Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2016;28(2):161-166
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20160031
To correlate the levels of thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor in the immediate postoperative period and at 24 hours postoperatively with the volume of intraoperative bleeding.
Twenty-one patients allocated immediately before (elective or emergency) liver transplantation were analyzed. Blood samples were collected for thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor analysis at three different time points: immediately before liver transplantation (preoperative thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor), immediately after the surgical procedure (immediate postoperative thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor), and 24 hours after surgery (thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor 24 hours after surgery). The primary outcome of the study was to correlate the preoperative and immediate postoperative levels of thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor with intraoperative blood loss.
There was a correlation between the preoperative thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor levels and bleeding volume (ρ = -0.469; p = 0.05) but no correlation between the immediate postoperative thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor and bleeding volume (ρ = -0.062; p = 0.79). No variable included in the linear regression analysis (prehemoglobin, prefibrinogen and preoperative thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor) was a bleeding predictor. There was a similar trend in the variation between the levels of thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor at the three different time points and fibrinogen levels. Patients who died within 6 months (14.3%) showed decreased preoperative and immediate postoperative levels of thrombin activatable fibrinolysis compared with survivors (preoperative: 1.3 ± 0.15 versus 2.55 ± 0.53, p = 0.06; immediate postoperative: 1.2 ± 0.15 versus 2.5 ± 0.42, p = 0.007).
There was a moderate correlation between preoperative thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor and intraoperative bleeding in liver transplantation patients, although the predictive role of this variable independent of other variables remains uncertain. Preoperative and immediate postoperative thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor levels may have a role in the survival prognosis of this population; however, this possibility requires confirmation in further studies with larger sample sizes.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2016;28(2):107-113
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20160024
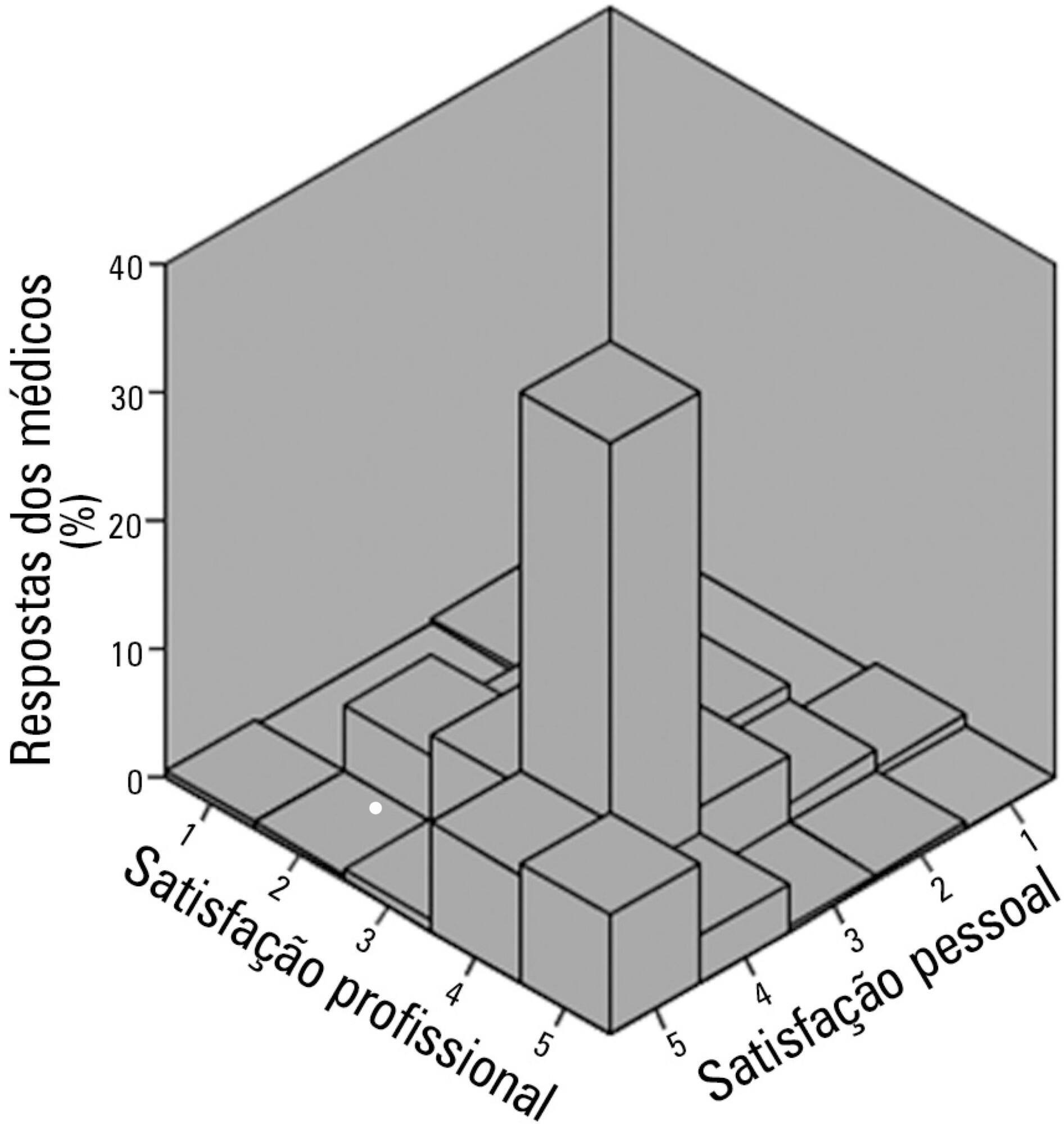
To evaluate job and personal satisfaction rates in physicians who work in adult intensive care units and to identify the factors associated with satisfaction.
A cross-sectional study performed with physicians who participated in two intensive medicine online discussion groups. A questionnaire designed to assess the physician's sociodemographic profile and job was available for both groups for 3 months. At the end of the questionnaire, the participants addressed their degrees of job and personal satisfaction using a Likert scale in which 1 represented "very dissatisfied" and 5 represented "very satisfied". The association between sociodemographic and job characteristics with job and personal satisfaction was evaluated. Variables independently associated with satisfaction were identified using a logistic regression model.
The questionnaire was answered by 250 physicians, of which 137 (54.8%) declared they were satisfied with their jobs and 34 (13.5%) were very satisfied. None of the evaluated characteristics were independently associated with job satisfaction. Regarding personal satisfaction, 136 (54.4%) physicians reported being satisfied, and 48 (19.9%) reported being very satisfied. Job satisfaction (OR = 7.21; 95%CI 3.21 - 16.20) and working in a university hospital (OR = 3.24; 95%CI 1.29 - 8.15) were factors independently associated with the personal satisfaction of the participants.
The participant physicians reported job and personal satisfaction with their work in intensive care. Job satisfaction and working in a university hospital were independently associated with greater personal satisfaction.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2016;28(2):114-119
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20160025
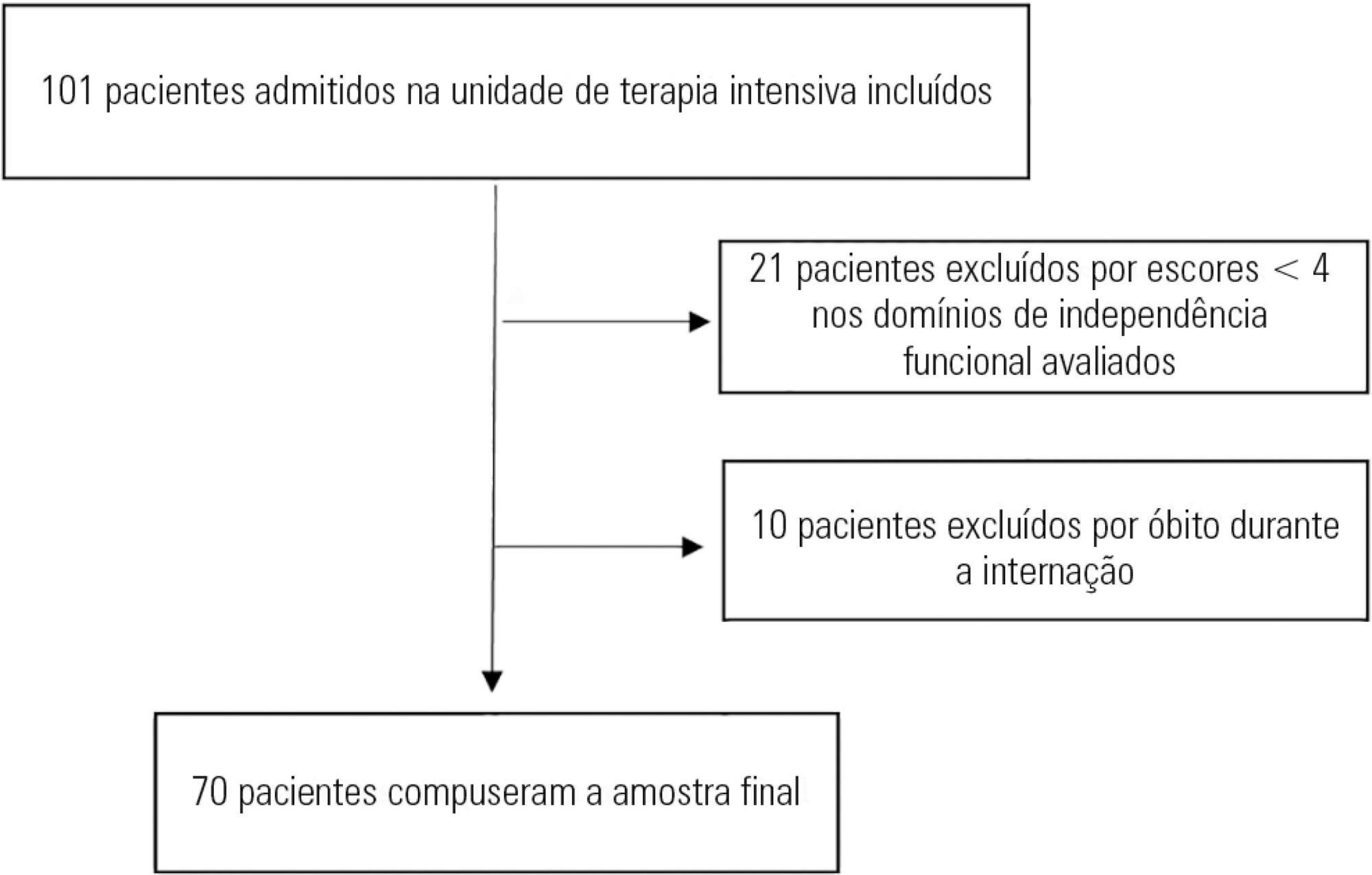
To evaluate the variation in mobility during hospitalization in an intensive care unit and its association with hospital mortality.
This prospective study was conducted in an intensive care unit. The inclusion criteria included patients admitted with an independence score of ≥ 4 for both bed-chair transfer and locomotion, with the score based on the Functional Independence Measure. Patients with cardiac arrest and/or those who died during hospitalization were excluded. To measure the loss of mobility, the value obtained at discharge was calculated and subtracted from the value obtained on admission, which was then divided by the admission score and recorded as a percentage.
The comparison of these two variables indicated that the loss of mobility during hospitalization was 14.3% (p < 0.001). Loss of mobility was greater in patients hospitalized for more than 48 hours in the intensive care unit (p < 0.02) and in patients who used vasopressor drugs (p = 0.041). However, the comparison between subjects aged 60 years or older and those younger than 60 years indicated no significant differences in the loss of mobility (p = 0.332), reason for hospitalization (p = 0.265), SAPS 3 score (p = 0.224), use of mechanical ventilation (p = 0.117), or hospital mortality (p = 0.063).
There was loss of mobility during hospitalization in the intensive care unit. This loss was greater in patients who were hospitalized for more than 48 hours and in those who used vasopressors; however, the causal and prognostic factors associated with this decline need to be elucidated.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2016;28(2):120-131
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20160026
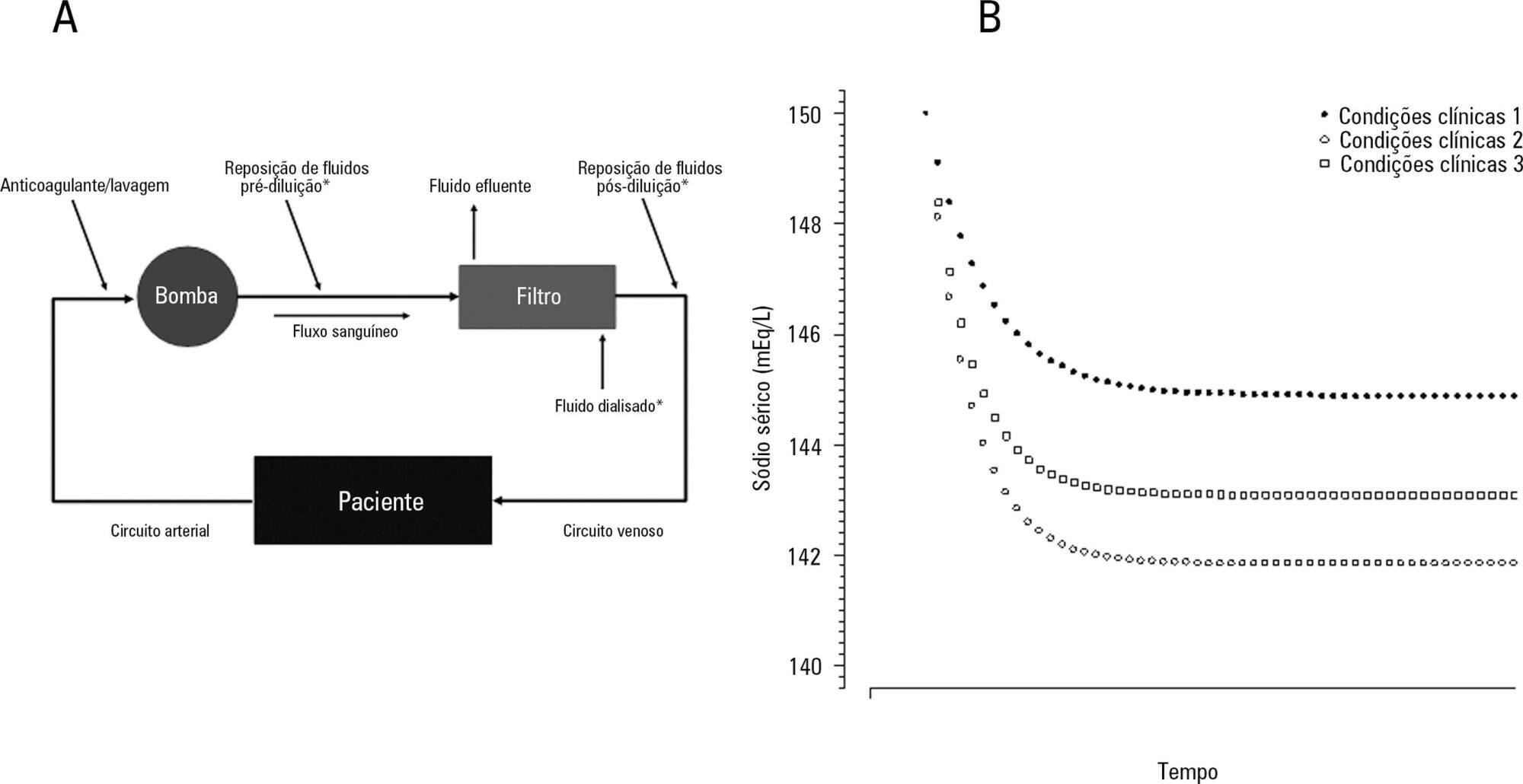
The aim of this study was to investigate the clinical and laboratorial factors associated with serum sodium variation during continuous renal replacement therapy and to assess whether the perfect admixture formula could predict 24-hour sodium variation.
Thirty-six continuous renal replacement therapy sessions of 33 patients, in which the affluent prescription was unchanged during the first 24 hours, were retrieved from a prospective collected database and then analyzed. A mixed linear model was performed to investigate the factors associated with large serum sodium variations (≥ 8mEq/L), and a Bland-Altman plot was generated to assess the agreement between the predicted and observed variations.
In continuous renal replacement therapy 24-hour sessions, SAPS 3 (p = 0.022) and baseline hypernatremia (p = 0.023) were statistically significant predictors of serum sodium variations ≥ 8mEq/L in univariate analysis, but only hypernatremia demonstrated an independent association (β = 0.429, p < 0.001). The perfect admixture formula for sodium prediction at 24 hours demonstrated poor agreement with the observed values.
Hypernatremia at the time of continuous renal replacement therapy initiation is an important factor associated with clinically significant serum sodium variation. The use of 4% citrate or acid citrate dextrose - formula A 2.2% as anticoagulants was not associated with higher serum sodium variations. A mathematical prediction for the serum sodium concentration after 24 hours was not feasible.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2016;28(1):19-26
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20160009
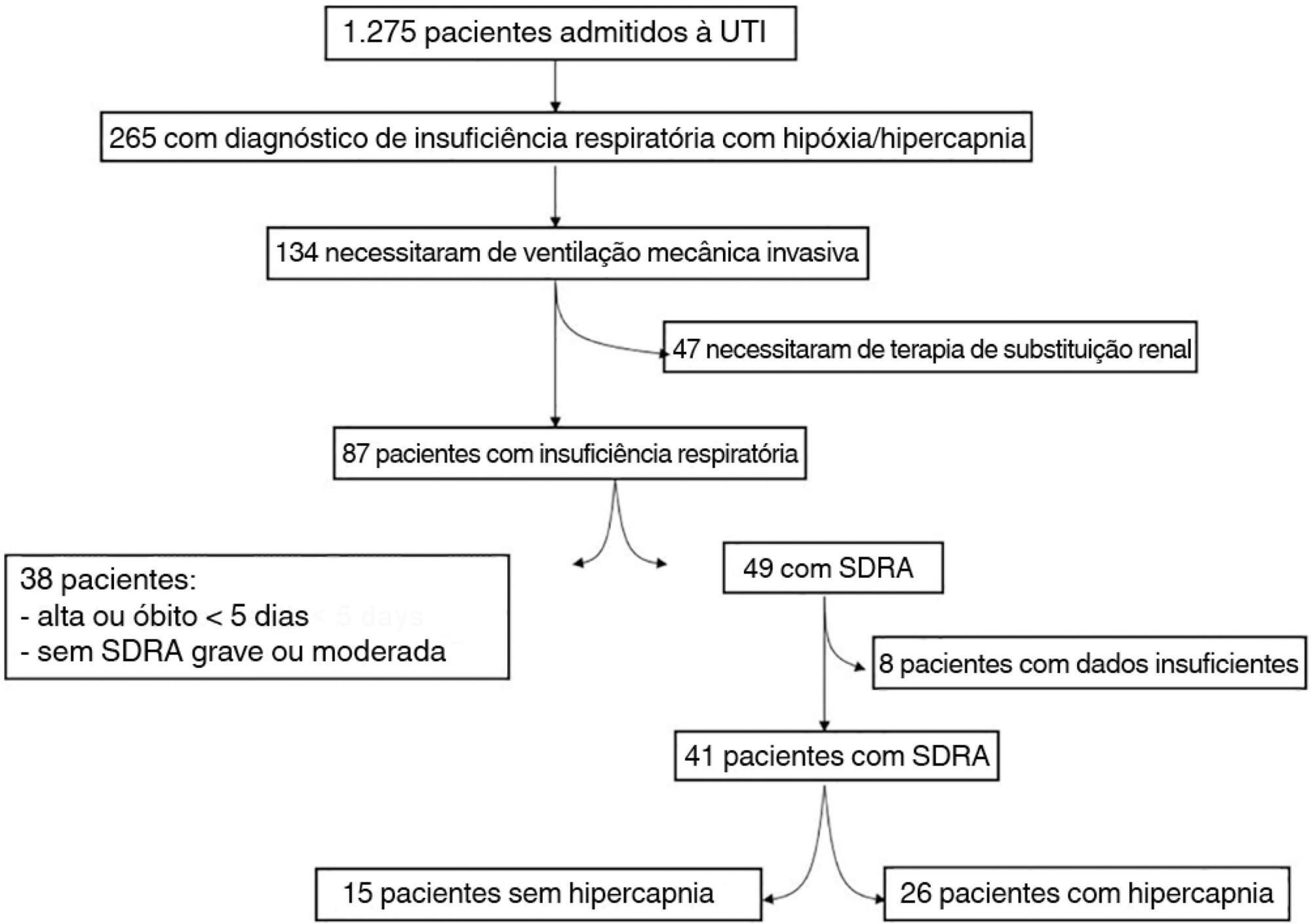
Hypercapnia resulting from protective ventilation in acute respiratory distress syndrome triggers metabolic pH compensation, which is not entirely characterized. We aimed to describe this metabolic compensation.
The data were retrieved from a prospective collected database. Variables from patients' admission and from hypercapnia installation until the third day after installation were gathered. Forty-one patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome were analyzed, including twenty-six with persistent hypercapnia (PaCO2 > 50mmHg > 24 hours) and 15 non-hypercapnic (control group). An acid-base quantitative physicochemical approach was used for the analysis.
The mean ages in the hypercapnic and control groups were 48 ± 18 years and 44 ± 14 years, respectively. After the induction of hypercapnia, pH markedly decreased and gradually improved in the ensuing 72 hours, consistent with increases in the standard base excess. The metabolic acid-base adaptation occurred because of decreases in the serum lactate and strong ion gap and increases in the inorganic apparent strong ion difference. Furthermore, the elevation in the inorganic apparent strong ion difference occurred due to slight increases in serum sodium, magnesium, potassium and calcium. Serum chloride did not decrease for up to 72 hours after the initiation of hypercapnia.
In this explanatory study, the results indicate that metabolic acid-base adaptation, which is triggered by acute persistent hypercapnia in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome, is complex. Furthermore, further rapid increases in the standard base excess of hypercapnic patients involve decreases in serum lactate and unmeasured anions and increases in the inorganic apparent strong ion difference by means of slight increases in serum sodium, magnesium, calcium, and potassium. Serum chloride is not reduced.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2016;28(1):27-32
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20160010
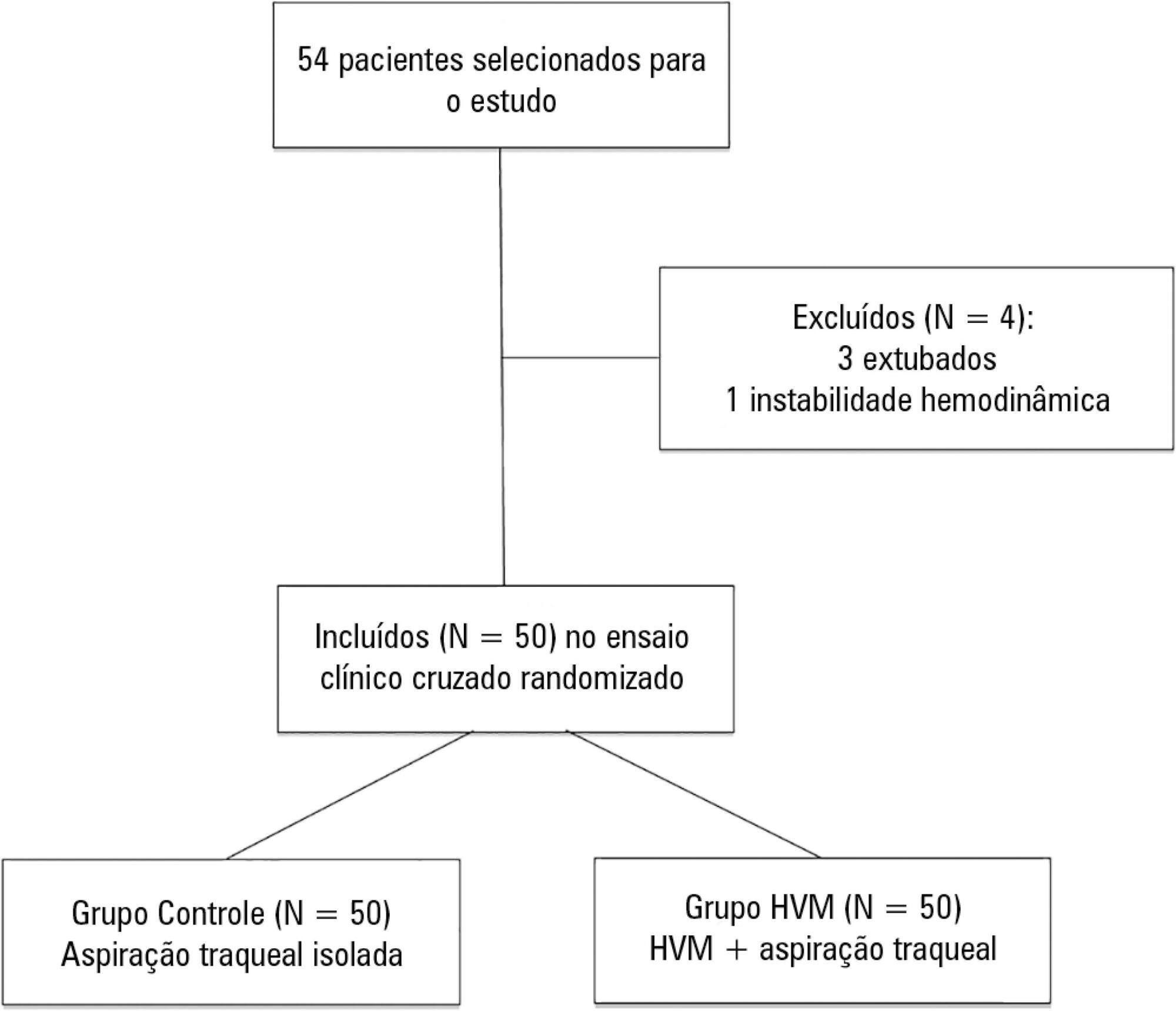
To determine the efficacy of lung hyperinflation maneuvers via a mechanical ventilator compared to isolated tracheal aspiration for removing secretions, normalizing hemodynamics and improving lung mechanics in patients on mechanical ventilation.
This was a randomized crossover clinical trial including patients admitted to the intensive care unit and on mechanical ventilation for more than 48 hours. Patients were randomized to receive either isolated tracheal aspiration (Control Group) or lung hyperinflation by mechanical ventilator (MVH Group). Hemodynamic and mechanical respiratory parameters were measured along with the amount of aspirated secretions.
A total of 50 patients were included. The mean age of the patients was 44.7 ± 21.6 years, and 31 were male. Compared to the Control Group, the MVH Group showed greater aspirated secretion amount (3.9g versus 6.4g, p = 0.0001), variation in mean dynamic compliance (-1.3 ± 2.3 versus -2.9 ± 2.3; p = 0.008), and expired tidal volume (-0.7 ± 0.0 versus -54.1 ± 38.8, p = 0.0001) as well as a significant decrease in peak inspiratory pressure (0.2 ± 0.1 versus 2.5 ± 0.1; p = 0.001).
In the studied sample, the MVH technique led to a greater amount of aspirated secretions, significant increases in dynamic compliance and expired tidal volume and a significant reduction in peak inspiratory pressure.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(4):376-382
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20150063
To evaluate the serum concentrations of vitamin D and their variations in patients with severe sepsis or septic shock and in control subjects upon admission and after 7 days of hospitalization in the intensive care unit and to correlate these concentrations with the severity of organ dysfunction.
This case-control, prospective, observational study involved patients aged > 18 years with severe sepsis or septic shock paired with a control group. Serum vitamin D concentrations were measured at inclusion (D0) and on the seventh day after inclusion (D7). Severe deficiency was defined as vitamin D levels < 10ng/ml, deficiency as levels between 10 and 20ng/ml, insufficiency as levels between 20 and 30ng/ml, and sufficiency as levels ≥ 30ng/mL. We considered a change to a higher ranking, together with a 50% increase in the absolute concentration, to represent an improvement.
We included 51 patients (26 with septic shock and 25 controls). The prevalence of vitamin D concentration ≤ 30ng/ml was 98%. There was no correlation between the serum concentration of vitamin D at D0 and the SOFA score at D0 or D7 either in the general population or in the group with septic shock. Patients with improvement in vitamin D deficiency had an improved SOFA score at D7 (p = 0.013).
In the population studied, patients with septic shock showed improvement in the serum concentrations of vitamin D on the seventh day compared with the controls. We also found a correlation between higher vitamin D concentrations and a greater decrease in the severity of organ dysfunction.