Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2009;21(2):190-196
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2009000200012
Use of ultrasound introduced as part of intensive care therapy makes viable bedside invasive procedures and diagnosis. Due to portability, combined with team training, its use guarantees less complications related to insertion, as well as patients' safety. It also reduces severe conditions related to the catheter, such as pneumothorax among others. Probably, in a near future, as purchase of ultrasound equipment becomes easier and team training more adequate, this tool will become essential in daily clinical practice.
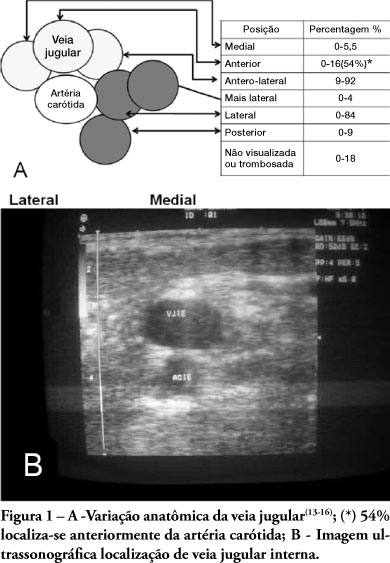
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2009;21(1):1-8
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2009000100001
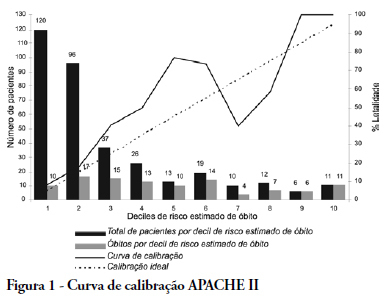
OBJECTIVE: The elderly constitute a population with their own features and frequent admissions in intensive care units. This study has the objective to evaluate the ability to predict the survival of these patients through the APACHE II, UNICAMP II, SAPS II and SAPS 3 indexes, global and Central America/South equations. METHODS: Elderly patients admitted from 01/01/2006 to 12/3/2006, defined as age > 60 years, were included in this study. Those who were readmitted were excluded. The rate of lethality standardized, calibration and discrimination for each index in the remaining patients were analysed. The outcome were death or hospital discharge. RESULTS: Three hundred eighty six elderly patients were included in this study, being 36 excluded by readmission, remaining 350 for analysis. The rate of lethality standardized came near to the unit in all indexes, except the SAPS II (TLP=1.5455) which underestimated the lethality. The calibration, via Hosmer-Lemeshow tests was inadequate (p < 0.05), except for the UNICAMP II (p > 0.5). On the calibration curve, the models have distanced themselves from the pattern line. All of them presented an excellent discrimination via receiver operating characteristics curves (> 0.8). CONCLUSIONS: In the studied population, the models presented an excellent discrimination and inadequate calibration. SAPS II underestimated the lethality.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2008;20(4):422-428
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2008000400016
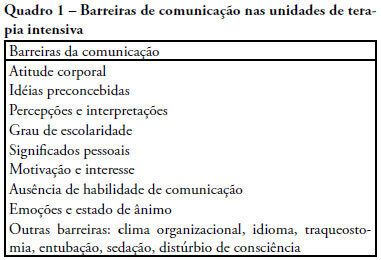
The objective of this review was to evaluate current knowledge regarding terminal illness and palliative care in the intensive care unit, to identify the major challenges involved and propose a research agenda on these issues The Brazilian Critical Care Association organized a specific forum on terminally ill patients, to which were invited experienced and skilled professionals on critical care. These professionals were divided in three groups: communication in the intensive care unit, the decision making process when faced with a terminally ill patient and palliative actions and care in the intensive care unit. Data and bibliographic references were stored in a restricted website. During a twelve hour meeting and following a modified Delphi methodology, the groups prepared the final document. Consensual definition regarding terminality was reached. Good communication was considered the cornerstone to define the best treatment for a terminally ill patient. Accordingly some communication barriers were described that should be avoided as well as some approaches that should be pursued. Criteria for palliative care and palliative action in the intensive care unit were defined. Acceptance of death as a natural event as well as respect for the patient's autonomy and the nonmaleficence principles were stressed. A recommendation was made to withdraw the futile treatment that prolongs the dying process and to elected analgesia and measures that alleviate suffering in terminally ill patients. To deliver palliative care to terminally ill patients and their relatives some principles and guides should be followed, respecting individual necessities and beliefs. The intensive care unit staff involved with the treatment of terminally ill patients is subject to stress and tension. Availability of a continuous education program on palliative care is desirable.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2008;20(4):344-348
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2008000400005
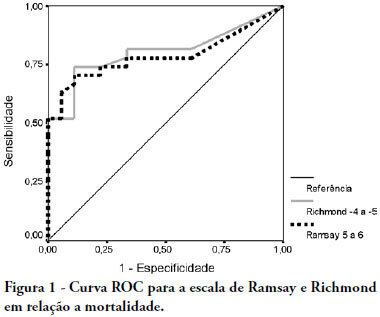
OBJECTIVE: The main purpose of this study was to compare performance of the Ramsay and Richmond sedation scores on mechanically ventilated critically ill patients, in a university-affiliated hospital. METHODS: This was a 4-month prospective study, which included a total of 45 patients mechanically ventilated, with at least 48 hours stay in the intensive care unit. Each patient was assessed daily for sedation mode, sedative and analgesic doses and sedation level using the Ramsay and Richmond scores. Statistical analysis was made using Student's t-test, Pearson's and Spearman's correlation, and constructing ROC-curves. RESULTS: A high general mortality of 60% was observed. The length of sedation and daily dose of medication did not correlate with mortality. Deep sedation (Ramsay > 4 or Richmond < -3) was positively correlated with probability of death with an AUC > 0.78. An adequate level of sedation (Ramsay 2 to 4 or Richmond 0 to -3) was sensitively correlated with probability of survival with an AUC > 0.80. A low level of sedation was observed in 63 days evaluated (8.64%), and no correlation was found between occurrence of agitation and unfavorable outcomes. Correlation between Ramsay and Richmond scores (Pearson's > 0.810 - p<0.0001) was good. CONCLUSION: In this study, Ramsay and Richmond sedation scores were similar for the assessment of deep, insufficient and adequate sedation. Both have good correlation with mortality in over sedated patients.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2008;20(3):249-253
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2008000300007
OBJECTIVES: Due to the high incidence in our service, we did object on this study describe the features and outcome of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) admitted to the intensive care unit of Walter Cantídio University Hospital METHODS: Patients were restrospectively characterized according to demography parameters, time of diagnosis of SLE, organ dysfunction and laboratorial parameters at admission, supportive therapies during their stay, length of stay in the hospital before admission, length of stay in the unit, readmission to the unit and outcome. We also evaluated Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity (SLEDAI) score, Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II (APACHE II) score, expected mortality and standardized mortality ratio. RESULTS: From November 2003 to October 2006, 1,052 patients were admitted to the intensive care unit. Fifty patients had SLE and were included in this retrospective study. Of the 50 patients with SLE admitted to the ICU, 88.2% were female. The mean age was 30.3 ± 12.8 years. The median time of diagnosis of SLE was 67 months. The most common organ dysfunctions were renal (70.6%), cardiovascular (61.8%), respiratory (55.9%) and neurological (55.9%). The main reasons for admission to the ICU were respiratory (38.2%), cardiologic (29.4%) and neurological (29.4%) dysfunctions. Among the intensive care therapies, 44.1% of the patients needed blood products, 41.2% vasopressor agents and 35.3% mechanical ventilation, 23.5% dialysis. The mean SLEDAI score was 15.0 ± 12.2. The mean APACHE II score was 19.3 ± 6.8, with a predicted mortality rate of 37.6%. The actual mortality rate in ICU was 29.4%, with 8.8% before 48 hours. The standardized mortality ratio was 0.78. Patients with APACHE II > 18, with more than 3 acute organ involvements, leukopenia (< 4000 cells/mm3) and gastrointestinal or metabolic involvement had higher mortality in the intensive care unit. CONCLUSION: Although the severity of patients at admission to the ICU, demonstrated by APACHE II and the acute dysfunctions, the outcomes of analysed patients sugest susceptibility to the therapy.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2008;20(3):286-295
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2008000300012
Considering the importance and the difficulties inherent to nutritional state assessment, as well as the results interpretation and the inexistence of specific and validated guidelines related to applied methods to the severely ill patient, the present revision aims to contribute to the analysis and recommendation of efficient methods, which are suitable to use and reliable in terms of interpretation in the context of the severely ill patient. The presence of edema and unspecific alterations in the plasmatic concentrations of proteins; altered anthropometrics variables reflecting more the rearrangement of the total body water than the nutritional state changes; inconclusive studies with electric bioimpedance; absence of data related to the application of the global subjective assessment to severely ill patients; altered biochemical markers as a consequence of the metabolic changes that, among others, indicate several method limitations to these patients. Notwithstanding the lack of studies to validate the various methods, recommendations based on clinical evidences, observation and physiopathology alterations are available. Independent from the methods, clinical observation by the health staff at all stages is mandatory. It is crucial to dedicate more efforts to identify methods and their specificity to detection, risk assessment or monitoring.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2006;18(1):95-98
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2006000100015
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: Iatrogenic conditions was due of the medical, correctly intervention or not, justified or not, which harmful consequences to the patient. The cares in Intensive Care Medicine present substantial challenges with relation to the security of the patient. The objective of this article is to make one brief revision of literature on the iatrogenic in its concepts and basic terms and its taxes prevalence in Intensive Care Medicine. CONTENTS: Intensive Care Medicine supplies subsidies that improve the morbidity and mortality, but that also the significant risks of adverse events and serious errors associate. The Iatrogenic can be minimized with the adequate monitorization or can be friction as waited aggravation, idiopathic and if to perpetuate in the anonymity. CONCLUSIONS: It is basic to recognize the necessity of the constant learning and recycling and conscience of the susceptibilities to the error; in this context, the respect for the human being must guide the professional behavior.
