Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(2):187-195
DOI 10.5935/2965-2774.20230378-pt
Evaluation of left ventricular systolic function using speckle tracking echocardiography is more sensitive than conventional echocardiographic measurement in detecting subtle left ventricular dysfunction in septic patients. Our purpose was to investigate the predictive significance of left ventricular global longitudinal strain in normotensive septic intensive care patients.
This observational, prospective cohort study included septic normotensive adults admitted to the intensive care unit between June 1, 2021, and August 31, 2021. Left ventricular systolic function was measured using speckle-tracking echocardiography within 24 hours of admission.
One hundred fifty-two patients were enrolled. The intensive care unit mortality rate was 27%. Left ventricular global longitudinal strain was less negative, which indicated worse left ventricular function in non-survivors than survivors (median [interquartile range], -15.2 [-17.2 - -12.5] versus -17.3 [-18.8 - -15.5]; p < 0.001). The optimal cutoff value for left ventricular global longitudinal strain was -17% in predicting intensive care unit mortality (area under the curve, 0.728). Patients with left ventricular global longitudinal strain > -17% (less negative than -17%, which indicated worse left ventricular function) showed a significantly higher mortality rate (39.2% versus 13.7%; p < 0.001). According to multivariate analysis, left ventricular global longitudinal strain was an independent predictor of intensive care unit mortality [OR (95%CI), 1.326 (1.038 - 1.693); p = 0.024], along with invasive mechanical ventilation and Glasgow coma scale, APACHE II, and SOFA risk scores.
Impaired left ventricular global longitudinal strain is associated with mortality and provided predictive data in normotensive septic intensive care patients.
Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(2):196-202
DOI 10.5935/2965-2774.20230036-pt
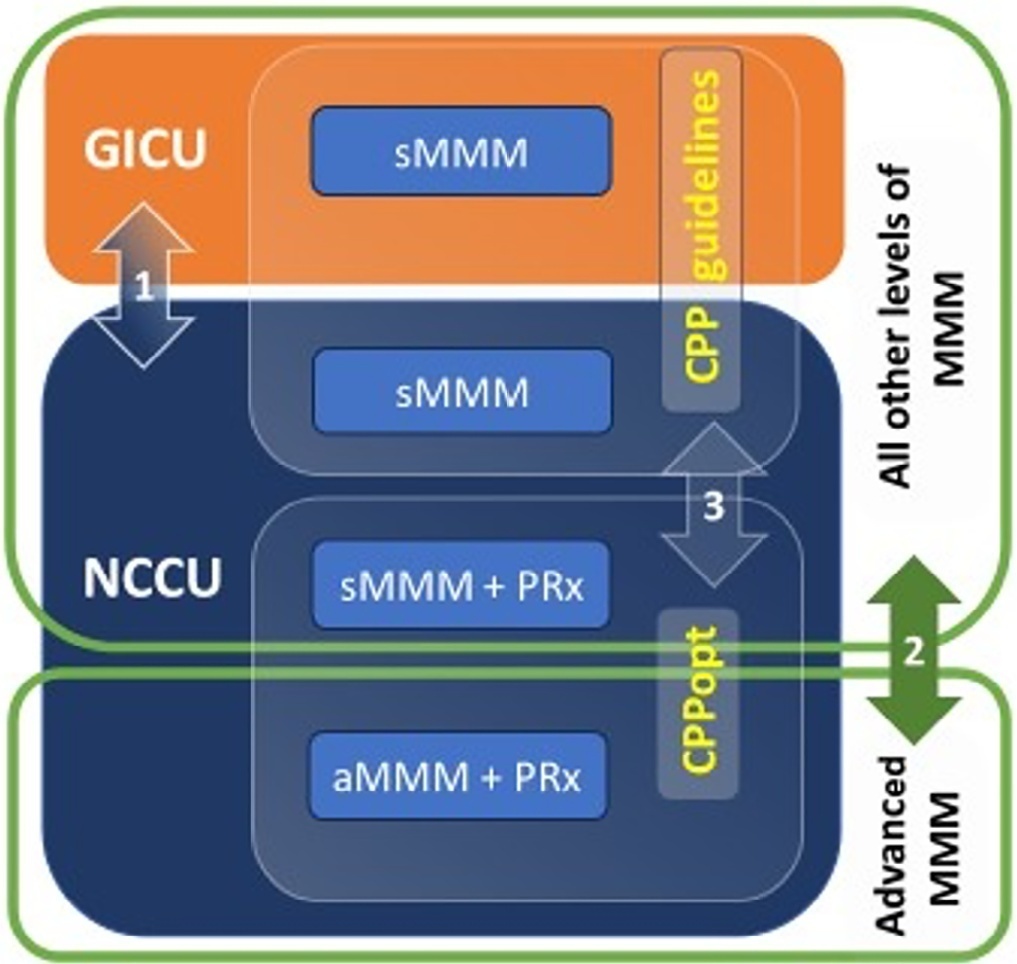
To evaluate the association between different intensive care units and levels of brain monitoring with outcomes in acute brain injury.
Patients with traumatic brain injury and subarachnoid hemorrhage admitted to intensive care units were included. Neurocritical care unit management was compared to general intensive care unit management. Patients managed with multimodal brain monitoring and optimal cerebral perfusion pressure were compared with general management patients. A good outcome was defined as a Glasgow outcome scale score of 4 or 5.
Among 389 patients, 237 were admitted to the neurocritical care unit, and 152 were admitted to the general intensive care unit. Neurocritical care unit management patients had a lower risk of poor outcome (OR = 0.228). A subgroup of 69 patients with multimodal brain monitoring (G1) was compared with the remaining patients (G2). In the G1 and G2 groups, 59% versus 23% of patients, respectively, had a good outcome at intensive care unit discharge; 64% versus 31% had a good outcome at 28 days; 76% versus 50% had a good outcome at 3 months (p < 0.001); and 77% versus 58% had a good outcome at 6 months (p = 0.005). When outcomes were adjusted by SAPS II severity score, using good outcome as the dependent variable, the results were as follows: for G1 compared to G2, the OR was 4.607 at intensive care unit discharge (p < 0.001), 4.22 at 28 days (p = 0.001), 3.250 at 3 months (p = 0.001) and 2.529 at 6 months (p = 0.006). Patients with optimal cerebral perfusion pressure management (n = 127) had a better outcome at all points of evaluation. Mortality for those patients was significantly lower at 28 days (p = 0.001), 3 months (p < 0.001) and 6 months (p = 0.001).
Multimodal brain monitoring with autoregulation and neurocritical care unit management were associated with better outcomes and should be considered after severe acute brain injury.
Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(2):203-208
DOI 10.5935/2965-2774.20230274-pt
To investigate whether family participation in intensive care unit interdisciplinary bedside rounds affects family satisfaction.
A cross-sectional study was conducted at a 56-bed, adult, mixed intensive care unit of a tertiary hospital in Southern Brazil. From May to June 2019, family members of patients who stayed in the intensive care unit for at least 48 hours were invited to participate in the study at the time of patient discharge. The main exposure variable was participation in intensive care unit bedside rounds during the intensive care unit stay. Family satisfaction was assessed by using the Brazilian version of the Family Satisfaction in the Intensive Care Unit questionnaire.
Of the 234 screened individuals, 118 were included. Eleven participants withdrew consent. A total of 107 individuals were assessed; 58 (54%) reported being present during bedside rounds, and 49 (46%) reported never being present. General satisfaction and satisfaction with the decision-making process were higher among families who were present during rounds than among families who were not (p = 0.01 and p = 0.007, respectively).
The presence during interdisciplinary rounds was associated with improved general satisfaction and satisfaction with the decision-making aspect. This outcome indicates that efforts must be directed to conduct studies with more robust methodologies to confirm this association.

Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(2):209-216
DOI 10.5935/2965-2774.20230010-pt
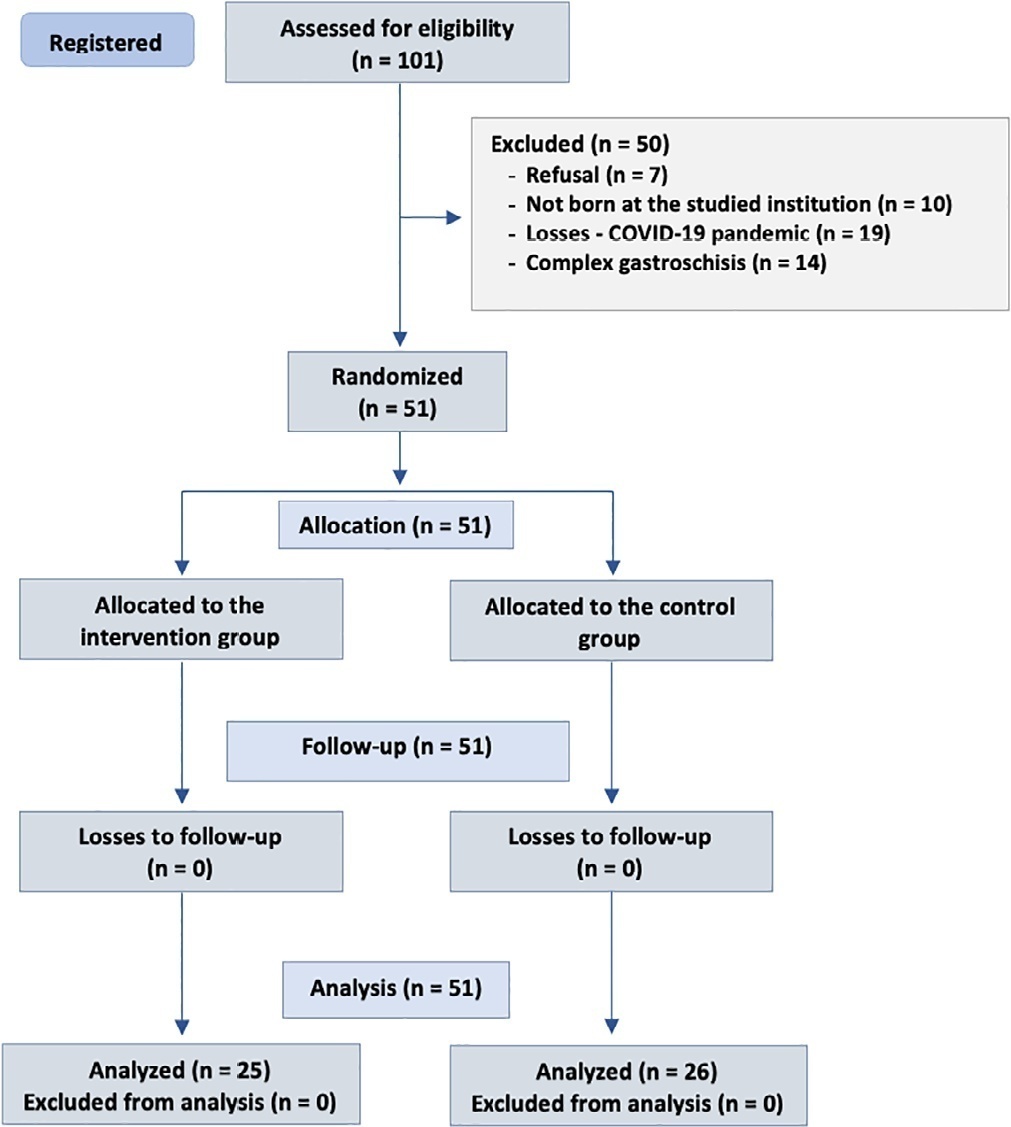
To evaluate the effect of colostrum therapy on days to start a suckling diet in newborns diagnosed with simple gastroschisis.
Randomized clinical trial with newborns diagnosed with simple gastroschisis at a federal hospital in Rio de Janeiro who were randomized to receive oropharyngeal administration of 0.2mL of colostrum or a “sham procedure” during the first 3 days of life. The analysis included clinical outcomes such as days without food, days with parenteral feeding, days until the start of enteral feeding, days to reach complete enteral feeding, sepsis and length of hospital stay.
The onset of oral feeding (suction) in patients with simple gastroschisis in both groups occurred at a median of 15 days.
The present study showed that there were no significant differences in the use of colostrum therapy and the number of days to the start of enteral feeding and suction diet between groups of newborns with simple gastroschisis.
Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(1):57-65
DOI 10.5935/2965-2774.20230350-pt
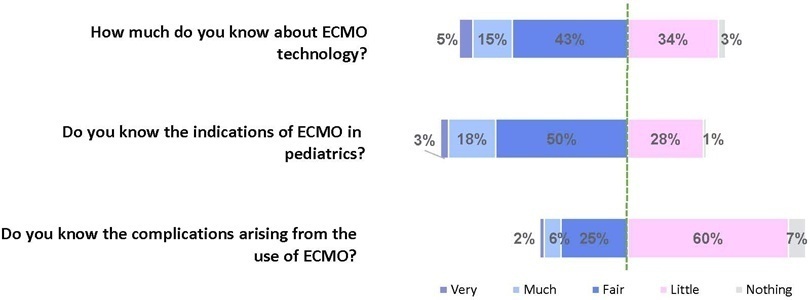
To assess Brazilian pediatric intensivists’ general knowledge of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, including evidence for its use, the national funding model, indications, and complications.
This was a multicenter cross-sectional survey including 45 Brazilian pediatric intensive care units. A convenience sample of 654 intensivists was surveyed regarding their knowledge on managing patients on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, its indications, complications, funding, and literature evidence.
The survey addressed questions regarding the knowledge and experience of pediatric intensivists with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, including two clinical cases and 6 optional questions about the management of patients on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Of the 45 invited centers, 42 (91%) participated in the study, and 412 of 654 (63%) pediatric intensivists responded to the survey. Most pediatric intensive care units were from the Southeast region of Brazil (59.5%), and private/for-profit hospitals represented 28.6% of the participating centers. The average age of respondents was 41.4 (standard deviation 9.1) years, and the majority (77%) were women. Only 12.4% of respondents had taken an extracorporeal membrane oxygenation course. Only 19% of surveyed hospitals have an extracorporeal membrane oxygenation program, and only 27% of intensivists reported having already managed patients on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Specific extracorporeal membrane oxygenation management questions were responded to by only 64 physicians (15.5%), who had a fair/good correct response rate (median 63.4%; range 32.8% to 91.9%).
Most Brazilian pediatric intensivists demonstrated limited knowledge regarding extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, including its indications and complications. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation is not yet widely available in Brazil, with few intensivists prepared to manage patients on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation and even fewer intensivists recognizing when to refer patients to extracorporeal membrane oxygenation centers.
Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(1):66-72
DOI 10.5935/2965-2774.20230312-pt
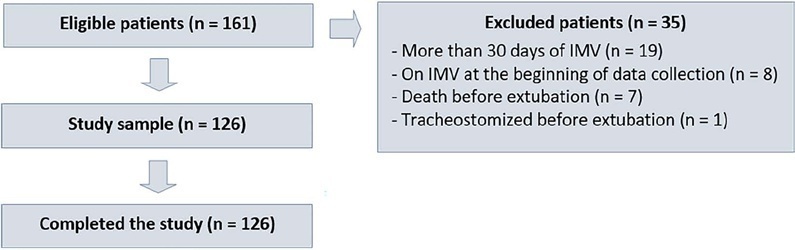
To evaluate whether a model of a daily fitness checklist for spontaneous breathing tests is able to identify predictive variables of extubation failure in pediatric patients admitted to a Brazilian intensive care unit.
This was a single-center, cross-sectional study with prospective data collection. The checklist model comprised 20 items and was applied to assess the ability to perform spontaneous breathing tests.
The sample consisted of 126 pediatric patients (85 males (67.5%)) on invasive mechanical ventilation, for whom 1,217 daily assessments were applied at the bedside. The weighted total score of the prediction model showed the highest discriminatory power for the spontaneous breathing test, with sensitivity and specificity indices for fitness failure of 89.7% or success of 84.6%. The cutoff point suggested by the checklist was 8, with a probability of extubation failure less than 5%. Failure increased progressively with increasing score, with a maximum probability of predicting extubation failure of 85%.
The extubation failure rate with the use of this model was within what is acceptable in the literature. The daily checklist model for the spontaneous breathing test was able to identify predictive variables of failure in the extubation process in pediatric patients.
Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(1):73-83
DOI 10.5935/2965-2774.20230374-pt
To understand the perception of medical communication and needs of family members with loved ones in intensive care.
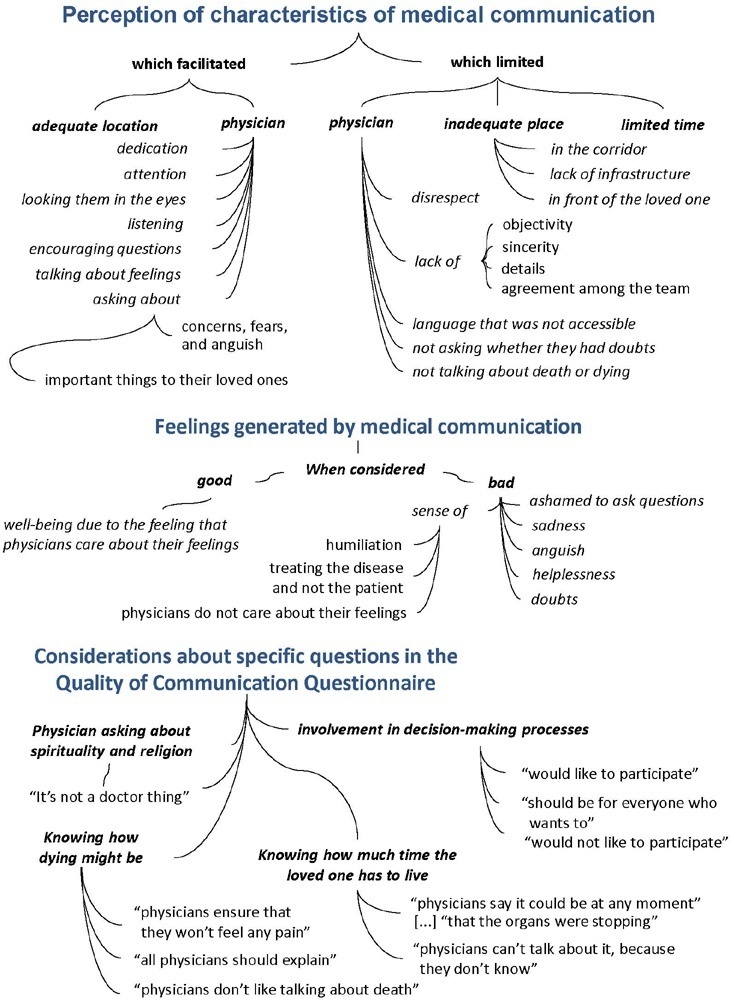
The study was mainly qualitative and exploratory, with thematic analysis of comments made by 92 family members with loved ones in intensive care units when answering in-person interviews comprising the Quality of Communication Questionnaire (QoC) and open-ended questions about their need for additional help, the appropriateness of the place where they received information, and additional comments.
The participants’ mean age was 46.8 years (SD = 11.8), and most of them were female, married and had incomplete or completed elementary education. The following themes were found: perception of characteristics of medical communication; feelings generated by communication; considerations about specific questions in the QoC; family members’ needs; and strategies to overcome needs regarding communication. Characteristics that facilitated communication included attention and listening. Characteristics that made communication difficult included aspects of information sharing, such as inaccessible language; lack of clarity, objectivity, sincerity, and agreement among the team; limited time; and inadequate location. Feelings such as shame, helplessness, and sadness were cited when communication was inadequate. Family members’ needs related to communication included more details about the loved one’s diagnosis, prognosis, and health condition; participation in decisionmaking; and being asked about feelings, spirituality, dying and death. Others were related to longer visitation time, psychological support, social assistance, and better infrastructure.
It is necessary to enhance medical communication and improve hospital infrastructure to improve the quality of care for family members.
Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(1):19-30
DOI 10.5935/2965-2774.20230203-pt
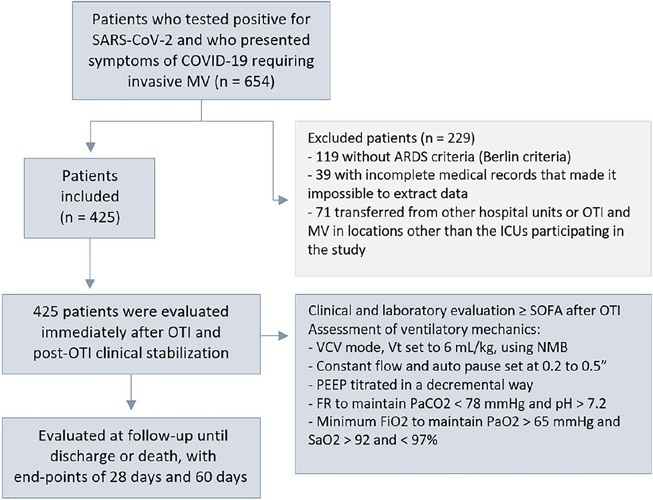
To evaluate the factors associated with mortality in mechanically ventilated patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome due to COVID-19.
This was a retrospective, multicenter cohort study that included 425 mechanically ventilated adult patients with COVID-19 admitted to 4 intensive care units. Clinical data comprising the SOFA score, laboratory data and mechanical characteristics of the respiratory system were collected in a standardized way immediately after the start of invasive mechanical ventilation. The risk factors for death were analyzed using Cox regression to estimate the risk ratios and their respective 95%CIs.
Body mass index (RR 1.17; 95%CI 1.11 - 1.20; p < 0.001), SOFA score (RR 1.39; 95%CI 1.31 - 1.49; p < 0.001) and driving pressure (RR 1.24; 95%CI 1.21 - 1.29; p < 0.001) were considered independent factors associated with mortality in mechanically ventilated patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome due to COVID-19. Respiratory system compliance (RR 0.92; 95%CI 0.90 - 0.93; p < 0.001) was associated with lower mortality. The comparative analysis of the survival curves indicated that patients with respiratory system compliance (< 30mL/cmH2O), a higher SOFA score (> 5 points) and higher driving pressure (> 14cmH2O) were more significantly associated with the outcome of death at 28 days and 60 days.
Patients with a body mass index > 32kg/m2, respiratory system compliance < 30mL/cmH2O, driving pressure > 14cmH2O and SOFA score > 5.8 immediately after the initiation of invasive ventilatory support had worse outcomes, and independent risk factors were associated with higher mortality in this population.