Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2010;22(2):175-185
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2010000200012
OBJECTIVE: The avoidance of pressure ulcers development in critically ill patients is a major nursing challenge. Prevention is thus relevant for assurance of high quality care. This study aimed to evaluate the applicability of the Braden scale in intensive care unit patients. METHODS: This was a prospective study based which evaluated all adult patients staying in the intensive care unit from July 14 to August 10, 2009. The data were collected using the Braden's scale by three examiners who identified the pressure ulcer development risk. The data were analyzed using the SAS Statistical Software. For determination of the examiners' rates degree of coincidence, the Kappa value was used (95%CI). RESULTS: Regarding the related risk factors: 36.4% had mild sensory perception impairment; 50.9% had occasionally moist skin; 97.3% bedfast; 39.1% had very limited mobility; 45% probably had inappropriate nutrition; 61.8% had friction and shear problems. An agreement between the examiners was identified for nutrition and physical activity (38.1% to 100.0%); the Kappa population zero hypothesis was rejected; a paired examiners agreement (41.7% to 100.0%) was identified for the items humidity and physical activity, and the Kappa values ranged from 0.13 to 1. CONCLUSIONS: These intensive care patients were identified to have increased risk of developing pressure ulcers. This tool was considered appropriate to support the implementation of preventive measures.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2010;22(2):103-111
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2010000200002
OBJECTIVES: To assess the physician’s knowledge on intubation techniques and to identify the common practices. METHODS: This was a prospective study, involving three different intensive care units within a University hospital: Anesthesiology (ANEST), Pulmonology (PULMO) and Emergency Department (ED). All physicians working in these units and consenting to participate in the study completed a questionnaire with their demographic data and questions on orotracheal intubation. RESULTS: 85 completed questionnaires were retrieved (90.42% of the physicians). ANEST had the higher mean age (p=0.001), being 43.5% of them intensivists. The use of hypnotic and opioid association was reported by 97.6%, and pre-oxygenation by 91.8%, but only 44.6% reported sub-occipital pad use, with no difference between the ICUs. On ANEST an increased neuromuscular blockade use was reported (p<0.000) as well as increased caution with full stomach (p=0.002). The rapid sequence knowledge was restricted (mean 2.20 ± 0.89), p=0.06 between the different units. The Sellick maneuver was known by 97.6%, but 72% used it inappropriately. CONCLUSIONS: Physicians knowledge on orotracheal intubation in the intensive care unit is unsatisfactory, even among qualified professionals. It is necessary to check if the responses to the questionnaire and actual clinical practices agree.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2010;22(2):133-137
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2010000200006
STUDY OBJECTIVE: Obese patients seem to have worse outcomes and more complications during intensive care unit (ICU) stay. This study describes the clinical course, complications and prognostic factors of obese patients admitted to an intensive care unit compared to a control group of nonobese patients. DESIGN: Retrospective observational study. SETTING: A 10-bed adult intensive care unit in a university-affiliated hospital. METHODS: All patients admitted to the intensive care unit over 52 months (April 01/2005 to November 30/2008) were included. Obese patients were defined as those with a body mass index (BMI) ≥ 30 Kg/M2. Demographic and intensive care unit related data were also collected. An clinical and demographical matching group of eutrophic patients selected from the data base as comparator for mortality and morbidity outcomes. The Mann-Whitney test was used for numeric data comparisons and the Chi Square test for categorical data comparisons. RESULTS: Two hundred nineteen patients were included. The obese group (n=73) was compared to the eutrophic group (n= 146). Most of this group BMI ranged between 30 - 35 Kg/M2. Only ten patients had body mass index ≥40 Kg/M2. Significant differences between the obese and eutrophic groups were observed in median APACHE II score (16 versus 12, respectively; p<0.05) and median intensive care unit length of stay (7 versus 5 days respectively; p<0,05). No significant differences were seen regarding risk of death, mortality rate, mechanical ventilation needs, days free of mechanical ventilation and tracheostomy rates. The observed mortality was higher than the APACHE II-predicted for both groups, but the larger differences were seen for morbid obese patients (BMI ≥40 Kg/M2). CONCLUSIONS: Obesity did not increase the mortality rate, but improved intensive care unit length of stay. The current prognostic scoring systems do not include BMI, possibly underestimating the risk of death, and other quality of care indexes in obese patients. New studies could be useful to clarify how body mass index impacts the mortality rate.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2010;22(1):64-68
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2010000100011
A sepsis staging system focused on predisposition, insult, host response and organ failure may provide a useful basis for risk stratification. Knowledge on interactions among predisposing factors, insult characteristics and host response might help us to improve our understanding on sepsis pathophysiology and allow more individual therapeutic approach. Recent clinical studies documented the clinical importance of PIRO approach for severity stratification in septic patients in intensive care unit, and also for specific conditions such as community acquired pneumonia and ventilator associated pneumonia , with a good performance for outcome prediction. In this review we describe how this new concept can be used in clinical practice and provide some insights on its usefulness to facilitate the stratification and potential for enrollment in clinical trials of sepsis therapies.

Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2010;22(1):19-26
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2010000100005
OBJECTIVE: To identify risk factors associated with death of infants admitted to neonatal intensive care unit of Taubaté University Hospital. METHODS: It is a longitudinal study with information obtained from medical records of newborns admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit of Taubaté University Hospital. Type of outcome, discharge or death, was dependent variable. The independent variables were maternal and gestational variables: maternal age, hypertension, diabetes, corticosteroid therapy and delivery; variables of the newborn: birth weight, gestation length, Apgar score in the first and fifth minutes of life, multiple birth, congenital malformations and sex; hospitalar variables: report of mechanical ventilation, positive pressure ventilation, reports of prolonged parenteral nutrition, sepsis, intubation, cardiac massage, phototherapy, hyaline membrane disease, oxygen and fraction of inspired oxygen. It was built a model in three hierarchical levels for the survival analysis by the Cox model; it was used the software Stata v9 and the final model contained variables with p <0.05. The risks were estimated by measure effect known as hazard ratio (HR) with confidence intervals of 95%. The newborns transferred during hospitalization to another service were excluded from the study. RESULTS: There were admitted during the study period 495 newborns, with 129 deaths (26.1%). In the final model, only the variables of steroid use (HR 1.64, 95% CI 1.02-2.70), malformation (HR 1.93, CI 95% 1,05-2,88), very low birth weight (HR 4.28, 95% CI 2,79-6,57) and Apgar scores lower than seven of no1 min (HR 1.87, 95% CI 1,19-2,93) and 5 min (HR 1.74, 95% CI 1,05-2,88) and the variables phototherapy (HR 0.34; 95% CI 0,22-0,53) and endotracheal intubation (HR 2.28, 95% CI 1 .41-3, 70). CONCLUSION: Factors related primarily to the newborn and the hospitalar internment (except therapy with corticosteroids) were identified as associated to mortality highlighting a possible protective factor of phototherapy and the risk of infants with very low birth weight.
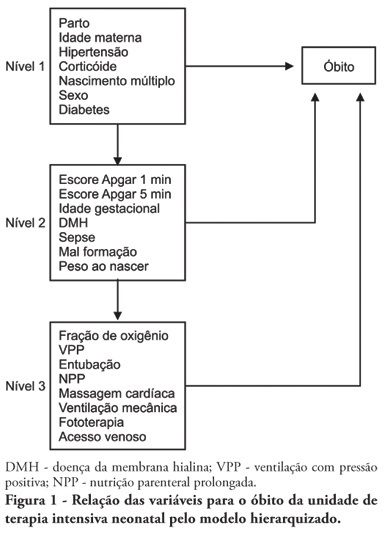
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2009;21(4):398-403
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2009000400010
OBJECTIVES: Stress-induced hyperglycemia is frequent in critically ill patients and has been associated with increased mortality and morbidity (both in diabetic and non-diabetic patients). This study objective was to evaluate the profile and long-term prognosis of critically ill patients undergoing tight glucose-control. METHODS: Prospective cohort. All patients admitted to the intensive care unit over 1-year were enrolled. We analyzed demographic data, therapeutic intervention, and short- (during the stay) and long-term (2 years after discharge) mortality. The patients were categorized in 2 groups: tight glucose control and non-tight glucose-control, based on the unit staff decision. RESULTS: From the 603 enrolled patients, 102 (16.9%) underwent tight control (glucose <150 mg/dL) while 501 patients (83.1%) non-tight control. Patients in the TGC-group were more severely ill than those in the non-tight control group [APACHE II score (14 ± 3 versus 11 ± 4, P=0.04), SOFA (4.9 ± 3.2 versus 3.5 ± 3.4, P<0.001) and TISS-24h (25.7 ± 6.9 versus 21.1 ± 7.2, P< 0.001)]. The tight control group patients also had worse prognosis: [acute renal failure (51% versus 18.5%, P<0.001), critical illness neuropathy (16.7% versus 5.6%, P<0.001)] and increased mortality (during the ICU-stay [60.7% versus 17.7%, P<0.001] and within 2-years of the discharge [77.5% versus 23.4%; P<0.001]). CONCLUSION: Critically ill patients needing tight glucose control during the unit stay have more severe disease and have worse short and long-term prognosis.
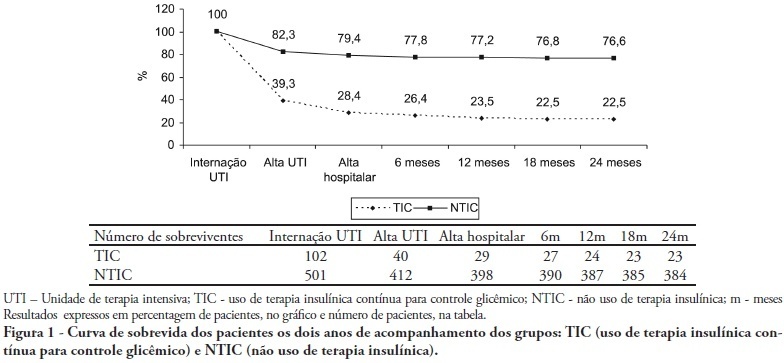
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2009;21(4):425-431
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2009000400013
Despite recent advances in diagnosis and care of critically ill patients sepsis related mortality rate remains unacceptably high. Therefore, new methods of evaluation are necessary to provide an earlier and more accurate characterization of septic patients. Based on the (oncologic) TNM system, the PIRO concept was introduced as a new staging system for sepsis in order to assess risk and predict prognosis, with potential to assist in inclusion of patients in clinical studies and estimate the probability of response of patients to specific therapeutic interventions.
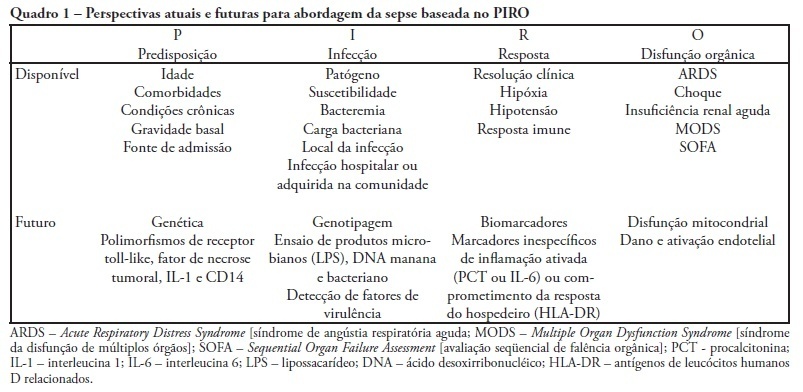
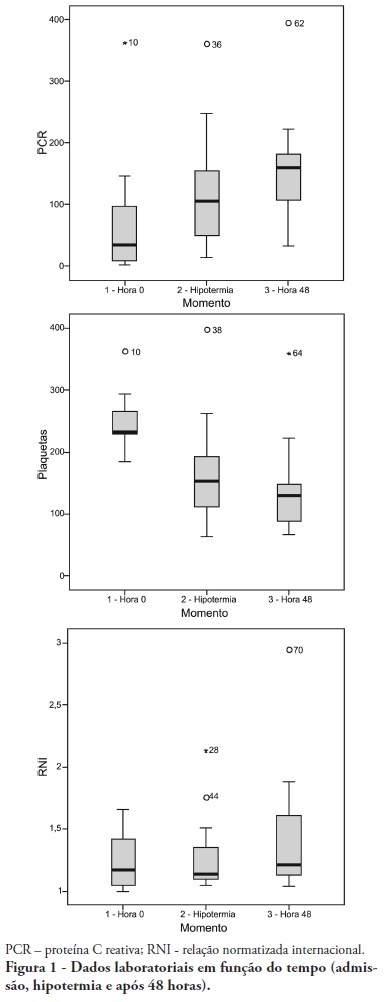
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2009;21(4):369-375
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2009000400006
OBJECTIVE: To determine the characteristics of patients undergoing standard institutional protocol for management of resuscitated patients after a cardiac arrest episode, including therapeutic hypothermia. METHODS: This was a retrospective analysis of 26 consecutive patients admitted following cardiac arrest, between January 2007 and November 2008. RESULTS: All cases underwent therapeutic hypothermia. Average age was 63 years, and the patients were predominantly male. Cardiac arrest event was out-of-hospital in 8 cases, in the emergency room in 3 cases, in the wards in 13 cases and in the operation room in 2 cases. The cardiac arrest rhythm was ventricular fibrillation in seven patients, asystolia in 11, pulseless electrical activity in 5 cases, and was undetermined in 3 patients. The interval between the cardiac arrest and return of spontaneous circulation was 12 minutes (SD ± 5 min). The time to reach the target temperature was 5 ± 4 hours, the hypothermia time was 22 ± 6 hours and time to rewarming 9 ± 5.9 hours. Fourteen patients died in the intensive care unit, a 54% mortality, and three patients died during the in-hospital stay, a 66% in-hospital mortality. There was statistically significant reduction in hemoglobin (p<0.001), leukocytes (p=0.001), platelets (p<0.001), lactate (p<0.001) and potassium (p=0.009), values and increased C reactive protein (p=0.001) and INR (p=0.004) after hypothermia. CONCLUSIONS: The creation of a standard operative protocol for therapeutic hypothermia in post cardiac arrest patients management resulted in a high use of therapeutic hypothermia. The clinical results of this protocol adapted from randomized studies are similar to the literature.