Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2012;24(4):362-368
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2012000400012
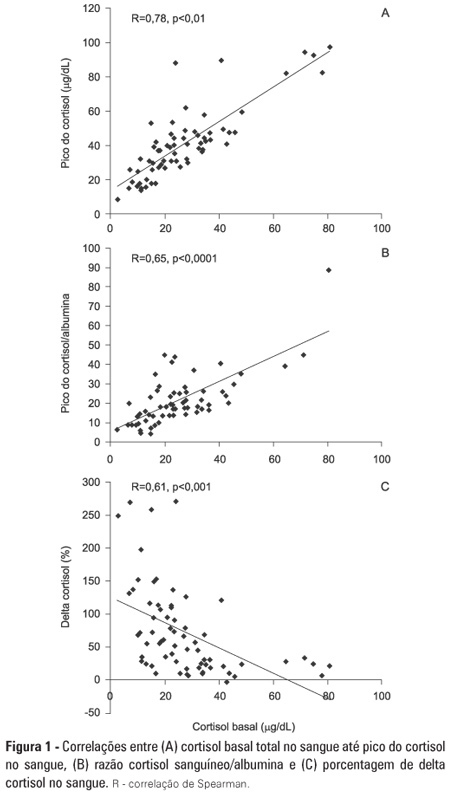
OBJECTIVE: To evaluate if cortisol responses to 250 µg of intravenously administered adrenocorticotropic hormone are related to disease severity and, hence, mortality. METHODS: This is a retrospective study in a medical-surgical intensive care unit of a university hospital. We studied 69 consecutive patients with septic shock over a 1-yr period; these patients underwent a short 250-µg adrenocorticotropic hormone test because they exhibited >6 hours of progressive hemodynamic instability requiring repeated fluid challenges and vasopressor treatment to maintain blood pressure. The test was performed by intravenously injecting 250 µg of synthetic adrenocorticotropic hormone and measuring cortisol immediately before injection, 30 minutes post-injection and 60 minutes post-injection. RESULTS: The mean APACHE II score was 22±7. The intensive care unit mortality rate at day 28 was 55%. Median baseline cortisol levels (19 [11-27] µg/dL versus 24 [18-34] µg/dL, p=0.047) and median baseline cortisol/albumin ratios (7.6 [4.6-12.3] versus 13.9 [8.8-18.5]; p=0.01) were lower in survivors than in non-survivors. Responders and non-responders had similar baseline clinical data and outcomes. The variables that were significantly correlated with outcome based on the area under the ROC curves (AUC) were APACHE II (AUC=0.67 [0.535 to 0.781]), baseline cortisol (µg/dl) (AUC=0.662 [0.536 to 0.773], peak cortisol (µg/dl) (AUC=0.642 [0.515 to 0.755]) and baseline cortisol/albumin (AUC=0.75 [0.621 to 0.849]). CONCLUSIONS: Increased basal cortisol is associated with mortality and disease severity. Cortisol responses upon adrenocorticotropic hormone stimulation were not related to outcome. The cortisol/albumin ratio does not predict unfavorable outcomes better than total cortisol levels or help to improve the accuracy of the adrenocorticotropic hormone test.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2011;23(4):478-483
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2011000400013
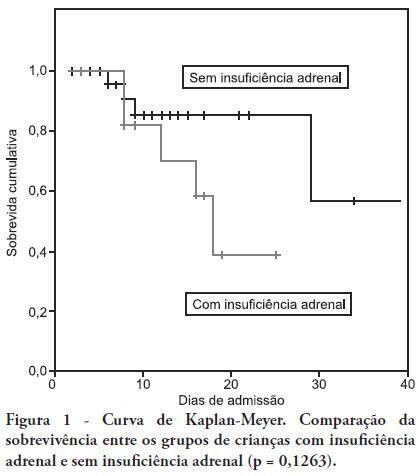
OBJECTIVE: To determine the frequency of adrenal insufficiency in children diagnosed with sepsis that were staying in pediatric intensive care units and to establish the association between adrenal function and the use of vasoactive drugs, mechanical ventilation time and mortality. METHODS: A cohort-designed study was conducted to assess the incidence of adrenal insufficiency in children aged 29 days to 12 years who were diagnosed with sepsis using the adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) stimulation test. RESULTS: Thirty-nine children were included in the study. The frequency of adrenal insufficiency was 30.7% (12 patients). Children with adrenal insufficiency had an increased need for vasoactive drugs as well as longer mechanical ventilation times; however, the differences were not statistically significant. A Kaplan-Meier curve indicated lower survival rates among the adrenal insufficiency children, but the differences were not statistically significant (p = 0.1263). No differences were identified between the adrenal sufficiency and adrenal insufficiency groups in regards to mechanical ventilation time, use of vasoactive drugs, infection type and chronic disease. CONCLUSION: This study determined the frequency of adrenal insufficiency in children with sepsis and its relationship to increased mortality within the first 28 post-admission days. No statistically significant association was found between adrenal insufficiency and mechanical ventilation time or the use of vasoactive drugs.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2006;18(1):86-94
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2006000100014
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: Corticosteroids were introduced in the treatment of severe infection as early as in the nineteen forties. Several " negative" randomized controlled trials of high-dose of glucocorticoids given for a short period of time in the early course of severe sepsis or acute respiratory distress syndrome raised serious doubts on the benefit of this treatment. Recently, a link between septic shock and adrenal insufficiency, or systemic inflammation induced glucocorticoids receptor resistance had been established. This finding prompted renewed interest of a replacement therapy with low doses of corticosteroids during longer periods. The goal of this article is to review the key role of corticosteroids in the host response to stress and will update the reader with the new validated indications of corticosteroids treatment in the ICU. CONTENTS: Extensive review of the adrenal physiology and its pathophysiological derangements and clinical implications in critically ill patients. CONCLUSIONS: During sepsis, hemodynamic instability and perpetuation of inflammatory state may result from adrenal insufficiency (AI). Thus, an ACTH test should be performed as soon as possible to identify non overt AI. It should be immediately followed by a replacement therapy with iv bolus of 50 mg of hydrocortisone every 6 hours combined to 50 µg of fludrocortisone once daily. When the results of the ACTH test are available, treatment should be continued for 7 days in the non responders to ACTH and withdraw in the responders. Whether responders to ACTH with high baseline cortisol levels (> 34 µg/dL) have tissue resistance to cortisol and also should receive exogenous hormones remains to be evaluated in clinical trials.