Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2006;18(1):86-94
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2006000100014
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: Corticosteroids were introduced in the treatment of severe infection as early as in the nineteen forties. Several " negative" randomized controlled trials of high-dose of glucocorticoids given for a short period of time in the early course of severe sepsis or acute respiratory distress syndrome raised serious doubts on the benefit of this treatment. Recently, a link between septic shock and adrenal insufficiency, or systemic inflammation induced glucocorticoids receptor resistance had been established. This finding prompted renewed interest of a replacement therapy with low doses of corticosteroids during longer periods. The goal of this article is to review the key role of corticosteroids in the host response to stress and will update the reader with the new validated indications of corticosteroids treatment in the ICU. CONTENTS: Extensive review of the adrenal physiology and its pathophysiological derangements and clinical implications in critically ill patients. CONCLUSIONS: During sepsis, hemodynamic instability and perpetuation of inflammatory state may result from adrenal insufficiency (AI). Thus, an ACTH test should be performed as soon as possible to identify non overt AI. It should be immediately followed by a replacement therapy with iv bolus of 50 mg of hydrocortisone every 6 hours combined to 50 µg of fludrocortisone once daily. When the results of the ACTH test are available, treatment should be continued for 7 days in the non responders to ACTH and withdraw in the responders. Whether responders to ACTH with high baseline cortisol levels (> 34 µg/dL) have tissue resistance to cortisol and also should receive exogenous hormones remains to be evaluated in clinical trials.
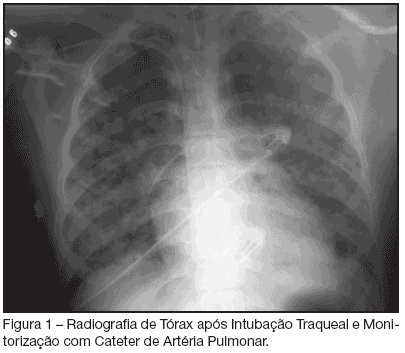
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2007;19(1):113-117
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2007000100015
BACKGROUNG AND OBJECTIVES: Varicella is an exantematic disease caused by varicella-zoster virus. Varicella pneumonia complicated with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is very rare in adults and is associated with high morbimortality. We report two cases of ARDS secondary to varicella-zoster virus pneumonia. CASES REPORT: We report two cases of ARDS and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) secondary to varicella-zoster virus pneumonia. A 15-year-old man with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection and a 29-year-old immunocompetent female were admitted in the ICU with primary varicella infection and pneumonia. Both cases progressed towards ARDS, severe thrombocytopenia and acidosis. In addition cardiovascular and renal failure occurred in the first and second patients, respectively. Treatment consisted of immediate administration of intravenous acyclovir and a lung-protective ventilation strategy. CONCLUSIONS: Both cases of varicella-zoster pneumonia, complicated with ARDS and MODS, had a favourable outcome.