Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(3):368-378
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190060
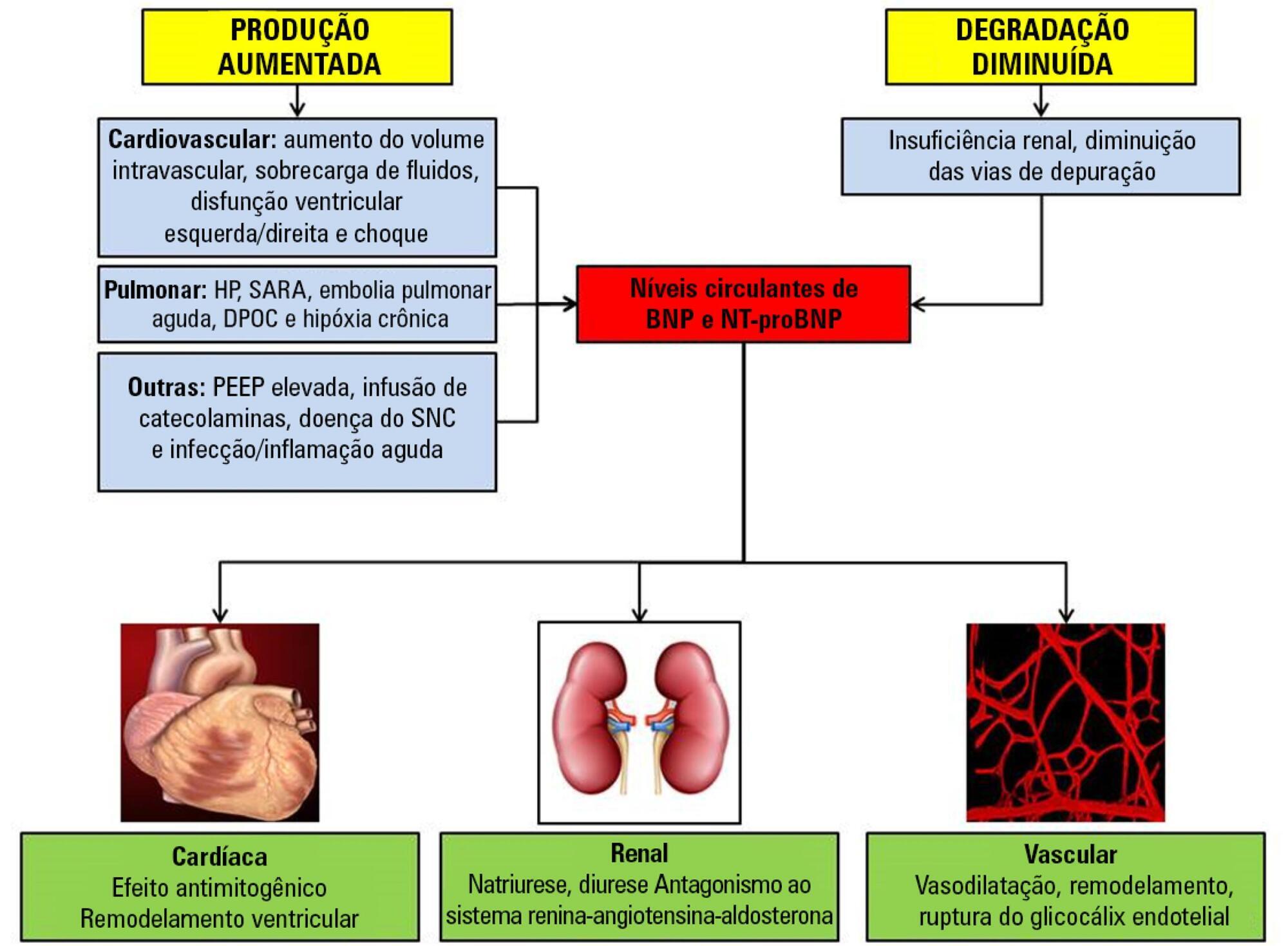
Sepsis continues to be a leading public health burden in the United States and worldwide. With the increasing use of advanced laboratory technology, there is a renewed interest in the use of biomarkers in sepsis to aid in more precise and targeted decision-making. Natriuretic peptides have been increasingly recognized to play a role outside of heart failure. They are commonly elevated among critically ill patients in the setting of cardiopulmonary dysfunction and may play a role in identifying patients with sepsis and septic shock. There are limited data on the role of these biomarkers in the diagnosis, management, outcomes and prognosis of septic patients. This review seeks to describe the role of natriuretic peptides in fluid resuscitation, diagnosis of ventricular dysfunction and outcomes and the prognosis of patients with sepsis. B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) and N-terminal pro-BNP (NT-proBNP) have been noted to be associated with left ventricular systolic and diastolic and right ventricular dysfunction in patients with septic cardiomyopathy. BNP/NT-proBNP may predict fluid responsiveness, and trends of these peptides may play a role in fluid resuscitation. Despite suggestions of a correlation with mortality, the role of BNP in mortality outcomes and prognosis during sepsis needs further evaluation.