Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2006;18(4):418-422
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2006000400017
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: Severe sepsis represents the systemic inflammatory response resulting from an infection, associated with one of the following: cardiovascular organ dysfunction, acute respiratory distress syndrome or two or more organ dysfunctions. Although the mortality rate from sepsis in children has steadily decreased in the last decades, the mortality rate in newborns remains high (20% to 40%) despite the development in intensive care. The authors describe a newborn who suffered from sepsis, shock and multiple organ dysfunction syndromes (MODS) that recovered after the administration of activated C protein. CASE REPORT: A premature newborn underwent cesarean section because of a premature rupture of membranes and acute fetal distress. The newborn developed acute respiratory distress due to intrauterine pneumonia and was taken to the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. The patient was given mechanical ventilation, exogenous pulmonary surfactant and antibiotics early in the treatment. Nevertheless, he developed persistent pulmonary hypertension and shock. The control of the infection was difficult, despite the adjustment of the antibiotics, resulting in the development of MODS. On the 28th day, activated C protein was given to the patient. The administration of the drug was successful and the patient recovered from the organ dysfunction without bleeding. CONCLUSIONS: The activated C protein can't be recommended as a routine in the treatment of newborns with severe sepsis. However, in this case, it contributed to the recovery of the organ dysfunctions presented by the patient.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2006;18(4):423-426
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2006000400018
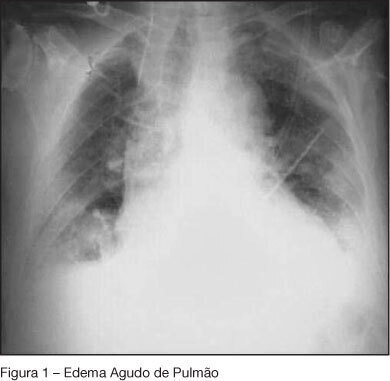
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: The presence of adverse reactions, inherent to all treatments, justifies the necessity of deep knowledge, by the medical team of the prevention and treatment of occasional organic dysfunctions, reducing its impact. The purpose of this paper is to report a case comprising the several systemic adverse reactions after perfusion of limb with melphalan and hyperthermia. CASE REPORT: A white female, 64-years old patient with diagnosis of melanoma in the medial malleoli region of the left lower limb. Six months after surgical removal of wound, an isolated perfusion of limb was carried out with melphalan and hyperthermia in order to curb the possible metastatic process in evolution. At admission in the ICU, the patient presented systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) with refractary hemodynamic instability to volemic expansion. During internation the patient evolved to acute lung edema and myocardial dysfunction, all reverted successfully. CONCLUSIONS: The potential presence of adverse reactions, inherent to all treatments, justify the necessity of knowledge by the intensive care team in the prevention and treatment of occasional organic dysfunctions, reducing the impact of morbidity and mortality.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2006;18(4):427-432
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2006000400019
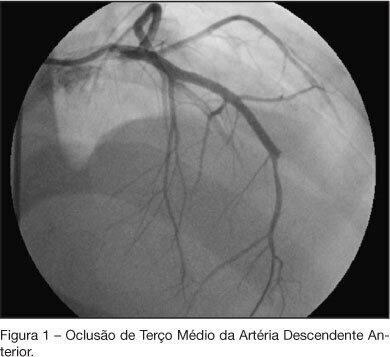
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: Cocaine is the most commonly used illicit drug and its acute and chronic effects are related to a variety of physiological changes, mainly in the cardiovascular system. This study is a case report of a patient with cardiomyopathy related to cocaine use. CASE REPORT: A 19 year old men, who has been using cocaine and crack since 15 years old, was admitted to the emergency department (ED) in February 2006 with progressive dyspnea during minimal efforts and bloody expectoration. During the physical exam it was observed legs edema, jugular stasis and dyspnea at rest. The echocardiogram demonstrated left ventricular hypocinesia, a 17 mm ventricular thrombus and a 12% ejection fraction. A bleeding from the left upper lobe was identified during a pulmonary bronchoscopy which was treated with arterial embolization. After 48h of the procedure, the patient was asymptomatic and an antithrombotic treatment with warfarin and enoxaparin was started. No obstruction was found at the cineangiography and the patient was discharged after clinical improvement. The patient was admitted again to the intensive care unit in July with intense chest pain and dyspnea at rest. A new cineangiography was performed and it was observed occlusion in the anterior descendent coronary artery. CONCLUSIONS: The cocaine acute effects are commonly seen at the ED but the chronic effects, as the cardiovascular manifestations, can take longer to be correlated as a side effect of cocaine use. Its prolonged use is related to left ventricular systolic dysfunction due to hypertrophy or myocardial dilation, atherosclerosis, arrhythmias, myocyte apoptosis and sympathetic damage.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2007;19(1):113-117
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2007000100015
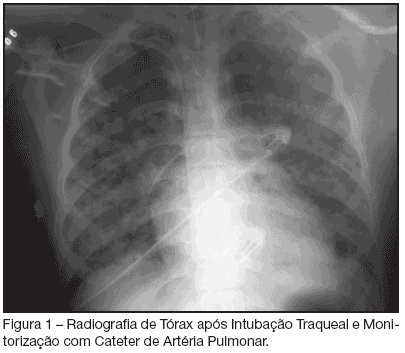
BACKGROUNG AND OBJECTIVES: Varicella is an exantematic disease caused by varicella-zoster virus. Varicella pneumonia complicated with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is very rare in adults and is associated with high morbimortality. We report two cases of ARDS secondary to varicella-zoster virus pneumonia. CASES REPORT: We report two cases of ARDS and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) secondary to varicella-zoster virus pneumonia. A 15-year-old man with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection and a 29-year-old immunocompetent female were admitted in the ICU with primary varicella infection and pneumonia. Both cases progressed towards ARDS, severe thrombocytopenia and acidosis. In addition cardiovascular and renal failure occurred in the first and second patients, respectively. Treatment consisted of immediate administration of intravenous acyclovir and a lung-protective ventilation strategy. CONCLUSIONS: Both cases of varicella-zoster pneumonia, complicated with ARDS and MODS, had a favourable outcome.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2007;19(1):118-122
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2007000100016
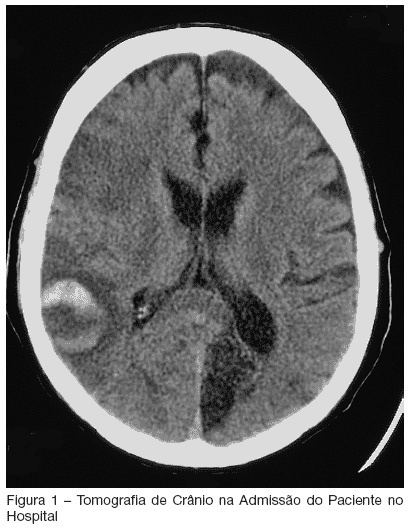
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: Critically ill patients represent a population with multiple risk factors for aspiration. Features such as decreased level of consciousness, mechanical ventilation, and comorbities as stroke, correlate with this increased threat in intensive care unit (ICU) patients. Recognition of deglutition dysfunction may identify patients at high risk of aspiration, and thereby help to avoid pulmonary complications such as recurrent pneumonia. The goal of our report is show a severe case of recurrent aspirative pneumonia after acute stroke and intubation, alerting to appropriate diagnosis and treatment of this condition. CASE REPORT: A male patient, 57 year old, was admitted to the hospital because of acute stroke. Ten days later, the patient began to have fever and severe shortness of breath. He was admitted to the ICU necessitating of intratracheal intubation. Four days after intubation he was extubated, however, he had a new aspirative pneumonia in ICU, newly treated. An evaluation of swallowing demonstrated a severe deglutition dysfunction with a high risk of aspiration. The patient was transferred, but aspirative pneumonia was diagnosed eight days after his ICU discharge and he was readmitted, stayed for a long time in ICU and presenting severe morbidity. CONCLUSIONS: ICU patients who are at risk for swallowing dysfunction and aspiration should be identified to prevent their associated morbidity and mortality.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2007;19(1):123-127
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2007000100017
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: Negative pressure pulmonary edema after acute upper airway obstruction is a well-described event, thought infrequently diagnosed and reported. This report aimed at presenting a case of postextubation negative pressure pulmonary edema refractory to use of diuretics and with successful therapeutic after using positive pressure noninvasive mechanic ventilation. CASE REPORT: A 22-year-old-woman underwent an operation to opened colecistectomy. The preoperative exams were abnormality us. Immediately after the extubation the patient presented with dyspnea and lungs stertors. The treatment for the acute pulmonary edema started with oxygen therapy under Venturi mask, lifting up chest and diuretic. The patient was transferred to Intensive Care Unit due to the lack of success with the treatment. A noninvasive ventilation (NIV) was started with support pressure of 15 cmH2O and PEEP of 5 cmH2O with resolution of symptoms. The patient was maintained under observation for 24 hours after the event with good conditions and received discharge to room without symptoms. CONCLUSIONS: Negative pressure pulmonary edema (NPPE) is a difficult diagnosed event and it must be always considered when patient develop with symptoms and signals of respiratory insufficiency postextubation. In our case was possible to treat with positive pressure non-invasive mechanical ventilation, but in case of the NIV failure the tracheal intubation and the invasive mechanical ventilatory support be initiated to improve the oxygen levels of the patient.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2007;19(1):128-131
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2007000100018
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: Strongyloides Stercoralis is a common cause of gastrointestinal infection. This nematode can produce an overwhelming hyperinfection syndrome, especially in the immunocompromised patient. Typically, patients present with pulmonary symptoms, but subsequently they can acquire Gram-negative sepsis. The objective of this report is to describe a lethal case and call attention to the importance of early diagnosis and treatment. CASE REPORT: Male patient, 60 year-old with diagnosis of timoma, treated with surgery, radiotherapy and chemotherapy in the past. He presented to the emergency room complaining of diarrhea and dyspnea, and then transferred to the ICU after development of hypoxemic acute respiratory failure and refractory septic shock, and despite treatment the patient died. A bronchial sample of sputum showed Strongyloides stercoralis worms. CONCLUSIONS: Strongyloides stercoralis infection symptoms are usually mild, but in the setting of impaired host immunity, a disseminated and severe illness may occur. Clinicians must be aware for patients from endemic areas. Diagnosis may be established through sputum and stool examination for Strongyloides stercoralis worms.