Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2013;25(1):32-38
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2013000100007
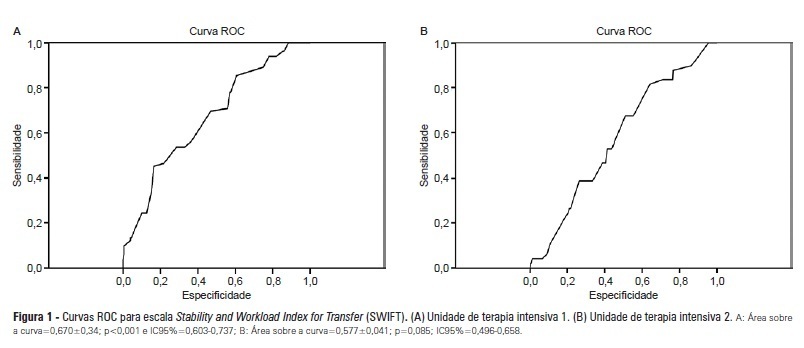
OBJECTIVES: Identify patients at risk for intensive care unit readmission, the reasons for and rates of readmission, and mortality after their stay in the intensive care unit; describe the sensitivity and specificity of the Stability and Workload Index for Transfer scale as a criterion for discharge from the intensive care unit. METHODS: Adult, critical patients from intensive care units from two public hospitals in Porto Alegre, Brazil, comprised the sample. The patients' clinical and demographic characteristics were collected within 24 hours of admission. They were monitored until their final outcome on the intensive care unit (death or discharge) to apply the Stability and Workload Index for Transfer. The deaths during the first intensive care unit admission were disregarded, and we continued monitoring the other patients using the hospitals' electronic systems to identify the discharges, deaths, and readmissions. RESULTS: Readmission rates were 13.7% in intensive care unit 1 (medical-surgical, ICU1) and 9.3% in intensive care unit 2 (trauma and neurosurgery, ICU2). The death rate following discharge was 12.5% from ICU1 and 4.2% from ICU2. There was a statistically significant difference in Stability and Workload Index for Transfer (p<0.05) regarding the ICU1 patients' outcome, which was not found in the ICU2 patients. In ICU1, 46.5% (N=20) of patients were readmitted very early (within 48 hours of discharge). Mortality was high among those readmitted: 69.7% in ICU1 and 48.5% in ICU2. CONCLUSIONS: The Stability and Workload Index for Transfer scale showed greater efficacy in identifying patients more prone to readmission and death following discharge from a medical-surgical intensive care unit. The patients' intensive care unit readmission during the same hospitalization resulted in increased morbidity, mortality, length of stay, and total costs.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2009;21(3):262-268
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2009000300005
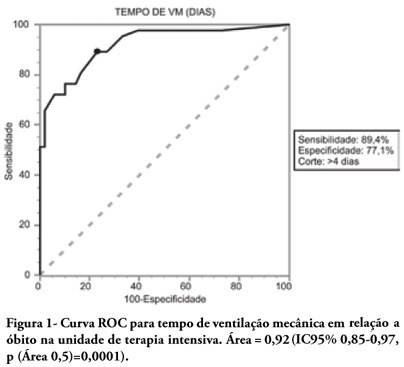
OBJECTIVES: To describe the population of aged as compared to young patients under mechanical ventilation and to analyze the mortality risk factors of this group in an intensive care unit. METHODS: This was a prospective observational trial in patients over 18 years of age, admitted in an intensive care unit and under mechanical ventilation, during one year. Patients were divided into two groups according to age: Group 1 - patients over 65 years old; and Group 2, 65 years old or younger. RESULTS: eighty one mechanic ventilation patients were included, 62 aged and 18 younger, mean ages from aged was 76 years, while in the younger it was 56 years. As compared to the control, aged patients had longer mechanic ventilation time , higher intensive care unit and hospital mortality: 63.1% versus 26.3% and 74.2% versus 47.4% (P<0.05), respectively. In addition, the aged under mechanic ventilation had increased desintubation failures, difficult ventilatory weaning and deaths directly related to respiratory dysfunction. The mechanic ventilation time was an independent risk factor for death in the intensive care unit in aged patients (OR= 2.7, p=0.02). The area under the ROC curve of mechanic ventilation about intensive care unit death was 0.92 (95% CI 0.85-0.97, p (area 0.5)=0.0001), cutoff point of 4 days, sensitivity 89.4% and specificity 77.1%. CONCLUSIONS: Mechanic ventilation patients over 65years of age have a worse prognosis than the younger, and the longer the mechanic ventilation time, the higher will be intensive care mortality.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (116) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)