Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2024;36:e20240246en
DOI 10.62675/2965-2774.20240246-en
To discuss the strengths and limitations of ventilator-free days and to provide a comprehensive discussion of the different analytic methods for analyzing and interpreting this outcome.
Using simulations, the power of different analytical methods was assessed, namely: quantile (median) regression, cumulative logistic regression, generalized pairwise comparison, conditional approach and truncated approach. Overall, 3,000 simulations of a two-arm trial with n = 300 per arm were computed using a two-sided alternative hypothesis and a type I error rate of α = 0.05.
When considering power, median regression did not perform well in studies where the treatment effect was mainly driven by mortality. Median regression performed better in situations with a weak effect on mortality but a strong effect on duration, duration only, and moderate mortality and duration. Cumulative logistic regression was found to produce similar power to the Wilcoxon rank-sum test across all scenarios, being the best strategy for the scenarios of moderate mortality and duration, weak mortality and strong duration, and duration only.
In this study, we describe the relative power of new methods for analyzing ventilator-free days in critical care research. Our data provide validation and guidance for the use of the cumulative logistic model, median regression, generalized pairwise comparisons, and the conditional and truncated approach in specific scenarios.
Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2024;36:e20240284en
DOI 10.62675/2965-2774.20240284-en
To examine the physical function and respiratory muscle strength of patients - who recovered from critical COVID-19 – after intensive care unit discharge to the ward on Days one (D1) and seven (D7), and to investigate variables associated with functional impairment.
This was a prospective cohort study of adult patients with COVID-19 who needed invasive mechanical ventilation, non-invasive ventilation or high-flow nasal cannula and were discharged from the intensive care unit to the ward. Participants were submitted to Medical Research Council sum-score, handgrip strength, maximal inspiratory pressure, maximal expiratory pressure, and short physical performance battery tests. Participants were grouped into two groups according to their need for invasive ventilation: the Invasive Mechanical Ventilation Group (IMV Group) and the Non-Invasive Mechanical Ventilation Group (Non-IMV Group).
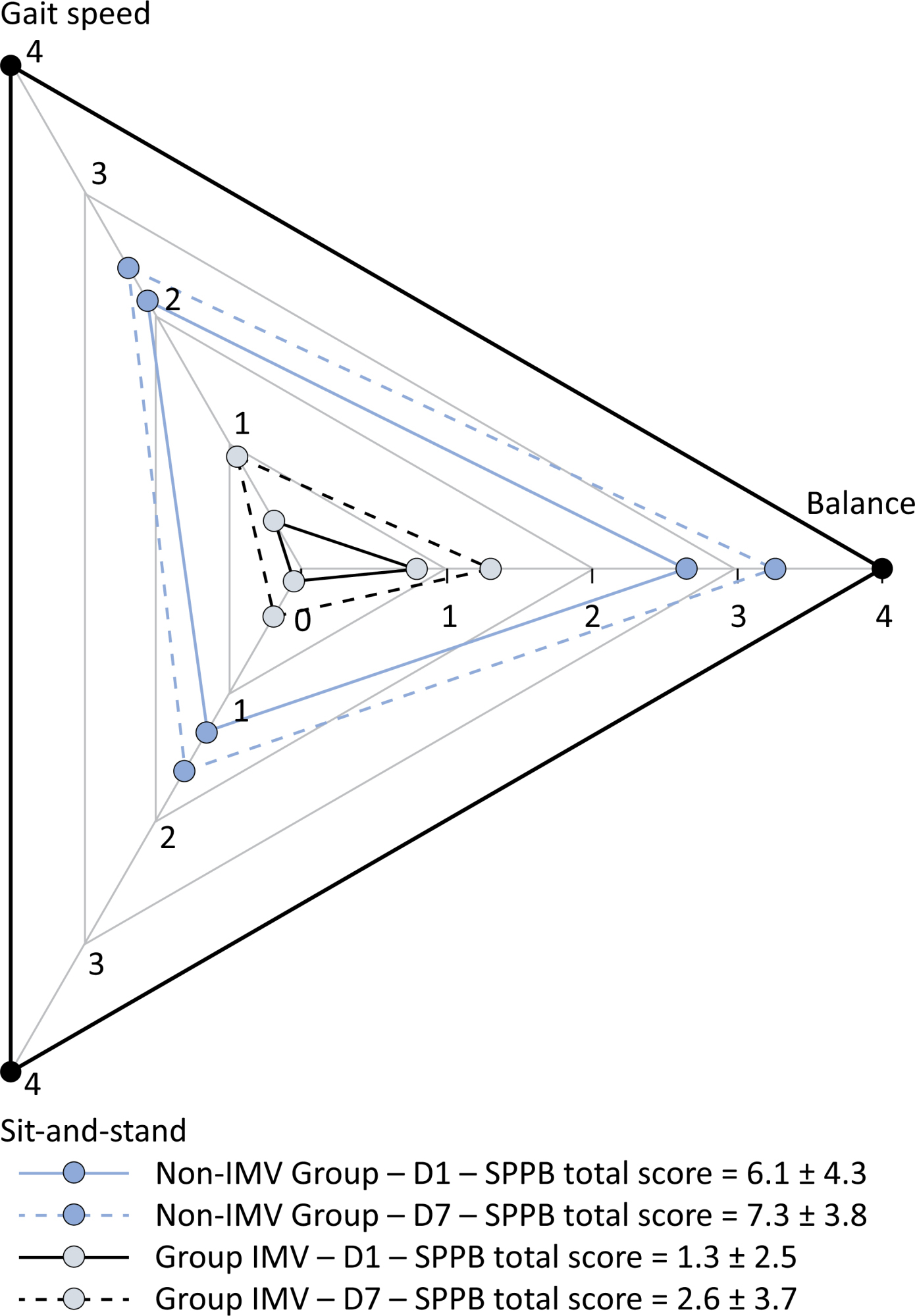
Patients in the IMV Group (n = 31) were younger and had higher Sequential Organ Failure Assessment scores than those in the Non-IMV Group (n = 33). The short physical performance battery scores (range 0 - 12) on D1 and D7 were 6.1 ± 4.3 and 7.3 ± 3.8, respectively for the Non-Invasive Mechanical Ventilation Group, and 1.3 ± 2.5 and 2.6 ± 3.7, respectively for the IMV Group. The prevalence of intensive care unit-acquired weakness on D7 was 13% for the Non-IMV Group and 72% for the IMV Group. The maximal inspiratory pressure, maximal expiratory pressure, and handgrip strength increased on D7 in both groups, but the maximal expiratory pressure and handgrip strength were still weak. Only maximal inspiratory pressure was recovered (i.e., > 80% of the predicted value) in the Non-IMV Group. Female sex, and the need and duration of invasive mechanical were independently and negatively associated with the short physical performance battery score and handgrip strength.
Patients who recovered from critical COVID-19 and who received invasive mechanical ventilation presented greater disability than those who were not invasively ventilated. However, they both showed marginal functional improvement during early recovery, regardless of the need for invasive mechanical ventilation. This might highlight the severity of disability caused by SARS-CoV-2.
Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(4):355-366
DOI 10.5935/2965-2774.20230015-pt
To compare, within a cohort of patients with acute respiratory failure, the phenotypes of patients with and without COVID-19 in the context of the pandemic and evaluate whether COVID-19 is an independent predictor of intensive care unit mortality.
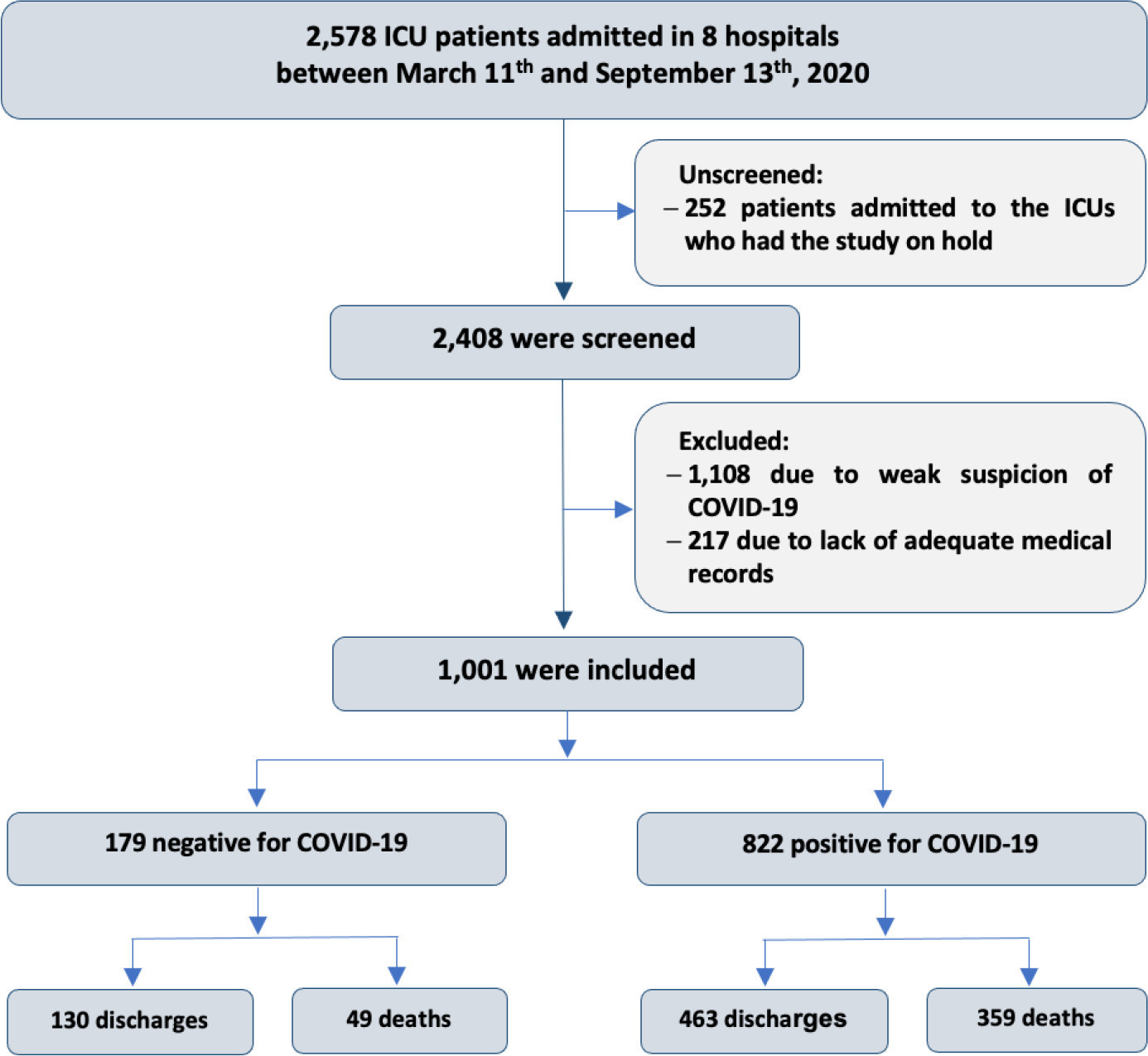
This historical cohort study evaluated 1001 acute respiratory failure patients with suspected COVID-19 admitted to the intensive care unit of 8 hospitals. Patients were classified as COVID-19 cases and non-COVID-19 cases according to real-time polymerase chain reaction results. Data on clinical and demographic characteristics were collected on intensive care unit admission, as well as daily clinical and laboratory data and intensive care unit outcomes.
Although the groups did not differ in terms of APACHE II or SOFA scores at admission, the COVID-19 group had more initial symptoms of fever, myalgia and diarrhea, had a longer duration of symptoms, and had a higher prevalence of obesity. They also had a lower PaO2/FiO2 ratio, lower platelet levels than non-COVID-19 patients, and more metabolic changes, such as higher levels of blood glucose, C-reactive protein, and lactic dehydrogenase. Patients with non-COVID-19 acute respiratory failure had a higher prevalence of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease/asthma and cardiopathy. Patients with COVID-19 stayed in the hospital longer and had more complications, such as acute kidney failure, severe acute respiratory distress syndrome and severe infection. The all-cause mortality rate was also higher in this group (43.7% in the COVID-19 group versus 27.4% in the non-COVID-19 group). The diagnosis of COVID-19 was a predictor of intensive care unit mortality (odds ratio, 2.77; 95%CI, 1.89 - 4.07; p < 0.001), regardless of age or Charlson Comorbidity Index score.
In a prospective cohort of patients admitted with acute respiratory failure, patients with COVID-19 had a clearly different phenotype and a higher mortality than non-COVID-19 patients. This may help to outline more accurate screening and appropriate and timely treatment for these patients.
Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(3):290-301
DOI 10.5935/2965-2774.20230388-pt
To determine the prevalence and factors associated with the physical rehabilitation of critically ill children in Brazilian pediatric intensive care units.
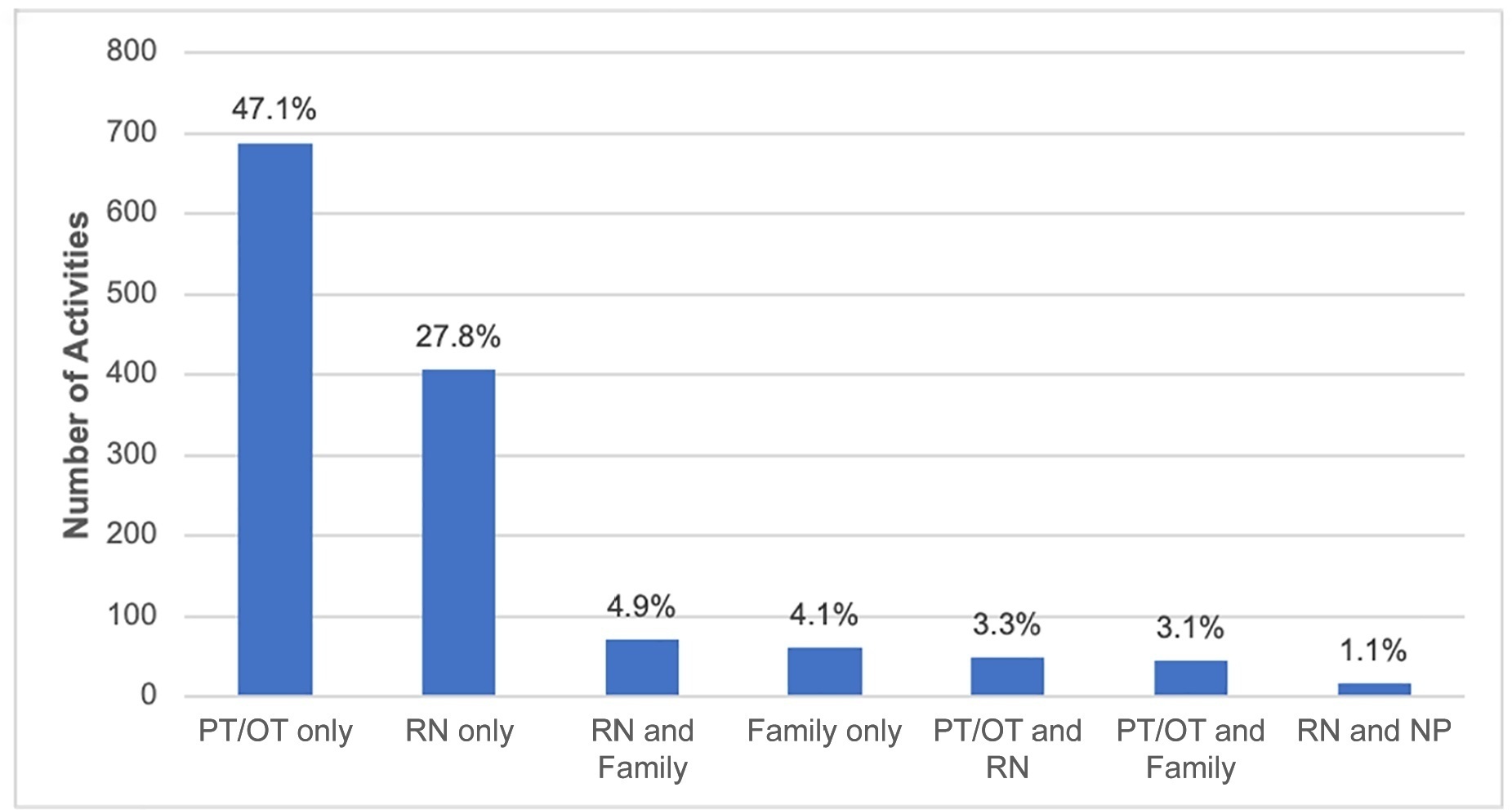
A 2-day, cross-sectional, multicenter point prevalence study comprising 27 pediatric intensive care units (out of 738) was conducted in Brazil in April and June 2019. This Brazilian study was part of a large multinational study called Prevalence of Acute Rehabilitation for Kids in the PICU (PARK-PICU). The primary outcome was the prevalence of mobility provided by physical therapy or occupational therapy. Clinical data on patient mobility, potential mobility safety events, and mobilization barriers were prospectively collected in patients admitted for ≥ 72 hours.
Children under the age of 3 years comprised 68% of the patient population. The prevalence of therapist-provided mobility was 74%, or 277 out of the 375 patient-days. Out-of-bed mobility was most positively associated with family presence (adjusted odds ratios 3.31;95%CI 1.70 - 6.43) and most negatively associated with arterial lines (adjusted odds ratios 0.16; 95%CI 0.05 - 0.57). Barriers to mobilization were reported on 27% of patient-days, the most common being lack of physician order (n = 18). Potential safety events occurred in 3% of all mobilization events.
Therapist-provided mobility in Brazilian pediatric intensive care units is frequent. Family presence was high and positively associated with out-of-bed mobility. The presence of physiotherapists 24 hours a day in Brazilian pediatric intensive care units may have a substantial impact on the mobilization of critically ill children.
Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(2):187-195
DOI 10.5935/2965-2774.20230378-pt
Evaluation of left ventricular systolic function using speckle tracking echocardiography is more sensitive than conventional echocardiographic measurement in detecting subtle left ventricular dysfunction in septic patients. Our purpose was to investigate the predictive significance of left ventricular global longitudinal strain in normotensive septic intensive care patients.
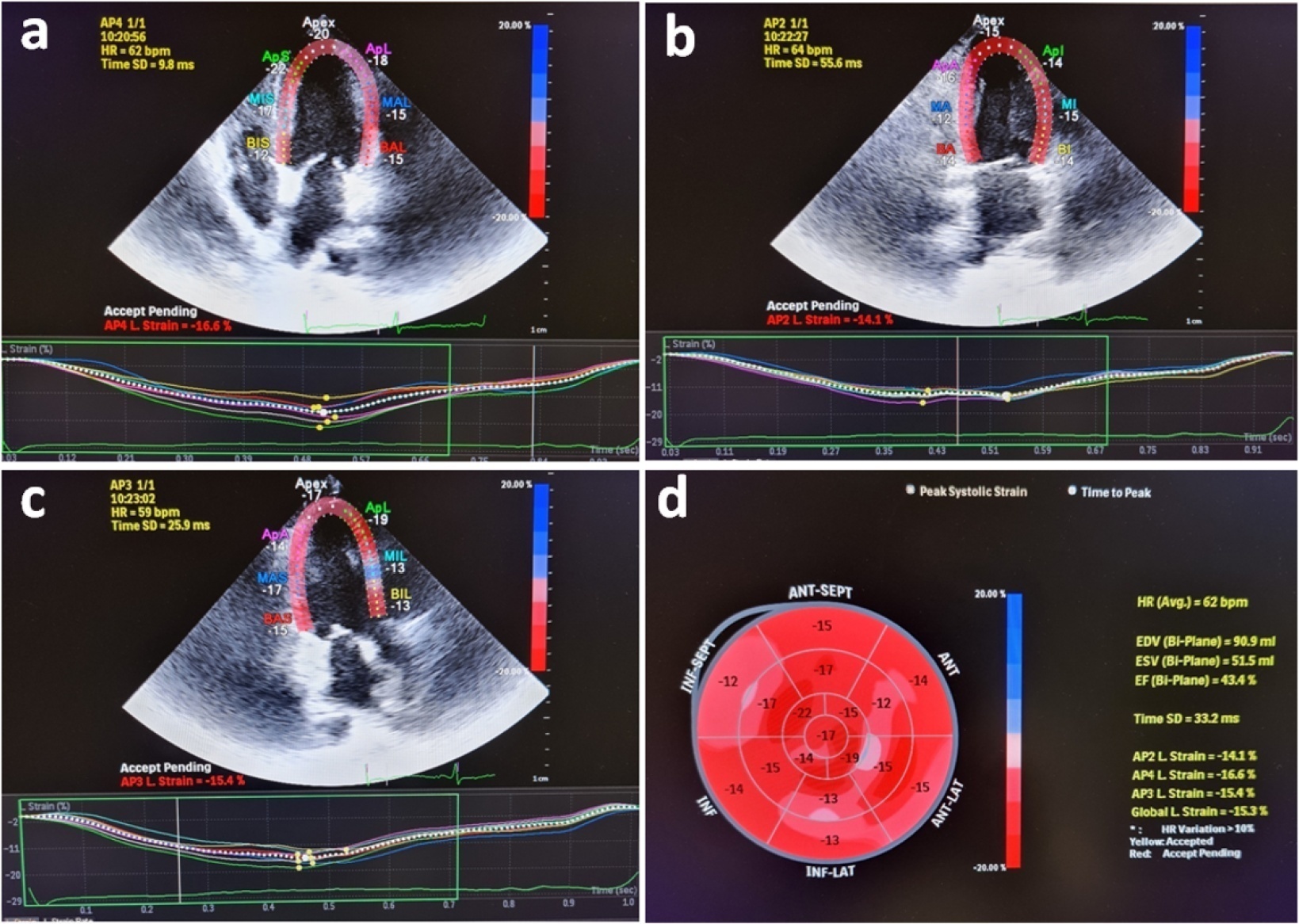
This observational, prospective cohort study included septic normotensive adults admitted to the intensive care unit between June 1, 2021, and August 31, 2021. Left ventricular systolic function was measured using speckle-tracking echocardiography within 24 hours of admission.
One hundred fifty-two patients were enrolled. The intensive care unit mortality rate was 27%. Left ventricular global longitudinal strain was less negative, which indicated worse left ventricular function in non-survivors than survivors (median [interquartile range], -15.2 [-17.2 - -12.5] versus -17.3 [-18.8 - -15.5]; p < 0.001). The optimal cutoff value for left ventricular global longitudinal strain was -17% in predicting intensive care unit mortality (area under the curve, 0.728). Patients with left ventricular global longitudinal strain > -17% (less negative than -17%, which indicated worse left ventricular function) showed a significantly higher mortality rate (39.2% versus 13.7%; p < 0.001). According to multivariate analysis, left ventricular global longitudinal strain was an independent predictor of intensive care unit mortality [OR (95%CI), 1.326 (1.038 - 1.693); p = 0.024], along with invasive mechanical ventilation and Glasgow coma scale, APACHE II, and SOFA risk scores.
Impaired left ventricular global longitudinal strain is associated with mortality and provided predictive data in normotensive septic intensive care patients.
Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(2):203-208
DOI 10.5935/2965-2774.20230274-pt
To investigate whether family participation in intensive care unit interdisciplinary bedside rounds affects family satisfaction.
A cross-sectional study was conducted at a 56-bed, adult, mixed intensive care unit of a tertiary hospital in Southern Brazil. From May to June 2019, family members of patients who stayed in the intensive care unit for at least 48 hours were invited to participate in the study at the time of patient discharge. The main exposure variable was participation in intensive care unit bedside rounds during the intensive care unit stay. Family satisfaction was assessed by using the Brazilian version of the Family Satisfaction in the Intensive Care Unit questionnaire.
Of the 234 screened individuals, 118 were included. Eleven participants withdrew consent. A total of 107 individuals were assessed; 58 (54%) reported being present during bedside rounds, and 49 (46%) reported never being present. General satisfaction and satisfaction with the decision-making process were higher among families who were present during rounds than among families who were not (p = 0.01 and p = 0.007, respectively).
The presence during interdisciplinary rounds was associated with improved general satisfaction and satisfaction with the decision-making aspect. This outcome indicates that efforts must be directed to conduct studies with more robust methodologies to confirm this association.

Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(1):2-10
DOI 10.5935/2965-2774.20230307-pt
The use of echocardiography by physicians who are not echocardiographers has become common throughout the world across highly diverse settings where the care of acutely ill patients is provided. Echocardiographic evaluation performed in a point-of-care manner can provide relevant information regarding the mechanism of causes of shock, for example, increasing the rates of correct diagnosis and allowing for faster informed decision-making than through evaluation methods. Considering that the accurate diagnosis of life-threatening situations is essential for professionals working with acutely ill patients, several international associations recommend that physicians responsible for critically ill patients acquire and develop the ability to perform bedside ultrasound examinations, including echocardiographic examinations. However, there is no consensus in the literature regarding which specific applications should be included in the list of skills for nonechocardiographer physicians. Taking into account the multiplicity of applications of echocardiography in different scenarios related to acutely ill patients; the differences in the published protocols, with regard to both the teaching methodology and competence verification; and the heterogeneity of training among highly diverse specialties responsible for their care at different levels, this consensus document aimed to reflect the position of representatives of related Brazilian medical societies on the subject and may thus serve as a starting point both for standardization among different specialties and for the transmission of knowledge and verification of the corresponding competencies.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2022;34(4):477-483
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20220280-en
To create and validate a model for predicting septic or hypovolemic shock from easily obtainable variables collected from patients at admission to an intensive care unit.
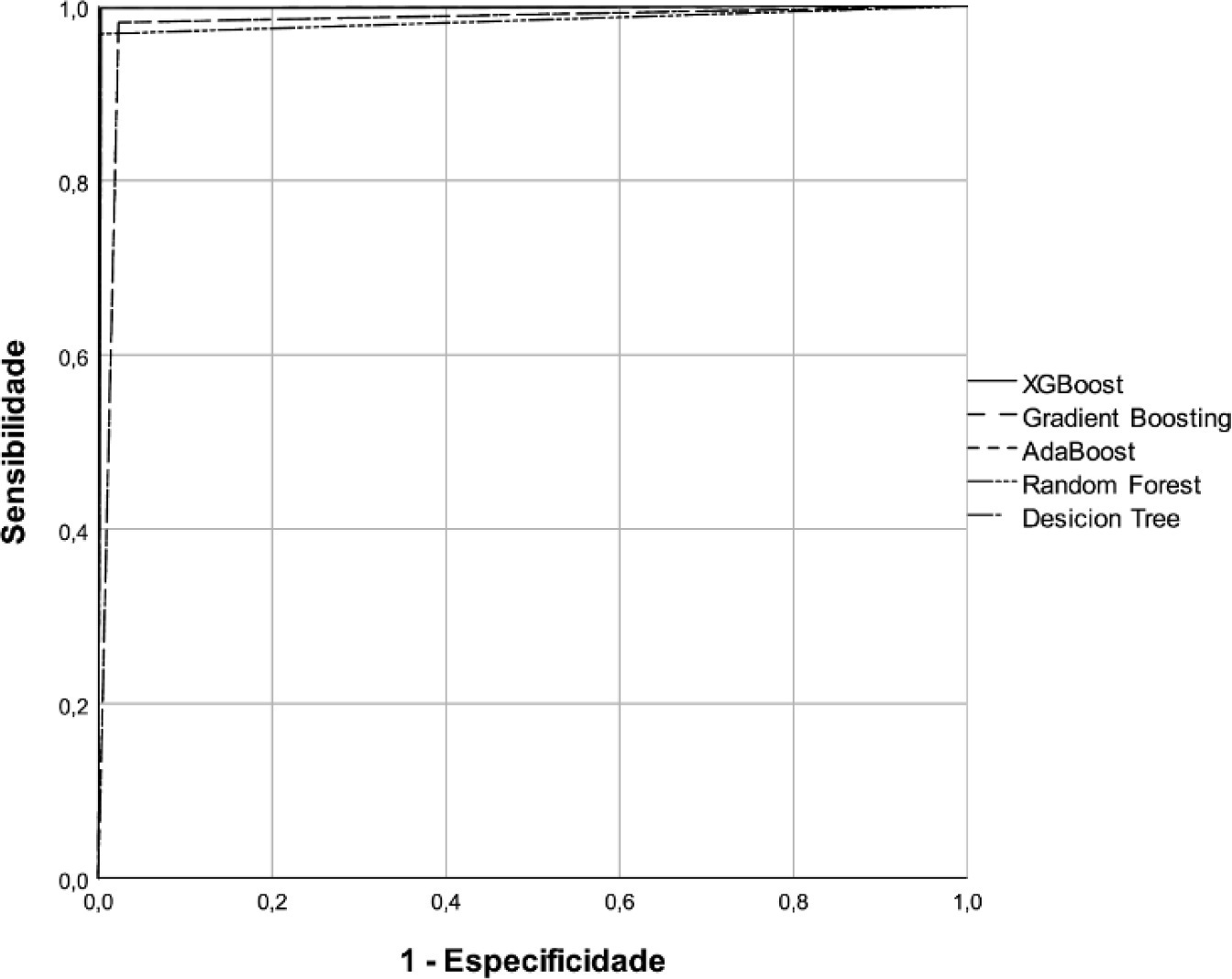
A predictive modeling study with concurrent cohort data was conducted in a hospital in the interior of northeastern Brazil. Patients aged 18 years or older who were not using vasoactive drugs on the day of admission and were hospitalized from November 2020 to July 2021 were included. The Decision Tree, Random Forest, AdaBoost, Gradient Boosting and XGBoost classification algorithms were tested for use in building the model. The validation method used was k-fold cross validation. The evaluation metrics used were recall, precision and area under the Receiver Operating Characteristic curve.
A total of 720 patients were used to create and validate the model. The models showed high predictive capacity with areas under the Receiver Operating Characteristic curve of 0.979; 0.999; 0.980; 0.998 and 1.00 for the Decision Tree, Random Forest, AdaBoost, Gradient Boosting and XGBoost algorithms, respectively.
The predictive model created and validated showed a high ability to predict septic and hypovolemic shock from the time of admission of patients to the intensive care unit.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (116) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)