Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(1):37-43
DOI 10.5935/2965-2774.20230275-pt
To compare the diagnostic performance of maximal expiratory pressure with maximal expiratory pressure during induced cough for predicting extubation failure within 72 hours in patients who completed a spontaneous breathing trial (SBT).
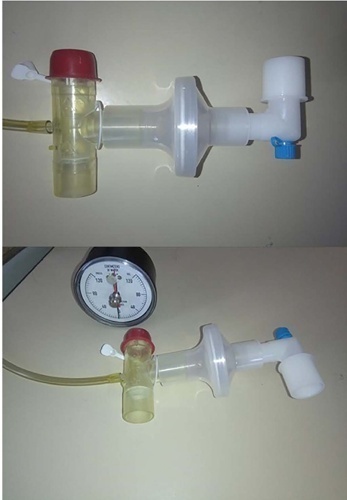
The study was conducted between October 2018 and September 2019. All patients aged over 18 years admitted to the intensive care unit who required invasive mechanical ventilation for over 48 hours and successfully completed a spontaneous breathing trial were included. The maximal expiratory pressure was assessed with a unidirectional valve for 40 seconds, and verbal encouragement was given. The maximal expiratory pressure during induced cough was measured with slow instillation of 2mL of a 0.9% saline solution. The primary outcome variable was extubation failure.
Eighty patients were included, of which 43 (54%) were male. Twenty-two patients [27.5% (95%CI 18.9 - 38.1)] failed extubation within 72 hours. Differences were observed in the maximal expiratory pressure during induced cough between the group who failed extubation, with a median of 0cmH2O (P25-75: 0 - 90), and the group without extubation failure, with a median of 120cmH2O (P25-75: 73 - 120); p < 0.001.
In patients who completed a spontaneous breathing trial, the maximal expiratory pressure during induced cough had a higher diagnostic performance for predicting extubation failure within 72 hours.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(3):445-456
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20210060
This systematic review was designed to assess the usefulness of cough peak flow to predict the extubation outcome in subjects who passed a spontaneous breathing trial.
The search covered the scientific databases MEDLINE, Lilacs, Ibecs, Cinahl, SciELO, Cochrane, Scopus, Web of Science and gray literature. The Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies was used to assess the methodological quality and risk of study bias. The statistical heterogeneity of the likelihood (LR) and diagnostic odds ratios were evaluated using forest plots and Cochran’s Q statistic, and a crosshair summary Receiver Operating Characteristic plot using the multiple cutoffs model was calculated.
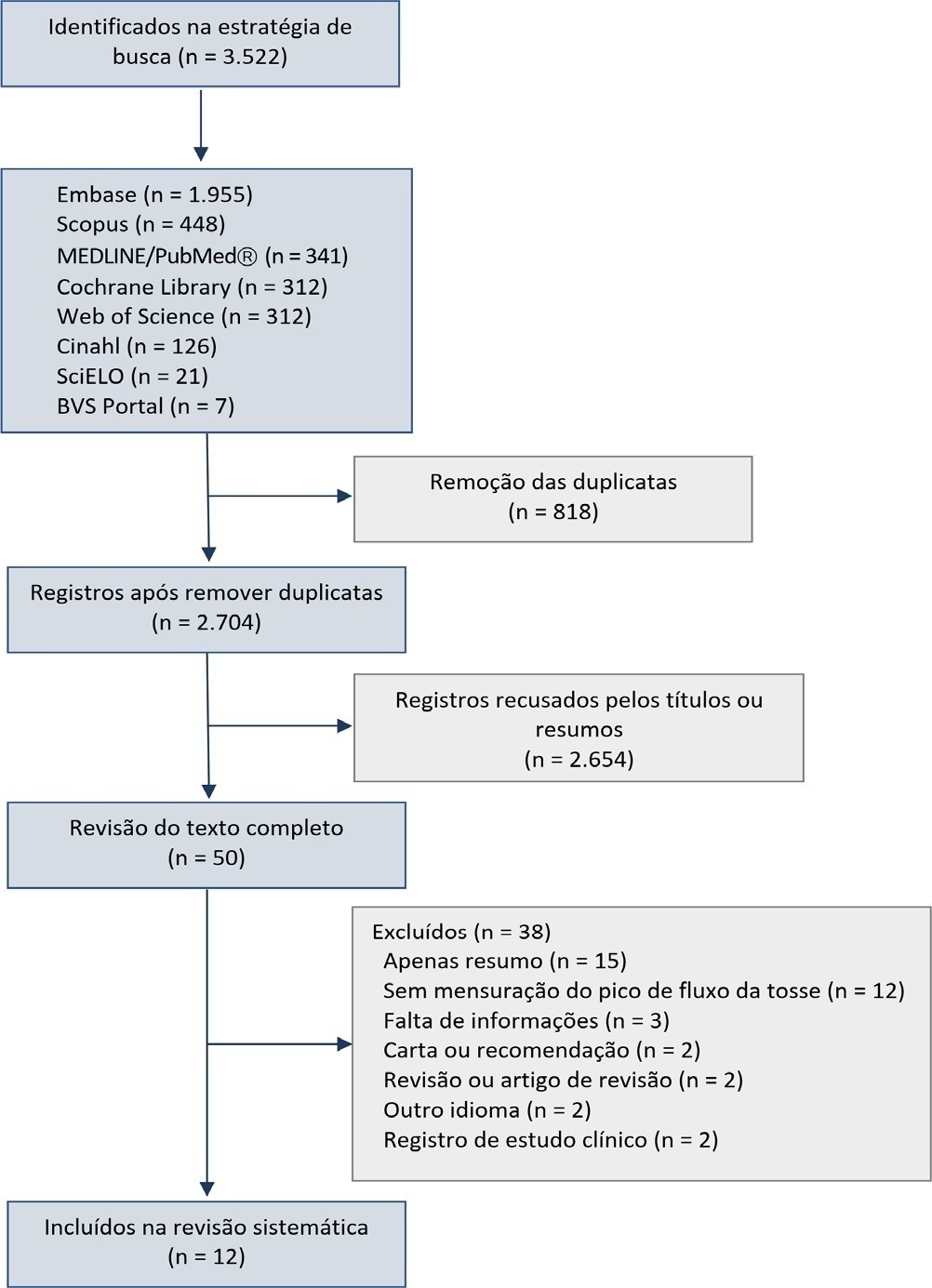
We initially retrieved 3,522 references from the databases; among these, 12 studies including 1,757 subjects were selected for the qualitative analysis. Many studies presented an unclear risk of bias in the “patient selection” and “flow and time” criteria. Among the 12 included studies, seven presented “high risk” and five “unclear risk” for the item “reference standard.” The diagnostic performance of the cough peak flow for the extubation outcome was low to moderate when we considered the results from all included studies, with a +LR of 1.360 (95%CI 1.240 - 1.530), -LR of 0.218 (95%CI 0.159 - 0.293) and a diagnostic odds ratio of 6.450 (95%CI 4.490 - 9.090). A subgroup analysis including only the studies with a cutoff between 55 and 65 L/minute showed a slightly better, although still moderate, performance.
A cough peak flow assessment considering a cutoff between 55 and 65L/minute may be useful as a complementary measurement prior to extubation. Additional well-designed studies are necessary to identify the best method and equipment to record the cough peak flow as well as the best cutoff.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (116) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)