Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(2):187-195
DOI 10.5935/2965-2774.20230378-pt
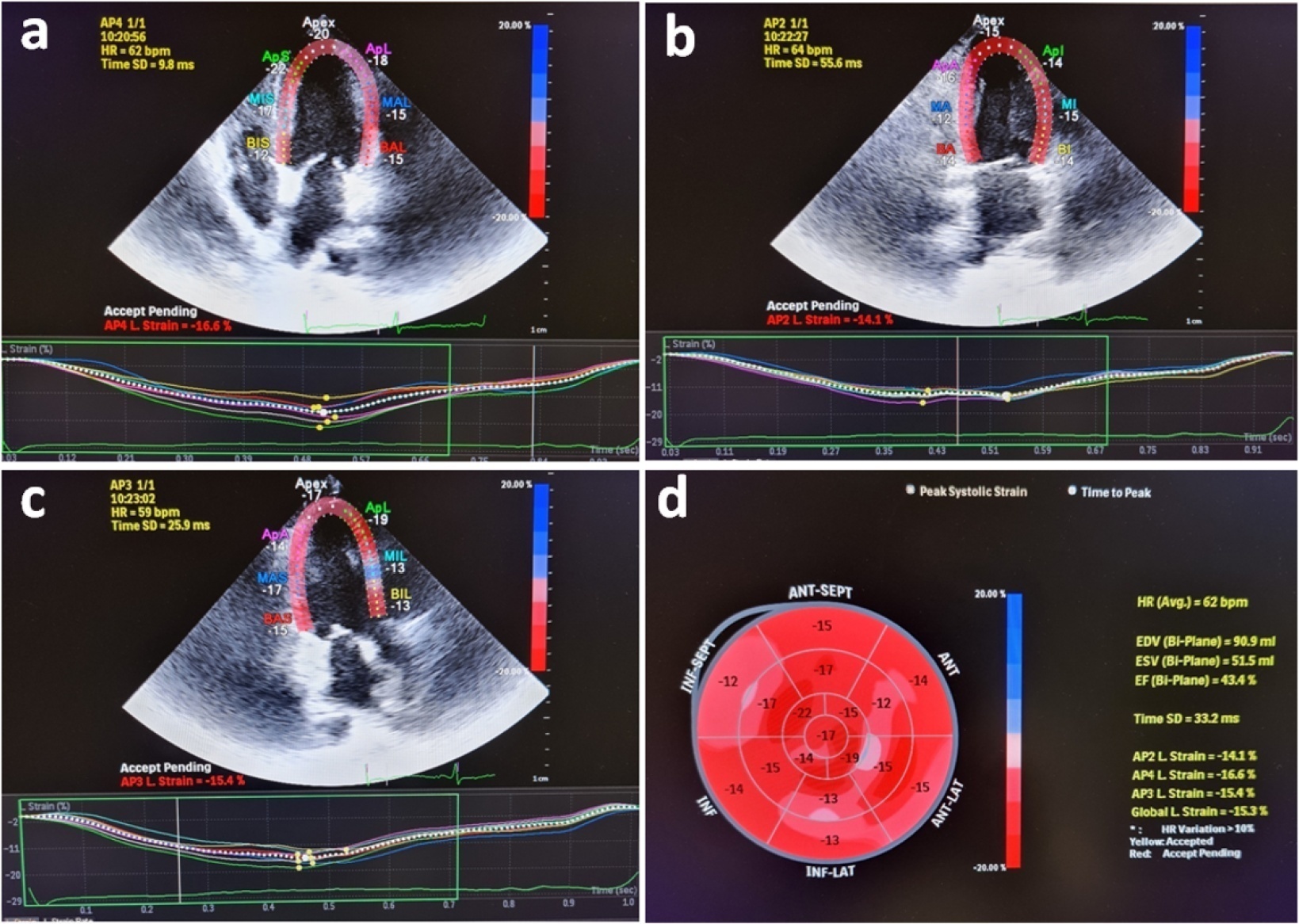
Evaluation of left ventricular systolic function using speckle tracking echocardiography is more sensitive than conventional echocardiographic measurement in detecting subtle left ventricular dysfunction in septic patients. Our purpose was to investigate the predictive significance of left ventricular global longitudinal strain in normotensive septic intensive care patients.
This observational, prospective cohort study included septic normotensive adults admitted to the intensive care unit between June 1, 2021, and August 31, 2021. Left ventricular systolic function was measured using speckle-tracking echocardiography within 24 hours of admission.
One hundred fifty-two patients were enrolled. The intensive care unit mortality rate was 27%. Left ventricular global longitudinal strain was less negative, which indicated worse left ventricular function in non-survivors than survivors (median [interquartile range], -15.2 [-17.2 - -12.5] versus -17.3 [-18.8 - -15.5]; p < 0.001). The optimal cutoff value for left ventricular global longitudinal strain was -17% in predicting intensive care unit mortality (area under the curve, 0.728). Patients with left ventricular global longitudinal strain > -17% (less negative than -17%, which indicated worse left ventricular function) showed a significantly higher mortality rate (39.2% versus 13.7%; p < 0.001). According to multivariate analysis, left ventricular global longitudinal strain was an independent predictor of intensive care unit mortality [OR (95%CI), 1.326 (1.038 - 1.693); p = 0.024], along with invasive mechanical ventilation and Glasgow coma scale, APACHE II, and SOFA risk scores.
Impaired left ventricular global longitudinal strain is associated with mortality and provided predictive data in normotensive septic intensive care patients.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(3):368-378
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190060
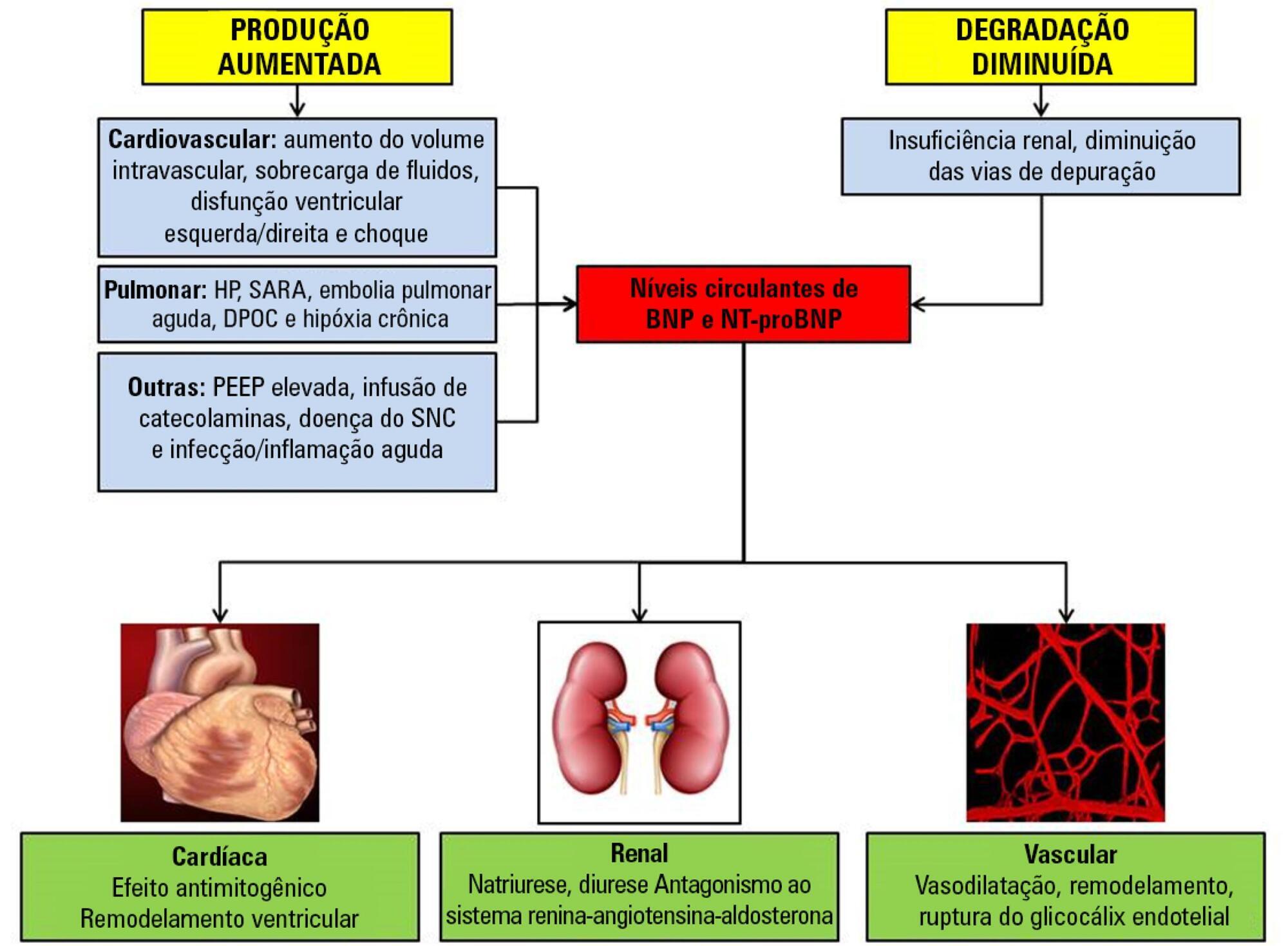
Sepsis continues to be a leading public health burden in the United States and worldwide. With the increasing use of advanced laboratory technology, there is a renewed interest in the use of biomarkers in sepsis to aid in more precise and targeted decision-making. Natriuretic peptides have been increasingly recognized to play a role outside of heart failure. They are commonly elevated among critically ill patients in the setting of cardiopulmonary dysfunction and may play a role in identifying patients with sepsis and septic shock. There are limited data on the role of these biomarkers in the diagnosis, management, outcomes and prognosis of septic patients. This review seeks to describe the role of natriuretic peptides in fluid resuscitation, diagnosis of ventricular dysfunction and outcomes and the prognosis of patients with sepsis. B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) and N-terminal pro-BNP (NT-proBNP) have been noted to be associated with left ventricular systolic and diastolic and right ventricular dysfunction in patients with septic cardiomyopathy. BNP/NT-proBNP may predict fluid responsiveness, and trends of these peptides may play a role in fluid resuscitation. Despite suggestions of a correlation with mortality, the role of BNP in mortality outcomes and prognosis during sepsis needs further evaluation.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(4):333-339
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20150057
To evaluate the prevalence of myocardial dysfunction and its prognostic value in patients with severe sepsis and septic shock.
Adult septic patients admitted to an intensive care unit were prospectively studied using transthoracic echocardiography within the first 48 hours after admission and thereafter on the 7th-10th days. Echocardiographic variables of biventricular function, including the E/e' ratio, were compared between survivors and non-survivors.
A total of 99 echocardiograms (53 at admission and 46 between days 7 - 10) were performed on 53 patients with a mean age of 74 (SD 13) years. Systolic and diastolic dysfunction was present in 14 (26%) and 42 (83%) patients, respectively, and both types of dysfunction were present in 12 (23%) patients. The E/e' ratio, an index of diastolic dysfunction, was the best predictor of hospital mortality according to the area under the ROC curve (0.71) and was an independent predictor of outcome, as determined by multivariate analysis (OR = 1.36 [1.05 - 1.76], p = 0.02).
In septic patients admitted to an intensive care unit, echocardiographic systolic dysfunction is not associated with increased mortality. In contrast, diastolic dysfunction is an independent predictor of outcome.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (116) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)