Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2007;19(4):456-462
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2007000400009
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: There are deficiencies on Intensive Medicine (IM) teaching in most of medical undergraduate schools. Those deficiencies may imply damages on their clinical competence. The objective of this study was to analyze current status of IM teaching and the medical undergraduate student interest in this speciality. METHODS: A cross-sectional study was performed in 2005. We applied a self-reported questionnaire to enrolled students between the sixth and the last semesters of two medical schools from Salvador-Bahia. The questionnaire contained questions about students' interest and knowledge on IM, and opinion on IM teaching in their schools. RESULTS: We studied 570 students. Most of them (57.5%) had never realized a clerkship in intensive care unit (ICU) despite classifying its usefulness as high (mean of 4.14 ± 1.05, in a scale from 1 to 5). IM interest was high or very high in 53.7% of sample. Almost all students (97%) thought that IM topics should be more explored at their curriculum. Only 42.1% reported to be able to assess a critical care patient and this assurance was higher among students with previous clerkship in ICU (p < 0.001). Shock, cardiopulmonary resuscitation and sepsis were the most interesting topics in ICU for students' opinion. CONCLUSIONS: This study revealed a high interest in IM among medical undergraduate students. However, most had never practice a clerkship in ICU, demonstrating to be an important factor on undergraduate student performance faced to a critical care patient.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2007;19(4):414-420
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2007000400002
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: To determine the prevalence of intensive care unit (ICU)-acquired infections and the risk factors for these infections, identify the predominant infecting organisms, and evaluate the relationship between ICU-acquired infection and mortality. METHODS: A 1-day point prevalence study. Sixteen ICU of the State of Rio Grande do Sul-Brazil, excluding coronary care and pediatric units. All patients < 12 yrs occupying an ICU bed over a 24-hour period. The 16 ICU provided 174 case reports. Main outcomes: rates of ICU-acquired infection, resistance patterns of microbiological isolates, and potential risks factors for ICU-acquired infection and death. RESULTS: A total of 122 patients (71%) was infected and 51 (29%) had ICU-acquired infection. Pneumonia (58.2%), lower tract respiratory infection (22.9%), urinary tract infection (18%) were the most frequents types of ICU infection. Most frequently microorganisms reported were staphylococcus aureus (42% [64% resistant to oxacilin]) and pseudomonas aeruginosa (31%). Six risk factors for ICU acquired infection were identified: urinary catheterization, central vascular line, tracheal intubation for prolonged time (> 4 days), chronic disease and increased length of ICU stay (> 30 days). The risks factors associated with death were age, APACHE II, organ dysfunction, and tracheal intubation with or without mechanical ventilation. CONCLUSIONS: ICU-acquired infection is common and often associated with microbiological isolates of resistant organisms. This study may serve as an epidemiological reference to help the discussion of regional infection control policies.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2007;19(3):304-309
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2007000300006
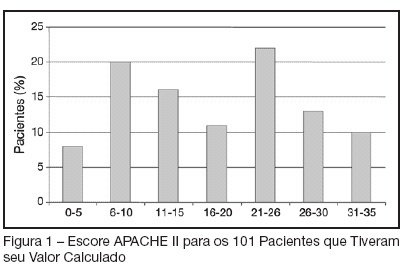
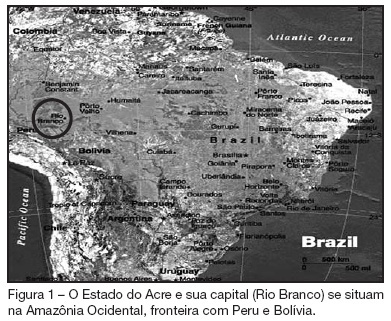
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: The intensive care Medicine was initiated in the State of the Acre in 1998. The aim of the present study was to establish clinical-epidemiological characteristics of adults and aged interned in a public intensive care unit (ICU) in the Amazon. METHODS: In 2004, a prospective study evaluated patients interned through the application of a questionnaire containing socioeconomics variables, invasive procedures, mechanical ventilation, nutritional support, surgical interventions and dialitic treatment. The gravity was established by APACHE II applied after 24 hours of internment. The follow up continued until the final destination in the unit: discharge or death. The statistical analysis used program SPSS, considering differences significant when p < 0.05. RESULTS: A total of 79 patients were assessed; 67.1% men; 59.5% white; 59.5% married; 50.4% came from other hospitals; 41.8% from the interior and 13.9% from others States and country (Bolivia) in frontier. The age varied from 20 to 104 (53.3 ± 18.6) years old; 30 (36.1%) aged (60 y old or more); 35 (44.3%) in surgical treatment; the median APACHE II was 18.4 ± 9.1. The stay in the UCI was of 10.2 ± 9.6 days; death occurred in 30 (38%) patients. Association between mortality and dialitic treatment, clinical indication, mechanical ventilation, vasoactive therapy, number of surgical interventions, hypoalbuminemia, lymphocytopenia and gravity was observed. CONCLUSIONS: The admission of severely ill patients coming from all over the State of Acre and frontier regions reflects the lack of ICU beds in the region.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2007;19(3):337-341
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2007000300012
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: Pressure ulcers (PU) constitute an important health problem in particular in the intensive care unit (ICU). The objective of the study was to identify the number, degree and total score of PU on admission, ICU stay and discharge as well as to recognize factors influencing the appearance or development of PU and to identify the number of healed PU, thus so the incidence and prevalence. METHODS: All patients admitted > 24 hrs were prospectively included during one year. Seventy patients were excluded for insufficient data. The prevention protocol (Norton scale; positioning according the risk grade) and therapeutic protocol (hydrocolloid dressings; hydrogel dressings if tissue necrosis and/or devitalized and alginate dressings if ulcer bleeds) was applied to all patients. RESULTS: One hundred and fifty five patients were studied. Eighteen patients were admitted already with PU. During ICU stay, 40 patients developed a total of 125 PU. The prevalence of PU was 37.41% and incidence was 25.8%. The development of new PU occurred on average by the 7th day. Patients with PU presented 2.6 PU on the average. Seventy nine percent of the patients admitted in the ICU remained stable or improved. Patients admitted with PU had a SAPS 2 significantly higher than those without, 54 ± 8.7 and 44 ± 17, respectively (p = 0.015). At the day of discharge, patients classified as high risk had significantly more PU (p = 0.039). Non-survivors had significantly more PU than survivors (p < 0.001). Patients with longer ICU stay had more PU (p < 0.001) CONCLUSIONS: In our patient population we found 37.41% prevalence and 25.8% incidence of PU. The present prevention protocol of PU was effective in 79% of the patients; severely ill patients developed PU more frequently.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2007;19(3):342-347
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2007000300013
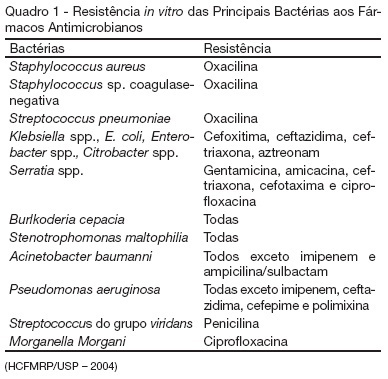
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: Care in the intensive care unit (ICU) is constantly challenged by infections related to invasive procedures, which result in increased morbidity and mortality, hospitalization term and costs. This study aimed to prospectively evaluate critical patients according to age, clinical conditions, hospitalization term, occurrence of hospital infection, topography of hospital infection, occurrence of microbial multi-resistance or not, use of invasive procedures and antimicrobial agents. METHODS: This is a prospective, observational, clinical research, carried out at an ICU between February and July 2006. The research subjects were critical patients hospitalized for more than 24 hours at the ICU, followed from admission until discharge, transference or death. RESULTS: The study group consisted of 71 patients with a mean age of 53.5 ± 18.75 years. Forty-seven of these patients (66.2%) acquired hospital infection. Twenty-nine infections (37.6%) occurred in the blood stream, 20 (26%) respiratory and 13 (16.9%) urinary. The most frequent multi-resistant strains were: 14 (10.85%) Pseudomonas aeruginosa, 4 (3.1%) coagulase-negative Staphylococcus sp and 4 (3.1%) Staphylococcus aureus. The most used antimicrobial agents were carbapenem (22.4%), glycopeptides (21.6%) and cephalosporin (21.6%). Twenty-nine (40.8%) of these patients died. CONCLUSIONS: Hospital infection is aggravated if associated to the increased resistance of the microorganisms to the antibiotics.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2007;19(2):151-160
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2007000200003
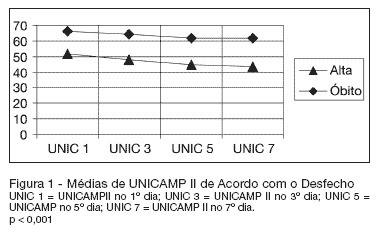
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: Currently, the reformulation of intensive care goals, often shifting from the search for a cure to offering comfort, has become more and more necessary. The intensivist is frequently confronted with the decision to suspend or not offer a specific therapy, despite its availability. The objective of this study was to estimate the developing risk of probability of death for individual ICU patients with respiratory failure, identify which life-sustaining therapies were administered, time of internment and outcome. Compare the death outcome in relation to UNICAMP II and APACHE II models, as well as verify if the life-sustaining therapies may be limited or suspended. METHODS: It is the observational, prospective cohort study of 150 patients with respiratory failure confined to the intensive care unit. Statistical analysis was carried out using Generalized Linear Models. RESULTS: Age, sex, race or morbidity did not reveal statistical significance in predicting outcome. This prediction was confirmed more accurately by means of changes in the individual prognostic index of death probability during the first seven days of ICU internment. A 10% worsening prognosis in patients who presented initial death risk of 70% to 80%, utilizing the UNICAMP II Model, showed a specificity of 97.4% - 98.6%. CONCLUSIONS: Prognostic changes in patients during the first seven days of ICU internment are of great aid, from an objective point of view, for ethical decision-making in relation to not-offering new life-sustaining therapies.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2007;19(2):221-225
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2007000200014
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: Mechanically ventilated patients usually present larger amounts of pulmonary secretions because of impairment in mucociliary function and mucus transport. The manual resuscitator is considered a resource for pulmonary hyperinflation with the aim of preventing mucus retention and pulmonary complications, improving oxygenation and reexpanding collapsed areas. Alternatively, the hyperinflation by mechanical ventilator is a reliable and practical device to promote lung expansion and desobstruction. The objective of this study was to review the literature concerning manual and ventilator hyperinflation treatments for patients in the intensive care units (ICU) setting. CONTENTS: Literature searches were performed using the databases MedLine, CINAHL, SciElo and LILACS with appropriate keywords, including: intensive care units, manual hyperinflation, mechanical ventilator, physiotherapy, physical therapy and ventilator hyperinflation. CONCLUSIONS: Although there are few studies demonstrating the efficacy of ventilator hyperinflation as a physical therapy device, it can be a safety option to promote therapeutic hyperinflation in ICU, compared to manual hyperinflation.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2007;19(1):118-122
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2007000100016
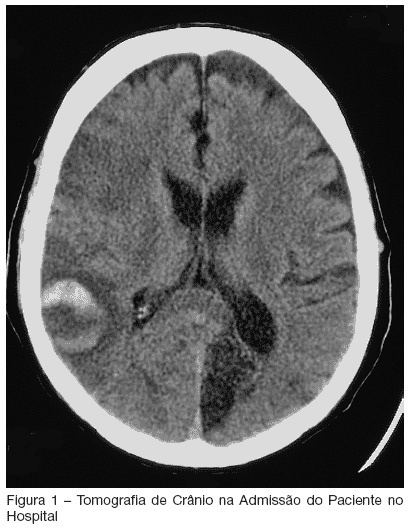
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: Critically ill patients represent a population with multiple risk factors for aspiration. Features such as decreased level of consciousness, mechanical ventilation, and comorbities as stroke, correlate with this increased threat in intensive care unit (ICU) patients. Recognition of deglutition dysfunction may identify patients at high risk of aspiration, and thereby help to avoid pulmonary complications such as recurrent pneumonia. The goal of our report is show a severe case of recurrent aspirative pneumonia after acute stroke and intubation, alerting to appropriate diagnosis and treatment of this condition. CASE REPORT: A male patient, 57 year old, was admitted to the hospital because of acute stroke. Ten days later, the patient began to have fever and severe shortness of breath. He was admitted to the ICU necessitating of intratracheal intubation. Four days after intubation he was extubated, however, he had a new aspirative pneumonia in ICU, newly treated. An evaluation of swallowing demonstrated a severe deglutition dysfunction with a high risk of aspiration. The patient was transferred, but aspirative pneumonia was diagnosed eight days after his ICU discharge and he was readmitted, stayed for a long time in ICU and presenting severe morbidity. CONCLUSIONS: ICU patients who are at risk for swallowing dysfunction and aspiration should be identified to prevent their associated morbidity and mortality.