Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(3):440-444
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20210054
To identify current evidence on the use of topiramate for refractory status epilepticus.
We reviewed the literature to investigate the efficacy of topiramate in the treatment of refractory status epilepticus. The search terms used were “status epilepticus”, “refractory”, “treatment” and “topiramate”. No restrictions were used.
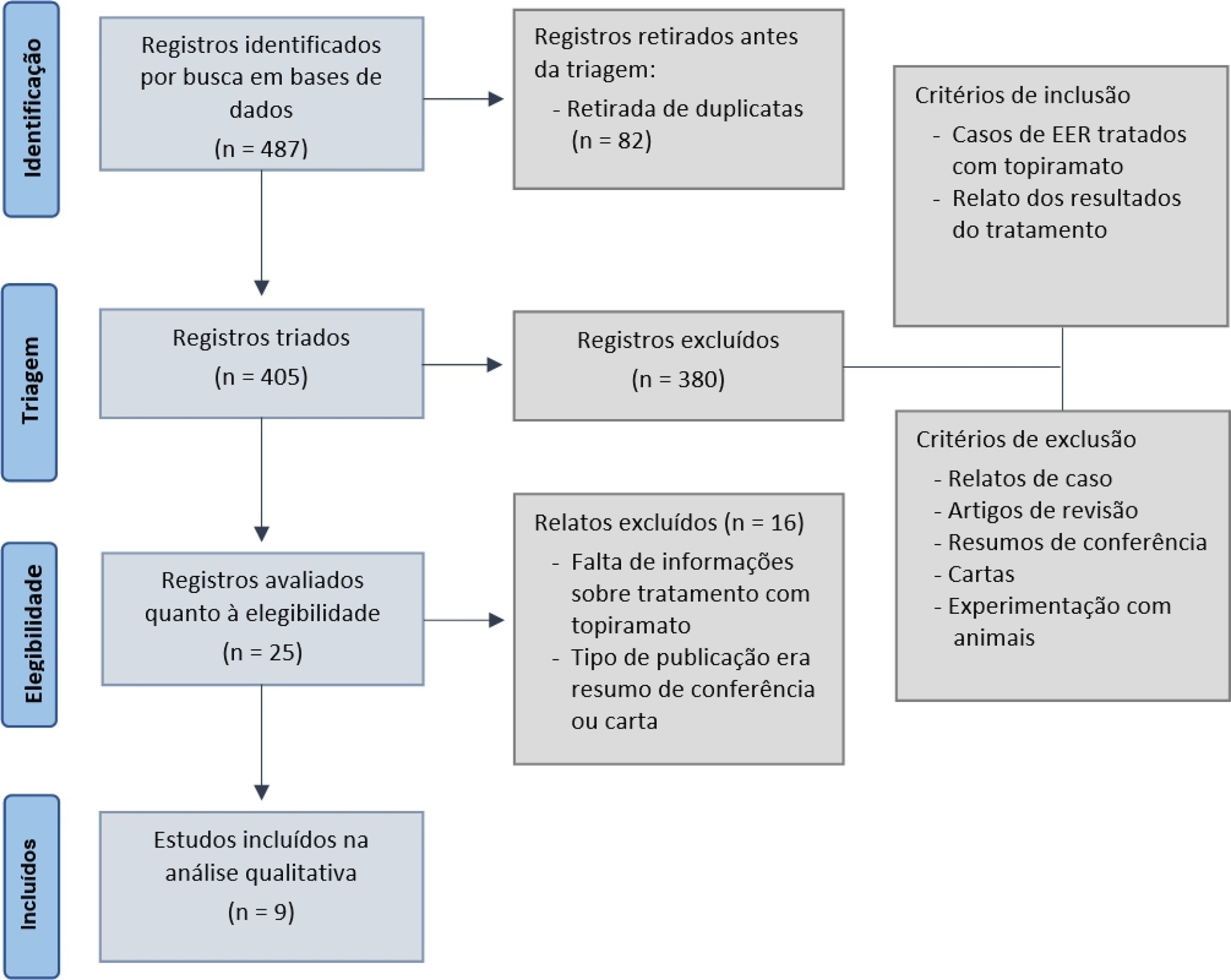
The search yielded 487 articles that reported using topiramate as a treatment for refractory status epilepticus and its outcomes. Case reports, review articles, and animal experiments were excluded. After excluding duplicates and applying inclusion and exclusion criteria, nine studies were included for analyses. Descriptive and qualitative analyses were performed, and the results were as follows: response rates (defined as termination in-hospital until 72 hours after the administration of topiramate) varied from 27% to 100%. The mortality rate varied from 5.9% to 68%. Positive functional long-term outcomes, defined as discharge, back to baseline or rehabilitation, were documented by seven studies, and the rates ranged between 4% and 55%. Most studies reported no or mild adverse effects.
Topiramate was effective in terminating refractory status epilepticus, presented relatively low mortality and was well tolerated. Therefore, topiramate could be a good option as a third-line therapy for refractory status epilepticus, but further studies are necessary.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(3):445-456
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20210060
This systematic review was designed to assess the usefulness of cough peak flow to predict the extubation outcome in subjects who passed a spontaneous breathing trial.
The search covered the scientific databases MEDLINE, Lilacs, Ibecs, Cinahl, SciELO, Cochrane, Scopus, Web of Science and gray literature. The Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies was used to assess the methodological quality and risk of study bias. The statistical heterogeneity of the likelihood (LR) and diagnostic odds ratios were evaluated using forest plots and Cochran’s Q statistic, and a crosshair summary Receiver Operating Characteristic plot using the multiple cutoffs model was calculated.
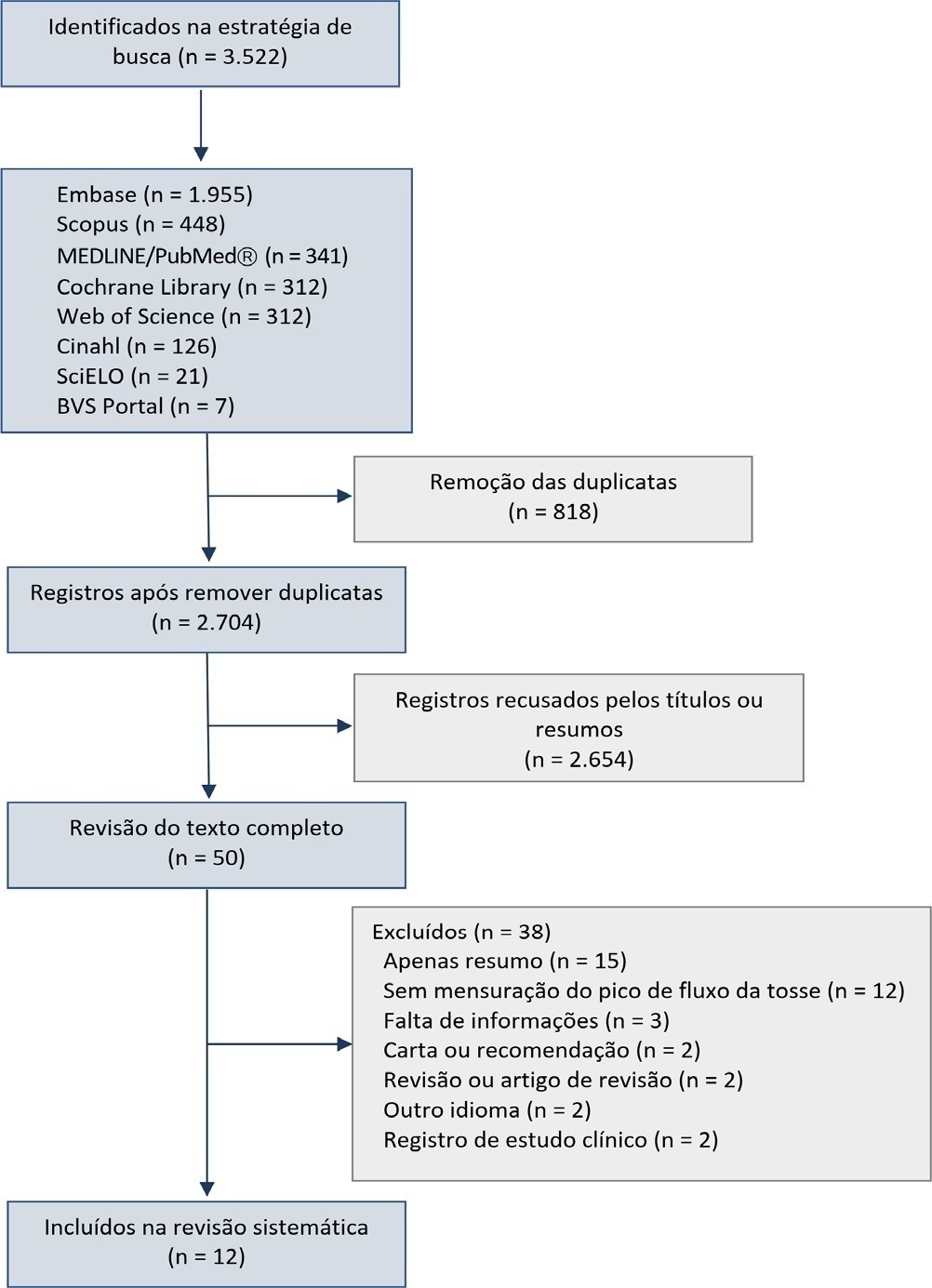
We initially retrieved 3,522 references from the databases; among these, 12 studies including 1,757 subjects were selected for the qualitative analysis. Many studies presented an unclear risk of bias in the “patient selection” and “flow and time” criteria. Among the 12 included studies, seven presented “high risk” and five “unclear risk” for the item “reference standard.” The diagnostic performance of the cough peak flow for the extubation outcome was low to moderate when we considered the results from all included studies, with a +LR of 1.360 (95%CI 1.240 - 1.530), -LR of 0.218 (95%CI 0.159 - 0.293) and a diagnostic odds ratio of 6.450 (95%CI 4.490 - 9.090). A subgroup analysis including only the studies with a cutoff between 55 and 65 L/minute showed a slightly better, although still moderate, performance.
A cough peak flow assessment considering a cutoff between 55 and 65L/minute may be useful as a complementary measurement prior to extubation. Additional well-designed studies are necessary to identify the best method and equipment to record the cough peak flow as well as the best cutoff.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(2):304-311
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20210039
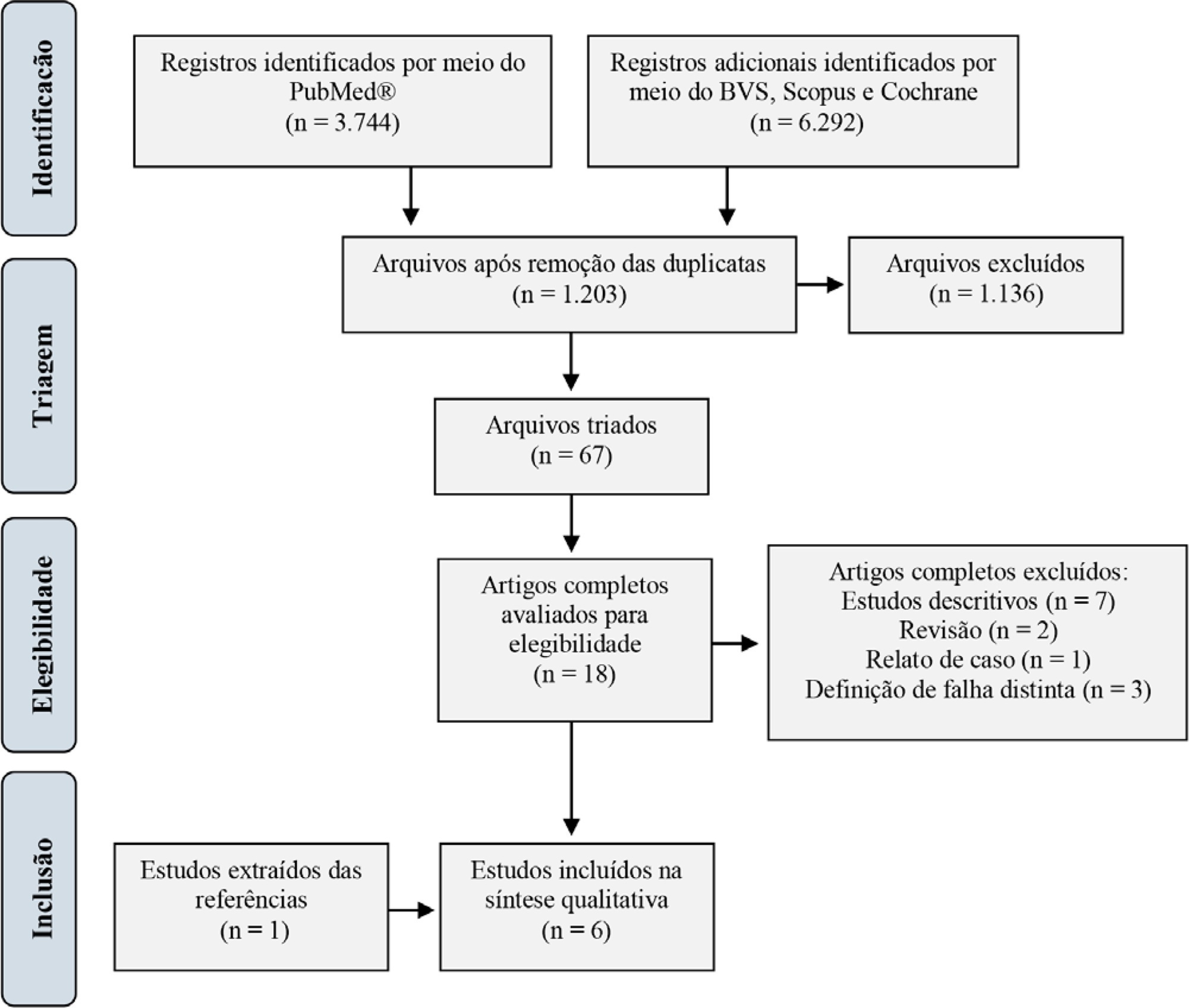
For extubation in pediatric patients, the evaluation of readiness is strongly recommended. However, a device or practice that is superior to clinical judgment has not yet been accurately determined. Thus, it is important to conduct a review on the techniques of choice in clinical practice to predict extubation failure in pediatric patients. Based on a search in the PubMed®, Biblioteca Virtual em Saúde, Cochrane Library and Scopus databases, we conducted a survey of the predictive variables of extubation failure most commonly used in clinical practice in pediatric patients. Of the eight predictors described, the three most commonly used were the spontaneous breathing test, the rapid shallow breathing index and maximum inspiratory pressure. Although the disparity of the data presented in the studies prevented statistical treatment, it was still possible to describe and analyze the performance of these tests.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(2):312-319
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20210040
Randomized clinical trials in intensive care prioritize disease-focused outcomes rather than patient-centered outcomes. A paradigm shift considering the evaluation of measures after hospital discharge and measures focused on quality of life and common symptoms, such as pain and dyspnea, could better reflect the wishes of patients and their families. However, barriers related to the systematization of the interpretation of these outcomes, the heterogeneity of measurement instruments and the greater difficulty in performing the studies, to date, seem to hinder this change. In addition, the joint participation of patients, families, researchers, and clinicians in the definition of study outcomes is not yet a reality.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(1):146-153
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20210016
Neurological diseases are estimated to affect 1 billion people worldwide and are the cause of one in 10 deaths. In Brazil, they are responsible for approximately 14% of clinical admissions to intensive care units, 9% of elective neurosurgeries and 14% of emergency neurosurgeries. Many of these conditions are incurable, result in reduced life expectancy and quality of life and increased dependence, and are associated with symptoms that are likely to cause suffering, which justifies the integration of palliative care into usual care. In addition, factors unique to acute neurological injuries, such as their catastrophic clinical presentation, complex and uncertain prognosis, associated communication difficulties and issues related to quality of life, require a specific approach, which has recently been termed "neuropalliative care". Although the topic is relevant and current, it is still little discussed, and much of what is known about palliative care in this context is extrapolated from approaches used under other conditions. Therefore, the objective of this study was to conduct a narrative literature review to identify the challenges of applying the palliative care approach in the care of neurocritically ill patients, with a focus on three groups: neurocritically ill patients, families and intensive care teams. This review identified that in intensive care, the main demands for palliative care are for prognostic definitions and care planning. Training in primary palliative care and improving communication were also needs identified by intensivists and families, respectively. In contrast with what has been found under other conditions, the management of symptoms was not indicated as a complex issue, although it is still relevant.
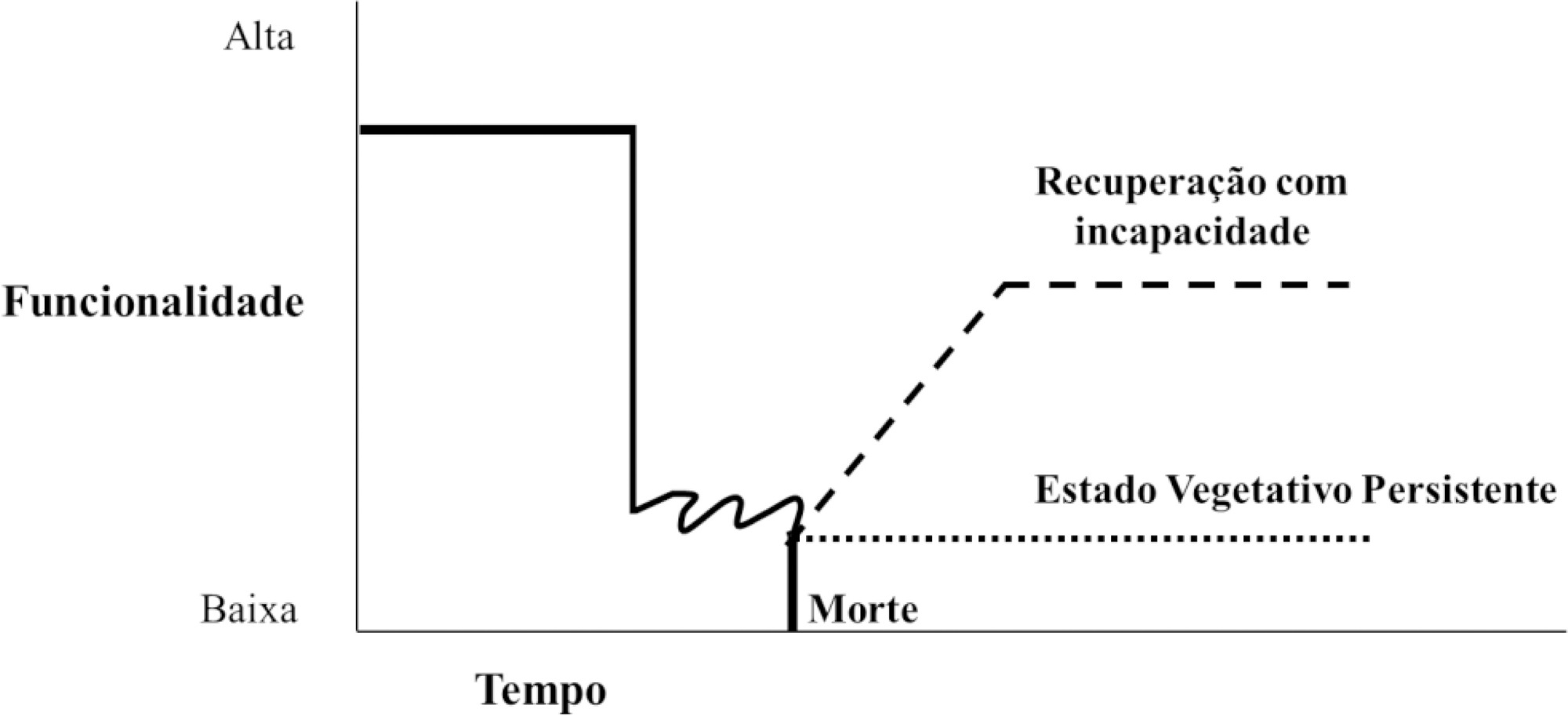
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(1):154-166
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20210017
Red blood cell transfusion is thought to improve cell respiration during septic shock. Nevertheless, its acute impact on oxygen transport and metabolism in this condition remains highly debatable. The objective of this study was to evaluate the impact of red blood cell transfusion on microcirculation and oxygen metabolism in patients with sepsis and septic shock. We conducted a search in the MEDLINE®, Elsevier and Scopus databases. We included studies conducted in adult humans with sepsis and septic shock. A systematic review and meta-analysis were performed using the DerSimonian and Laird random-effects model. A p value < 0.05 was considered significant. Nineteen manuscripts with 428 patients were included in the analysis. Red blood cell transfusions were associated with an increase in the pooled mean venous oxygen saturation of 3.7% (p < 0.001), a decrease in oxygen extraction ratio of -6.98 (p < 0.001) and had no significant effect on the cardiac index (0.02L/minute; p = 0,96). Similar results were obtained in studies including simultaneous measurements of venous oxygen saturation, oxygen extraction ratio, and cardiac index. Red blood cell transfusions led to a significant increase in the proportion of perfused small vessels (2.85%; p = 0.553), while tissue oxygenation parameters revealed a significant increase in the tissue hemoglobin index (1.66; p = 0.018). Individual studies reported significant improvements in tissue oxygenation and sublingual microcirculatory parameters in patients with deranged microcirculation at baseline. Red blood cell transfusions seemed to improve systemic oxygen metabolism with apparent independence from cardiac index variations. Some beneficial effects have been observed for tissue oxygenation and microcirculation parameters, particularly in patients with more severe alterations at baseline. More studies are necessary to evaluate their clinical impact and to individualize transfusion decisions.
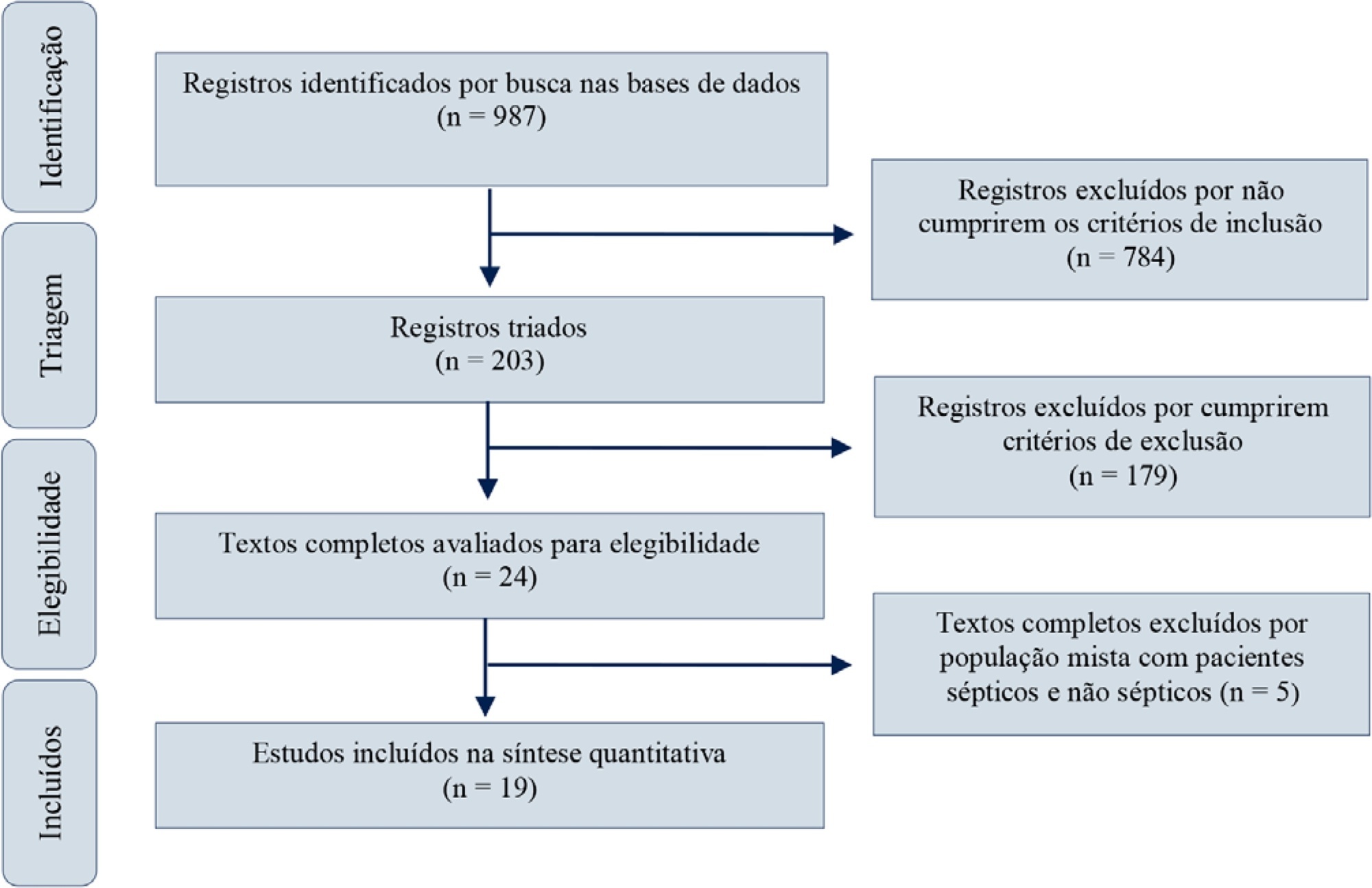
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2020;32(4):585-591
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20200084
Sepsis is a systemic infection that causes multiple organ dysfunction. HSP70 is a protein responsive to cell stress, in particular oxidative stress. Therefore, this literature review sought to investigate the roles of HSP70 and oxidative stress in the pathophysiology of sepsis and the possibility of HSP70 as a therapeutic target. HSP70 exerts a protective effect when located in cells (iHSP70), and its decrease, as well as its increase in the extracellular environment (eHSP70), under oxidative stress is a biomarker of sepsis severity. In addition, therapies that increase iHSP70 and treatment with HSP70 promote sepsis improvement.