Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2018;30(4):496-507
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20180071
To assess the long-term, health-related quality of life of intensive care unit survivors by systematic review.
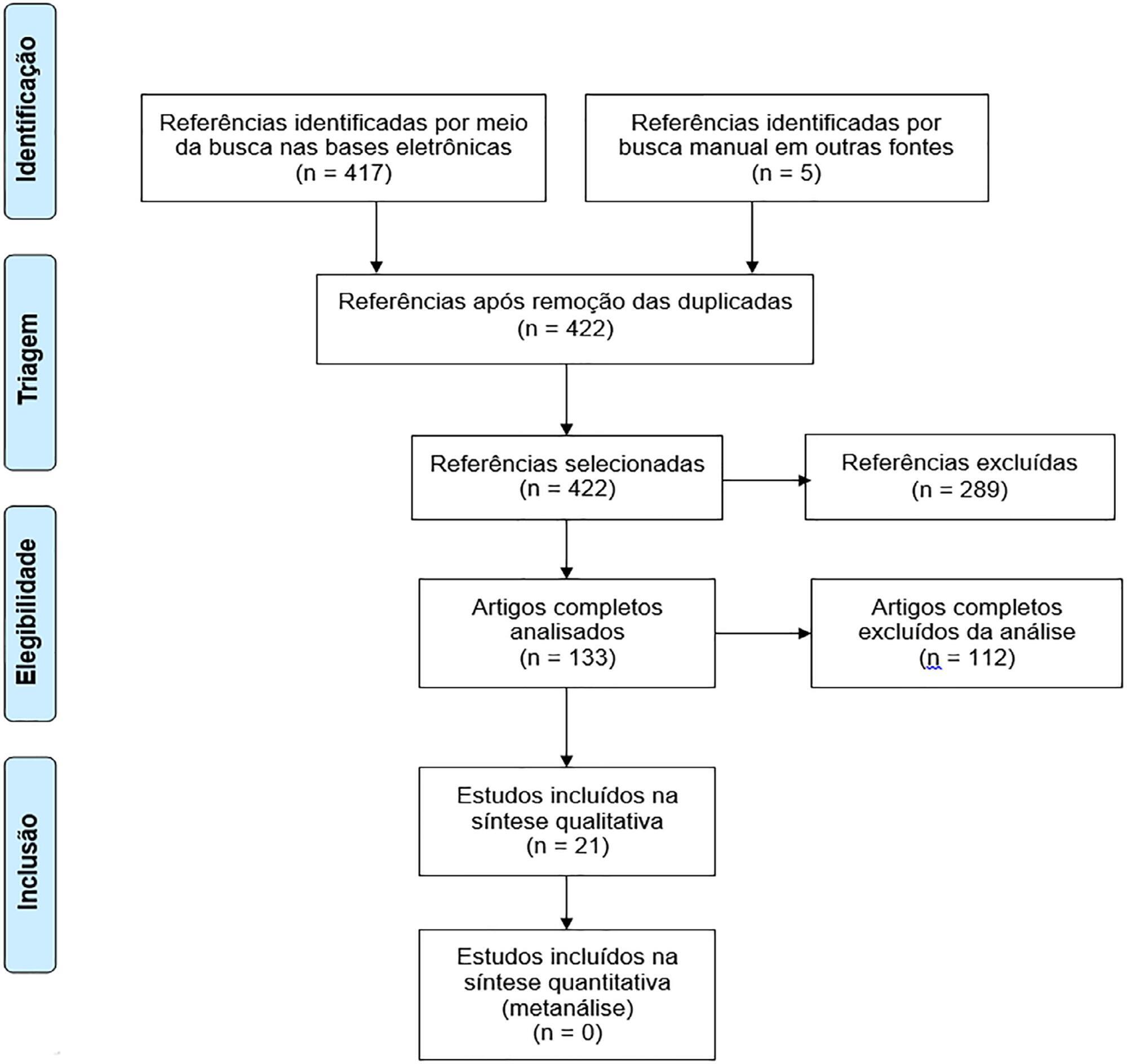
The search for, and selection and analysis of, observational studies that assessed the health-related quality of life of intensive care unit survivors in the electronic databases LILACS and MEDLINE® (accessed through PubMed) was performed using the indexed MESH terms "quality of life [MeSH Terms]" AND "critically illness [MeSH Terms]". Studies on adult patients without specific prior diseases published in English in the last 5 years were included in this systematic review. The citations were independently selected by three reviewers. Data were standardly and independently retrieved by two reviewers, and the quality of the studies was assessed using the Newcastle-Ottawa scale.
In total, 19 observational cohort and 2 case-control studies of 57,712 critically ill patients were included. The follow-up time of the studies ranged from 6 months to 6 years, and most studies had a 6-month or 1-year follow up. The health-related quality of life was assessed using two generic tools, the EuroQol and the Short Form Health Survey. The overall quality of the studies was low.
Long-term, health-related quality of life is compromised among intensive care unit survivors compared with the corresponding general population. However, it is not significantly affected by the occurrence of sepsis, delirium, and acute kidney injury during intensive care unit admission when compared with that of critically ill patient control groups. High-quality studies are necessary to quantify the health-related quality of life among intensive care unit survivors.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2017;29(4):418-426
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20170062
To describe the Epimed Monitor Database®, a Brazilian intensive care unit quality improvement database.
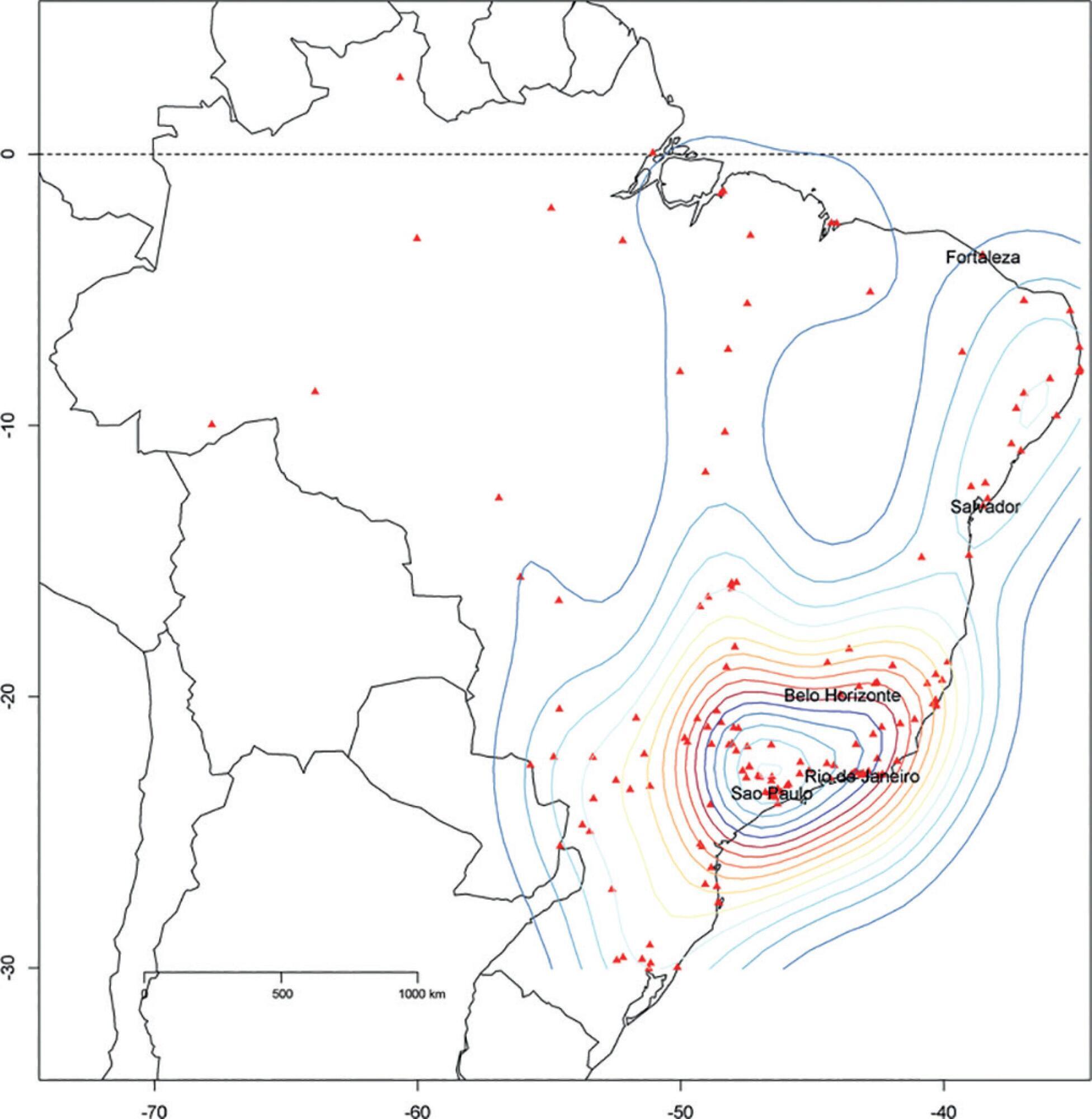
We described the Epimed Monitor® Database, including its structure and core data. We presented aggregated informative data from intensive care unit admissions from 2010 to 2016 using descriptive statistics. We also described the expansion and growth of the database along with the geographical distribution of participating units in Brazil.
The core data from the database includes demographic, administrative and physiological parameters, as well as specific report forms used to gather detailed data regarding the use of intensive care unit resources, infectious episodes, adverse events and checklists for adherence to best clinical practices. As of the end of 2016, 598 adult intensive care units in 318 hospitals totaling 8,160 intensive care unit beds were participating in the database. Most units were located at private hospitals in the southeastern region of the country. The number of yearly admissions rose during this period and included a predominance of medical admissions. The proportion of admissions due to cardiovascular disease declined, while admissions due to sepsis or infections became more common. Illness severity (Simplified Acute Physiology Score - SAPS 3 - 62 points), patient age (mean = 62 years) and hospital mortality (approximately 17%) remained reasonably stable during this time period.
A large private database of critically ill patients is feasible and may provide relevant nationwide epidemiological data for quality improvement and benchmarking purposes among the participating intensive care units. This database is useful not only for administrative reasons but also for the improvement of daily care by facilitating the adoption of best practices and use for clinical research.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2017;29(2):195-205
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20170019
To identify factors that may influence outcomes in patients with severe skin and soft tissue infections in the intensive care unit.
A retrospective observational study was conducted in a cohort of 1,123 critically ill patients admitted to an intensive care unit with a primary or secondary diagnosis of severe skin and soft tissues infection between January 2006 and December 2014.
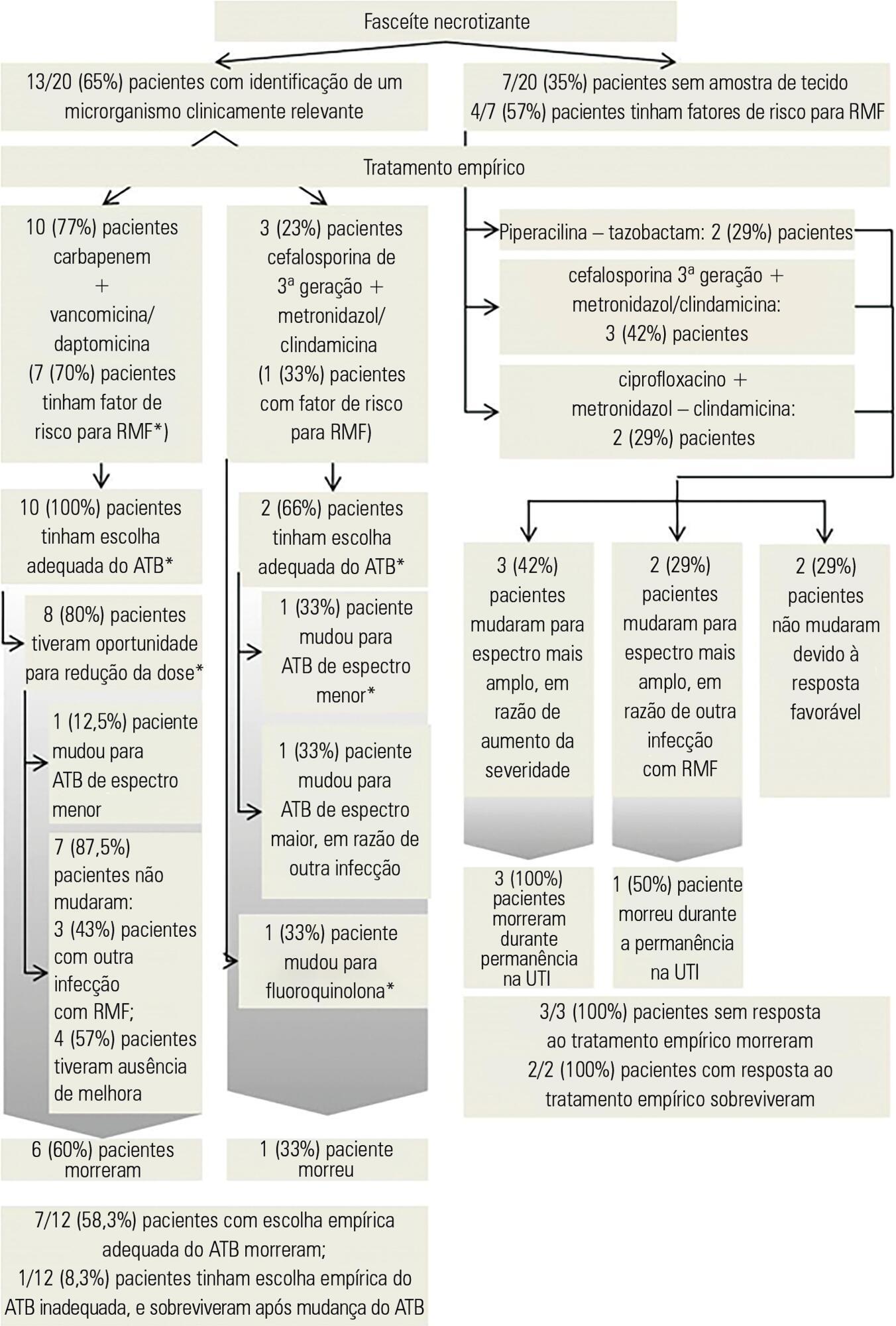
Thirty patients were included, 20 (66.7%) of whom were diagnosed with necrotizing fasciitis; in these patients, perineal area involvement was most commonly identified. Abscess was diagnosed in 8 (26.7%) patients, most commonly involving the cervical area. Risk factors such as immunosuppression and previous surgical trauma were commonly observed in this population. The most commonly isolated microorganism was Escherichia coli. Multidrug resistant microorganisms were commonly detected, even in the absence of traditional risk factors; among these patients, previous use of antibiotics was the most common risk factor for drug resistance. The rate of mortality was significantly higher in patients with necrotizing fasciitis (55%, p = 0.035) and associated with disease severity, presence of septic shock, cardiac arrest and leucocytosis.
Different risk factors and etiologies of severe skin and soft tissue infections were identified. Necrotizing fasciitis and drug-resistant bacteria were significant predictors of mortality, even in the absence of traditional risk factors. Obtaining a better understanding of trends in the risk factors and microorganisms associated with severe skin infections may help in the determination of prompt treatment and antibiotic choices.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2017;29(1):14-22
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20170004
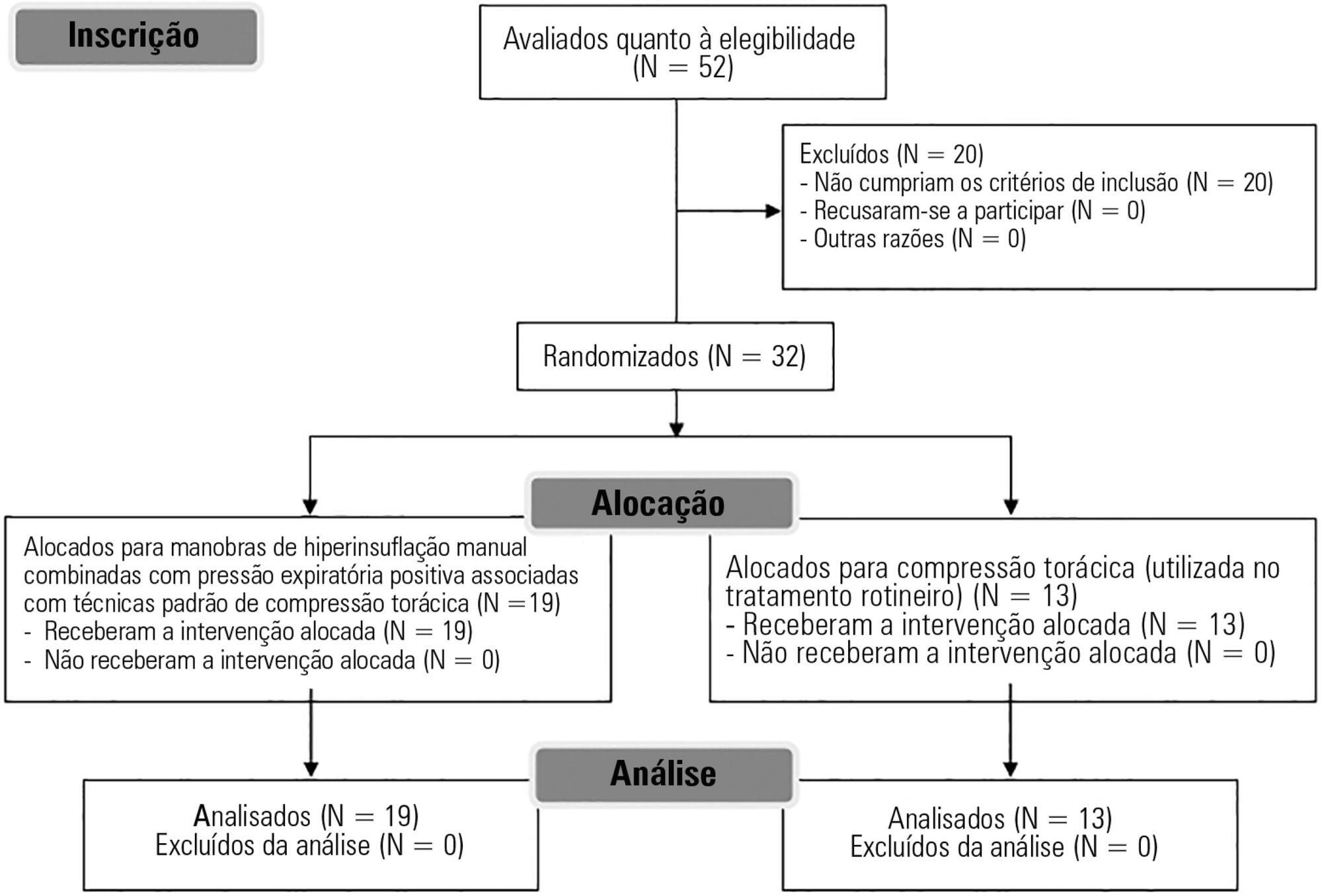
To evaluate the effects of bag-valve breathing maneuvers combined with standard manual chest compression techniques on safety, hemodynamics and oxygenation in stable septic shock patients.
A parallel, assessor-blinded, randomized trial of two groups. A computer-generated list of random numbers was prepared by an independent researcher to allocate treatments.
The Intensive Care Unit at Hospital São Lucas, Pontifícia Universidade Católica do Rio Grande do Sul.
Fifty-two subjects were assessed for eligibility, and 32 were included. All included subjects (n = 32) received the allocated intervention (n = 19 for the Experimental Group and n = 13 for the Control Group).
Twenty minutes of bag-valve breathing maneuvers combined with manual chest compression techniques (Experimental Group) or chest compression, as routinely used at our intensive care unit (Control Group). Follow-up was performed immediately after and at 30 minutes after the intervention.
Mean artery pressure.
All included subjects completed the trial (N = 32). We found no relevant effects on mean artery pressure (p = 0.17), heart rate (p = 0.50) or mean pulmonary artery pressure (p = 0.89) after adjusting for subject age and weight. Both groups were identical regarding oxygen consumption after the data adjustment (p = 0.84). Peripheral oxygen saturation tended to increase over time in both groups (p = 0.05), and there was no significant association between cardiac output and venous oxygen saturation (p = 0.813). No clinical deterioration was observed.
A single session of bag-valve breathing maneuvers combined with manual chest compression is hemodynamically safe for stable septic-shocked subjects over the short-term.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2017;29(1):34-38
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20170006
The aim of the present study was to translate and cross-culturally adapt the Functional Status Score for the intensive care unit (FSS-ICU) into Brazilian Portuguese.
This study consisted of the following steps: translation (performed by two independent translators), synthesis of the initial translation, back-translation (by two independent translators who were unaware of the original FSS-ICU), and testing to evaluate the target audience's understanding. An Expert Committee supervised all steps and was responsible for the modifications made throughout the process and the final translated version.
The testing phase included two experienced physiotherapists who assessed a total of 30 critical care patients (mean FSS-ICU score = 25 ± 6). As the physiotherapists did not report any uncertainties or problems with interpretation affecting their performance, no additional adjustments were made to the Brazilian Portuguese version after the testing phase. Good interobserver reliability between the two assessors was obtained for each of the 5 FSS-ICU tasks and for the total FSS-ICU score (intraclass correlation coefficients ranged from 0.88 to 0.91).
The adapted version of the FSS-ICU in Brazilian Portuguese was easy to understand and apply in an intensive care unit environment.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2017;29(1):39-46
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20170007
To determine the effectiveness of a quality management program in reducing the incidence and severity of pressure ulcers in critical care patients.
This was a quasi-experimental, before-and-after study that was conducted in a medical-surgical intensive care unit. Consecutive patients who had received mechanical ventilation for ≥ 96 hours were included. A "Process Improvement" team designed a multifaceted interventional process that consisted of an educational session, a pressure ulcer checklist, a smartphone application for lesion monitoring and decision-making, and a "family prevention bundle".
Fifty-five patients were included in Pre-I group, and 69 were included in the Post-I group, and the incidence of pressure ulcers in these groups was 41 (75%) and 37 (54%), respectively. The median time for pressure ulcers to develop was 4.5 [4 - 5] days in the Pre-I group and 9 [6 - 20] days in the Post-I group after admission for each period. The incidence of advanced-grade pressure ulcers was 27 (49%) in the Pre-I group and 7 (10%) in the Post-I group, and finally, the presence of pressure ulcers at discharge was 38 (69%) and 18 (26%), respectively (p < 0.05 for all comparisons). Family participation totaled 9% in the Pre-I group and increased to 57% in the Post-I group (p < 0.05). A logistic regression model was used to analyze the predictors of advanced-grade pressure ulcers. The duration of mechanical ventilation and the presence of organ failure were positively associated with the development of pressure ulcers, while the multifaceted intervention program acted as a protective factor.
A quality program based on both a smartphone application and family participation can reduce the incidence and severity of pressure ulcers in patients on prolonged acute mechanical ventilation.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2017;29(2):154-162
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20170025
To evaluate the factors potentially associated with the decision of admission to the intensive care unit in Brazil.
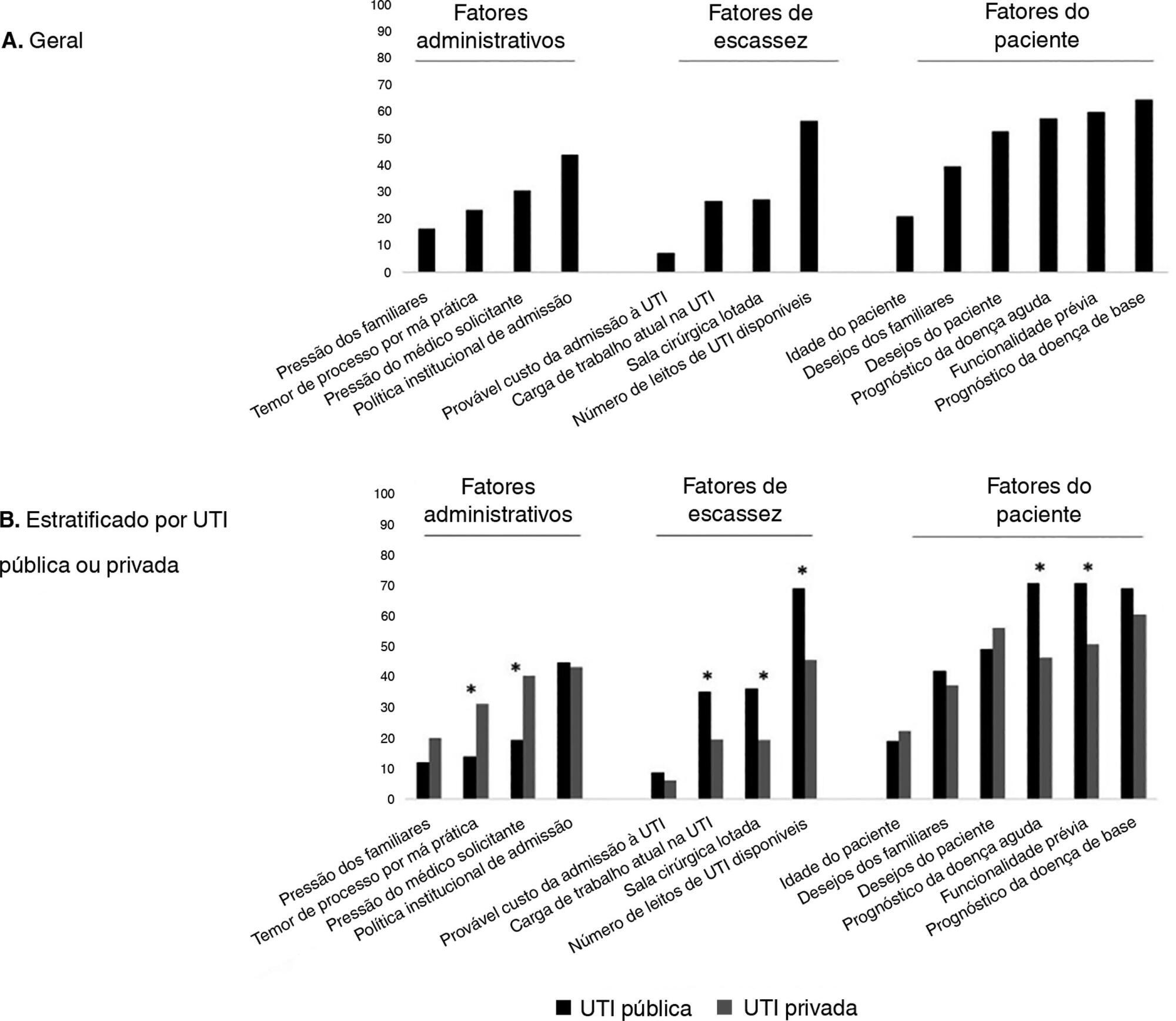
An electronic survey of Brazilian physicians working in intensive care units. Fourteen variables that were potentially associated with the decision of admission to the intensive care unit were rated as important (from 1 to 5) by the respondents and were later grouped as "patient-related," "scarcity-related" and "administrative-related" factors. The workplace and physician characteristics were evaluated for correlation with the factor ratings.
During the study period, 125 physicians completed the survey. The scores on patient-related factors were rated higher on their potential to affect decisions than scarcity-related or administrative-related factors, with a mean ± SD of 3.42 ± 0.7, 2.75 ± 0.7 and 2.87 ± 0.7, respectively (p < 0.001). The patient's underlying illness prognosis was rated by 64.5% of the physicians as always or frequently affecting decisions, followed by acute illness prognosis (57%), number of intensive care unit beds available (56%) and patient's wishes (53%). After controlling for confounders, receiving specific training on intensive care unit triage was associated with higher ratings of the patient-related factors and scarcity-related factors, while working in a public intensive care unit (as opposed to a private intensive care unit) was associated with higher ratings of the scarcity-related factors.
Patient-related factors were more frequently rated as potentially affecting intensive care unit admission decisions than scarcity-related or administrative-related factors. Physician and workplace characteristics were associated with different factor ratings.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2017;29(1):63-69
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20170010
To determine the impact of the day and time of admission and discharge from the intensive care unit on mortality.
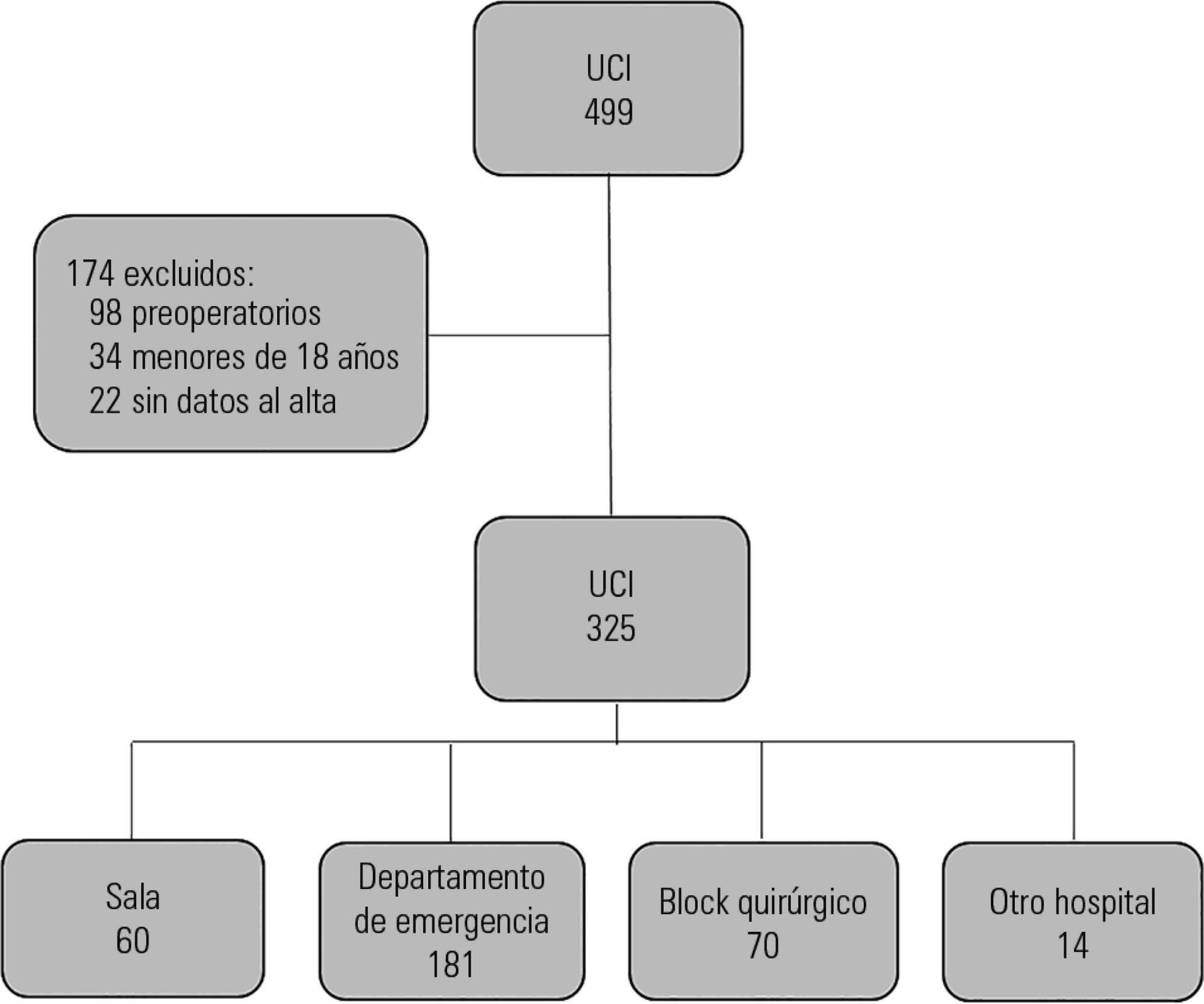
Prospective observational study that included patients admitted to the intensive care unit of the Hospital Maciel in Montevideo between April and November 2014.
We analyzed 325 patients with an average age of 55 (36 - 71) years and a SAPS II value of 43 (29 - 58) points. No differences were found in the mortality of patients in the intensive care unit when time of admission (35% on the weekend versus 31% on weekdays, p = ns) or the hour of entry (35% at night versus 31% in the daytime, p = ns) were compared. The time of discharge was associated with higher hospital mortality rates (57% for weekend discharges versus 14% for weekday discharges, p = 0.000). The factors independently associated with hospital mortality after discharge from the intensive care unit were age > 50 years (OR 2.4, 95%CI, 1.1 - 5.4) and weekend discharge (OR 7.7, 95%CI, 3.8-15.6).
This study identified the time of discharge from the intensive care unit as a factor that was independently associated with hospital mortality.