Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2022;34(3):351-359
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20220383-en
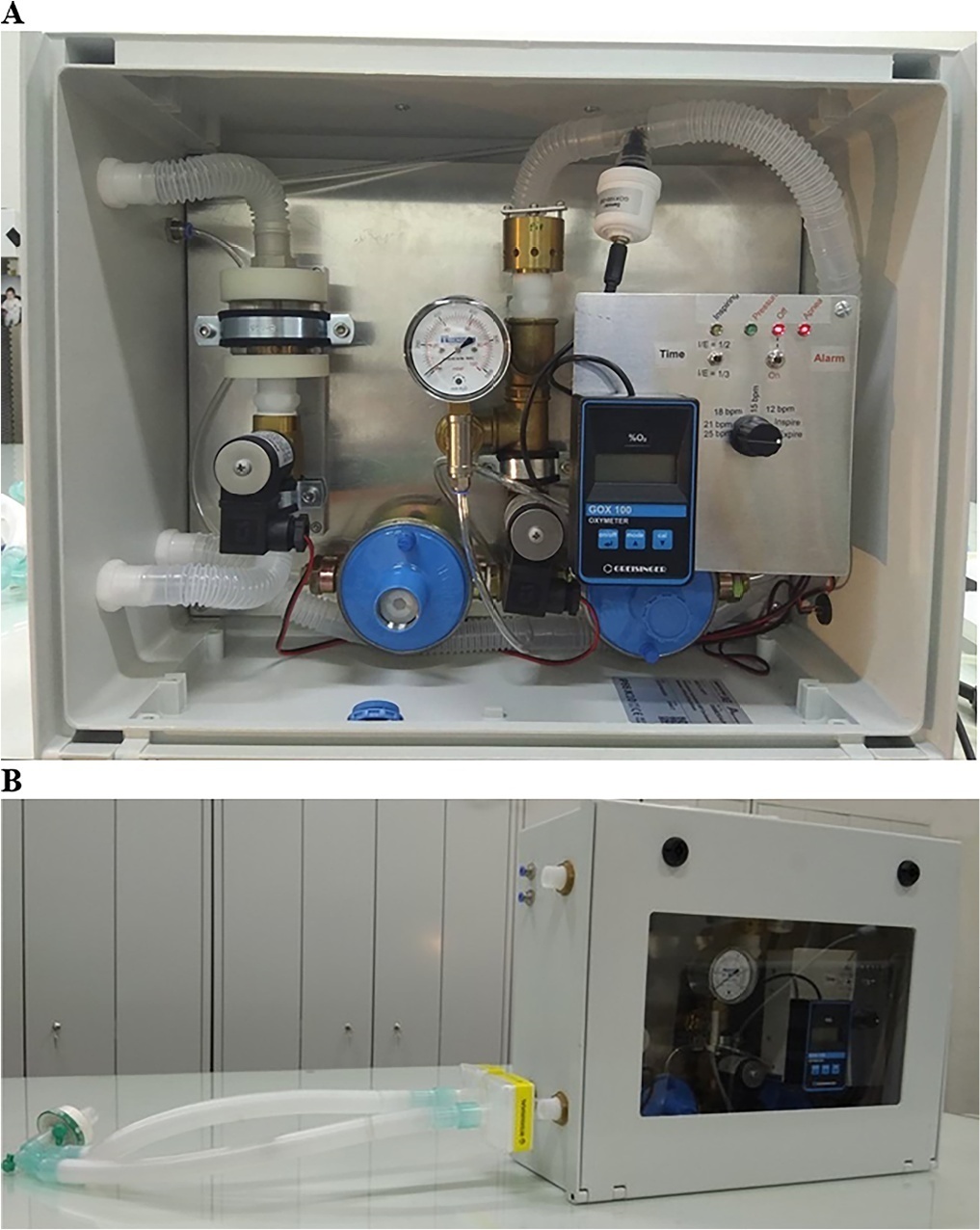
To develop a simple, robust, safe and efficient invasive mechanical ventilator that can be used in remote areas of the world or war zones where the practical utility of more sophisticated equipment is limited by considerations of maintainability, availability of parts, transportation and/or cost.
The device implements the pressure-controlled continuous mandatory ventilation mode, complemented by a simple assist-control mode. Continuous positive airway pressure is also possible. The consumption of compressed gases is minimized by avoiding a continuous flow of oxygen or air. Respiratory rates and inspiration/expiration time ratios are electronically determined, and an apnea/power loss alarm is provided.
The pressure profiles were measured for a range of conditions and found to be adjustable within a ± 2.5cmH2O error margin and stable well within this range over a 41-hour period. Respiratory cycle timing parameters were precise within a few percentage points over the same period. The device was tested for durability for an equivalent period of four months. Chemical and biological tests failed to identify any contamination of the gas by volatile organic compounds or microorganisms. A ventilation test on a large animal, in comparison with a well established ventilator, showed that the animal could be adequately ventilated over a period of 60 minutes, without any noticeable negative aftereffects during the subsequent 24-hour period.
This ventilator design may be viable, after further animal tests and formal approval by the competent authorities, for clinical application in the abovementioned atypical circumstances.

Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(4):616-623
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20210071
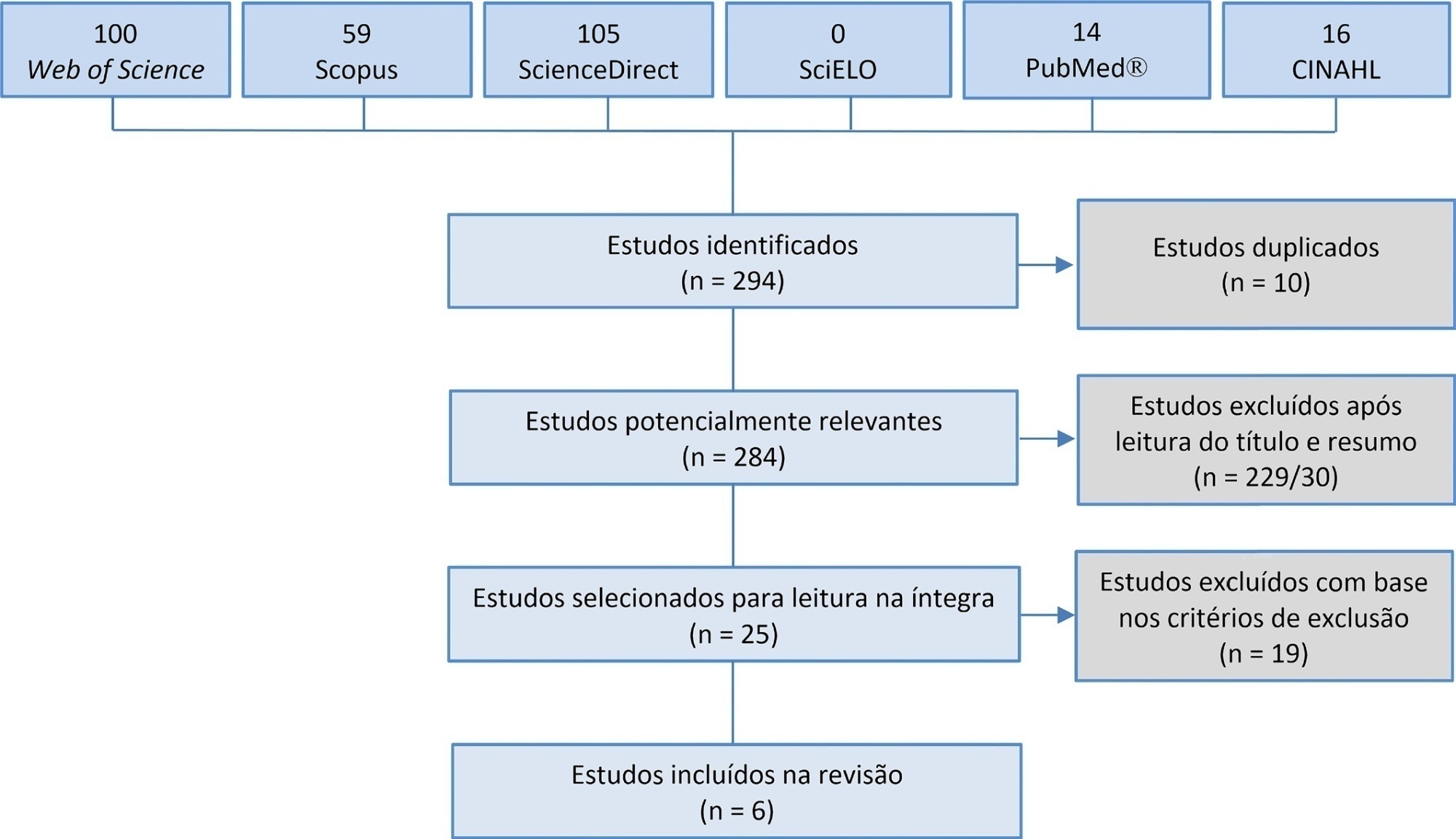
Manual hyperinflation is used in neonatal and pediatric intensive care units to promote expiratory flow bias, but there is no consensus on the benefits of the technique. Thus, a review that presents supporting evidence is necessary. This study aims to review the literature on the manual hyperinflation maneuver in neonatal and pediatric intensive care units to analyze the evidence for this technique in terms of the forms of application (associated with other techniques or not), its safety, the performance of manual resuscitators and the influence of the physical therapist’s experience, in addition to evaluating the methodological quality of the identified articles. A search was performed in the following databases: Web of Science, ScienceDirect, PubMedⓇ, Scopus, CINAHL and SciELO. Two researchers independently selected the articles. Duplicate studies were assessed, evaluated by title and abstract and then read in full. The quality of the articles was analyzed using the PEDro scale. Six articles were included, two of which had high methodological quality. The main results provided information on the contribution of the positive end-expiratory pressure valve to increasing lung volumes and the use of chest compressions to optimize expiratory flow bias, the negative influence of operator experience on the increase in peak inspiratory flow, the performance of different manual resuscitators when used with the technique and the safety of application in terms of maintaining hemodynamic stability and increasing peripheral oxygen saturation. The available studies point to a positive effect of the manual hyperinflation maneuver in children who are admitted to intensive care units.
Registration PROSPERO: CRD42018108056.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2007;19(2):221-225
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2007000200014
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: Mechanically ventilated patients usually present larger amounts of pulmonary secretions because of impairment in mucociliary function and mucus transport. The manual resuscitator is considered a resource for pulmonary hyperinflation with the aim of preventing mucus retention and pulmonary complications, improving oxygenation and reexpanding collapsed areas. Alternatively, the hyperinflation by mechanical ventilator is a reliable and practical device to promote lung expansion and desobstruction. The objective of this study was to review the literature concerning manual and ventilator hyperinflation treatments for patients in the intensive care units (ICU) setting. CONTENTS: Literature searches were performed using the databases MedLine, CINAHL, SciElo and LILACS with appropriate keywords, including: intensive care units, manual hyperinflation, mechanical ventilator, physiotherapy, physical therapy and ventilator hyperinflation. CONCLUSIONS: Although there are few studies demonstrating the efficacy of ventilator hyperinflation as a physical therapy device, it can be a safety option to promote therapeutic hyperinflation in ICU, compared to manual hyperinflation.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (116) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)