Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(1):84-96
DOI 10.5935/2965-2774.20230405-pt
The number of patients with cancer requiring intensive care unit admission is increasing around the world. The improvement in the pathophysiological understanding of this group of patients, as well as the increasingly better and more targeted treatment options for their underlying disease, has led to a significant increase in their survival over the past three decades. Within the organizational concepts, it is necessary to know what adds value in the care of critical oncohematological patients. Practices in medicine that do not benefit patients and possibly cause harm are called low-value practices, while high-value practices are defined as high-quality care at relatively low cost. In this article, we discuss ten domains with high-value evidence in the care of cancer patients: (1) intensive care unit admission policies; (2) intensive care unit organization; (3) etiological investigation of hypoxemia; (4) management of acute respiratory failure; (5) management of febrile neutropenia; (6) urgent chemotherapy treatment in critically ill patients; (7) patient and family experience; (8) palliative care; (9) care of intensive care unit staff; and (10) long-term impact of critical disease on the cancer population. The disclosure of such policies is expected to have the potential to change health care standards. We understand that it is a lengthy process, and initiatives such as this paper are one of the first steps in raising awareness and beginning a discussion about high-value care in various health scenarios.

Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(4):583-591
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20210085
To ascertain the cumulative incidence of acute organ failure and intensive care unit admission in cancer patients.
This was a single-center prospective cohort study of adult cancer patients admitted for unscheduled inpatient care while on systemic cancer treatment.
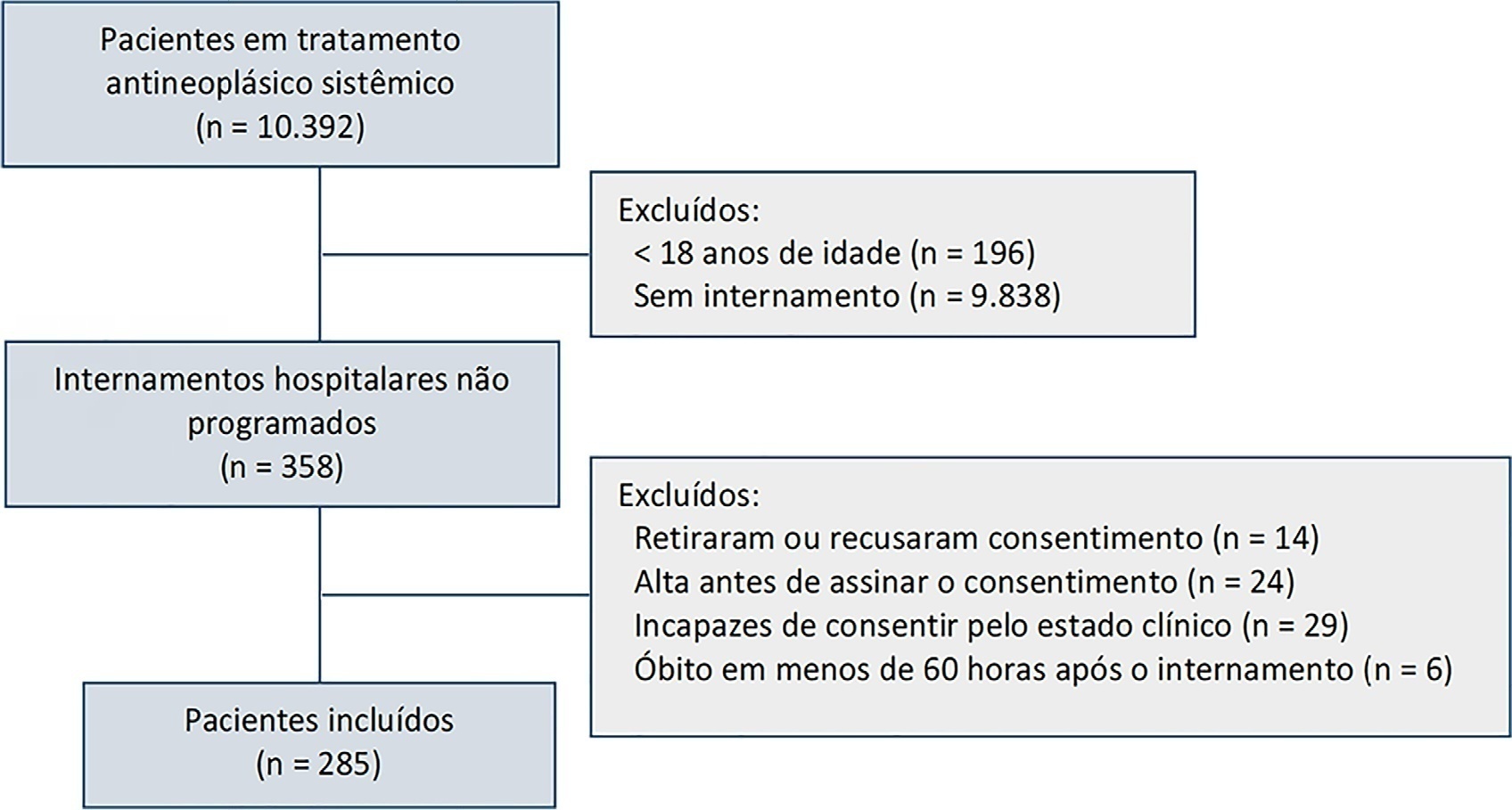
Between August 2018 and February 2019, 10,392 patients were on systemic treatment, 358 had unscheduled inpatient care and were eligible for inclusion, and 285 were included. The mean age was 60.9 years, 50.9% were male, and 17.9% of patients had hematologic cancers. The cumulative risk of acute organ failure was 39.6% (95%CI: 35 - 44), and that of intensive care unit admission among patients with acute organ failure was 15.0% (95%CI: 12 - 18). On admission, 62.1% of patients were considered not eligible for artificial organ replacement therapy. The median follow-up time was 9.5 months. Inpatient mortality was 17.5%, with an intensive care unit mortality rate of 58.8% and a median cohort survival of 134 days (95%CI: 106 - 162). In multivariate analysis, acute organ failure was associated with 6-month postdischarge mortality (HR 1.6; 95%CI: 1.2 - 2.2).
The risk of acute organ failure in cancer patients admitted for unscheduled inpatient care while on systemic treatment was 39.6%, and the risk of intensive care unit admission was 15.0%. Acute organ failure in cancer patients was an independent poor prognostic factor for inpatient hospital mortality and 6-month survival.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(2):298-303
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20210038
To evaluate how performance status impairment and acute organ dysfunction influence hospital mortality in critically ill patients with cancer who were admitted with suspected sepsis.
Data were obtained from a retrospective cohort of patients, admitted to an intensive care unit, with cancer and with a suspected infection who received parenteral antibiotics and underwent the collection of bodily fluid samples. We used logistic regression with hospital mortality as the outcome and the Sequential Organ Failure Assessment score, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group status, and their interactions as predictors.
Of 450 patients included, 265 (58.9%) died in the hospital. For patients admitted to the intensive care unit with lower Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (≤ 6), performance status impairment influenced the in-hospital mortality, which was 32% among those with no and minor performance status impairment and 52% among those with moderate and severe performance status impairment, p < 0.01. However, for those with higher Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (> 6), performance status impairment did not influence the in-hospital mortality (73% among those with no and minor impairment and 84% among those with moderate and severe impairment; p = 0.1).
Performance status impairment seems to influence hospital mortality in critically ill cancer patients with suspected sepsis when they have less severe acute organ dysfunction at the time of intensive care unit admission.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2020;32(4):521-527
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20200089
To compare the performance of the Simplified Acute Physiology Score 3 (SAPS 3) in patients with and without solid cancer who were admitted to the intensive care unit of a comprehensive oncological hospital in Brazil.
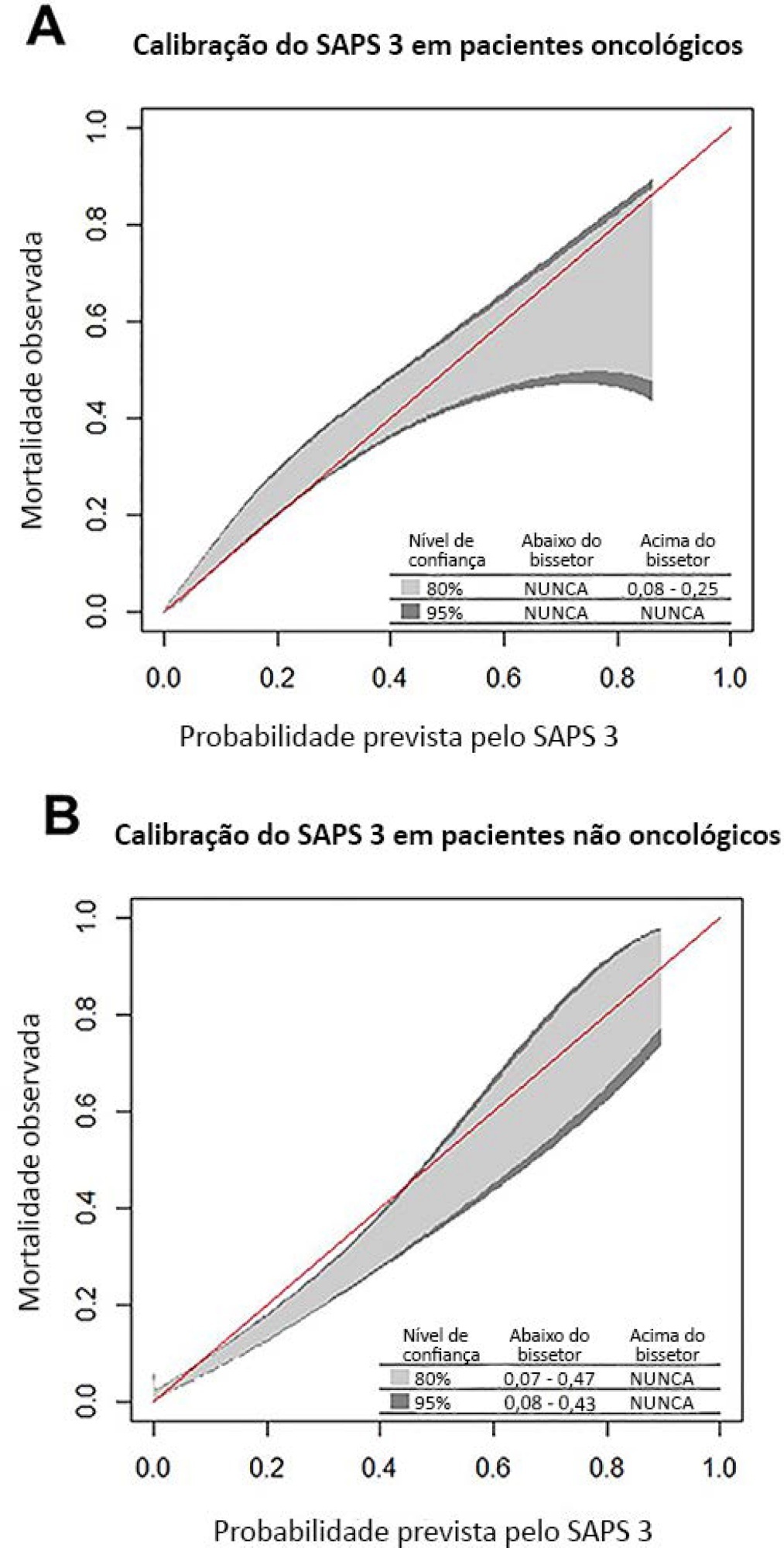
We performed a retrospective cohort analysis of our administrative database of the first admission of adult patients to the intensive care unit from 2012 to 2016. The patients were categorized according to the presence of solid cancer. We evaluated discrimination using the area under the Receiver Operating Characteristic curve (AUROC) and calibration using the calibration belt approach.
We included 7,254 patients (41.5% had cancer, and 12.1% died during hospitalization). Oncological patients had higher hospital mortality than nononcological patients (14.1% versus 10.6%, respectively; p < 0.001). SAPS 3 discrimination was better for oncological patients (AUROC = 0.85) than for nononcological patients (AUROC = 0.79) (p < 0.001). After we applied the calibration belt in oncological patients, the SAPS 3 matched the average observed rates with a confidence level of 95%. In nononcological patients, the SAPS 3 overestimated mortality in those with a low-middle risk. Calibration was affected by the time period only for nononcological patients.
SAPS 3 performed differently between oncological and nononcological patients in our single-center cohort, and variation over time (mainly calibration) was observed. This finding should be taken into account when evaluating severity-of-illness score performance.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2016;28(4):436-443
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20160077
To evaluate the clinical course and respiratory parameters of mechanically ventilated children with cancer suffering from sepsis-related acute respiratory distress syndrome.
This 2-year prospective, longitudinal, observational cohort study enrolled 29 children and adolescents. Clinical data, measurements of blood gases and ventilation parameters were collected at four different time points. Fluctuations between measurements as well as differences in estimated means were analyzed by linear mixed models in which death within 28 days from the onset of acute respiratory distress syndrome was the primary endpoint.
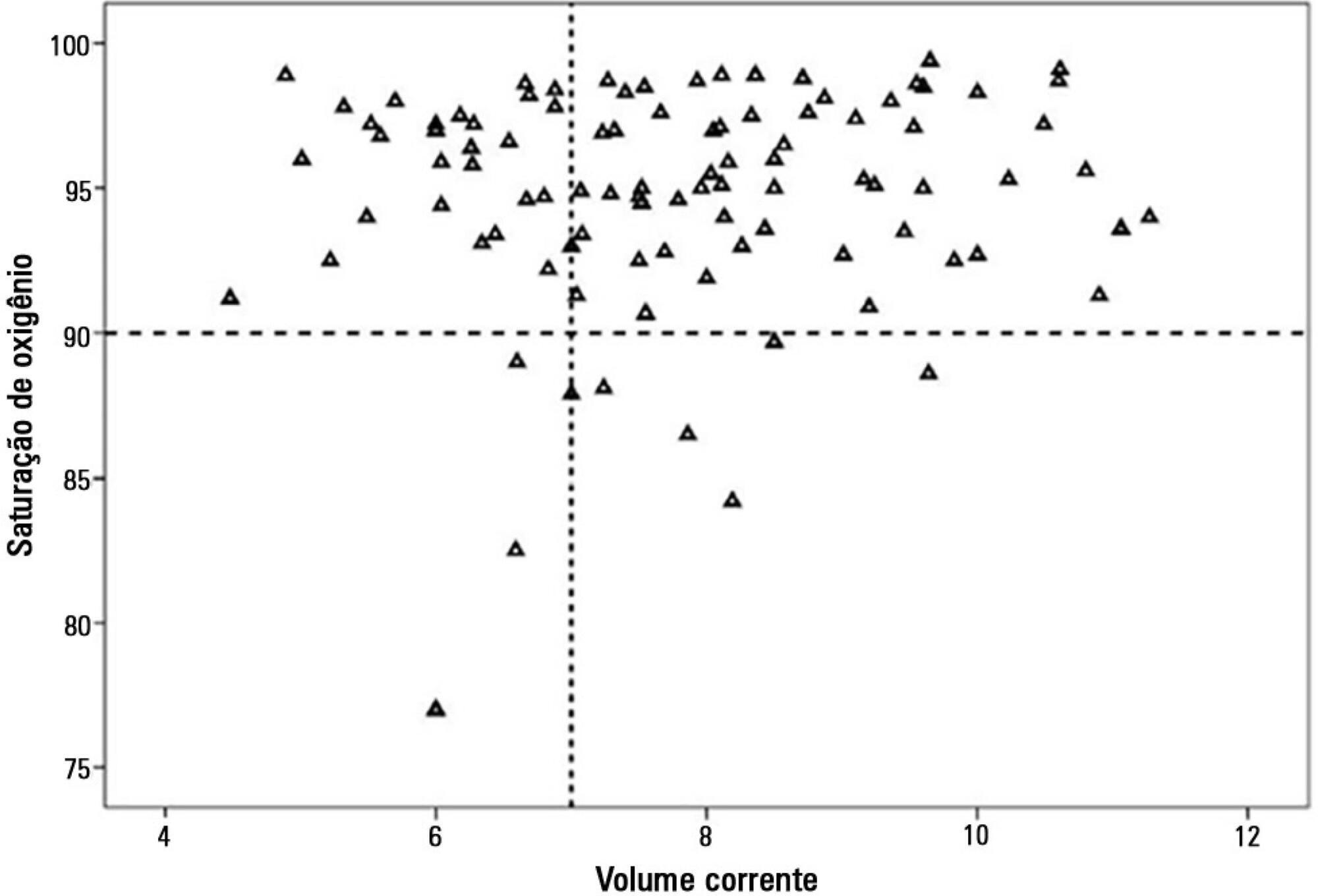
There were 17 deaths within 28 days of acute respiratory distress syndrome onset and another 7 between 29 - 60 days. Only 5 patients survived for more than 60 days. Nine (31%) patients died as a direct consequence of refractory hypoxemia, and the others died of multiple organ failure and catecholamine-refractory shock. In 66% of the measurements, the tidal volume required to obtain oxygen saturation equal to or above 90% was greater than 7mL/kg. The estimated means of dynamic compliance were low and were similar for survivors and non-survivors but with a negative slope between the first and final measurements, accompanied by a negative slope of the tidal volume for non-survivors. Non-survivors were significantly more hypoxemic, with PaO2/FiO2 ratios showing lower estimated means and a negative slope along the four measurements. Peak, expiratory and mean airway pressures showed positive slopes in the non-survivors, who also had more metabolic acidosis.
In most of our children with cancer, sepsis and acute respiratory distress syndrome progressed with deteriorating ventilation indexes and escalating organic dysfunction, making this triad nearly fatal in children.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2010;22(3):236-244
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2010000300004
OBJECTIVES: Critically ill cancer patients are at increased risk for acute kidney injury, but studies on these patients are scarce and were all single centered conducted in specialized intensive care units. The objective was to evaluate the characteristics and outcomes in a prospective cohort of cancer patients admitted to several intensive care units with acute kidney injury. METHODS: Prospective multicenter cohort study conducted in intensive care units from 28 hospitals in Brazil over a two-month period. Univariate and multivariate logistic regression were used to identify factors associated with hospital mortality. RESULTS: Out of all 717 intensive care unit admissions, 87 (12%) had acute kidney injury and 36% of them received renal replacement therapy. Kidney injury developed more frequently in patients with hematological malignancies than in patients with solid tumors (26% vs. 11%, P=0.003). Ischemia/shock (76%) and sepsis (67%) were the main contributing factor for and kidney injury was multifactorial in 79% of the patients. Hospital mortality was 71%. General and renal-specific severity-of-illness scores were inaccurate in predicting outcomes for these patients. In a multivariate analysis, length of hospital stay prior to intensive care unit, acute organ dysfunctions, need for mechanical ventilation and a poor performance status were associated with increased mortality. Moreover, cancer-related characteristics were not associated with outcomes. CONCLUSIONS: The present study demonstrates that intensive care units admission and advanced life-support should be considered in selected critically ill cancer patients with kidney injury.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (116) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)