Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2008;20(4):376-384
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2008000400010
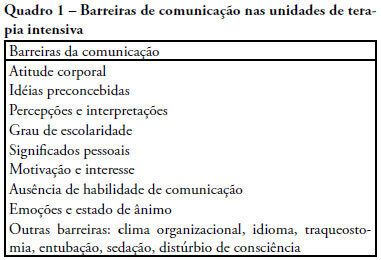
OBJECTIVES: Due to the dramatic medical breakthroughs and an increasingly ageing population, the proportion of patients who are at risk of dying following surgery is increasing over time. The aim of this study was to evaluate the outcomes and the epidemiology of non-cardiac surgical patients admitted to the intensive care unit. METHODS: A multicenter, prospective, observational, cohort study was carried out in 21 intensive care units. A total of 885 adult surgical patients admitted to a participating intensive care unit from April to June 2006 were evaluated and 587 patients were enrolled. Exclusion criteria were trauma, cardiac, neurological, gynecologic, obstetric and palliative surgeries. The main outcome measures were postoperative complications and intensive care unit and 90-day mortality rates. RESULTS: Major and urgent surgeries were performed in 66.4% and 31.7% of the patients, respectively. The intensive care unit mortality rate was 15%, and 38% of the patients had postoperative complications. The most common complication was infection or sepsis (24.7%). Myocardial ischemia was diagnosed in only 1.9% of the patients. A total of 94 % of the patients who died after surgery had co-morbidities at the time of surgery (3.4 ± 2.2). Multiple organ failure was the main cause of death (53%). CONCLUSION: Sepsis is the predominant cause of morbidity in patients undergoing non-cardiac surgery. In this patient population, multiple organ failure prevailed as the most frequent cause of death in the hospital.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2008;20(4):385-393
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2008000400011
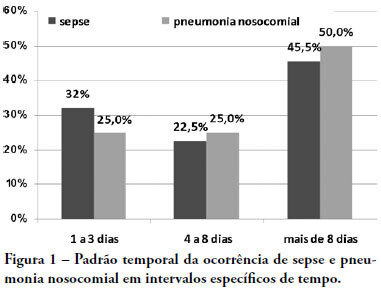
OBJECTIVES: The early assessment of renal dysfunction using common markers does not provide either a sensitive or specific indication of renal dysfunction in critically ill patients. More specific and sensitive markers are desirable for the early detection of an initial renal pathophysiological process. Urinary retinol-binding protein could be an alternative method to early evaluation of renal function in these patients. METHODS: This study followed-up 100 critical care patients and assessed their clinical and laboratory variables, including plasma creatinine and urinary retinol-binding ratio, and demographic variables. RESULTS: The sample was characterized by geriatric (63.4±15.6 years), male (68%), being 53% surgical patients. Statistical analysis showed association between plasma creatinine and the following variables: gender (p-0.026), age (p-0.038), use of vasoactive drugs (p-0.003), proteinuria (p-0.025), Acute Physiological Chronic Health Evaluation (APACHE) II score (p-0.000), urea (p-0.000), potassium (p-0.003) and estimated creatinine clearance (p-0.000). Urinary retinol-binding protein was correlated with more variables: weight, use of invasive ventilation (p-0.000), use of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (p-0.018), use of vasoactive drugs (p-0.021), high temperature (>37.5ºC) (p-0.005), proteinuria (p-0.000), bilirubinuria (p-0.004), urinary flow (p-0.019), minimal diastolic pressure (p-0.032), minimal systolic pressure (p-0.029), APACHE II (p-0.000), creatinine (p-0.001), urea (p-0.001), estimated creatinine clearance (p-0.000). Urinary retinol-binding protein also tended to associate with previous renal disease, vasculopathy and neoplasm. Sodium excretion fraction correlated with plasma creatinine and urinary retinol-binding protein in univariate analysis. CONCLUSIONS: Urinary retinol-binding protein might be considered in clinical practice as a better marker regarding diagnostic performance in patients at risk of developing acute kidney injury, when compared with other markers routinely used. Moreover, urinary retinol-binding protein has other features of a good diagnostic test - it is a practical and non-invasive method.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2008;20(4):394-397
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2008000400012
OBJECTIVES: To evaluate risks for persistent pulmonary hypertension in the newborn, confirmed by echocardiography, associated with cesarean deliveries and other factors. METHODS: Cohort of all deliveries >36 weeks within a period of 23 months. A nested case-control study was performed in a subset of the cohort, involving newborns admitted into neonatal intensive care unit with diagnosis of persistent pulmonary hypertension matched with normal controls, with application of questionnaires to mothers to identify risks. Logistic regression was used to calculate odds ratios. RESULTS: From 9452 newborns, 8388 (88.7%) were delivered by cesarean and 1064 (11.3%) by vaginal delivery. Questionnaires were applied to 173 mothers. Infants from cesareans had a fivefold increased risk of persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn: 42 (0.5%) versus 1 case (0.09%) in the vaginal group (OR 5.32, p=0.027). No interactions were found between smoking, parity, arterial hypertension and labor before cesarean section and persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. First minute Apgar score <7 and maternal diabetes were related to increased risk. CONCLUSION: Reducing cesarean deliveries could prevent many cases of serious persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2008;20(4):398-404
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2008000400013
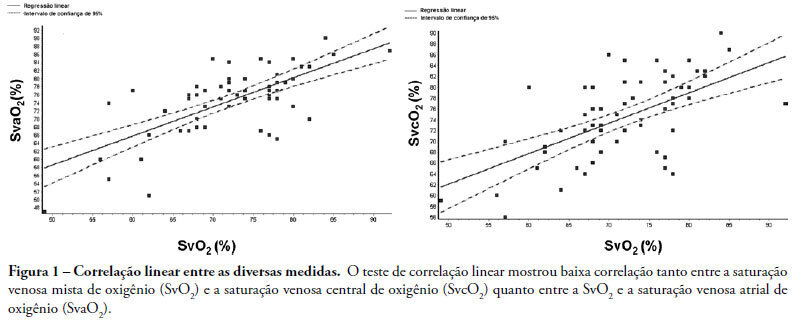
INTRODUCTION: Central venous oxygen saturation (SvcO2) has been proposed as an alternative for mixed venous oxygen saturation (SvO2), with a variable level of acceptance according to available data. This study aimed to evaluate possible differences between SvO2 and SvcO2 or atrial venous saturation (SvaO2), with emphasis on the role of cardiac output and their impact on clinical management of the septic patient. METHODS: This is an observational, prospective study of patients with septic shock monitored by pulmonary artery catheter. Blood was obtained simultaneously for SvcO2, SvO2 and SvaO2 determination. Linear correlation (significant if p<0.05) and agreement analysis (Bland-Altman) were performed with samples and subgroups according to cardiac output. Moreover, agreement about clinical management based on these samples was evaluated. RESULTS: Sixty one measurements from 23 patients were obtained, median age of 65.0 (49.0-75.0) years and mean APACHE II of 27.7±6.3. Mean values of SvO2, SvcO2 and SvaO2 were 72.20±8.26%, 74.61±7.60% and 74.64±8.47%. Linear correlation test showed a weak correlation between SvO2 and SvcO2 (r=0.61, p<0.0001) and also between SvO2 and SvaO2 (r=0.70, p<0.0001). Agreements between SvcO2/SvO2 and SvaO2/SvO2 were -2.40±1.96 (-16.20 and 11.40) and -2.40±1.96 (-15.10 and 10.20), respectively, with no difference in the cardiac output subgroups. No agreement was found in clinical management for 27.8% of the cases, both for SvcO2/SvO2 and for SvaO2/SvO2. CONCLUSION: This study showed that the correlation and agreement between SvO2 and SvcO2 is weak and may lead to different clinical management.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2008;20(4):405-410
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2008000400014
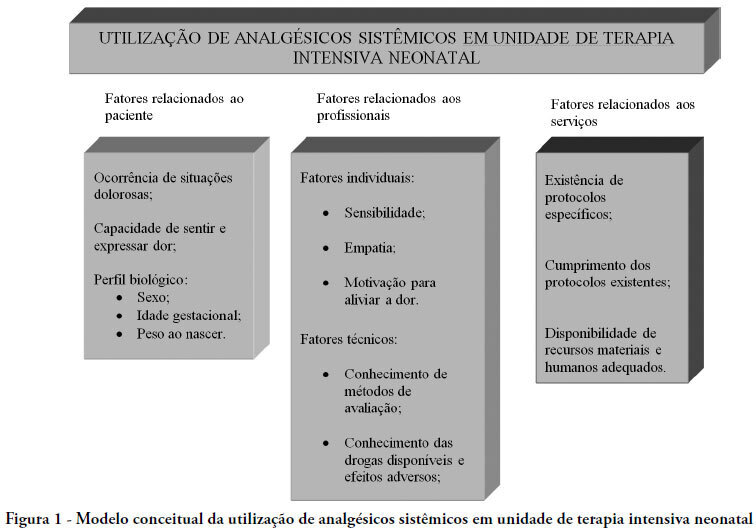
The purpose of this paper was to carry out a review of literature on the history and current stage of the knowledge of systemic analgesia in neonatology and the factors influencing its use. A search for scientific articles was made in the MEDLINE, SciELO and LILACS databases using the keywords: analgesia, systemic analgesics, pain, neonatology, newborn, intensive care units and neonatal intensive care units. Additional research was made on dissertations and thesis databanks as well as text books. Literature consulted disclosed that, in general, analgesia is not a routine practice in neonatal intensive care units, despite the numerous studies demonstrating its importance. Although pain relief is a basic principle of medicine, involving ethic and humanitarian issues and despite the current availability of a number of practical guidelines and consensus regarding pain management in newborns at risk, findings of the present study fall far short of current recommendations. Urgent intervention is required to redress this situation.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2008;20(4):411-421
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2008000400015
Trauma is the leading cause of death of people from 1 to 44 years of age. Traumatic brain injury is the main determinant for mortality and morbidity caused by trauma. Outcome prediction is one of the major problems related to severe traumatic brain injury because clinical evaluation has an unreliable predictive value and complicates identification of patients with higher risk of developing secondary lesions and fatal outcome. That is why, there is considerable interest in development of biomarkers that reflect the severity of brain injury and correlate with mortality and functional outcome. Proteins S100B and neuron specific enolases are among the markers most studied for this purpose, however some studies are investigating glial fibrillary acidic protein, creatinine phospokinase, isoenzime B, myelin basic protein, plasma desoxiribonucleic acid, heat shock protein 70, von Willebrand factor, metalloproteinases and brain-derived neurotrophic factor, among others. Evidence suggests that inflammation, oxidative stress, excitotoxicity, neuroendocrine responses and apoptosis play an important role in the development of secondary lesions. Markers involved in these processes are being studied in traumatic brain injury. We reviewed these biomarkers, some of which present promising results for future clinical application.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2008;20(4):422-428
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2008000400016
The objective of this review was to evaluate current knowledge regarding terminal illness and palliative care in the intensive care unit, to identify the major challenges involved and propose a research agenda on these issues The Brazilian Critical Care Association organized a specific forum on terminally ill patients, to which were invited experienced and skilled professionals on critical care. These professionals were divided in three groups: communication in the intensive care unit, the decision making process when faced with a terminally ill patient and palliative actions and care in the intensive care unit. Data and bibliographic references were stored in a restricted website. During a twelve hour meeting and following a modified Delphi methodology, the groups prepared the final document. Consensual definition regarding terminality was reached. Good communication was considered the cornerstone to define the best treatment for a terminally ill patient. Accordingly some communication barriers were described that should be avoided as well as some approaches that should be pursued. Criteria for palliative care and palliative action in the intensive care unit were defined. Acceptance of death as a natural event as well as respect for the patient's autonomy and the nonmaleficence principles were stressed. A recommendation was made to withdraw the futile treatment that prolongs the dying process and to elected analgesia and measures that alleviate suffering in terminally ill patients. To deliver palliative care to terminally ill patients and their relatives some principles and guides should be followed, respecting individual necessities and beliefs. The intensive care unit staff involved with the treatment of terminally ill patients is subject to stress and tension. Availability of a continuous education program on palliative care is desirable.