Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2016;28(3):310-314
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20160041
To investigate possible stressors to which newborns are exposed in the neonatal intensive care unit.
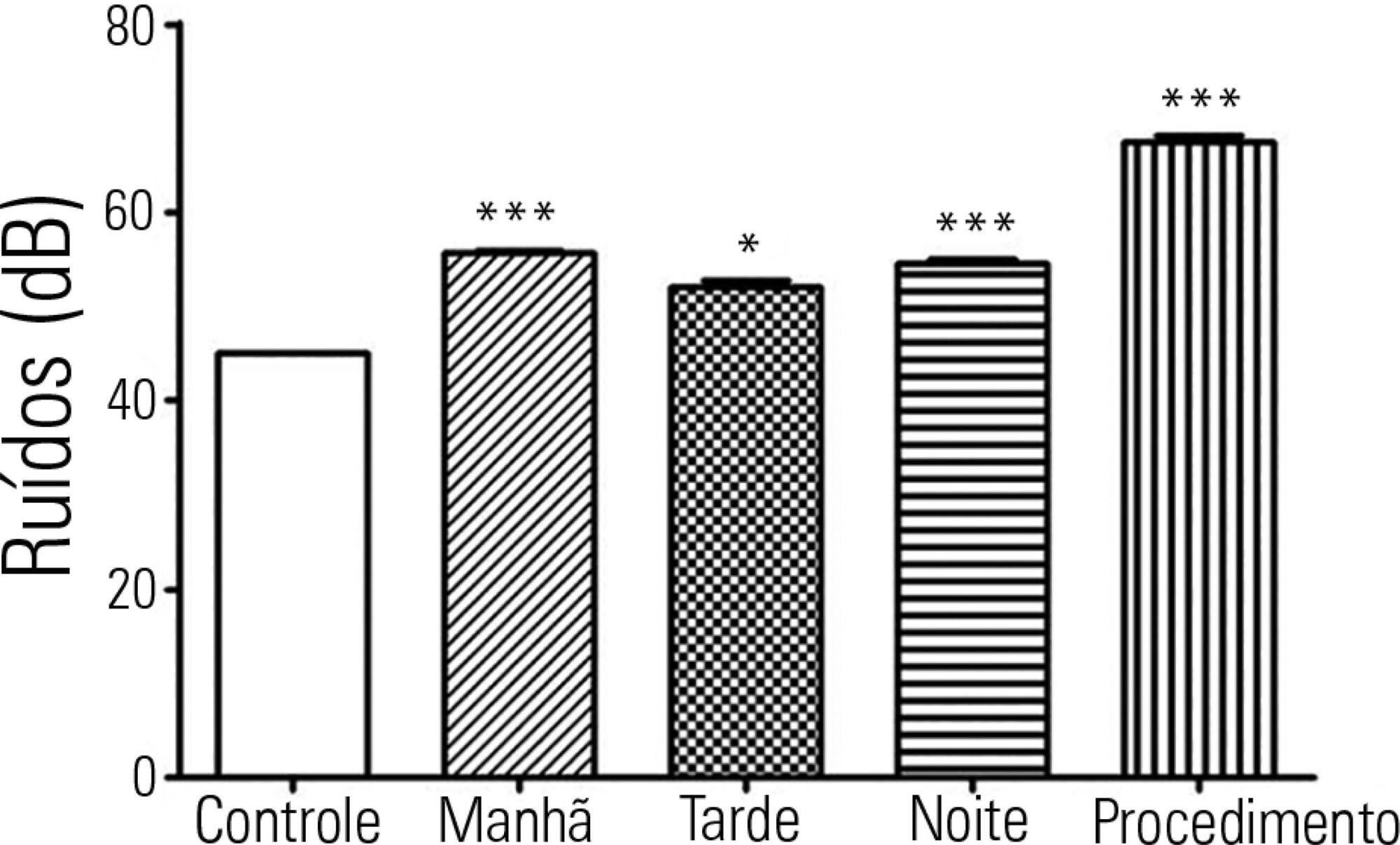
The levels of continuous noise were checked by a decibel meter positioned near the ear of the newborn, brightness was observed by a light meter positioned in the incubator in front of the newborn's eyes, and temperature was checked through the incubator display. The evaluations were performed in three periods of the day, with ten measurements taken at one-minute intervals during each shift for the subsequent statistical analysis.
All shifts showed noise above acceptable levels. Morning (p < 0.001), afternoon (p < 0.05) and night (p < 0.001) showed a significant increase compared to the control. The brightness significantly exceeded the normal range (p < 0.01) in the morning. We observed that only one of the incubators was within the normal temperature limits.
The noise, brightness and temperature intensities were not in accordance with regulatory standards and thus might be possible stressors to newborns.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2016;28(2):147-153
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20160029
This study sought to identify the physical and chemical incompatibilities among the drugs administered intravenously to patients admitted to an adult intensive care unit. We also aimed to establish pharmaceutical guidelines for administering incompatible drugs.
This cross-sectional, prospective, and quantitative study was conducted from July to September 2015. Drug incompatibilities were identified based on an analysis of the patient prescriptions available in the hospital online management system. A pharmaceutical intervention was performed using the guidelines on the preparation and administration of incompatible drugs. Adherence to those guidelines was subsequently assessed among the nursing staff.
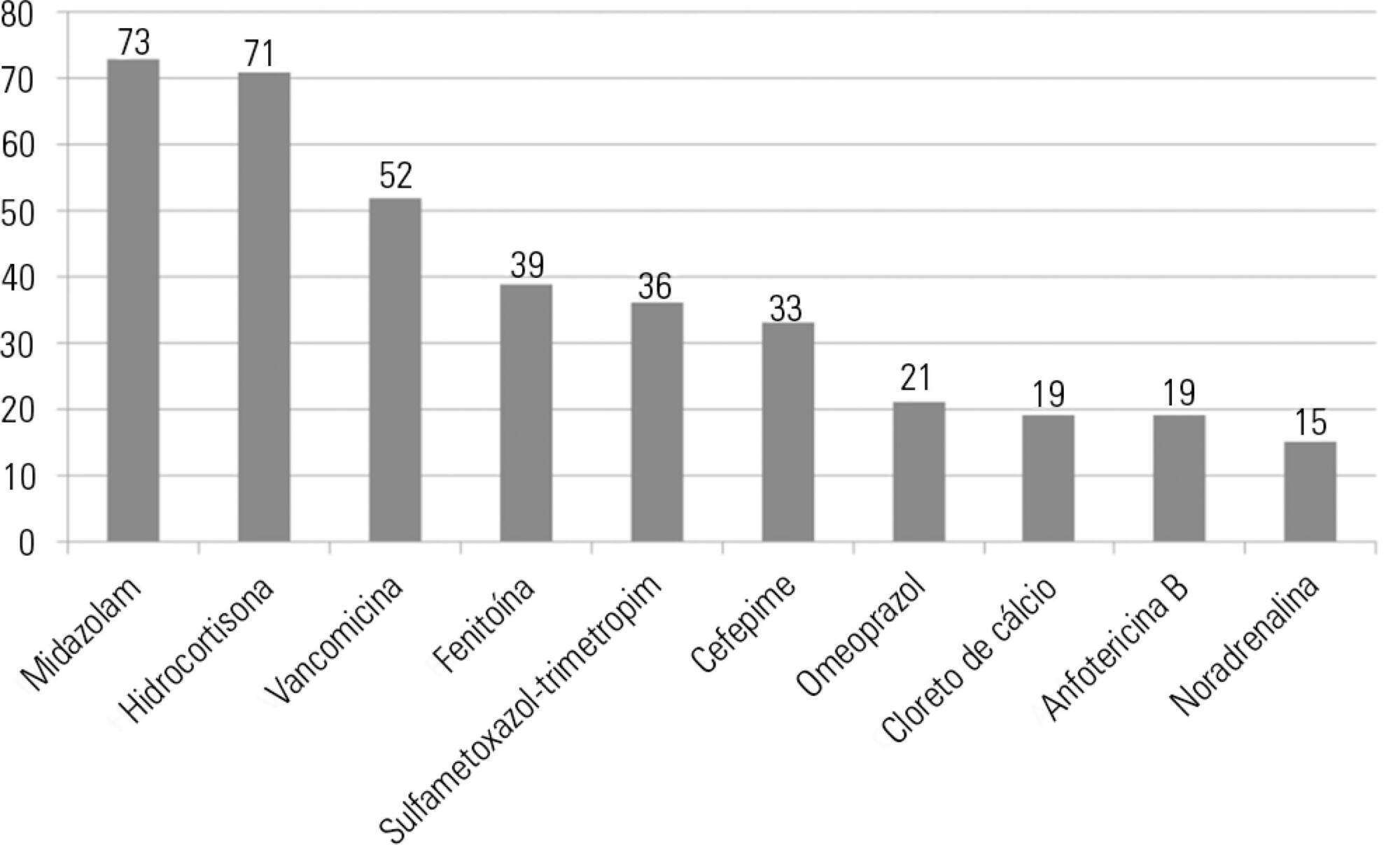
A total of 100 prescriptions were analyzed; 68 were incompatible with the intravenous drugs prescribed. A total of 271 drug incompatibilities were found, averaging 4.0 ± 3.3 incompatibilities per prescription. The most commonly found drug incompatibilities were between midazolam and hydrocortisone (8.9%), between cefepime and midazolam (5.2%), and between hydrocortisone and vancomycin (5.2%). The drugs most commonly involved in incompatibilities were midazolam, hydrocortisone, and vancomycin. The most common incompatibilities occurred when a drug was administered via continuous infusion and another was administered intermittently (50%). Of the 68 prescriptions that led to pharmaceutical guidelines, 45 (66.2%) were fully adhered to by the nursing staff.
Patients under intensive care were subjected to a high rate of incompatibilities. Drug incompatibilities can be identified and eliminated by the pharmacist on the multidisciplinary team, thereby reducing undesirable effects among patients.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2016;28(3):323-329
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20160055
To identify and stratify the main stressors for the relatives of patients admitted to the adult intensive care unit of a teaching hospital.
Cross-sectional descriptive study conducted with relatives of patients admitted to an intensive care unit from April to October 2014. The following materials were used: a questionnaire containing identification information and demographic data of the relatives, clinical data of the patients, and 25 stressors adapted from the Intensive Care Unit Environmental Stressor Scale. The degree of stress caused by each factor was determined on a scale of values from 1 to 4. The stressors were ranked based on the average score obtained.
The main cause of admission to the intensive care unit was clinical in 36 (52.2%) cases. The main stressors were the patient being in a state of coma (3.15 ± 1.23), the patient being unable to speak (3.15 ± 1.20), and the reason for admission (3.00 ± 1.27). After removing the 27 (39.1%) coma patients from the analysis, the main stressors for the relatives were the reason for admission (2.75 ± 1.354), seeing the patient in the intensive care unit (2.51 ± 1.227), and the patient being unable to speak (2.50 ± 1.269).
Difficulties in communication and in the relationship with the patient admitted to the intensive care unit were identified as the main stressors by their relatives, with the state of coma being predominant. By contrast, the environment, work routines, and relationship between the relatives and intensive care unit team had the least impact as stressors.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2016;28(2):120-131
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20160026
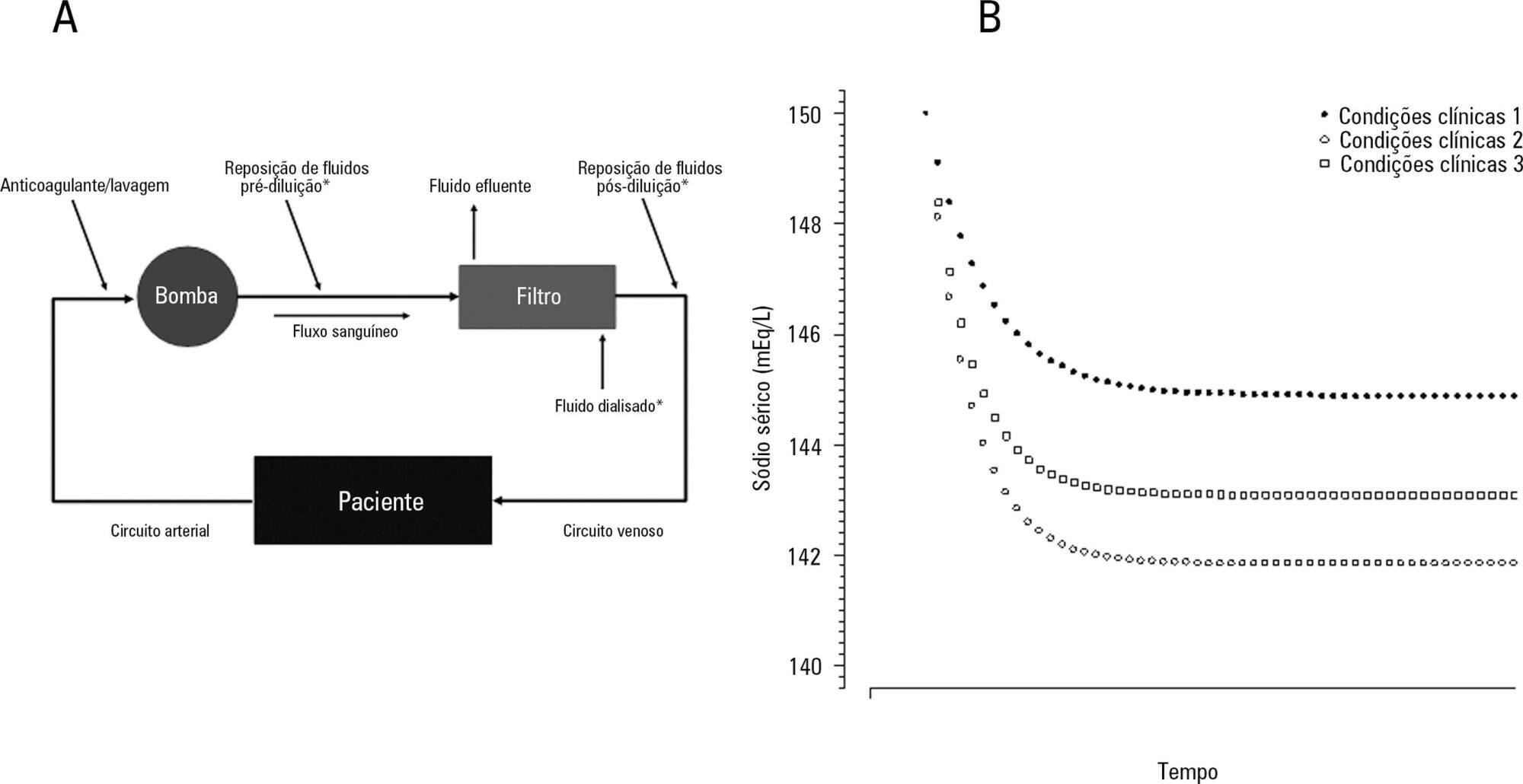
The aim of this study was to investigate the clinical and laboratorial factors associated with serum sodium variation during continuous renal replacement therapy and to assess whether the perfect admixture formula could predict 24-hour sodium variation.
Thirty-six continuous renal replacement therapy sessions of 33 patients, in which the affluent prescription was unchanged during the first 24 hours, were retrieved from a prospective collected database and then analyzed. A mixed linear model was performed to investigate the factors associated with large serum sodium variations (≥ 8mEq/L), and a Bland-Altman plot was generated to assess the agreement between the predicted and observed variations.
In continuous renal replacement therapy 24-hour sessions, SAPS 3 (p = 0.022) and baseline hypernatremia (p = 0.023) were statistically significant predictors of serum sodium variations ≥ 8mEq/L in univariate analysis, but only hypernatremia demonstrated an independent association (β = 0.429, p < 0.001). The perfect admixture formula for sodium prediction at 24 hours demonstrated poor agreement with the observed values.
Hypernatremia at the time of continuous renal replacement therapy initiation is an important factor associated with clinically significant serum sodium variation. The use of 4% citrate or acid citrate dextrose - formula A 2.2% as anticoagulants was not associated with higher serum sodium variations. A mathematical prediction for the serum sodium concentration after 24 hours was not feasible.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2016;28(4):444-451
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20160078
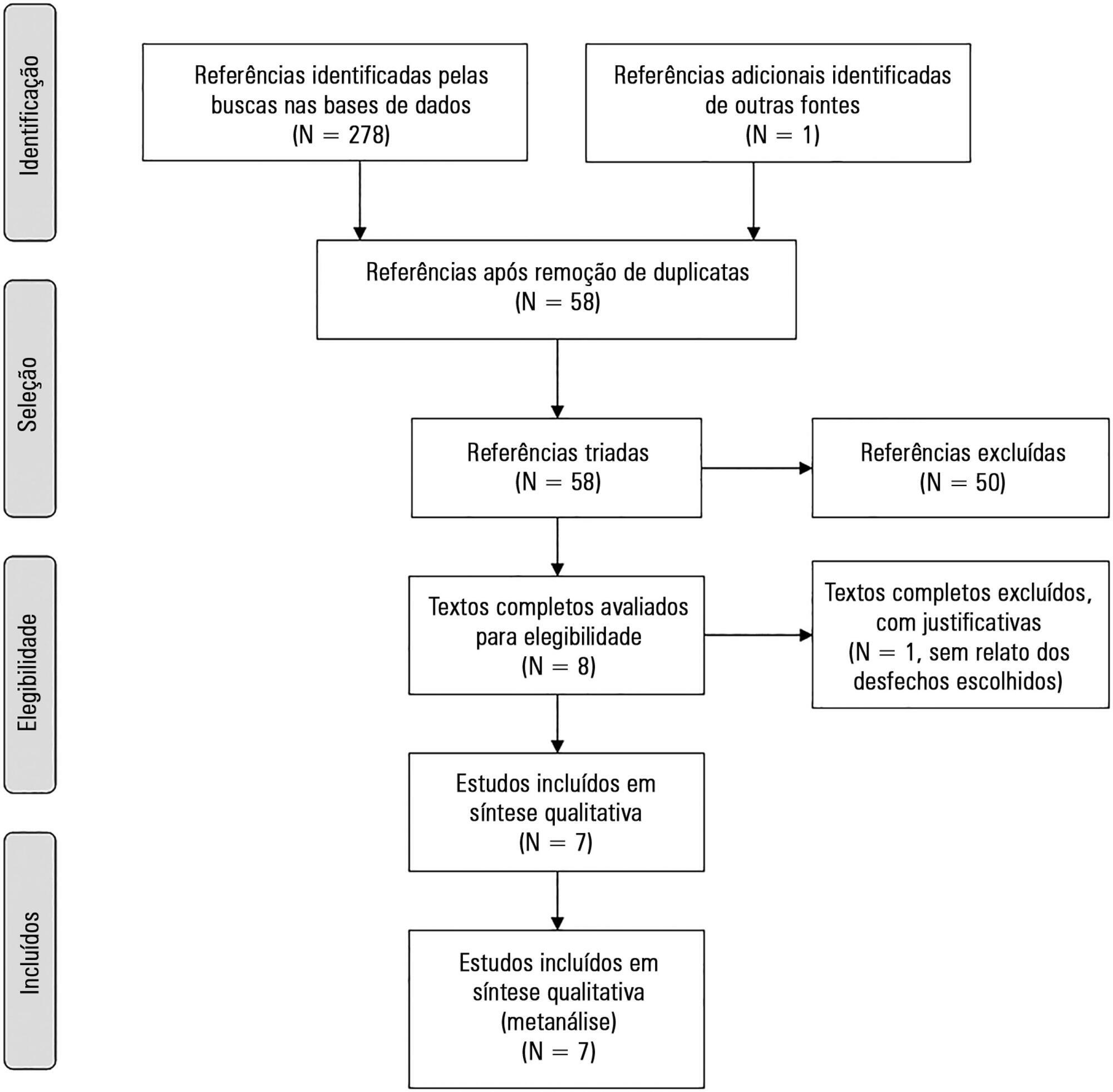
The aim of this study was to systematically review studies that compared a mild target sedation protocol with daily sedation interruption and to perform a meta-analysis with the data presented in these studies.
We searched Medline, Scopus and Web of Science databases to identify randomized clinical trials comparing sedation protocols with daily sedation interruption in critically ill patients requiring mechanical ventilation. The primary outcome was mortality in the intensive care unit.
Seven studies were included, with a total of 892 patients. Mortality in the intensive care unit did not differ between the sedation protocol and daily sedation interruption groups (odds ratio [OR] = 0.81; 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.60 - 1.10; I2 = 0%). Hospital mortality, duration of mechanical ventilation, intensive care unit and hospital length of stay did not differ between the groups either. Sedation protocols were associated with an increase in the number of days free of mechanical ventilation (mean difference = 6.70 days; 95%CI 1.09 - 12.31 days; I2 = 87.2%) and a shorter duration of hospital length of stay (mean difference = -5.05 days, 95%CI -9.98 - -0.11 days; I2 = 69%). There were no differences in regard to accidental extubation, extubation failure and the occurrence of delirium.
Sedation protocols and daily sedation interruption do not appear to differ in regard to the majority of analyzed outcomes. The only differences found were small and had a high degree of heterogeneity.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(1):18-25
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20150005
To evaluate and compare stressors identified by patients of a coronary intensive care unit with those perceived by patients of a general postoperative intensive care unit.
This cross-sectional and descriptive study was conducted in the coronary intensive care and general postoperative intensive care units of a private hospital. In total, 60 patients participated in the study, 30 in each intensive care unit. The stressor scale was used in the intensive care units to identify the stressors. The mean score of each item of the scale was calculated followed by the total stress score. The differences between groups were considered significant when p < 0.05.
The mean ages of patients were 55.63 ± 13.58 years in the coronary intensive care unit and 53.60 ± 17.47 years in the general postoperative intensive care unit. For patients in the coronary intensive care unit, the main stressors were “being in pain”, “being unable to fulfill family roles” and “being bored”. For patients in the general postoperative intensive care unit, the main stressors were “being in pain”, “being unable to fulfill family roles” and “not being able to communicate”. The mean total stress scores were 104.20 ± 30.95 in the coronary intensive care unit and 116.66 ± 23.72 (p = 0.085) in the general postoperative intensive care unit. When each stressor was compared separately, significant differences were noted only between three items. “Having nurses constantly doing things around your bed” was more stressful to the patients in the general postoperative intensive care unit than to those in the coronary intensive care unit (p = 0.013). Conversely, “hearing unfamiliar sounds and noises” and “hearing people talk about you” were the most stressful items for the patients in the coronary intensive care unit (p = 0.046 and 0.005, respectively).
The perception of major stressors and the total stress score were similar between patients in the coronary intensive care and general postoperative intensive care units.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(2):161-169
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20150028
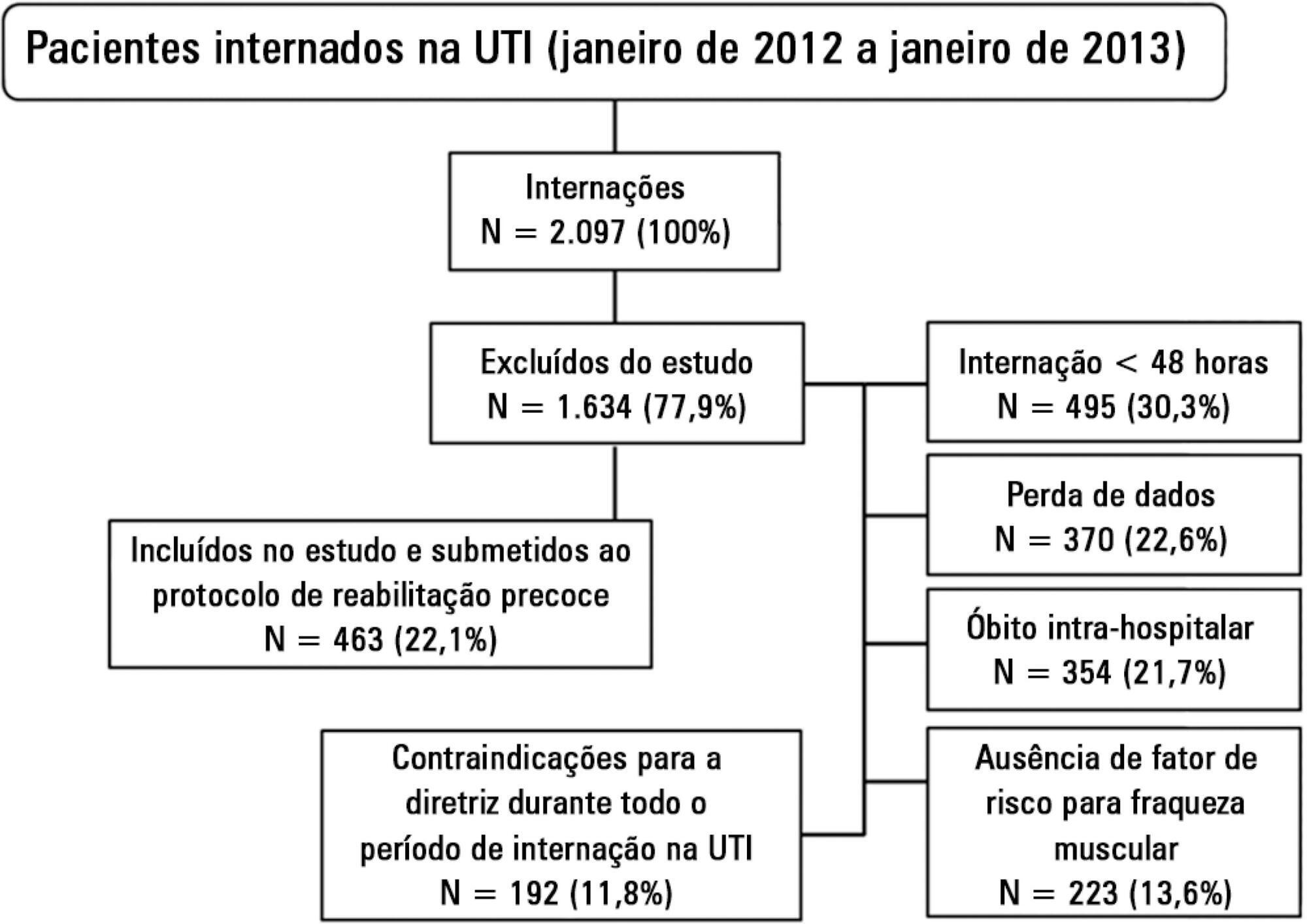
Evaluation of the functional outcomes of patients undergoing an early rehabilitation protocol for critically ill patients from admission to discharge from the intensive care unit.
A retrospective cross-sectional study was conducted that included 463 adult patients with clinical and/or surgical diagnosis undergoing an early rehabilitation protocol. The overall muscle strength was evaluated at admission to the intensive care unit using the Medical Research Council scale. Patients were allocated to one of four intervention plans according to the Medical Research Council score, the suitability of the plan’s parameters, and the increasing scale of the plan expressing improved functional status. Uncooperative patients were allocated to intervention plans based on their functional status. The overall muscle strength and/or functional status were reevaluated upon discharge from the intensive care unit by comparison between the Intervention Plans upon admission (Planinitial) and discharge (Planfinal). Patients were classified into three groups according to the improvement of their functional status or not: responsive 1 (Planfinal > Planinitial), responsive 2 (Planfinal = Planinitial) and unresponsive (Planfinal < Planinitial).
In total, 432 (93.3%) of 463 patients undergoing the protocol responded positively to the intervention strategy, showing maintenance and/or improvement of the initial functional status. Clinical patients classified as unresponsive were older (74.3 ± 15.1 years of age; p = 0.03) and had longer lengths of intensive care unit (11.6 ± 14.2 days; p = 0.047) and hospital (34.5 ± 34.1 days; p = 0.002) stays.
The maintenance and/or improvement of the admission functional status were associated with shorter lengths of intensive care unit and hospital stays. The results suggest that the type of diagnosis, clinical or surgical, fails to define the positive response to an early rehabilitation protocol.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(4):360-368
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20150061
To conduct a multinational survey of intensive care unit professionals to determine the practices on delirium assessment and management, in addition to their perceptions and attitudes toward the evaluation and impact of delirium in patients requiring noninvasive ventilation.
An electronic questionnaire was created to evaluate the profiles of the respondents and their related intensive care units, the systematic delirium assessment and management and the respondents' perceptions and attitudes regarding delirium in patients requiring noninvasive ventilation. The questionnaire was distributed to the cooperative network for research of the Associação de Medicina Intensiva Brasileira (AMIB-Net) mailing list and to researchers in different centers in Latin America and Europe.
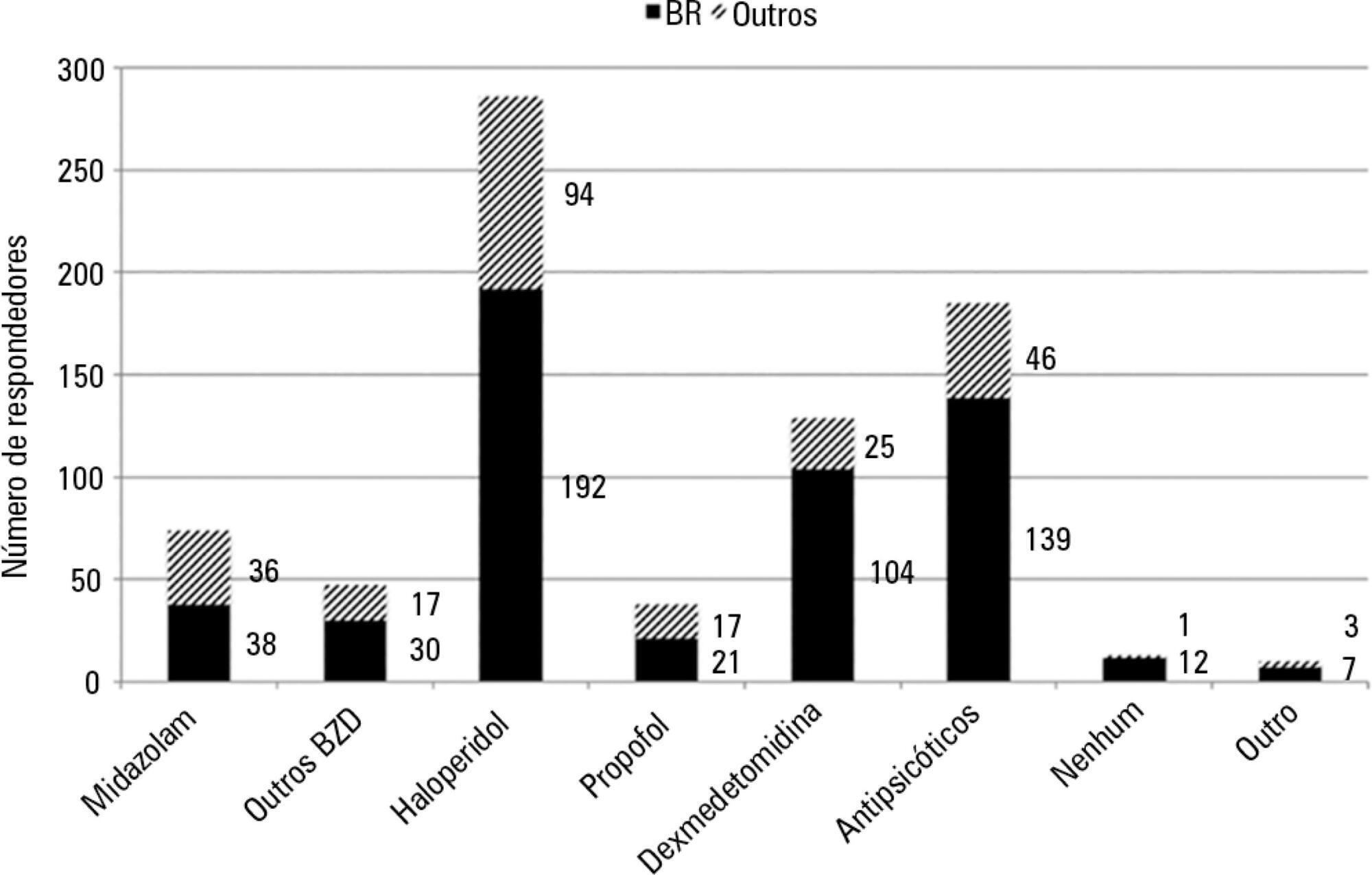
Four hundred thirty-six questionnaires were available for analysis; the majority of the questionnaires were from Brazil (61.9%), followed by Turkey (8.7%) and Italy (4.8%). Approximately 61% of the respondents reported no delirium assessment in the intensive care unit, and 31% evaluated delirium in patients under noninvasive ventilation. The Confusion Assessment Method for the intensive care unit was the most reported validated diagnostic tool (66.9%). Concerning the indication of noninvasive ventilation in patients already presenting with delirium, 16.3% of respondents never allow the use of noninvasive ventilation in this clinical context.
This survey provides data that strongly reemphasizes poor efforts toward delirium assessment and management in the intensive care unit setting, especially regarding patients requiring noninvasive ventilation.