2% vs. G2: 69.1%; P < 0.0001) and use of vasoactive drugs (G1: 78.3% vs. G2: 56.1%; P < 0.0001). Higher rates of diabetes mellitus, congestive heart failure, chronic renal disease and use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs were more frequent in acute kidney injury patients (28.2% vs. 19.7%, P = 0.03; 23.6 vs. 11.6%, P = 0.0002; 21.5% vs. 11.5%, P < 0.0001 and 23.5% vs. 71.%, P < 0.0001, for G1 versus G2, respectively). Length of hospital stay and mortality were also higher for acute kidney injury patients (G1: 6.6 ± 2.7 days versus G2: 12.9 ±5.6 days, P < 0.0001 and G1: 62.5% versus G2: 16.4%, P < 0.0001). Multivariate analysis identified the following as risk factors for acute kidney injury: age above 55 years, APACHE II score above 16, baseline creatinine above 1.2 and use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (odds ratio (OR) = 1.36, 95% confidence interval (95%CI): 1.22 - 1.85; OR = 1.2, 95%CI: 1.11 - 1.33; OR = 5.2, 95%CI: 2.3 - 11.6 and OR = 2.15, 95%CI: 1.1 - 4.2, respectively). Acute kidney injury was independently associated with longer hospital stay and increased mortality (OR = 1.18, 95%CI: 1.05 - 1.26 and OR = 1.24, 95%CI: 1.09 - 1.99, respectively). Analysis of the survival curve 30 days after admission showed 83.3% mortality for acute kidney injury patients and 45.2% for non-acute kidney injury patients (P < 0.0001). CONCLUSION: The incidence of acute kidney injury was high in this intensive care unit; the independent risk factors associated with acute kidney injury were age > 55 years, APACHE II > 16, baseline serum creatinine > 1.2 and use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Acute kidney injury is an independent risk factor for longer intensive care unit stay and mortality.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2011;23(3):352-357
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2011000300014
The progression into multi-organ failure continues to be a common feature of sepsis and is directly related to microcirculatory dysfunction. Based on a PubMed database search using the key words microcirculation and sepsis, twenty-six articles were selected for this review. The relevant references from these articles were also selected and included in this analysis. Orthogonal polarization spectral imaging allows for the bedside assessment of the microcirculation of critically ill patients. Such imaging has established a correlation between microvascular dysfunction and patient outcomes, which allows practitioners to directly assess the effects of therapeutic interventions. However, the causal relationships between microcirculatory dysfunction, adverse outcomes, and the effects of therapies aimed at these microcirculatory changes in sepsis, are not clear.