Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2016;28(3):301-309
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20160054
To describe the characteristics of patients with HIV/AIDS and to compare the therapeutic interventions and end-of-life care before and after evaluation by the palliative care team.
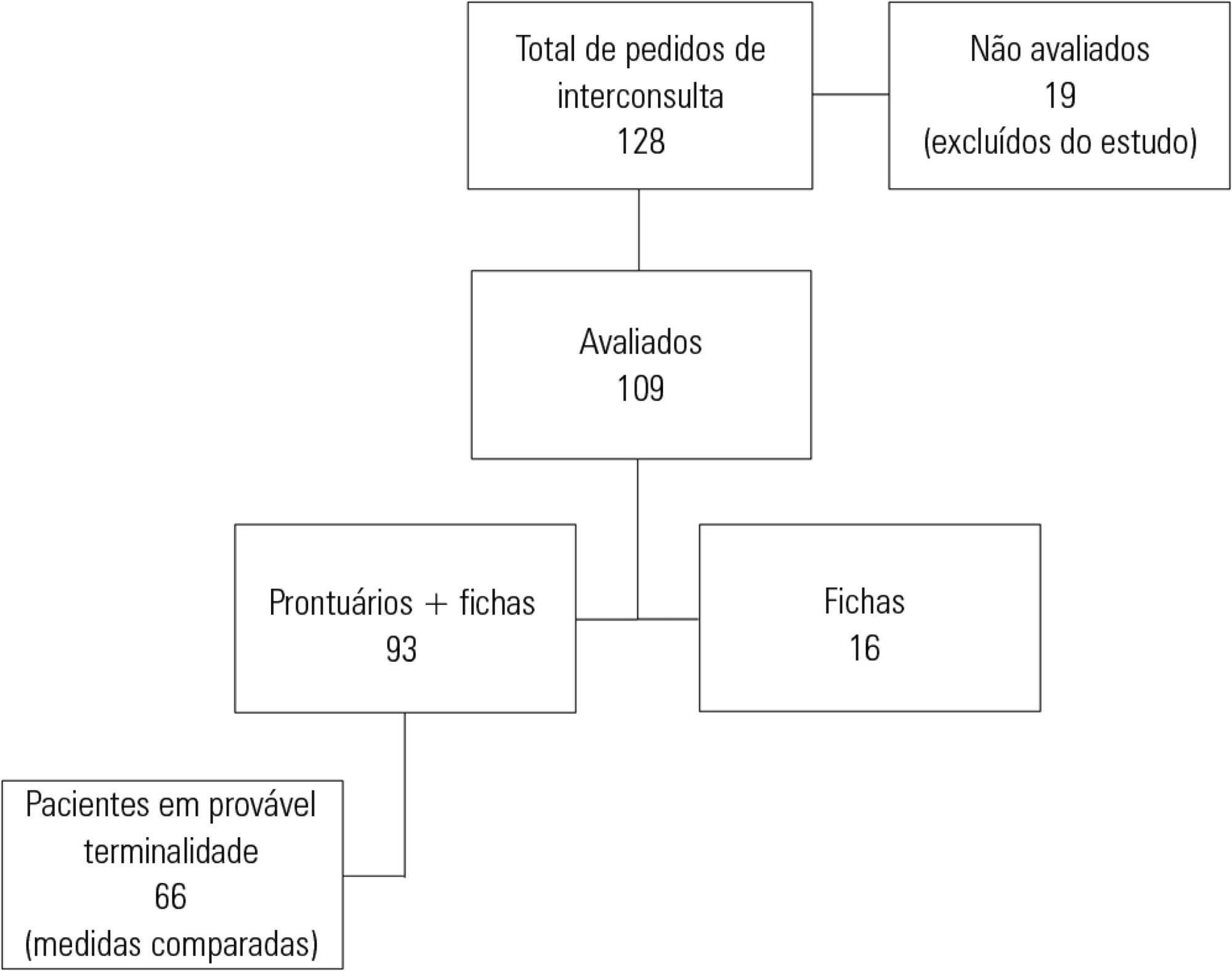
This retrospective cohort study included all patients with HIV/AIDS admitted to the intensive care unit of the Instituto de Infectologia Emílio Ribas who were evaluated by a palliative care team between January 2006 and December 2012.
Of the 109 patients evaluated, 89% acquired opportunistic infections, 70% had CD4 counts lower than 100 cells/mm3, and only 19% adhered to treatment. The overall mortality rate was 88%. Among patients predicted with a terminally ill (68%), the use of highly active antiretroviral therapy decreased from 50.0% to 23.1% (p = 0.02), the use of antibiotics decreased from 100% to 63.6% (p < 0.001), the use of vasoactive drugs decreased from 62.1% to 37.8% (p = 0.009), the use of renal replacement therapy decreased from 34.8% to 23.0% (p < 0.0001), and the number of blood product transfusions decreased from 74.2% to 19.7% (p < 0.0001). Meetings with the family were held in 48 cases, and 23% of the terminally ill patients were discharged from the intensive care unit.
Palliative care was required in patients with severe illnesses and high mortality. The number of potentially inappropriate interventions in terminally ill patients monitored by the palliative care team significantly decreased, and 26% of the patients were discharged from the intensive care unit.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2007;19(1):113-117
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2007000100015
BACKGROUNG AND OBJECTIVES: Varicella is an exantematic disease caused by varicella-zoster virus. Varicella pneumonia complicated with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is very rare in adults and is associated with high morbimortality. We report two cases of ARDS secondary to varicella-zoster virus pneumonia. CASES REPORT: We report two cases of ARDS and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) secondary to varicella-zoster virus pneumonia. A 15-year-old man with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection and a 29-year-old immunocompetent female were admitted in the ICU with primary varicella infection and pneumonia. Both cases progressed towards ARDS, severe thrombocytopenia and acidosis. In addition cardiovascular and renal failure occurred in the first and second patients, respectively. Treatment consisted of immediate administration of intravenous acyclovir and a lung-protective ventilation strategy. CONCLUSIONS: Both cases of varicella-zoster pneumonia, complicated with ARDS and MODS, had a favourable outcome.