Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2010;22(4):339-345
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2010000400005
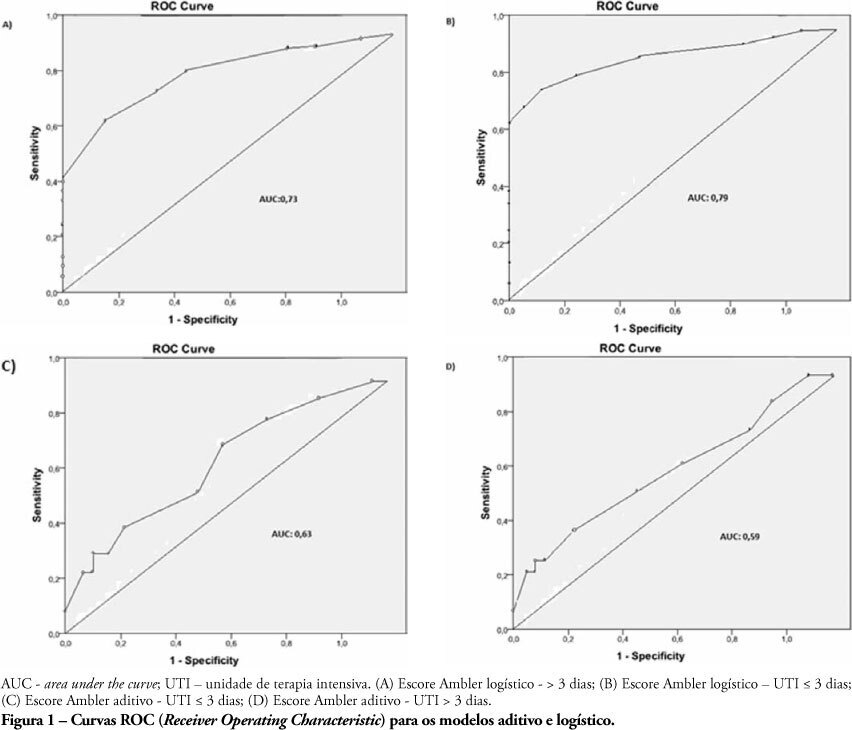
OBJECTIVES: The length of stay after prolonged cardiac surgery has been associated with poor immediate outcomes and increased costs. This study aimed to evaluate the predictive power of the Ambler Score to anticipate the length of stay in the intensive care unit. METHODS: This was a retrospective cohort study based on data collected from 110 patients undergoing valve replacement surgery alone or in combination with other procedures. Additive and logistic Ambler Scores were obtained and their predictive performances calculated using the Receiver Operating Characteristic curve. The normal length stay in the intensive care unit was assumed to be <3 days and prolonged >3 days. The areas under the receiver operating curves for both the additive and logistic models were compared using the Hanley-MacNeil test. RESULTS: The mean intensive care unit length of stay was 4.2 days. Sixty-three patients were male. The logistic model showed areas under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.73 and 0.79 for hospitalization > 3 days and < 3 days, respectively, showing good discriminative power. For the additive model, the areas were 0.63 and 0.59 for hospitalization > 3 days and < 3 days, respectively, a poor discriminative power. CONCLUSIONS: In our database, prolonged length of stay in the intensive care unit was positively correlated with the logistic Ambler score. The performance of the logistic Ambler Score had good discriminative power for correlation with the intensive care unit length of stay.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2010;22(3):220-228
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2010000300002
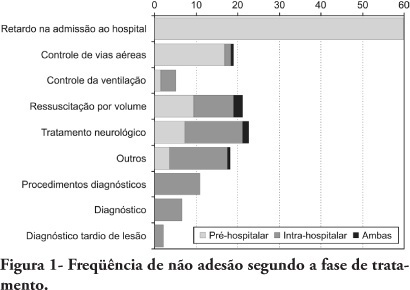
OBJECTIVES: To evaluate patients treated for traumatic injuries and to identify adherence to guidelines recommendations of treatment and association with death. The recommendations adopted were defined by the committee on trauma of the American College of Surgeons in advanced trauma life support. METHODS: Retrospective cohort study conducted at a teaching hospital. The study population was victims of trauma > 12 years of age with injury severity scores > 16 who were treated between January 1997 and December 2001. Data collection was divided into three phases: pre-hospital, in-hospital, and post-mortem. The data collected were analyzed using EPI INFO. RESULTS: We analyzed 207 patients, 147 blunt trauma victims (71%) and 60 (29%) penetrating trauma victims. Trauma victims had a 40.1% mortality rate. We identified 221 non adherence events that occurred in 137 patients. We found a mean of 1.61 non adherence per patient, and it occurred less frequently in survivors (1.4) than in non-survivors (1.9; p=0.033). According to the trauma score and injury severity score methodology, 54.2% of deaths were considered potentially preventable. Non adherence occurred 1.77 times more frequently in those considered potentially preventable deaths compared to other non-survivors (95% CI: 1.12-2.77; p=0.012), and 92.9% of the multiple non adherence occurred in the first group (p=0.029). CONCLUSIONS: Non adherence occurred more frequently in patients with potentially preventable deaths. Non adherence to guidelines recommendations can be considered a contributing factor to death in trauma victims and can lead to an increase in the number of potentially preventable deaths.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2010;22(3):250-256
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2010000300006
OBJECTIVE: The intensive care unit is synonymous of high severity, and its mortality rates are between 5.4 and 33%. With the development of new technologies, a patient can be maintained for long time in the unit, causing high costs, psychological and moral for all involved. This study aimed to evaluate the risk factors for mortality and prolonged length of stay in an adult intensive care unit. METHODS: The study included all patients consecutively admitted to the adult medical/surgical intensive care unit of Hospital das Clínicas da Universidade Estadual de Campinas, for six months. We collected data such as sex, age, diagnosis, personal history, APACHE II score, days of invasive mechanical ventilation orotracheal reintubation, tracheostomy, days of hospitalization in the intensive care unit and discharge or death in the intensive care unit. RESULTS: Were included in the study 401 patients; 59.6% men and 40.4% women, age 53.8±18.0. The mean intensive care unit stay was 8.2±10.8 days, with a mortality rate of 13.5%. Significant data for mortality and prolonged length of stay in intensive care unit (p <0.0001), were: APACHE II>11, OT-Re and tracheostomy. CONCLUSION: The mortality and prolonged length of stay in intensive care unit intensive care unit as risk factors were: APACHE>11, orotracheal reintubation and tracheostomy.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2010;22(2):138-143
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2010000200007
BACKGROUND: The elderly population is increasing all over the world. The need of intensive care by the elderly is also increasing. There is a lack of studies investigating the risk factors for death among critically ill elderly patients. This study aims to investigate the factors associated with death in a population of critically ill elderly patients admitted to an intensive care unit in Brazil. METHODS: This is a retrospective cohort study including all elderly patients (>60 years) admitted to an intensive care unit in Fortaleza, Brazil, from January to December 2007. A comparison between survivors and nonsurvivors was done and the risk factors for death were investigated through univariate and multivariate analysis. RESULTS: A total of 84 patients were included, with an average age of 73 ± 7.6 years; 59% were female. Mortality was 62.8%. The main cause of death was multiple organ dysfunction (42.3%), followed by septic shock (36.5%) and cardiogenic shock (9.7%). Complications during intensive care unit ICU stay associated with death were respiratory failure (OR=61, p<0.001), acute kidney injury (OR=23, p<0.001), sepsis (OR=12, p<0.001), metabolic acidosis (OR=17, p<0.001), anemia (OR=8.6, p<0.005), coagulation disturbance (OR=5.9, p<0.001) and atrial fibrillation (OR=4.8, p<0.041). Independent risk factors for death were age (OR=1.15, p<0.005), coma (OR=7.51, p<0.003), hypotension (OR=21.75, p=0.003), respiratory failure (OR=9.93, p<0.0001) and acute kidney injury (OR=16.28, p<0.014). CONCLUSION: Mortality is high among critically ill elderly patients. Factors associated with death were age, coma, hypotension, respiratory failure and acute kidney injury.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2009;21(3):255-261
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2009000300004
Currently, aging of the population is a widespread global phenomenon. Therefore, the assessment of prognosis in elderly patients is needed. This study aims to identify risk factors in a population of elderly patients admitted in the intensive care unit METHODS: A prospective study in the intensive care unit of a general tertiary hospital was carried out for five months. Patients with 65 years or more of age, who stayed in the intensive care unit for 24 hours or more were included and those at the-end-of-life, patients readmitted to intensive care unit during the same hospital stay were excluded. RESULTS: In this study 199 patients were involved, with a mean age of 75.4±6.8 years, and 58.8% were female. Mortality was 57.3%. The mean APACHE II, SOFA, MODS and Katz index (assessment of daily activities) were respectively 20.0±5.8, 6.8±3.9, 2.4±1.9 and 5.3±1.6. Most patients were postoperative 59.3% and 41.6% were under invasive mechanical ventilation. At regression analysis, the independent determinants of higher mortality were: older age (76.9±6.7 years death versus 73.3±6.5 years discharge, P<0.001, OR=1.08, CI 95% 1.01-1. 16), the Katz index (4.9±1.9 deaths versus 5.7±0.9 discharge, p=0.001, OR=0.66, CI 95% 0.45-0.98), hyperglycemia (158.1±69.0 death versus 139.6±48.5 discharge p=0.041; OR=1.02; CI 95% 1.01-1.03) and need for mechanical ventilation at admission to the intensive care unit (57.0% death versus 20.5% discharge p <0.001, OR=3.57, CI 95% 1.24-10.3). CONCLUSION: Elderly patients admitted to the intensive care unit that have difficulties in performing daily activities, hyperglycemia and who are under invasive mechanical ventilation had a worse hospital prognosis.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2009;21(3):262-268
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2009000300005
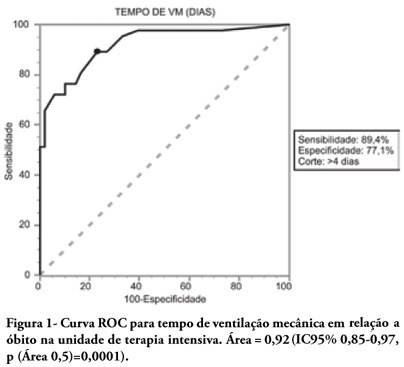
OBJECTIVES: To describe the population of aged as compared to young patients under mechanical ventilation and to analyze the mortality risk factors of this group in an intensive care unit. METHODS: This was a prospective observational trial in patients over 18 years of age, admitted in an intensive care unit and under mechanical ventilation, during one year. Patients were divided into two groups according to age: Group 1 - patients over 65 years old; and Group 2, 65 years old or younger. RESULTS: eighty one mechanic ventilation patients were included, 62 aged and 18 younger, mean ages from aged was 76 years, while in the younger it was 56 years. As compared to the control, aged patients had longer mechanic ventilation time , higher intensive care unit and hospital mortality: 63.1% versus 26.3% and 74.2% versus 47.4% (P<0.05), respectively. In addition, the aged under mechanic ventilation had increased desintubation failures, difficult ventilatory weaning and deaths directly related to respiratory dysfunction. The mechanic ventilation time was an independent risk factor for death in the intensive care unit in aged patients (OR= 2.7, p=0.02). The area under the ROC curve of mechanic ventilation about intensive care unit death was 0.92 (95% CI 0.85-0.97, p (area 0.5)=0.0001), cutoff point of 4 days, sensitivity 89.4% and specificity 77.1%. CONCLUSIONS: Mechanic ventilation patients over 65years of age have a worse prognosis than the younger, and the longer the mechanic ventilation time, the higher will be intensive care mortality.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2008;20(4):394-397
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2008000400012
OBJECTIVES: To evaluate risks for persistent pulmonary hypertension in the newborn, confirmed by echocardiography, associated with cesarean deliveries and other factors. METHODS: Cohort of all deliveries >36 weeks within a period of 23 months. A nested case-control study was performed in a subset of the cohort, involving newborns admitted into neonatal intensive care unit with diagnosis of persistent pulmonary hypertension matched with normal controls, with application of questionnaires to mothers to identify risks. Logistic regression was used to calculate odds ratios. RESULTS: From 9452 newborns, 8388 (88.7%) were delivered by cesarean and 1064 (11.3%) by vaginal delivery. Questionnaires were applied to 173 mothers. Infants from cesareans had a fivefold increased risk of persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn: 42 (0.5%) versus 1 case (0.09%) in the vaginal group (OR 5.32, p=0.027). No interactions were found between smoking, parity, arterial hypertension and labor before cesarean section and persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. First minute Apgar score <7 and maternal diabetes were related to increased risk. CONCLUSION: Reducing cesarean deliveries could prevent many cases of serious persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2006;18(1):38-44
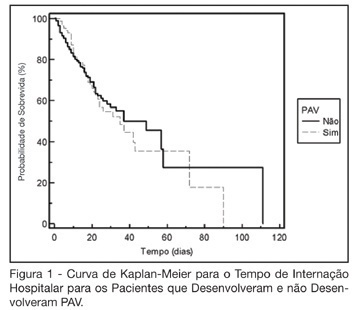
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2006000100008
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: The ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP) is a severe infection that presents multiple causes which can vary depending on the type of intensive care unit, type of patients, emphasizing the needs for vigilance measures with local data. The aim of this study is to describe the incidence, risk factors and mortality of VAP in patients in a surgical ICU. METHODS: Prospective cohort conducted from January 2004 to January 2005. It was included all the patients in mechanical ventilation, followed daily to collect data about demographics, diagnostic, APACHE II and TISS 28 scores, duration of mechanical ventilation, length of stay, incidence of VAP and mortality. RESULTS: 462 patients were studied; age 57.2 ± 16.6 years, 55% men. The mean APACHE II score was 18.3 and the incidence of VAP was 18.8%. The TISS score at admission OR = 1.050 (IC 95%: 1.003-1.050) and the enteral nutrition OR = 5.609 (IC 3.351-9.388) were factors associated with VAP and the prophylactic use of antibiotics was a factor of protection OR = 0.399 (IC95%: 0.177-0.902). The patients with VAP had longer length of stay in ICU (10.3 ± 10.7 vs 4.9 ± 3.3 days), higher median of duration of mechanical ventilation (4 vs 1 days), higher mean of TISS 28 (24.4 ± 4.6 vs 22.8 ± 4.5), and higher crude mortality (46 vs 28.8%) when compared with the patients without VAP. CONCLUSIONS: VAP was a frequent infection in surgical patients in mechanical ventilation. Enteral nutrition and admission TISS were risk factors and the previous use of antibiotics was protection factor to develop VAP. In our sample the results demonstrate that VAP is associated with higher duration in mechanical ventilation, longer length of stay and higher mortality.