Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(1):47-56
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190011
To determine the association between the primary site of infection and in-hospital mortality as the main outcome, or the need for admission to the intensive care unit as a secondary outcome, in patients with sepsis admitted to the emergency department.
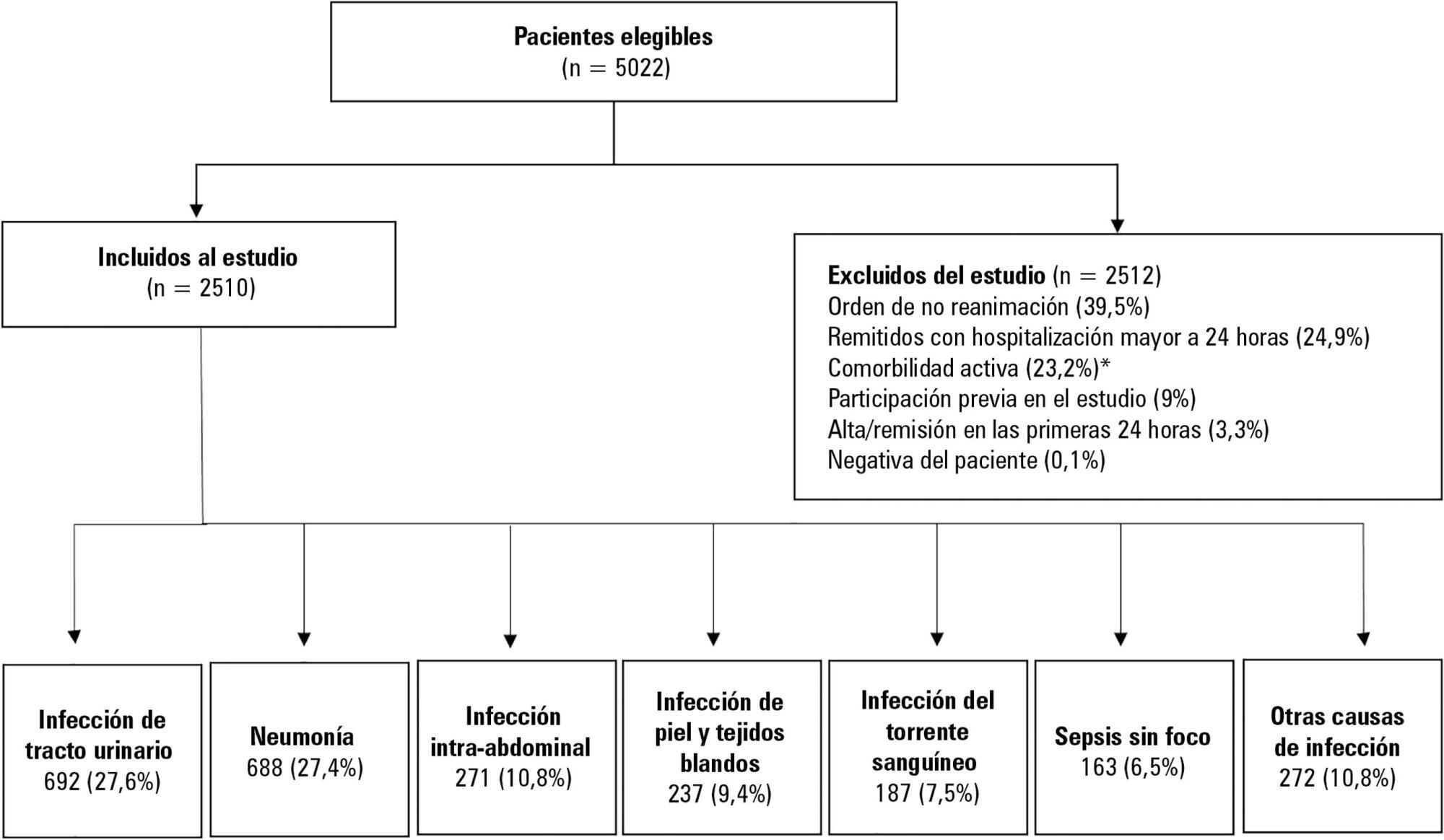
This was a secondary analysis of a multicenter prospective cohort. Patients included in the study were older than 18 years with a diagnosis of severe sepsis or septic shock who were admitted to the emergency departments of three tertiary care hospitals. Of the 5022 eligible participants, 2510 were included. Multiple logistic regression analysis was performed for mortality.
The most common site of infection was the urinary tract, present in 27.8% of the cases, followed by pneumonia (27.5%) and intra-abdominal focus (10.8%). In 5.4% of the cases, no definite site of infection was identified on admission. Logistic regression revealed a significant association between the following sites of infection and in-hospital mortality when using the urinary infection group as a reference: pneumonia (OR 3.4; 95%CI, 2.2 - 5.2; p < 0.001), skin and soft tissues (OR 2.6; 95%CI, 1.4 - 5.0; p = 0.003), bloodstream (OR 2.0; 95%CI, 1.1 - 3.6; p = 0.018), without specific focus (OR 2.0; 95%CI, 1.1 - 3.8; p = 0.028), and intra-abdominal focus (OR 1.9; 95%CI, 1.1 - 3.3; p = 0.024).
There is a significant association between the different sites of infection and in-hospital mortality or the need for admission to an intensive care unit in patients with sepsis or septic shock. Urinary tract infection shows the lowest risk, which should be considered in prognostic models of these conditions.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(1):71-78
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190013
To compare the clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients with community-acquired and hospital-acquired sepsis.
This is a retrospective cohort study that included all patients with a diagnosis of sepsis detected between January 2010 and December 2015 at a private hospital in southern Brazil. Outcomes (mortality, intensive care unit and hospital lengths of stay) were measured by analyzing electronic records.
There were 543 hospitalized patients with a diagnosis of sepsis, with a frequency of 90.5 (85 to 105) cases/year. Of these, 319 (58%) cases were classified as hospital-acquired sepsis. This group exhibited more severe disease and had a larger number of organ dysfunctions, with higher hospital [8 (8 - 10) versus 23 (20 - 27) days; p < 0.001] and intensive care unit [5 (4 - 7) versus 8.5 (7 - 10); p < 0.001] lengths of stay and higher in-hospital mortality (30.7% versus 15.6%; p < 0.001) than those with community-acquired sepsis. After adjusting for age, APACHE II scores, and hemodynamic and respiratory dysfunction, hospital-acquired sepsis remained associated with increased mortality (OR 1.96; 95%CI 1.15 - 3.32, p = 0.013).
The present results contribute to the definition of the epidemiological profile of sepsis in the sample studied, in which hospital-acquired sepsis was more severe and was associated with higher mortality.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2018;30(4):423-428
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20180060
To evaluate the short-term evolution of patients with septic shock refractory to norepinephrine treated with vasopressin in an intensive care unit of a university hospital.
An unmatched retrospective study (case series) was performed. Clinical, laboratory, and anthropometric data were collected from patients who received vasopressin infusion for treatment of catecholamine-refractory shock from December 2014 to June 2016. For the assessment of severity, APACHE II and SOFA scores were used. The main outcome was mortality at 3 and 30 days.
A total of 80 patients were included, of which 60% were male. In 86.3% of the cases, APACHE II was observed in the highest ranges (> 20). The 30-day mortality was 86.2%, and 75% of the patients died within 72 hours after starting vasopressin.
The series evaluated had high mortality in the first 72 hours of treatment with vasopressin. The use of vasopressin in patients who are refractory to norepinephrine had little or no impact on mortality. It was not possible to exclude the possibility that the high mortality in the present study was linked to the relatively late onset (after established refractoriness of norepinephrine) of vasopressin; this hypothesis should be further evaluated in a randomized study.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2017;29(3):317-324
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20170047
This study intended to determine whether the systemic inflammatory response syndrome criteria can predict hospital mortality in a Brazilian cohort of critically ill patients.
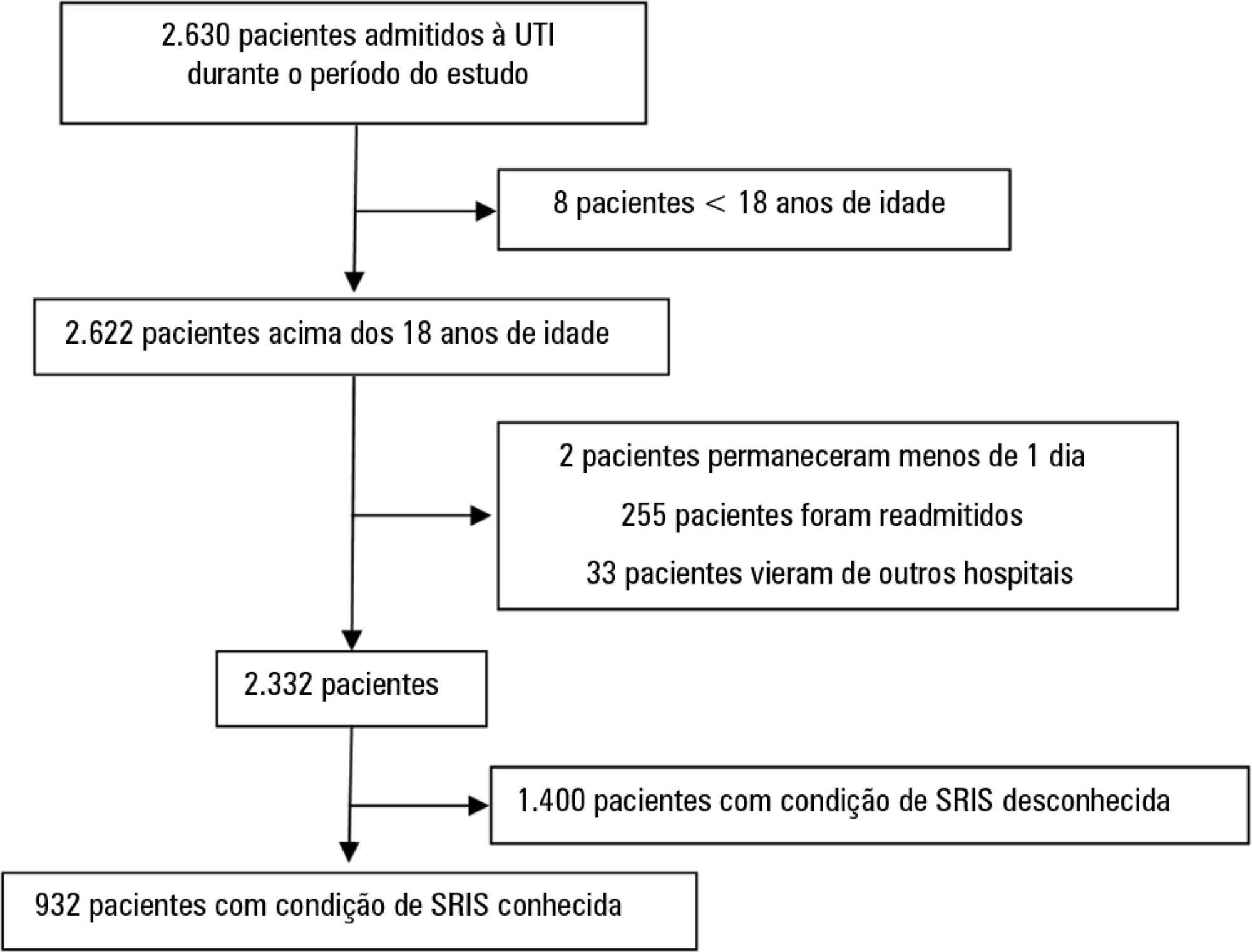
We performed a retrospective cohort study at a private tertiary hospital in São Paulo (SP), Brazil. We extracted information from the adult intensive care unit database (Sistema EpimedTM). We compared the SAPS 3 and the systemic inflammatory response syndrome model as dichotomous (≥ 2 criteria: systemic inflammatory response syndrome -positive versus 0 - 1 criterion: systemic inflammatory response syndrome -negative) and ordinal variables from 0 to 4 (according to the number of systemic inflammatory response syndrome criteria met) in the prediction of hospital mortality at intensive care unit admission. Model discrimination was compared using the area under the receiver operating characteristics (AUROC) curve.
From January to December 2012, we studied 932 patients (60.4% were systemic inflammatory response syndrome -positive). systemic inflammatory response syndrome -positive patients were more critically ill than systemic inflammatory response syndrome -negative patients and had higher hospital mortality (16.9% versus 8.1%, p < 0.001). In the adjusted analysis, being systemic inflammatory response syndrome -positive independently increased the risk of death by 82% (odds ratio 1.82; 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.12 - 2.96, p = 0.016). However, the AUROC curve for the SAPS 3 model was higher (0.81, 95%CI 0.78 - 0.85) compared to the systemic inflammatory response syndrome model with the systemic inflammatory response syndrome criteria as a dichotomous variable (0.60, 95%CI 0.55 - 0.65) and as an ordinal variable (0.62, 95%CI 0.57 - 0.68; p < 0.001) for hospital mortality.
Although systemic inflammatory response syndrome is associated with hospital mortality, the systemic inflammatory response syndrome criteria show low accuracy in the prediction of mortality compared with the SAPS 3.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2017;29(2):195-205
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20170019
To identify factors that may influence outcomes in patients with severe skin and soft tissue infections in the intensive care unit.
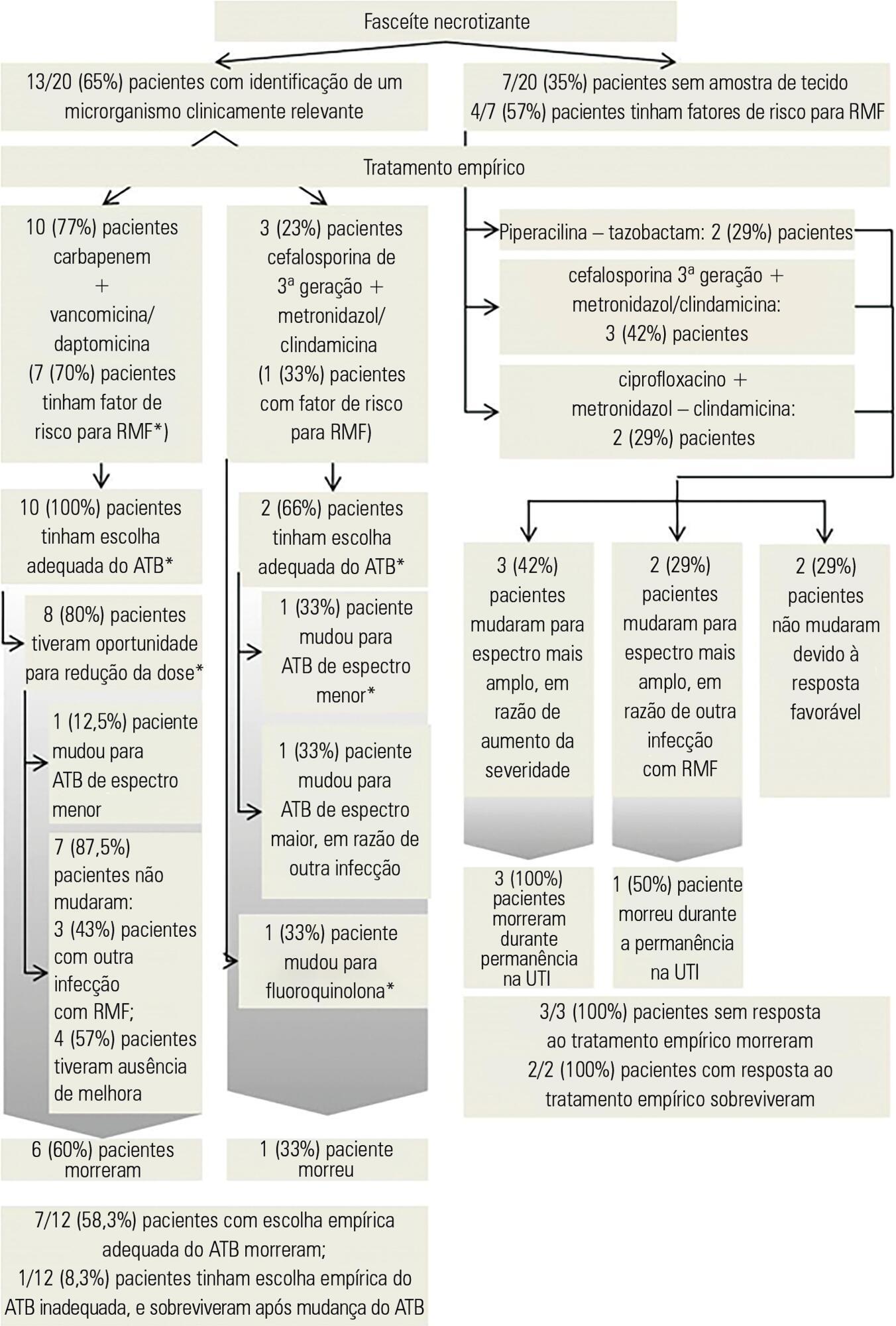
A retrospective observational study was conducted in a cohort of 1,123 critically ill patients admitted to an intensive care unit with a primary or secondary diagnosis of severe skin and soft tissues infection between January 2006 and December 2014.
Thirty patients were included, 20 (66.7%) of whom were diagnosed with necrotizing fasciitis; in these patients, perineal area involvement was most commonly identified. Abscess was diagnosed in 8 (26.7%) patients, most commonly involving the cervical area. Risk factors such as immunosuppression and previous surgical trauma were commonly observed in this population. The most commonly isolated microorganism was Escherichia coli. Multidrug resistant microorganisms were commonly detected, even in the absence of traditional risk factors; among these patients, previous use of antibiotics was the most common risk factor for drug resistance. The rate of mortality was significantly higher in patients with necrotizing fasciitis (55%, p = 0.035) and associated with disease severity, presence of septic shock, cardiac arrest and leucocytosis.
Different risk factors and etiologies of severe skin and soft tissue infections were identified. Necrotizing fasciitis and drug-resistant bacteria were significant predictors of mortality, even in the absence of traditional risk factors. Obtaining a better understanding of trends in the risk factors and microorganisms associated with severe skin infections may help in the determination of prompt treatment and antibiotic choices.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2017;29(4):490-498
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20170068
Dobutamine is the inotrope most commonly used in septic shock patients to increase cardiac output and correct hypoperfusion. Although some experimental and clinical studies have shown that dobutamine can improve systemic and regional hemodynamics, other research has found that its effects are heterogenous and unpredictable. In this review, we analyze the pharmacodynamic properties of dobutamine and its physiologic effects. Our goal is to show that the effects of dobutamine might differ between healthy subjects, in experimental and clinical cardiac failure, in animal models and in patients with septic shock. We discuss evidence supporting the claim that dobutamine, in septic shock, frequently behaves as a chronotropic and vasodilatory drug, without evidence of inotropic action. Since the side effects are very common, and the therapeutic benefits are unclear, we suggest that dobutamine should be used cautiously in septic shock. Before a definitive therapeutic decision, the efficacy and tolerance of dobutamine should be assessed during a brief time with close monitoring of its positive and negative side effects.
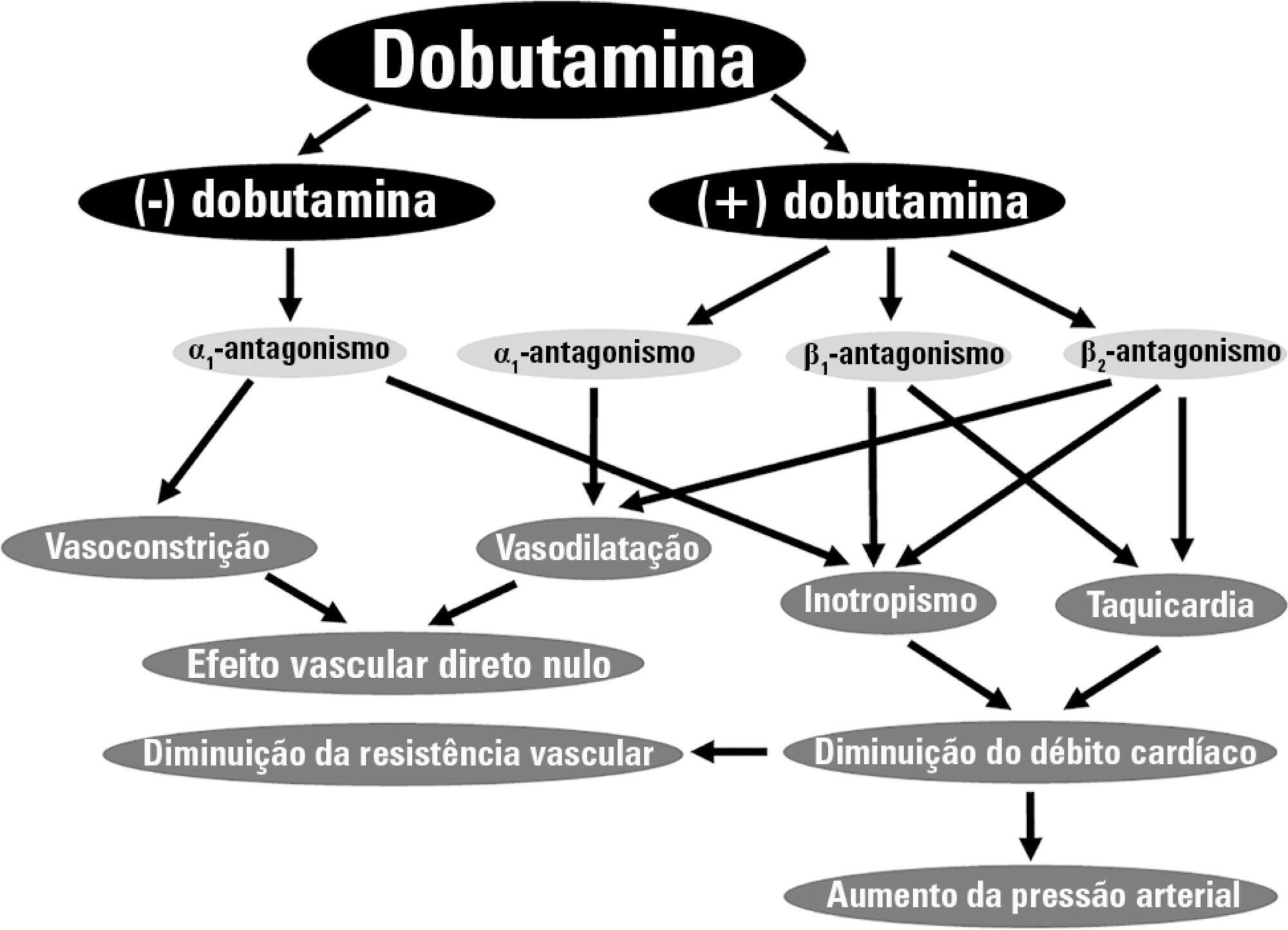
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2016;28(2):179-189
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20160019
Lower respiratory tract infections are common and potentially lethal conditions and are a major cause of inadequate antibiotic prescriptions. Characterization of disease severity and prognostic prediction in affected patients can aid disease management and can increase accuracy in determining the need for and place of hospitalization. The inclusion of biomarkers, particularly procalcitonin, in the decision taken process is a promising strategy. This study aims to present a narrative review of the potential applications and limitations of procalcitonin as a prognostic marker in hospitalized patients with lower respiratory tract infections. The studies on this topic are heterogeneous with respect to procalcitonin measurement techniques, cutoff values, clinical settings, and disease severity. The results show that procalcitonin delivers moderate performance for prognostic prediction in patients with lower respiratory tract infections; its predictive performance was not higher than that of classical methods, and knowledge of procalcitonin levels is most useful when interpreted together with other clinical and laboratory results. Overall, repeated measurement of the procalcitonin levels during the first days of treatment provides more prognostic information than a single measurement; however, information on the cost-effectiveness of this procedure in intensive care patients is lacking. The results of studies that evaluated the prognostic value of initial procalcitonin levels in patients with community-acquired pneumonia are more consistent and have greater potential for practical application; in this case, low procalcitonin levels identify those patients with a low risk of adverse outcomes.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2016;28(4):472-482
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20160080
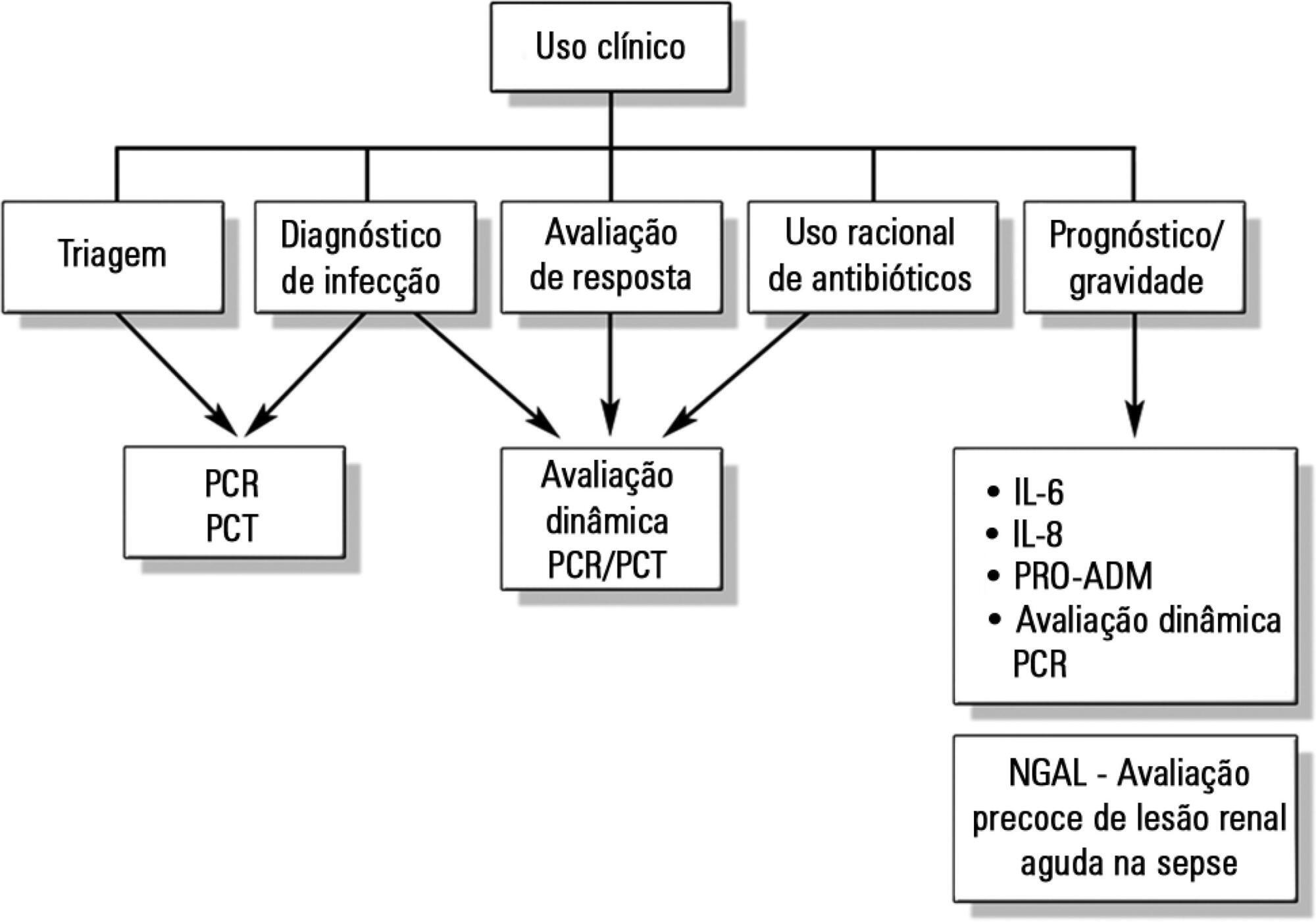
Despite advances in recent years, sepsis is still a leading cause of hospitalization and mortality in infants and children. The presence of biomarkers during the response to an infectious insult makes it possible to use such biomarkers in screening, diagnosis, prognosis (risk stratification), monitoring of therapeutic response, and rational use of antibiotics (for example, the determination of adequate treatment length). Studies of biomarkers in sepsis in children are still relatively scarce. This review addresses the use of biomarkers in sepsis in pediatric patients with emphasis on C-reactive protein, procalcitonin, interleukins 6, 8, and 18, human neutrophil gelatinase, and proadrenomedullin. Assessment of these biomarkers may be useful in the management of pediatric sepsis.