Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2010;22(2):159-165
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2010000200010
OBJECTIVE: Neonates mechanic ventilation weaning has become a major clinical challenge, and constitutes a large portion of neonatal intensive care units workload. The spontaneous breathing trial (SBT), performed immediately before extubation, can provide useful information on the patient's spontaneous breathing ability. This study aimed to assess the SBT effectiveness for extubation success prediction in mechanically ventilated preterm infants. METHODS: After Ethics Committee approval, an observational, longitudinal, prospective study was conducted. A sample of 60 preterm infants compliant with the weaning criteria was categorized in two groups: 'SBT' group (n=30), with the patients who underwent 30 minutes spontaneous breathing trial (SBT) with continuous positive pressure airway (CPAP), and the control group (n=30) where the extubation was performed without spontaneous breathing trial. The heart rate (HR), respiratory rate (RR), pulse oxymetry oxygen saturation (SpO2) and the Silverman-Andersen score were recorded before and 10, 20 and 30 minutes after the spontaneous breathing trial. Were also assessed for both groups, and versus extubation success or failure, the weight, gestational age, Apgar score, mean airway pressure, inspired oxygen concentration, and tracheal tube time. The Chi-square test was used for categorical variables and the Mann-Whitney test for non-normal distribution. Extubation success was defined as a 48 hours period with no reintubation requirement. RESULTS: No significant differences were identified between the groups for the analyzed variables, except for the mean airway pressure. A significant association was shown between spontaneous breathing trial and successful extubation. CONCLUSION: The significant association between SBT and extubation success may contribute for prediction of successful weaning in preterm infants.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2010;22(2):166-174
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2010000200011
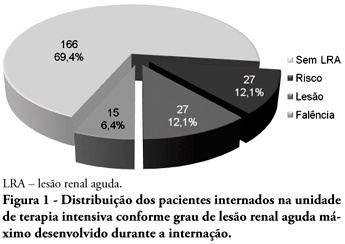
OBJECTIVES: Acute kidney injury is characterized by sudden and generally revertible renal function impairment involving inability to maintain homeostasis. In pediatrics, the main causes of acute kidney injury are sepsis, use of nephrotoxic drugs and renal ischemia in critically ill patients. The incidence of acute kidney injury in these patients ranges from 20 to 30%, resulting in increased morbid-mortality, a 40 to 90% rate. This study aimed to evaluate the incidence of acute kidney injury in intensive care unit patients, to categorize the severity of the acute kidney injury according to the Pediatric Risk, Injury, Failure, Loss, End-Stage (pRIFLE), examine the relationship between the acute kidney injury and severity using the Pediatric Index of Mortality (PIM) and to analyze outcome predictors. METHODS: A prospective study of the patients admitted to the intensive care unit of Hospital Infantil Joana de Gusmão - Florianópolis / SC - Brazil was conducted between July 2008 and January 2009. Were evaluated daily the urine output and serum creatinine, and the patients were categorized according to the pRIFLE criteria. RESULTS: During the follow-up period, 235 children were admitted. The incidence of acute kidney injury was 30.6%, and the maximal pRIFLE score during hospitalization was 12.1% for R, 12.1% for I and 6.4% for F. The mortality rate was 12.3%. The patients who developed acute kidney injury had a ten times bigger risk of death versus the not exposed patients. CONCLUSIONS: Acute kidney injury is frequent in critically ill patients. Early diagnosis and prompt and appropriate therapy for each clinical aspect may change this condition's course and severity, and reduce the patients' morbidity and mortality.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2010;22(2):175-185
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2010000200012
OBJECTIVE: The avoidance of pressure ulcers development in critically ill patients is a major nursing challenge. Prevention is thus relevant for assurance of high quality care. This study aimed to evaluate the applicability of the Braden scale in intensive care unit patients. METHODS: This was a prospective study based which evaluated all adult patients staying in the intensive care unit from July 14 to August 10, 2009. The data were collected using the Braden's scale by three examiners who identified the pressure ulcer development risk. The data were analyzed using the SAS Statistical Software. For determination of the examiners' rates degree of coincidence, the Kappa value was used (95%CI). RESULTS: Regarding the related risk factors: 36.4% had mild sensory perception impairment; 50.9% had occasionally moist skin; 97.3% bedfast; 39.1% had very limited mobility; 45% probably had inappropriate nutrition; 61.8% had friction and shear problems. An agreement between the examiners was identified for nutrition and physical activity (38.1% to 100.0%); the Kappa population zero hypothesis was rejected; a paired examiners agreement (41.7% to 100.0%) was identified for the items humidity and physical activity, and the Kappa values ranged from 0.13 to 1. CONCLUSIONS: These intensive care patients were identified to have increased risk of developing pressure ulcers. This tool was considered appropriate to support the implementation of preventive measures.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2010;22(2):186-191
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2010000200013
OBJECTIVES: To evaluate the applicability of the bag squeezing and zeep maneuvers in mechanically ventilated patients. METHODS: Twenty stable mechanically ventilated patients were studied. All patients were randomly allocated to either bag squeezing techinique followed by zeep maneuver, or the reversed sequence. Each group crossed to the other sequence four hours later. Heart rate, respiratory rate, peripheral oxygen saturation and blood pressure were measured before, during and after each technique use. The suctioned secretions were collected and measured. The data were analyzed by pairwise statistical analysis for inter-group comparisons, and ANOVA for each group results analysis. RESULTS: The heart rate was significantly increased, from 92.6 ± 18.3 bpm to 99.8 ± 18.5 bpm and the peripheral oxygen saturation significantly decreased from 96.9 ± 3.0% to 94.5 ± 4.3% during the bag squeezing maneuver, although the values remained within the normal range. No significant changes were seen for the zeep maneuver. Peripheral oxygen saturation during the maneuvers was found to change when the techniques were compared. No differences were found for the suctionedsecretions amounts. CONCLUSION: The results suggest that both techniques are feasible as they cause few hemodynamic changes, and both are effective for bronchial secretions removal.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2010;22(2):192-195
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2010000200014
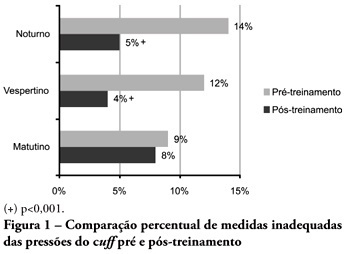
OBJECTIVES: Direct cuff pressure to the tracheal wall can cause damage. This paper aimed to verify the effectiveness of nursing team training on cuff pressure control. METHODS: A retrospective survey was initially made on the records of cuff pressure measurements from January 2007 to June 2008 and the inadequacy percent was verified. Next, a nursing team training program was provided involving all nursing shift teams during June 2008, and after the training the appropriate cuff pressures proportion was prospectively recorded between June and December 2008. The proportion of inappropriate cuff pressure was compared between the work shifts (morning, afternoon and evening-night) and between pre- and post-training, using the qualitative Chi-square test. The 5% limit (p<0.05) was considered for significant differences. RESULTS: For the pre-training period, inappropriate cuff pressure measures (over 30cmH2O) during morning, afternoon and evening-night shifts were 9.2%, 11.9% and 13.7%, respectively. For the post-training phase, 7.6%, 4.1% and 5.2% inappropriate cuff-pressures were identified for the morning, afternoon and evening-night shifts, respectively, with a significant reduction for the afternoon and evening-night shifts, respectively (p<0.001). CONCLUSION: Nursing team training was effective for inadequate cuff pressure harms awareness improvement, and resulted in safer pressure levels.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2010;22(2):196-205
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2010000200015
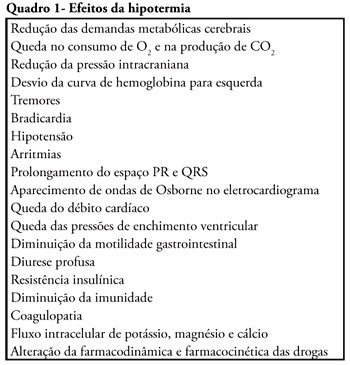
Cardiac arrest is a high mortality event and the associated brain ischemia frequently causes severe neurological damage and persistent vegetative state. Therapeutic hypothermia is an important tool for the treatment of post-anoxic coma after cardiopulmonary resuscitation. It has been shown to reduce mortality and to improve neurological outcomes after cardiac arrest. Nevertheless, hypothermia is underused in critical care units. This manuscript aims to review the hypothermia mechanism of action in cardiac arrest survivors and to propose a simple protocol, feasible to be implemented in any critical care unit.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2010;22(2):206-211
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2010000200016
In patients with renal failure, encephalopathy is a common problem that may be caused by uremia, thiamine deficiency, dialysis, transplant rejection, hypertension, fluid and electrolyte disturbances or drug toxicity. In general, encephalopathy presents with a symptom complex progressing from mild sensorial clouding to delirium and coma. This review discusses important issues regarding the mechanisms underlying the pathophysiology of uremic encephalopathy. The pathophysiology of uremic encephalopathy up to now is uncertain, but several factors have been postulated to be involved; it is a complex and probably multifactorial process. Hormonal disturbances, oxidative stress, accumulation of metabolites, imbalance in excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters, and disturbance of the intermediary metabolism have been identified as contributing factors. Despite continuous therapeutic progress, most neurological complications of uremia, like uremic encephalopathy, fail to fully respond to dialysis and many are elicited or aggravated by dialysis or renal transplantation. On the other hand, previous studies showed that antioxidant therapy could be used as an adjuvant therapy for the treatment of these neurological complications.
Abstract