Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2017;29(1):39-46
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20170007
To determine the effectiveness of a quality management program in reducing the incidence and severity of pressure ulcers in critical care patients.
This was a quasi-experimental, before-and-after study that was conducted in a medical-surgical intensive care unit. Consecutive patients who had received mechanical ventilation for ≥ 96 hours were included. A "Process Improvement" team designed a multifaceted interventional process that consisted of an educational session, a pressure ulcer checklist, a smartphone application for lesion monitoring and decision-making, and a "family prevention bundle".
Fifty-five patients were included in Pre-I group, and 69 were included in the Post-I group, and the incidence of pressure ulcers in these groups was 41 (75%) and 37 (54%), respectively. The median time for pressure ulcers to develop was 4.5 [4 - 5] days in the Pre-I group and 9 [6 - 20] days in the Post-I group after admission for each period. The incidence of advanced-grade pressure ulcers was 27 (49%) in the Pre-I group and 7 (10%) in the Post-I group, and finally, the presence of pressure ulcers at discharge was 38 (69%) and 18 (26%), respectively (p < 0.05 for all comparisons). Family participation totaled 9% in the Pre-I group and increased to 57% in the Post-I group (p < 0.05). A logistic regression model was used to analyze the predictors of advanced-grade pressure ulcers. The duration of mechanical ventilation and the presence of organ failure were positively associated with the development of pressure ulcers, while the multifaceted intervention program acted as a protective factor.
A quality program based on both a smartphone application and family participation can reduce the incidence and severity of pressure ulcers in patients on prolonged acute mechanical ventilation.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2012;24(3):263-269
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2012000300010
OBJECTIVE: This study evaluated the relationship between nutritional intake and protein and caloric requirements and observed clinical outcomes on the 7th day of intensive care unit stay. METHODS: This was a retrospective cohort study of 126 patients who were admitted to the intensive care unit for >7 days. The patients were categorized according to the adequacy of energy and protein intake in relation to requirements (a >60% Adequate Intake Group and a <60% Inadequate Intake Group). The length of stay, ventilator free time and mortality in the intensive care unit and hospital were evaluated. RESULTS: Enteral nutrition was used in 95.6% of the 126 included patients, and nutrition was initiated 41 hours after admission to the intensive care unit. The adequacy of intake was 84% for energy and 72.5% for protein. No differences in the length of stay [16 (11-23) versus 15 (11-21) days, p=0.862], ventilator free time [2 (0-7) versus 3 (0-6) days, p=0.985] or mortality in the intensive care unit [12 (41.4%) versus 38 (39.1%), p=0.831] and hospital [15 (51.7%) versus 44 (45.4%), p=0.348] were observed between the adequate and inadequate energy intake groups, respectively. Similar results in protein intake and the length of hospital stay [15 (12-21) versus 15 (11-21) days, p=0.996], ventilator free time [2 (0-7) versus 3 (0-6) days, p=0.846], and mortality in the intensive care unit [15 (28.3%) versus 35 (47.9%), p=0.536)] and hospital [18 (52.9%) versus 41 (44.6%), p=0.262] were observed between groups. CONCLUSION: The results did not establish that energy and protein intakes of greater or less than 60% of nutritional requirements were reliable dividers of clinical outcomes.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2011;23(3):312-320
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2011000300009
OBJECTIVE: To evaluate associations between post-operative complications in patients who survive surgery and in-hospital deaths and lengths of hospital stays of patients who undergo coronary artery bypass graft surgery METHODS: Patients who underwent coronary artery bypass graft surgery and survived the operating theater were randomly selected. Information on complications and hospital lengths of stay until hospital discharge or death were retrospectively collected based on medical records and declarations of death. These aspects were estimated according to the presence of complications, frequency of complications, mortality, relative risk and attributable population risk. Mean hospital lengths of stay were compared using Wald's statistics. RESULTS: Medical records indicating deaths in the operating theater were excluded, and 86.9% of the included records reported complications; the greatest loss of information (43.9%) was related to kidney failure. Hyperglycemia was estimated as the most frequent complication (74.6%), with an attributable risk of 31.6%. The population's attributable risks were greater than 60% for low cardiac output (77.0%), kidney failure (64.3%) and cardiorespiratory failure (60.4%). Twelve different situations were identified for paired combinations of significant differences between average post-operative hospitalization times and complications, according to the outcome of discharge or death. CONCLUSION: Several complications were identified during the postoperative period of coronary artery bypass graft surgery, with different frequencies and impacts on mortality. Control of the myocardium at the risk of ischemia, hemodynamic stabilization and volume replacement strategies may be effective for controlling mortality rates and shortening hospital lengths of stay.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2010;22(4):339-345
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2010000400005
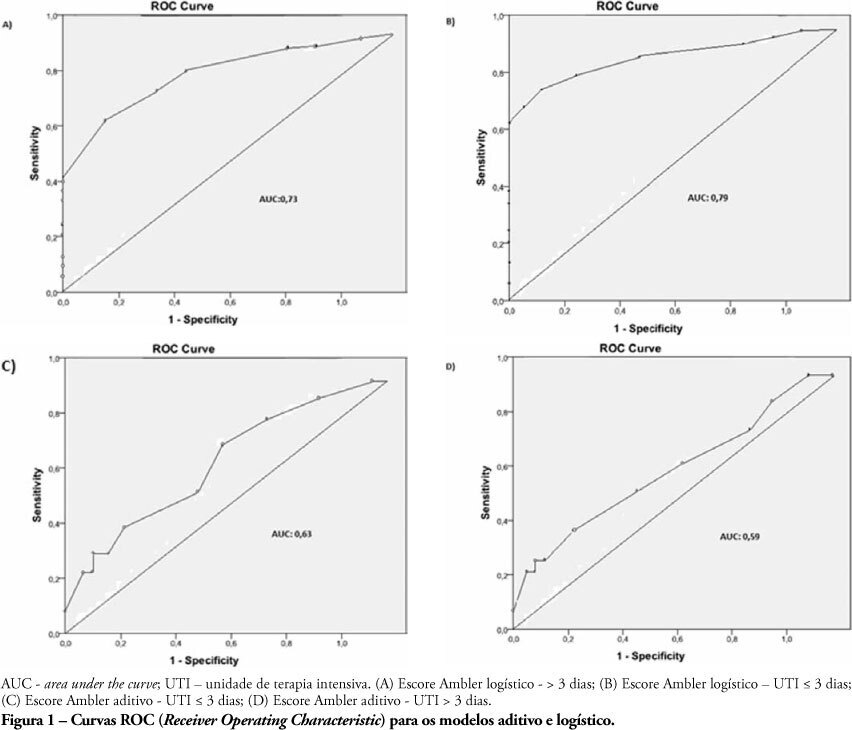
OBJECTIVES: The length of stay after prolonged cardiac surgery has been associated with poor immediate outcomes and increased costs. This study aimed to evaluate the predictive power of the Ambler Score to anticipate the length of stay in the intensive care unit. METHODS: This was a retrospective cohort study based on data collected from 110 patients undergoing valve replacement surgery alone or in combination with other procedures. Additive and logistic Ambler Scores were obtained and their predictive performances calculated using the Receiver Operating Characteristic curve. The normal length stay in the intensive care unit was assumed to be <3 days and prolonged >3 days. The areas under the receiver operating curves for both the additive and logistic models were compared using the Hanley-MacNeil test. RESULTS: The mean intensive care unit length of stay was 4.2 days. Sixty-three patients were male. The logistic model showed areas under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.73 and 0.79 for hospitalization > 3 days and < 3 days, respectively, showing good discriminative power. For the additive model, the areas were 0.63 and 0.59 for hospitalization > 3 days and < 3 days, respectively, a poor discriminative power. CONCLUSIONS: In our database, prolonged length of stay in the intensive care unit was positively correlated with the logistic Ambler score. The performance of the logistic Ambler Score had good discriminative power for correlation with the intensive care unit length of stay.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2010;22(3):250-256
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2010000300006
OBJECTIVE: The intensive care unit is synonymous of high severity, and its mortality rates are between 5.4 and 33%. With the development of new technologies, a patient can be maintained for long time in the unit, causing high costs, psychological and moral for all involved. This study aimed to evaluate the risk factors for mortality and prolonged length of stay in an adult intensive care unit. METHODS: The study included all patients consecutively admitted to the adult medical/surgical intensive care unit of Hospital das Clínicas da Universidade Estadual de Campinas, for six months. We collected data such as sex, age, diagnosis, personal history, APACHE II score, days of invasive mechanical ventilation orotracheal reintubation, tracheostomy, days of hospitalization in the intensive care unit and discharge or death in the intensive care unit. RESULTS: Were included in the study 401 patients; 59.6% men and 40.4% women, age 53.8±18.0. The mean intensive care unit stay was 8.2±10.8 days, with a mortality rate of 13.5%. Significant data for mortality and prolonged length of stay in intensive care unit (p <0.0001), were: APACHE II>11, OT-Re and tracheostomy. CONCLUSION: The mortality and prolonged length of stay in intensive care unit intensive care unit as risk factors were: APACHE>11, orotracheal reintubation and tracheostomy.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2009;21(4):353-358
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2009000400004
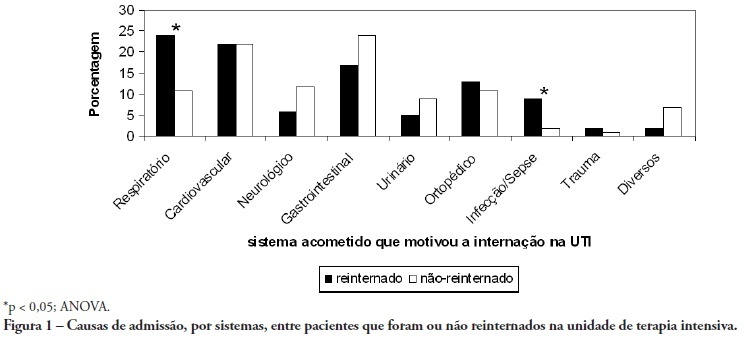
OBJECTIVE: To predict readmission in intensive care unit analyzing the first 24 hours data after intensive care unit admission. METHODS: The first intensive care unit admission of patients was analyzed from January to May 2009 in a mixed unit. Readmission to the unit was considered those during the same hospital stay or within 3 months after intensive care unit discharge. Deaths during the first admission were excluded. Demographic data, use of mechanical ventilation, and report of stay longer than 3 days were submitted to uni and multivariate analysis for readmission. RESULTS: Five hundred seventy-seven patients were included (33 excluded deaths). The readmission group had 59 patients, while 518 patients were not readmitted. The lead time between the index admission and readmission was 9 (3-28) days (18 were readmitted in less than 3 days), and 10 died. Patients readmitted at least once to the intensive care unit had the differences below in comparison to the control group: older age: 75 (67-81) versus 67 (56-78) years, P<0.01; admission for respiratory insufficiency or sepsis: 33 versus 13%, P<0.01; medical admission: 49 versus 32%, P<0.05; higher SAPS II score: 27 (21-35) versus 23 (18-29) points, P<0.01; Charlson index: 2 (1-2) versus 1 (0-2) points, P<0.01; first ICU stay longer than 3 days: 35 versus 23%, P<0.01. After logistic regression, higher age, Charlson index and admission for respiratory and sepsis were independently associated to readmissions in intensive care unit. CONCLUSION: Age, comorbidities and respiratory- and/or sepsis-related admission are associated with increased readmission risk in the studied sample.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2009;21(4):359-368
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2009000400005
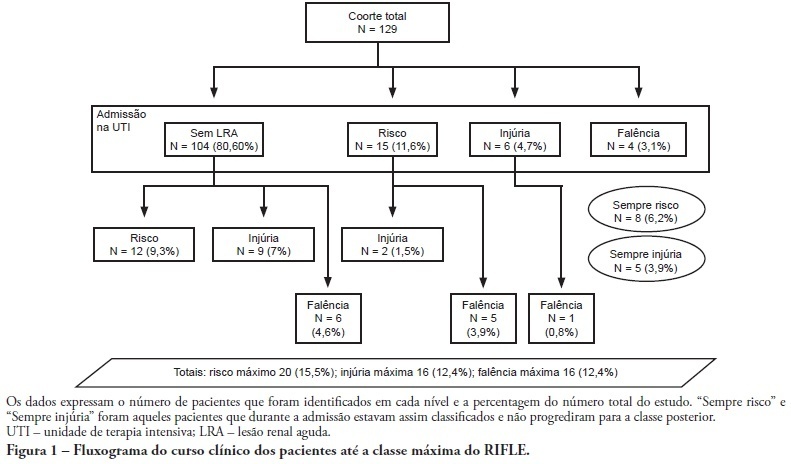
OBJECTIVE: To correlate the RIFLE classification with mortality and length of stay both in the intensive care unit and hospital. METHODS: A prospective, observational, longitudinal cohort study, approved by the Institution's Ethics Committee. Data were collected for all patients staying longer than 24 hours in the intensive care unit of Hospital Universitário Polydoro Ernani de São Thiago - Universidade Federal de Santa Catarina from September 2007 to March 2008, followed-up either until discharge or death. Patients were divided in two groups: with or without acute kidney injury. The acute kidney injury group was additionally divided according to the RIFLE and sub-divided according to the maximal score in Risk, Injury of Failure. Loss and End-stage classes were not included in the study. APACHE II and SOFA were also evaluated. The t Student and Chi-Square tests were used. A P<0.05 was considered statistically significant. RESULTS: The sample included 129 patients, 52 (40.3%) with acute kidney injury according to RIFLE. Patients were more severely ill in this group, with higher APACHE and SOFA scores (P<0.05). Compared to the without kidney injury group, the kidney injury severity caused increased intensive care unity (Risk 25%; Injury 37.5%; Failure 62.5%) and in-hospital (Risk 50%; Injury 37.5%; Failure 62.5%) mortality, and longer intensive care unit stay (P<0.05). CONCLUSION: The RIFLE system, according to the severity class, was a marker for risk of increased intensive care unit and in-hospital mortality, and longer intensive care unit stay. No relationship with in-hospital length of stay was found.